Phase Transition of α-FePO4 under High Pressure: A Raman Spectroscopy Study
-
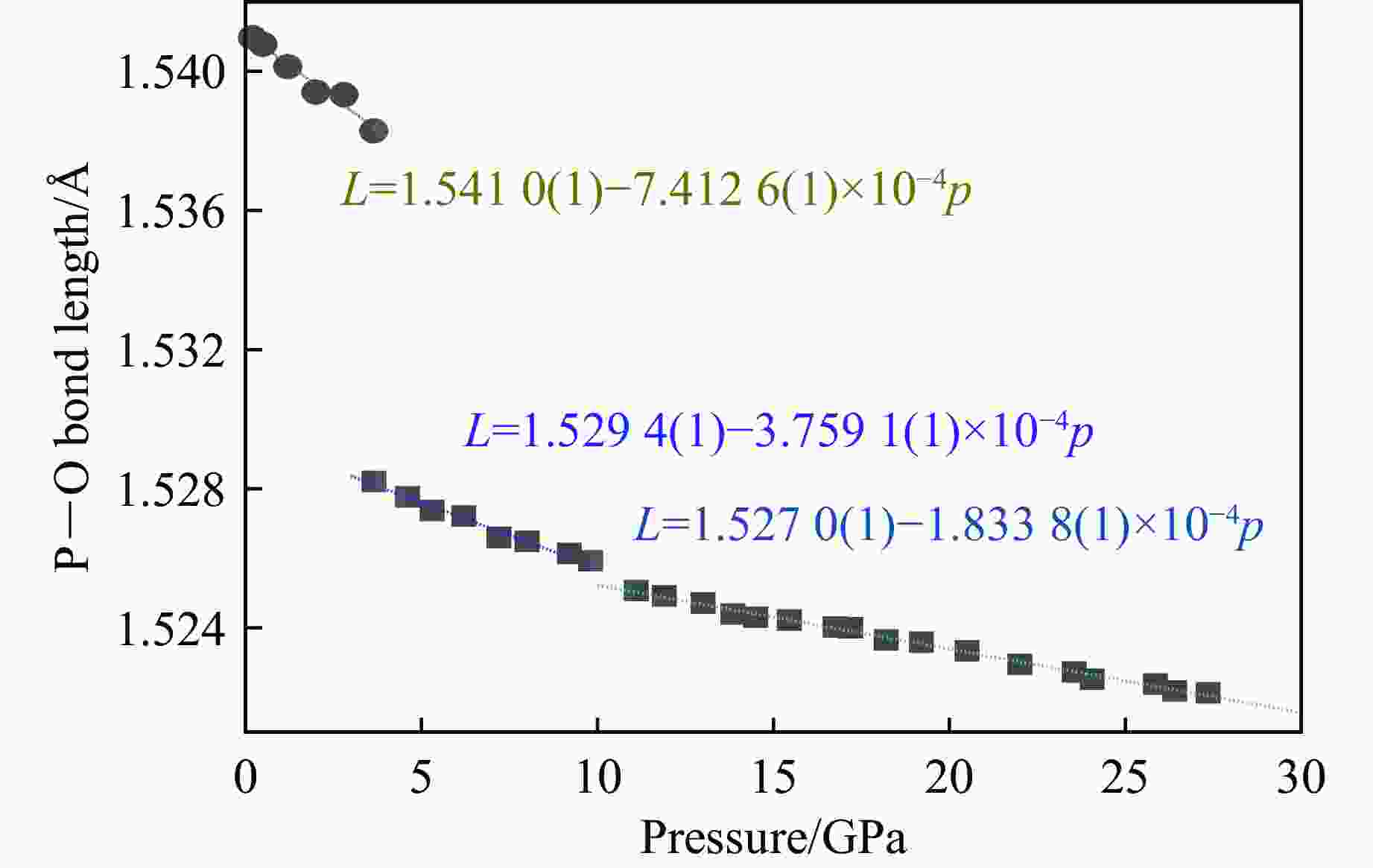
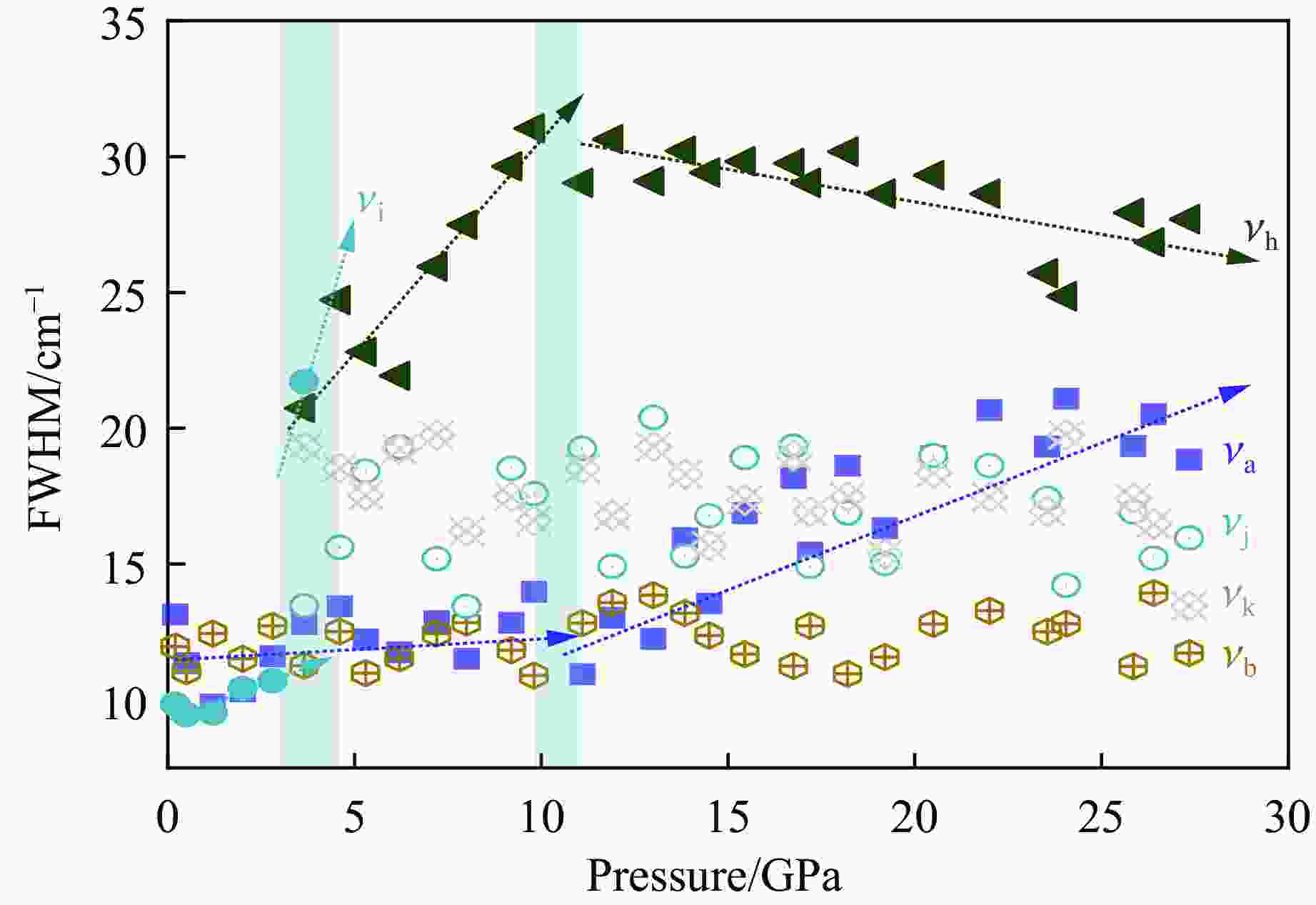
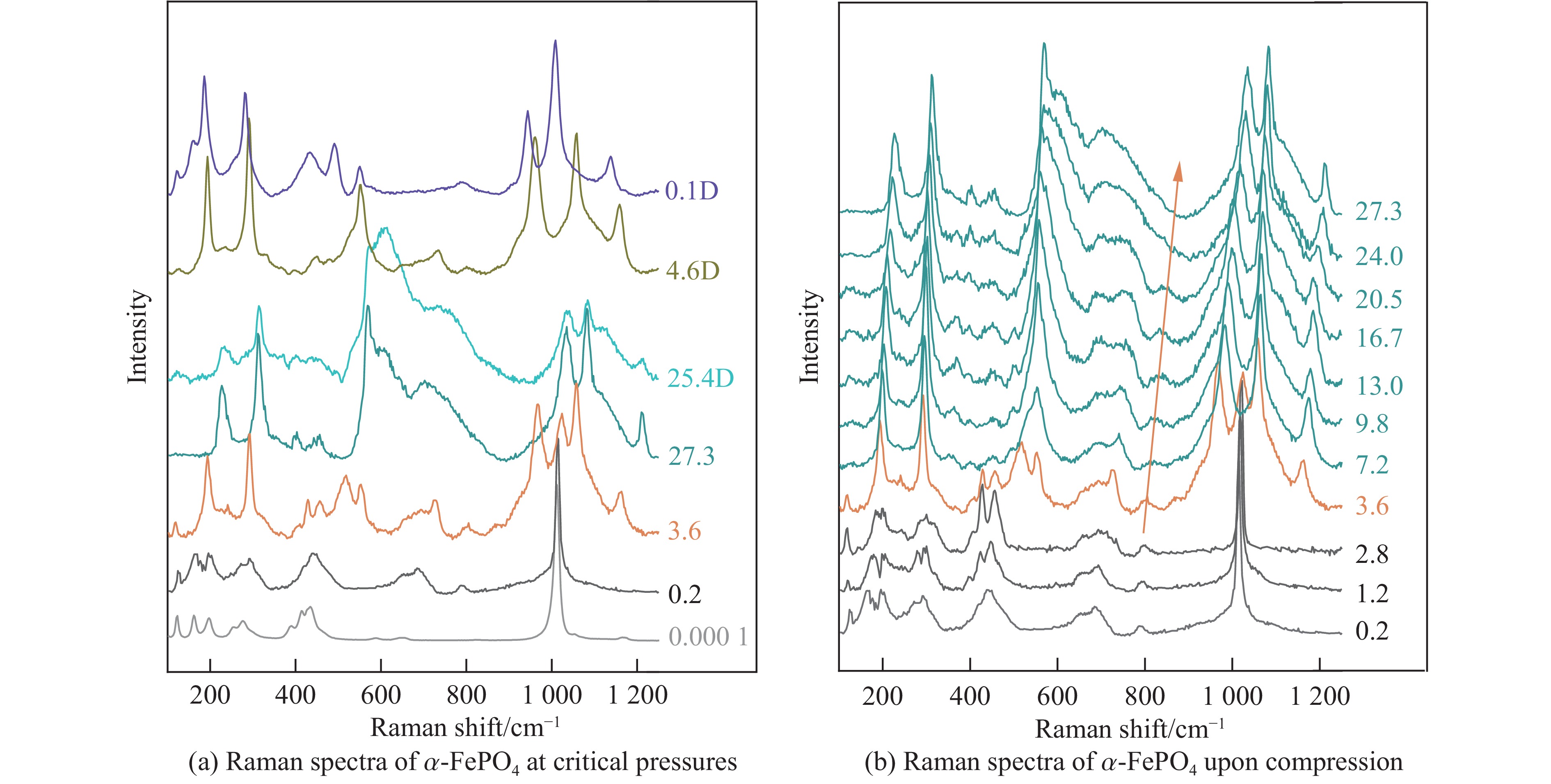
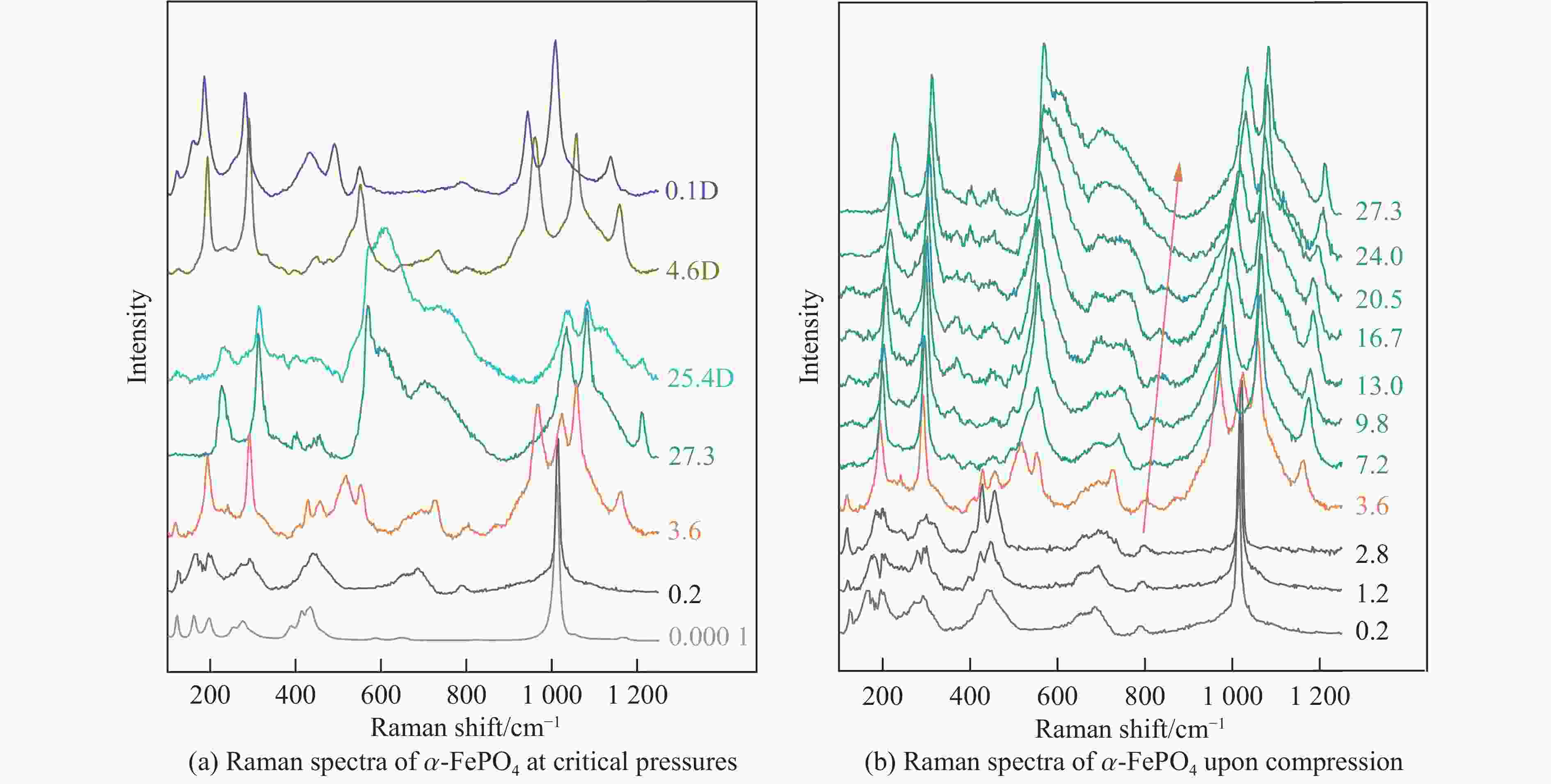
摘要: 鉴于α-FePO4和α-石英的拓扑同构性,采用金刚石压腔结合拉曼光谱技术,从分子尺度上原位厘定了α-FePO4在常温高压下的相变行为。在0.2~27.3 GPa压力范围内,揭示了其3个阶段的结构演化特征。在2.8~3.6 GPa区间,α-FePO4开始发生相变,并于4.6 GPa时完全转变为FePO4-Ⅱ。在宽泛的4.6~27.3 GPa区间,FePO4-Ⅱ的结构稳定/亚稳定性依赖于柔性[FeO6]八面体与刚性[PO4]四面体的协同形变。在该压力区间,结构无序度增加,振动频率漂移速率减缓,表明结构进入非线性压缩阶段。值得注意的是,在9.8~11.1 GPa临界窗口,P―O键的平均键长和部分振动峰半高宽出现不连续变化,暗示[FeO6]-[PO4]网络中存在压力诱导的非均匀应变,推测FePO4-Ⅱ开始进入亚稳定域。直到卸压至4.6 GPa,FePO4-Ⅱ的部分结构才恢复有序性,并在常压下保持亚稳态,表现出独特的结构记忆功能。研究结果系统地限定了α-FePO4的相变压力边界,阐明了正磷酸盐高压结构稳定性的内在调控机制,并预测了其未来结构演化趋势,为解析类石英矿物的高压动态响应提供了重要参考。Abstract: Given the topological isomorphism between α-FePO4 and α-quartz, this study employed a diamond anvil cell coupled with Raman spectroscopy to examine the phase transition of α-FePO4. The structural evolution across a pressure range of 0.2−27.3 GPa was delineated into three stages. At 2.8−3.6 GPa, α-FePO4 initiates a phase transition, achieving a complete transformation to FePO4-Ⅱ at 4.6 GPa. Between 4.6−27.3 GPa, the (meta) stability of FePO4-Ⅱ is predicated on the cooperative deformation of the adaptable [FeO6] octahedra and the rigid [PO4] tetrahedra. The progressive increase in structural disorder and the slowing of vibrational frequency shifts signify a transition to a non-linear compression regime. Notably, in the 9.8−11.1 GPa threshold, discontinuous variations in P―O bond lengths and mode widths serve as evidences of pressure-induced heterogeneous strain within the [FeO6]-[PO4] network, suggesting entry into a metastable region. Upon decompression to 4.6 GPa, FePO4-Ⅱ exhibits partial recovery of structural order, maintaining metastability at ambient conditions, which underscores its unique pressure memory characteristics. This study demarcates the stability boundary of α-FePO4, elucidates the fundamental mechanisms underpinning stability in orthophosphates, and forecasts structural evolution pathways. The findings offer insights into high-pressure dynamic response of quartz-like minerals.
-
Key words:
- α-quartz /
- orthophosphate /
- diamond anvil cell /
- Raman spectroscopy /
- phase transition
-
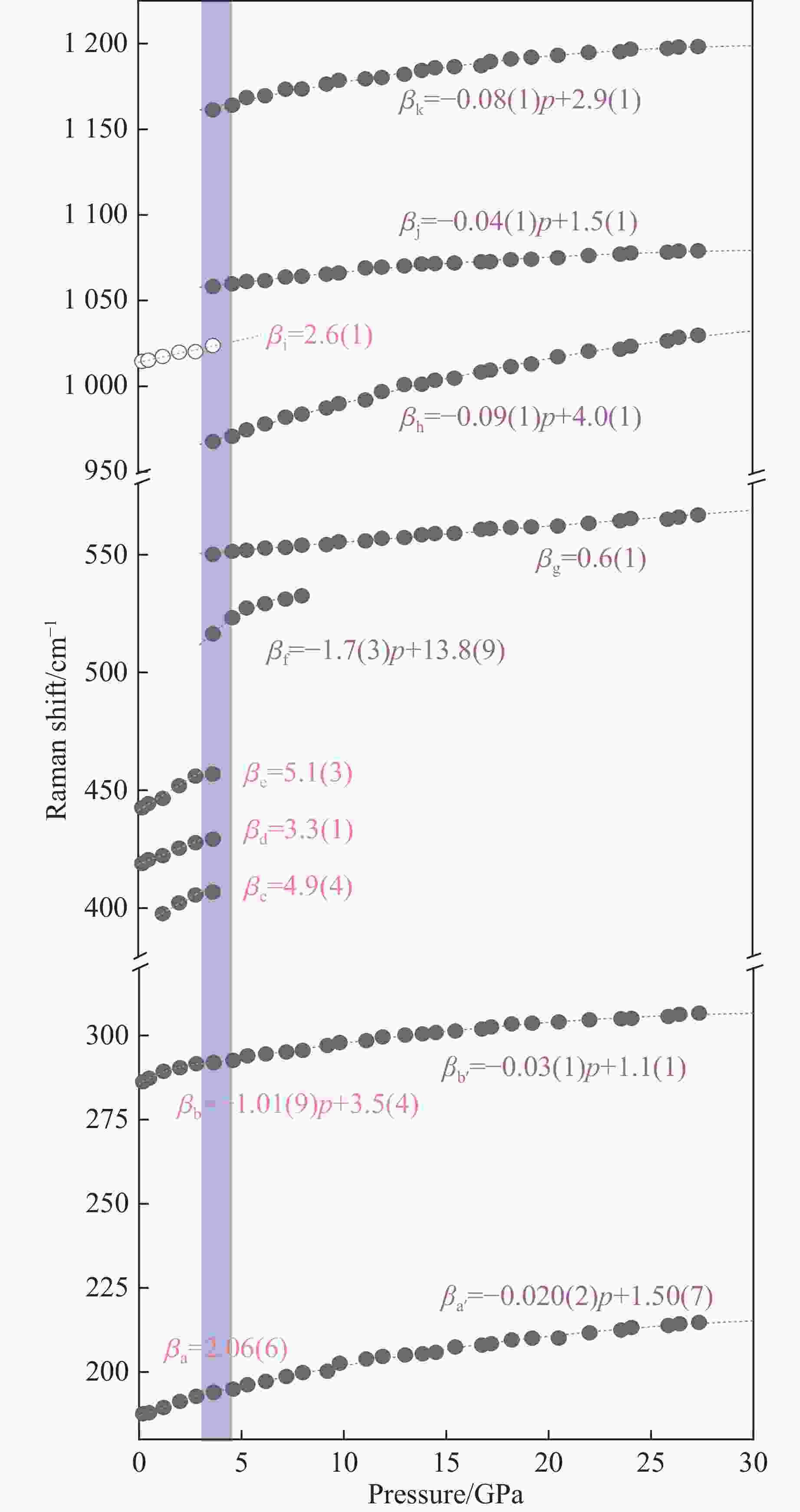
表 1 不同压力下α-FePO4或FePO4-Ⅱ的拉曼振动峰峰位和半高宽(100~700 cm−1)
Table 1. Raman shifts and the FWHM of α-FePO4 or FePO4-Ⅱ under different pressures (100−700 cm−1)
p/GPa νa(νa′)/
cm−1FWHM(νa, νa′)/
cm−1νb(νb′)/
cm−1FWHM(νb, νb′)/
cm−1νc/cm−1 νd/cm−1 νe/cm−1 νf/cm−1 νg/cm−1 10−4 186.70(1) 6.8(1) 284.89(1) 7.4(1) 389.98(1) 415.99(1) 439.61(1) 0.2 187.55(1) 13.1(1) 286.24(1) 11.9(1) 418.87(1) 442.53(1) 0.5 187.90(1) 11.3(1) 287.27(1) 11.0(1) 420.55(1) 444.29(1) 1.2 189.45(1) 9.8(1) 289.33(1) 12.4(1) 397.59(1) 422.21(1) 446.54(1) 2.0 191.25(1) 10.3(1) 290.39(1) 11.5(1) 402.20(1) 425.39(1) 451.92(1) 2.8 192.77(1) 11.6(1) 291.58(1) 12.7(1) 405.51(1) 427.74(1) 455.99(1) 3.6 193.95(1) 12.7(1) 291.93(1) 11.2(1) 406.79(1) 429.17(1) 456.85(1) 516.39(1) 550.13(1) 4.6 194.88(1) 13.4(1) 292.57(1) 12.5(1) 523.21(1) 551.41(1) 5.3 196.21(1) 12.2(1) 293.91(1) 10.9(1) 527.35(1) 551.88(1) 6.2 197.20(1) 11.7(1) 294.49(1) 11.5(1) 529.14(1) 552.78(1) 7.2 198.66(1) 12.9(1) 295.08(1) 12.4(1) 531.08(1) 553.03(1) 8.0 199.80(1) 11.5(1) 295.55(1) 12.8(1) 532.51(1) 553.99(1) 9.2 200.22(1) 12.8(2) 297.00(1) 11.8(1) 554.27(1) 9.8 202.60(1) 13.9(1) 297.89(1) 10.9(1) 555.51(1) 11.1 203.84(1) 10.9(1) 298.46(1) 12.8(1) 555.83(1) 11.9 204.62(1) 13.0(2) 299.56(1) 13.5(1) 556.92(1) 13.0 205.06(1) 12.2(1) 300.12(1) 13.8(1) 557.22(1) 13.8 205.42(1) 15.9(2) 300.45(1) 13.2(1) 558.42(2) 14.5 205.82(1) 13.5(2) 300.85(1) 12.3(1) 558.92(1) 15.4 207.44(1) 16.8(2) 301.31(1) 11.6(1) 559.02(2) 16.7 207.98(1) 18.1(2) 301.88(1) 11.2(1) 560.70(1) 17.2 208.42(1) 15.4(2) 302.53(1) 12.7(1) 561.07(1) 18.2 209.53(1) 18.6(1) 303.45(1) 10.9(1) 561.52(3) 19.2 210.02(1) 16.3(2) 303.62(1) 11.5(1) 561.77(1) 20.5 210.08(1) 18.9(2) 303.98(1) 12.8(1) 562.12(3) 22.0 211.62(1) 20.6(3) 304.63(1) 13.2(1) 563.32(2) 23.5 212.45(1) 19.3(2) 304.93(1) 12.5(1) 564.38(2) 24.0 213.19(1) 21.0(2) 305.06(1) 12.8(1) 565.32(2) 25.8 213.82(1) 19.3(2) 305.62(1) 11.2(1) 564.99(1) 26.4 214.31(1) 20.5(3) 306.24(1) 13.9(1) 565.92(1) 27.3 214.72(1) 18.8(3) 306.62(1) 11.7(1) 566.85(3) 表 2 不同压力下α-FePO4或FePO4-Ⅱ的拉曼振动峰峰位和半高宽(900~
1200 cm−1)Table 2. Raman shifts and the FWHM of α-FePO4 or FePO4-Ⅱ under different pressures (900−
1200 cm−1)p/GPa νh/cm−1 FWHM(νh)/
cm−1νi/cm−1 FWHM(νi)/
cm−1νj/cm−1 FWHM(νj)/
cm−1νk(νk′)/cm−1 FWHM(νk, νk′)/
cm−110−4 1012.82 (1)4.3(1) 1053.04 (1)8.3(1) 1168.20 (1)11.3(1) 0.2 1014.46 (1)9.8(1) 0.5 1015.14 (1)9.4(1) 1.2 1017.35 (1)9.5(1) 2.0 1019.84 (1)10.4(1) 2.8 1020.12 (1)10.7(1) 3.6 967.78(1) 20.7(1) 1023.69 (1)21.7(1) 1058.21 (1)13.4(1) 1161.24 (1)19.3(1) 4.6 970.73(1) 24.7(1) 1059.75 (1)15.6(1) 1164.04 (1)18.5(1) 5.3 974.53(1) 22.8(1) 1061.09 (1)18.4(1) 1168.42 (1)17.5(1) 6.2 977.97(1) 21.9(1) 1061.64 (1)19.3(1) 1169.47 (1)19.2(1) 7.2 981.90(1) 25.9(1) 1063.75 (1)15.2(1) 1173.29 (1)19.7(1) 8.0 983.70(1) 27.4(1) 1064.13 (1)13.4(1) 1173.49 (1)16.2(1) 9.2 987.32(1) 29.6(1) 1065.34 (1)18.5(1) 1176.32 (1)17.4(1) 9.8 989.82(1) 31.0(1) 1066.05 (1)17.5(1) 1178.51 (1)16.6(1) 11.1 991.95(1) 29.0(1) 1068.99 (1)19.2(1) 1179.35 (1)18.5(1) 11.9 996.82(1) 30.6(1) 1069.51 (1)14.9(1) 1180.20 (1)16.7(1) 13.0 1000.92 (1)29.0(1) 1070.21 (1)20.4(1) 1182.01 (1)19.3(1) 13.8 1001.12 (1)30.2(1) 1071.31 (1)15.2(1) 1184.32 (1)18.3(1) 14.5 1003.45 (1)29.4(1) 1071.62 (1)16.7(1) 1185.85 (1)15.6(1) 15.4 1004.62 (1)29.8(1) 1071.89 (1)18.9(1) 1186.44 (1)17.3(1) 16.7 1008.22 (1)29.7(1) 1072.57 (1)19.3(1) 1187.02 (1)19.0(1) 17.2 1009.41 (1)29.0(1) 1072.65 (1)14.9(1) 1189.54 (1)16.9(1) 18.2 1011.42 (1)30.1(1) 1073.86 (1)16.8(1) 1190.96 (1)17.4(1) 19.2 1012.94 (1)28.6(1) 1074.09 (1)15.0(1) 1192.02 (1)15.3(1) 20.5 1017.18 (1)29.3(1) 1074.91 (1)19.0(1) 1193.11 (1)18.3(1) 22.0 1020.42 (1)28.6(1) 1076.29 (1)18.6(1) 1194.82 (1)17.4(1) 23.5 1021.52 (1)25.7(1) 1077.02 (1)17.4(1) 1195.21 (1)16.9(1) 24.0 1023.31 (1)24.8(1) 1077.73 (1)14.2(1) 1196.74 (1)19.7(1) 25.8 1026.42 (1)27.9(1) 1078.21 (1)16.9(1) 1197.12 (1)17.4(1) 26.4 1028.52 (1)26.8(1) 1078.89 (1)15.2(1) 1197.94 (1)16.4(1) 27.3 1029.68 (1)27.6(1) 1079.08 (1)15.9(1) 1198.22 (1)13.4(1) -
[1] UNTERBORN C T, PANERO W R. The pressure and temperature limits of likely rocky exoplanets [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2019, 124(7): 1704–1716. doi: 10.1029/2018JE005844 [2] COPPARI F, SMITH R F, WANG J, et al. Implications of the iron oxide phase transition on the interiors of rocky exoplanets [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(3): 121–126. doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-00684-y [3] 章军锋, 金振民. 超高压变质岩中柯石英-石英相变动力学研究的评述 [J]. 地质科技情报, 1999, 18(3): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.1999.03.002ZHANG J F, JIN Z M. Review on phase transformation of coesite-quartz from ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1999, 18(3): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.1999.03.002 [4] HU S, LI Y, GU L X, et al. Discovery of coesite from the Martian shergottite Northwest Africa 8657 [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 286: 404–417. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.07.021 [5] LIU W, WU X B, LIANG Y F, et al. Multiple pathways in pressure-induced phase transition of coesite [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(49): 12894–12899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710651114 [6] 吴也, 陈星, 黄海军. 高压下α-石英和柯石英的相变行为 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(1): 011201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200587WU Y, CHEN X, HUANG H J. Phase transitions of α-quartz and coesite at high pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(1): 011201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200587 [7] PANG R L, YANG J, DU W, et al. New occurrence of seifertite and stishovite in Chang’E-5 regolith [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(12): e2022GL098722. doi: 10.1029/2022GL098722 [8] TSE J S, KLUG D D. Structural memory in pressure-amorphized AlPO4 [J]. Science, 1992, 255(5051): 1559–1561. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5051.1559 [9] LI N, HU H, GUO F, et al. Uncovering the phase transition of berlinite (α-AlPO4) under high pressure: insights from first-principles calculations [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Materials Science Edition), 2021, 36(2): 248–254. doi: 10.1007/s11595-021-2402-1 [10] SATO T, FUNAMORI N. High-pressure structural transformation of SiO2 glass up to 100 GPa [J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 82(18): 184102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.184102 [11] MURLI C, SHARMA S M, KULSHRESHTHA S K, et al. High pressure study of phase transitions in α-FePO4 [J]. Pramana, 1997, 49(3): 285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF02875204 [12] ARROYO-DE DOMPABLO M E, GALLARDO-AMORES J M, AZCONDO M T, et al. Towards innovative electrode materials obtained by high-pressure: experimental and computational study of HP-FePO4 [J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2006, 67(5/6): 1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2006.01.053 [13] LETHOLE N L, CHAUKE H R, NGOEPE P E. Thermodynamic stability and pressure dependence of FePO4 polymorphs [J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2019, 1155: 67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2019.03.009 [14] BULL C L, RIDLEY C J, FUNNELL N P, et al. The distortion of two FePO4 polymorphs with high pressure [J]. Materials Advances, 2021, 2(15): 5096–5104. doi: 10.1039/D1MA00227A [15] BURBA C M, FRECH R. Raman and FTIR spectroscopic study of LixFePO4 (0≤x≤1) [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2004, 151(7): A1032–A1038. doi: 10.1149/1.1756885 [16] KLOTZ S, CHERVIN J C, MUNSCH P, et al. Hydrostatic limits of 11 pressure transmitting media [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2009, 42(7): 075413. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/7/075413 [17] SCHMIDT C, STEELE-MACINNIS M, WATENPHUL A, et al. Calibration of zircon as a Raman spectroscopic pressure sensor to high temperatures and application to water-silicate melt systems [J]. American Mineralogist, 2013, 98(4): 643–650. doi: 10.2138/am.2013.4143 [18] PASTERNAK M P, ROZENBERG G K, MILNER A P, et al. Pressure-induced concurrent transformation to an amorphous and crystalline phase in berlinite-type FePO4 [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 79(22): 4409–4412. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.79.4409 [19] CÎNTǍ PÎNZARU S, ONAC B P. Raman study of natural berlinite from a geological phosphate deposit [J]. Vibrational Spectroscopy, 2009, 49(2): 97–100. doi: 10.1016/j.vibspec.2008.05.003 [20] GAO J, HUANG W F, WU X, et al. Compressibility of carbonophosphate bradleyite Na3Mg(CO3)(PO4) by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy [J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2015, 42: 191–201. doi: 10.1007/s00269-014-0710-0 [21] BATTLE P D, GIBB T C, HU G, et al. The magnetic properties of the high pressure phase of ferric phosphate, FePO4-Ⅱ [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1986, 65(3): 343–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-4596(86)90106-4 [22] SZYMANSKI H A. Raman spectroscopy: theory and practice [M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1970. [23] BRIDGMAN P W. The physics of high pressure [M]. London: G. Bell, 1949. [24] POPOVIĆ L, DE WAAL D, BOEYENS J C A. Correlation between Raman wavenumbers and P―O bond lengths in crystalline inorganic phosphates [J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2005, 36(1): 2–11. doi: 10.1002/jrs.1253 [25] GARG N, SHARMA S M. A molecular dynamical investigation of high pressure phase transformations in berlinite (α-AlPO4) [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2000, 12(4): 375–397. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/12/4/303 [26] 徐桦, 邵俊. 正磷酸铝高压下相变的分子动力学模拟 [J]. 物理化学学报, 2000, 16(6): 512–516. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20000607XU H, SHAO J. Molecular dynamics simulation of the phase transition of α-berlinite under high pressure [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2000, 16(6): 512–516. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20000607 [27] JORGENSEN C K. Absorption spectra and chemical bonding in complexes [M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1962. [28] BORN M, HUANG K. Dynamical theory of crystal lattices [M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1954. [29] TAKENO S. A theory of the lattice vibration of anharmonic solids [J]. Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement, 1970, 45: 137–173. doi: 10.1143/PTPS.45.137 [30] LÓPEZ-MORENO S, ERRANDONEA D. Ab initio prediction of pressure-induced structural phase transitions of CrVO4-type orthophosphates [J]. Physical Review B, 2012, 86(10): 104112. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.104112 [31] PAULING L. The nature of the chemical bond [M]. 3rd ed. New York: Cornell University Press, 1960. -






 下载:
下载: