Advances in the Application of Machine Learning Potential to the Calculation of Mineral States and Properties in the Earth’s Deep Interior
-
摘要: 地球深部处于极端高温高压环境,其物质组成、相变行为和物理性质对于理解地球内部结构、动力学过程及演化具有重要意义。在极端条件下,传统实验手段面临热力学状态难以维持、物理量诊断困难的挑战,而第一性原理计算虽然具有量子精度,却受限于计算效率,难以直接应用于大时空尺度的地球深部矿物模拟。机器学习方法带来了新的机遇,基于第一性原理精度的数据集构建的高精度、高效率的机器学习势函数,显著拓展了第一性原理模拟的时空尺度,为研究地球深部矿物的物态、相变、弹性、输运等性质提供了革命性工具。系统地综述了机器学习方法在地球深部主要矿物(包括上地幔、过渡带与下地幔矿物、俯冲带组分以及地核物质)研究中的应用进展,总结了其在揭示相变、热导率、扩散、熔化和弹性性质等方面的代表性成果,并探讨了当前研究存在的局限性及未来发展方向。Abstract: The deep interior of the Earth is under extreme high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Its material composition, phase transition behavior, and physical properties are crucial for understanding the Earth’s internal structure, dynamic processes, and evolution. Traditional experimental methods face challenges in maintaining thermodynamic states and diagnosing physical quantities under such extreme conditions. While first-principles calculations offer quantum-level precision, their computational efficiency limits their direct application to simulating deep-Earth minerals across large spatiotemporal scales. Machine learning methods present new opportunities. By constructing high-precision, efficient machine learning potentials based on first-principles datasets, machine learning methods significantly extend the spatiotemporal scale of first-principles simulations, which provide revolutionary tools for studying the physical states, phase transitions, elasticity, and transport properties of deep-Earth minerals. This paper systematically reviews the progress of machine learning applications in studying major deep-Earth minerals, including those in the upper mantle, transition zone, lower mantle, subduction zone components, and core materials, and summarizes the representative achievements of machine learning methods in revealing phase transitions, thermal conductivity, diffusion, melting, and elastic properties, while also discussing current limitations and future research directions.
-
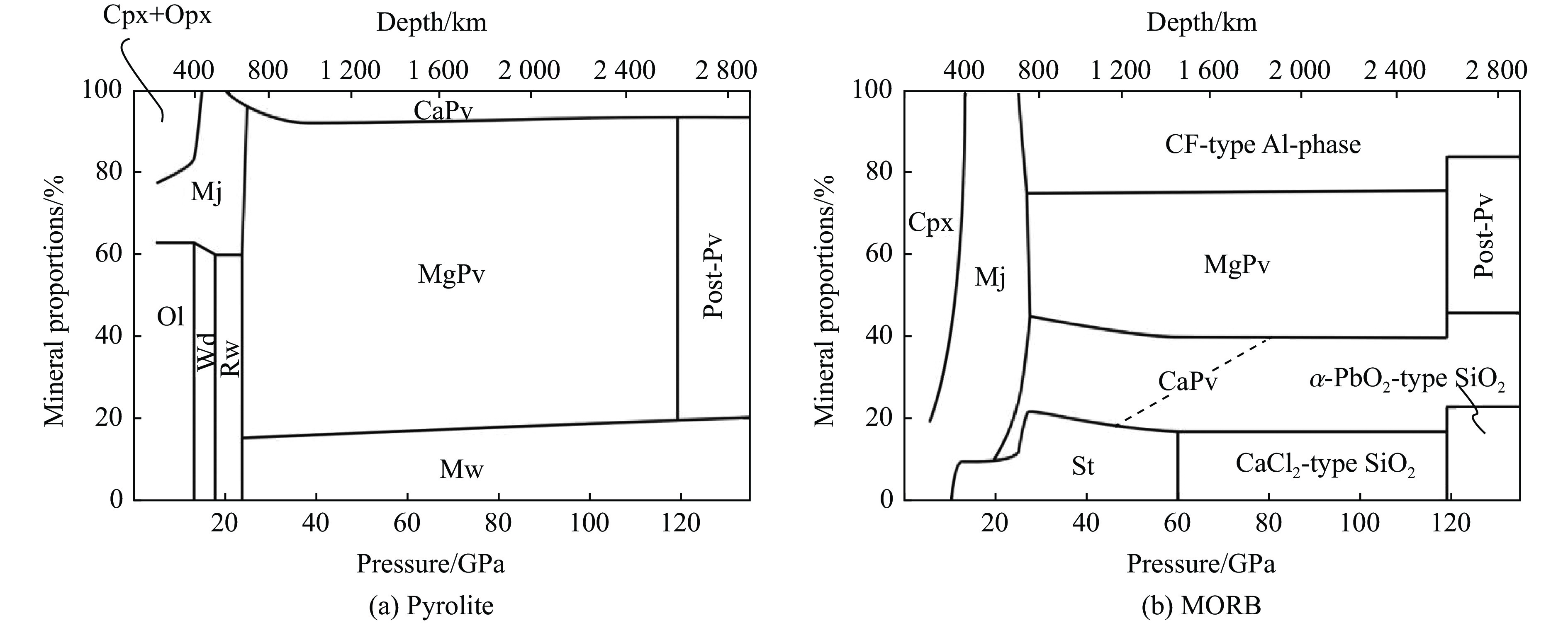
图 1 (a) 地幔岩和(b) MORB中的矿物丰度[5](缩写:Cpx,单斜辉石;Opx,斜方辉石;Mj,镁铁榴石;Ol,橄榄石;Wd,瓦兹利石;Rw,林伍德石;CaPv,CaSiO3钙钛矿;MgPv,富MgSiO3钙钛矿;Post-Pv,富MgSiO3后钙钛矿;Mw,铁方镁石;St,斯石英)
Figure 1. Change in mineral abundance in (a) pyrolitic mantle and (b) MORB composition[5] (Abbreviations: Cpx, clinopyroxene; Opx, orthopyroxene; Mj, majorite garnet; Ol, olivine; Wd, wadsleyite; Rw, ringwoodite; CaPv, CaSiO3 perovskite; MgPv, MgSiO3-rich perovskite; Post-Pv, MgSiO3-rich postperovskite; Mw, magnesiowüstite; St, stishovite.)
-
[1] MURAKAMI M, KHAN A, SOSSI P A, et al. The composition of Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2024, 52(1): 605–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-031621-075657 [2] POIRIER J P. Introduction to the physics of the Earth’s interior [M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. [3] WEIS D, HARPP K S, HARRISON L N, et al. Earth’s mantle composition revealed by mantle plumes [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2023, 4(9): 604–625. doi: 10.1038/s43017-023-00467-0 [4] DZIEWONSKI A M, ANDERSON D L. Preliminary reference Earth model [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1981, 25(4): 297–356. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(81)90046-7 [5] HIROSE K. Postperovskite phase transition and its geophysical implications [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2006, 44(3): 2005RG000186. doi: 10.1029/2005RG000186 [6] HIROSE K, LABROSSE S, HERNLUND J. Composition and state of the core [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2013, 41: 657–691. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-050212-124007 [7] TSUTSUMI Y, SAKAMOTO N, HIROSE K, et al. Retention of water in subducted slabs under core-mantle boundary conditions [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2024, 17(7): 697–704. doi: 10.1038/s41561-024-01464-8 [8] WALTER M J. Water transport to the core-mantle boundary [J]. National Science Review, 2021, 8(4): nwab007. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab007 [9] OHTANI E. The role of water in Earth’s mantle [J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(1): 224–232. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz071 [10] FU S Y, CHARITON S, PRAKAPENKA V B, et al. Core origin of seismic velocity anomalies at Earth’s core-mantle boundary [J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7953): 646–651. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05713-5 [11] MAO Z, SUN N Y, WEI W. Perspective for elasticity of minerals in the Earth’s top lower mantle [J]. National Science Review, 2021, 8(4): nwaa270. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa270 [12] WILLIAMS Q. The thermal conductivity of Earth’s core: a key geophysical parameter’s constraints and uncertainties [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2018, 46: 47–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-082517-010154 [13] LANDEAU M, FOURNIER A, NATAF H C, et al. Sustaining Earth’s magnetic dynamo [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(4): 255–269. doi: 10.1038/s43017-022-00264-1 [14] MARQUARDT H, THOMSON A R. Experimental elasticity of Earth’s deep mantle [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(9): 455–469. doi: 10.1038/s43017-020-0077-3 [15] ZHAO X Y, REN F L, HE J Z, et al. Ultrahigh-pressure generation above 50 GPa in a Kawai-type large-volume press [J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2025, 10(4): 047801. doi: 10.1063/5.0249620 [16] YUAN X H, CHEN G W, CHENG Y, et al. Direct synthesis of millimeter-sized hexagonal diamond from graphite [J]. Science Bulletin, 2025, 70(8): 1257–1263. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2025.03.003 [17] YANG L X, LAU K C, ZENG Z D, et al. Synthesis of bulk hexagonal diamond [J]. Nature, 2025, 644(8076): 370–375. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09343-x [18] KUPENKO I, APRILIS G, VASIUKOV D M, et al. Magnetism in cold subducting slabs at mantle transition zone depths [J]. Nature, 2019, 570(7759): 102–106. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1254-8 [19] KO B, GREENBERG E, PRAKAPENKA V, et al. Calcium dissolution in bridgmanite in the Earth’s deep mantle [J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7934): 88–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05237-4 [20] SUN N Y, SHI W G, MAO Z, et al. High pressure-temperature study on the thermal equations of state of seifertite and CaCl2-type SiO2 [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2019, 124(12): 12620–12630. doi: 10.1029/2019JB017853 [21] PIERRU R, PISON L, MATHIEU A, et al. Solidus melting of pyrolite and bridgmanite: implication for the thermochemical state of the Earth’s interior [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2022, 595: 117770. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2022.117770 [22] BALUGANI S, HERNANDEZ J A, SÉVELIN-RADIGUET N, et al. New constraints on the melting temperature and phase stability of shocked iron up to 270 GPa probed by ultrafast X-ray absorption spectroscopy [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2024, 133(25): 254101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.254101 [23] MILLOT M, DUBROVINSKAIA N, ČERNOK A, et al. Shock compression of stishovite and melting of silica at planetary interior conditions [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6220): 418–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1261507 [24] FEI Y W, SEAGLE C T, TOWNSEND J P, et al. Melting and density of MgSiO3 determined by shock compression of bridgmanite to 1 254 GPa [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 876. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21170-y [25] LI M, ZHANG S, ZHANG H P, et al. Continuous sound velocity measurements along the shock Hugoniot curve of quartz [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(21): 215703. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.215703 [26] LI Z, SCANDOLO S. Competing phases of iron at Earth’s core conditions from deep-learning-aided ab-initio simulations [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51(19): e2024GL110357. doi: 10.1029/2024GL110357 [27] CHANG X J, CHEN B, ZENG Q Y, et al. Theoretical evidence of H-He demixing under Jupiter and Saturn conditions [J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 8543. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52868-4 [28] ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, ZHANG S, et al. Full-scale ab initio simulations of laser-driven atomistic dynamics [J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2023, 9(1): 213. doi: 10.1038/s41524-023-01168-4 [29] QIU R, ZENG Q Y, WANG H, et al. Anomalous thermal transport across the superionic transition in ice [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2023, 40(11): 116301. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/40/11/116301 [30] CHANG X J, KANG D D, CHEN B, et al. H-He demixing driven by anisotropic hydrogen diffusion [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2025, 42(5): 053704. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/42/5/053704 [31] 曾启昱, 陈博, 康冬冬, 等. 大规模、量子精度的分子动力学模拟: 以极端条件液态铁为例 [J]. 物理学报, 2023, 72(18): 187102. doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20231258ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, KANG D D, et al. Large scale and quantum accurate molecular dynamics simulation: liquid iron under extreme condition [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2023, 72(18): 187102. doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20231258 [32] HERNANDEZ J A, MOHN C E, GUREN M G, et al. Ab initio atomistic simulations of Ca-perovskite melting [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(20): e2021GL097262. doi: 10.1029/2021GL097262 [33] STIXRUDE L, KARKI B. Structure and freezing of MgSiO3 liquid in Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Science, 2005, 310(5746): 297–299. doi: 10.1126/science.1116952 [34] BAJGAIN S K, ASHLEY A W, MOOKHERJEE M, et al. Insights into magma ocean dynamics from the transport properties of basaltic melt [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 7590. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35171-y [35] KOHN W, SHAM L J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects [J]. Physical Review, 1965, 140(4A): A1133–A1138. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.140.A1133 [36] CEPERLEY D M, ALDER B J. Ground state of the electron gas by a stochastic method [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1980, 45(7): 566–569. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.45.566 [37] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865–3868. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 [38] PERDEW J P, RUZSINSZKY A, CSONKA G I, et al. Restoring the density-gradient expansion for exchange in solids and surfaces [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(13): 136406. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.136406 [39] SUN J W, MARSMAN M, CSONKA G I, et al. Self-consistent meta-generalized gradient approximation within the projector-augmented-wave method [J]. Physical Review B, 2011, 84(3): 035117. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.84.035117 [40] SUN J W, RUZSINSZKY A, PERDEW J P. Strongly constrained and appropriately normed semilocal density functional [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 115(3): 036402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.036402 [41] SUN Y C, ZHOU H Q, YIN K, et al. First-principles study of thermodynamics and spin transition in FeSiO3 liquid at high pressure [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(7): 3706–3716. doi: 10.1029/2018GL081421 [42] SUN Y, COCOCCIONI M, WENTZCOVITCH R M. LDA+Usc calculations of phase relations in FeO [J]. Physical Review Materials, 2020, 4(6): 063605. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.4.063605 [43] LENNARD-JONES J E. Cohesion [J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1931, 43(5): 461–482. doi: 10.1088/0959-5309/43/5/301 [44] DAW M S, BASKES M I. Semiempirical, quantum mechanical calculation of hydrogen embrittlement in metals [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1983, 50(17): 1285–1288. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.1285 [45] ZHANG L F, HAN J Q, WANG H, et al. Deep potential molecular dynamics: a scalable model with the accuracy of quantum mechanics [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(14): 143001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.143001 [46] WANG H, ZHANG L F, HAN J Q, et al. DeePMD-kit: a deep learning package for many-body potential energy representation and molecular dynamics [J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 228: 178–184. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.03.016 [47] ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, YU X X, et al. Towards large-scale and spatiotemporally resolved diagnosis of electronic density of states by deep learning [J]. Physical Review B, 2022, 105(17): 174109. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.105.174109 [48] BARTÓK A P, PAYNE M C, KONDOR R, et al. Gaussian approximation potentials: the accuracy of quantum mechanics, without the electrons [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(13): 136403. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.136403 [49] FAN Z Y, ZENG Z Z, ZHANG C Z, et al. Neuroevolution machine learning potentials: combining high accuracy and low cost in atomistic simulations and application to heat transport [J]. Physical Review B, 2021, 104(10): 104309. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.104.104309 [50] CHANYSHEV A, ISHII T, BONDAR D, et al. Depressed 660 km discontinuity caused by akimotoite-bridgmanite transition [J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7891): 69–73. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04157-z [51] WARREN J M, HAURI E H. Pyroxenes as tracers of mantle water variations [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2014, 119(3): 1851–1881. doi: 10.1002/2013JB010328 [52] WOOD B J, KISEEVA E S, MATZEN A K. Garnet in the Earth’s mantle [J]. Elements, 2013, 9(6): 421–426. doi: 10.2113/gselements.9.6.421 [53] CHEN L Y, ZHAO X Y, XU C W, et al. The role of pyrope garnet in water transport into the topmost lower mantle [J]. National Science Review, 2025, 12(6): nwaf133. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaf133 [54] CHEN T, LIEBERMANN R C, ZOU Y T, et al. Tracking silica in Earth’s upper mantle using new sound velocity data for coesite to 5.8 GPa and 1 073 K [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(15): 7757–7765. doi: 10.1002/2017GL073950 [55] ISHII T, FROST D J, KIM E J, et al. Buoyancy of slabs and plumes enhanced by curved post-garnet phase boundary [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2023, 16(9): 828–832. doi: 10.1038/s41561-023-01244-w [56] IRIFUNE T. Absence of an aluminous phase in the upper part of the Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Nature, 1994, 370(6485): 131–133. doi: 10.1038/370131a0 [57] WANG D, WU Z Q, DENG X. Thermal conductivity of hydrous wadsleyite determined by non-equilibrium molecular dynamics based on machine learning [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(22): e2022GL100337. doi: 10.1029/2022GL100337 [58] ZHONG X, HÖFLING F, JOHN T. Hydrogen diffusion in garnet: insights from atomistic simulations [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2025, 26(2): e2024GC011951. doi: 10.1029/2024GC011951 [59] KAMINSKY F V. The Earth’s lower mantle: composition and structure [M]. Cham: Springer, 2017. [60] ROST S, GARNERO E J, WILLIAMS Q, et al. Seismological constraints on a possible plume root at the core-mantle boundary [J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7042): 666–669. doi: 10.1038/nature03620 [61] LI R P, DANNBERG J, GASSMÖLLER R, et al. How phase transitions impact changes in mantle convection style throughout Earth’s history: from stalled plumes to surface dynamics [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2025, 26(2): e2024GC011600. doi: 10.1029/2024GC011600 [62] VAN DER HILST R D, KÁRASON H. Compositional heterogeneity in the bottom 1 000 kilometers of Earth’s mantle: toward a hybrid convection model [J]. Science, 1999, 283(5409): 1885–1888. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5409.1885 [63] STIXRUDE L, LITHGOW-BERTELLONI C. Geophysics of chemical heterogeneity in the mantle [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2012, 40(1): 569–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.36.031207.124244 [64] TSCHAUNER O, MA C, BECKETT J R, et al. Discovery of bridgmanite, the most abundant mineral in Earth, in a shocked meteorite [J]. Science, 2014, 346(6213): 1100–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.1259369 [65] MURAKAMI M, HIROSE K, KAWAMURA K, et al. Post-perovskite phase transition in MgSiO3 [J]. Science, 2004, 304(5672): 855–858. doi: 10.1126/science.1095932 [66] OGANOV A R, ONO S. Theoretical and experimental evidence for a post-perovskite phase of MgSiO3 in Earth’s D″ layer [J]. Nature, 2004, 430(6998): 445–448. doi: 10.1038/nature02701 [67] LAY T, HELMBERGER D V. A lower mantle S-wave triplication and the shear velocity structure of D″ [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1983, 75(3): 799–837. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1983.tb05010.x [68] BELONOSHKO A B, SKORODUMOVA N V, ROSENGREN A, et al. High-pressure melting of MgSiO3 [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 94(19): 195701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.195701 [69] OHTA K, YAGI T, TAKETOSHI N, et al. Lattice thermal conductivity of MgSiO3 perovskite and post-perovskite at the core-mantle boundary [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 349/350: 109–115. [70] TSUCHIYA T, TSUCHIYA J, UMEMOTO K, et al. Phase transition in MgSiO3 perovskite in the Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 224(3/4): 241–248. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.05.017 [71] DENG J, STIXRUDE L. Thermal conductivity of silicate liquid determined by machine learning potentials [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(17): e2021GL093806. doi: 10.1029/2021GL093806 [72] YANG F H, ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, et al. Lattice thermal conductivity of MgSiO3 perovskite and post-perovskite under lower mantle conditions calculated by deep potential molecular dynamics [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2022, 39(11): 116301. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/39/11/116301 [73] WANG D, WU Z Q, DENG X. Thermal conductivity of Fe-bearing bridgmanite and post-perovskite: implications for the heat flux from the core [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2023, 621: 118368. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2023.118368 [74] PENG Y H, DENG J. Thermal conductivity of MgSiO3-H2O system determined by machine learning potentials [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51(5): e2023GL107245. doi: 10.1029/2023GL107245 [75] DENG J, NIU H Y, HU J W, et al. Melting of MgSiO3 determined by machine learning potentials [J]. Physical Review B, 2023, 107(6): 064103. [76] PENG Y H, DENG J. Hydrogen diffusion in the lower mantle revealed by machine learning potentials [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2024, 129(4): e2023JB028333. doi: 10.1029/2023JB028333 [77] WAN T Q, LUO C X, SUN Y, et al. Thermoelastic properties of bridgmanite using deep-potential molecular dynamics [J]. Physical Review B, 2024, 109(9): 094101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.109.094101 [78] SWIFT D C, EGGERT J H, HICKS D G, et al. MASS-radius relationships for exoplanets [J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2012, 744(1): 59. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/744/1/59 [79] SOUBIRAN F, MILITZER B. Anharmonicity and phase diagram of magnesium oxide in the megabar regime [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(17): 175701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.175701 [80] WICKS J K, SINGH S, MILLOT M, et al. B1-B2 transition in shock-compressed MgO [J]. Science Advances, 2024, 10(23): eadk0306. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk0306 [81] BRAITHWAITE J, STIXRUDE L. Partitioning of iron between liquid and crystalline phases of (Mg, Fe)O [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(16): e2022GL099116. doi: 10.1029/2022GL099116 [82] HOLMSTRÖM E, STIXRUDE L. Spin crossover in liquid (Mg, Fe)O at extreme conditions [J]. Physical Review B, 2016, 93(19): 195142. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.195142 [83] REALI R, JACKSON J M, VAN ORMAN J, et al. Modeling viscosity of (Mg, Fe)O at lowermost mantle conditions [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2019, 287: 65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2018.12.005 [84] QIU R, ZENG Q Y, HAN J S, et al. Coupled temperature-density dependence of lattice thermal conductivity of MgO at extreme conditions [J]. Physical Review B, 2025, 111(6): 064103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.111.064103 [85] WISESA P, ANDOLINA C M, SAIDI W A. Machine-learning accelerated first-principles accurate modeling of the solid-liquid phase transition in MgO under mantle conditions [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2023, 14(39): 8741–8748. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c02424 [86] DENG J. Large-scale atomistic simulations of magnesium oxide exsolution driven by machine learning potentials: implications for the early geodynamo [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51(16): e2024GL109793. doi: 10.1029/2024GL109793 [87] PENG Y H, YOSHINO T, DENG J. Grain boundary diffusion cannot explain the W isotope heterogeneities of the deep mantle [J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 1866. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57120-1 [88] YANG T, CAI Z F, HUANG Z T, et al. Deep learning illuminates spin and lattice interaction in magnetic materials [J]. Physical Review B, 2024, 110(6): 064427. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.110.064427 [89] YUAN Z L, XU Z M, LI H, et al. Equivariant neural network force fields for magnetic materials [J]. Quantum Frontiers, 2024, 3(1): 8. doi: 10.1007/s44214-024-00055-3 [90] TSCHAUNER O, HUANG S C, YANG S Y, et al. Discovery of davemaoite, CaSiO3-perovskite, as a mineral from the lower mantle [J]. Science, 2021, 374(6569): 891–894. doi: 10.1126/science.abl8568 [91] WALTER M J, KOHN S C, PEARSON D G, et al. Comment on “discovery of davemaoite, CaSiO3-perovskite, as a mineral from the lower mantle” [J]. Science, 2022, 376(6593): eabo0882. doi: 10.1126/science.abo0882 [92] WALTER M J, THOMSON A R, SMITH E M. Geochemistry of silicate and oxide inclusions in sublithospheric diamonds [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2022, 88(1): 393–450. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2022.88.07 [93] WANG L, MIYAJIMA N, WANG F, et al. Persistence of davemaoite at lower-mantle conditions [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2025, 18(4): 365–369. doi: 10.1038/s41561-025-01657-9 [94] MUIR J M R, THOMSON A R, ZHANG F W. The miscibility of calcium silicate perovskite and bridgmanite: a single perovskite solid solution in hot, iron-rich regions [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2021, 566: 116973. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2021.116973 [95] IRIFUNE T, SHINMEI T, MCCAMMON C A, et al. Iron partitioning and density changes of pyrolite in Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Science, 2010, 327(5962): 193–195. doi: 10.1126/science.1181443 [96] THOMSON A R, CRICHTON W A, BRODHOLT J P, et al. Seismic velocities of CaSiO3 perovskite can explain LLSVPs in Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Nature, 2019, 572(7771): 643–647. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1483-x [97] WU F L, SUN Y, WAN T Q, et al. Deep-learning-based prediction of the tetragonal→cubic transition in davemaoite [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51(12): e2023GL108012. doi: 10.1029/2023GL108012 [98] ZHANG C, YANG J Y, SUN T, et al. Strong precursor softening in cubic CaSiO3 perovskite [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2025, 122(5): e2410910122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410910122 [99] WAN T Q, LUO C C, ZHANG Z, et al. Ferroelasticity, shear modulus softening, and the tetragonal-cubic transition in davemaoite [EB/OL]. arXiv: 2505.01529. (2025-05-02)[2025-08-15]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2505.01529. [100] YIN K, BELONOSHKO A B, LI Y, et al. Davemaoite as the mantle mineral with the highest melting temperature [J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(49): eadj2660. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj2660 [101] WANG Z F, HE Y, MAO H K, et al. Superionicity of oxygen-deficient davemaoite and its impact on the deep-Earth oxidation cycle [J]. Science Advances, 2025, 11(22): eadu8401. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu8401 [102] PRADHAN G K, FIQUET G, SIEBERT J, et al. Melting of MORB at core-mantle boundary [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 431: 247–255. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.09.034 [103] SCHMIDT M W, POLI S. Experimentally based water budgets for dehydrating slabs and consequences for arc magma generation [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 163(1/2/3/4): 361–379. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00142-3 [104] HELFFRICH G, BRODHOLT J. Relationship of deep seismicity to the thermal structure of subducted lithosphere [J]. Nature, 1991, 353(6341): 252–255. doi: 10.1038/353252a0 [105] LIN Y H, HU Q Y, MENG Y, et al. Evidence for the stability of ultrahydrous stishovite in Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(1): 184–189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914295117 [106] LIN Y H, HU Q Y, WALTER M J, et al. Hydrous SiO2 in subducted oceanic crust and H2O transport to the core-mantle boundary [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2022, 594: 117708. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2022.117708 [107] OHTANI E, LITASOV K, SUZUKI A, et al. Stability field of new hydrous phase, δ-AlOOH, with implications for water transport into the deep mantle [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(20): 3991–3993. doi: 10.1029/2001GL013397 [108] HOU M Q, HE Y, JANG B G, et al. Superionic iron oxide-hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(3): 174–178. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00696-2 [109] VAN KEKEN P E, HACKER B R, SYRACUSE E M, et al. Subduction factory: 4. depth-dependent flux of H2O from subducting slabs worldwide [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(B1): B01401. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007922 [110] OKAMOTO K, MARUYAMA S. The high-pressure synthesis of lawsonite in the MORB+H2O system [J]. American Mineralogist, 1999, 84(3): 362–373. doi: 10.2138/am-1999-0320 [111] LI J W, LIN Y H, MEIER T, et al. Silica-water superstructure and one-dimensional superionic conduit in Earth’s mantle [J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(35): eadh3784. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh3784 [112] SUN X W, CAO J L, WANG X X, et al. Investigating the impact of temperature on hydrous magnesium silicate phase D using deep-learning-driven interatomic potentials [J]. Physical Review B, 2025, 111(18): 184109. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.111.184109 [113] LUO C X, SUN Y, WENTZCOVITCH R M. Probing the state of hydrogen in δ-AlOOH at mantle conditions with machine learning potential [J]. Physical Review Research, 2024, 6(1): 013292. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.013292 [114] LUO C X, SUN Y, WENTZCOVITCH R M. Elasticity and acoustic velocities of δ-AlOOH at extreme conditions: a methodology assessment [J]. Physical Review Materials, 2024, 8(10): 103601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.8.103601 [115] HE Y, ZHANG W, HU Q, et al. Absence of dehydration due to superionic transition at Earth’s core-mantle boundary [EB/OL]. arXiv: 2503.17906. (2025-03-23)[2025-09-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.17906. [116] LAIO A, BERNARD S, CHIAROTTI G L, et al. Physics of iron at Earth’s core conditions [J]. Science, 2000, 287(5455): 1027–1030. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5455.1027 [117] ANDERSON O L. The Earth’s core and the phase diagram of iron [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1982, 306(1492): 21–35. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1982.0063 [118] OLSON P. Core dynamics: an introduction and overview [M]//SCHUBERT G. Treatise on Geophysics. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015: 1–25. [119] STIXRUDE L. Structure of iron to 1 Gbar and 40 000 K [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(5): 055505. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.055505 [120] TATENO S, HIROSE K, OHISHI Y, et al. The structure of iron in Earth’s inner core [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6002): 359–361. doi: 10.1126/science.1194662 [121] ANZELLINI S, DEWAELE A, MEZOUAR M, et al. Melting of iron at Earth’s inner core boundary based on fast X-ray diffraction [J]. Science, 2013, 340(6131): 464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.1233514 [122] KRAUS R G, HEMLEY R J, ALI S J, et al. Measuring the melting curve of iron at super-Earth core conditions [J]. Science, 2022, 375(6577): 202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.abm1472 [123] BELONOSHKO A B, LUKINOV T, FU J, et al. Stabilization of body-centred cubic iron under inner-core conditions [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2017, 10(4): 312–316. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2892 [124] SMIRNOV G S, PEIL O E, RUBAN A V, et al. Impact of magnetism on Fe phase diagram under extreme conditions [J]. Physical Review Materials, 2025, 9(4): L040601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.9.L040601 [125] HRUBIAK R, MENG Y, SHEN G Y. Experimental evidence of a body centered cubic iron at the Earth’s core condition [EB/OL]. arXiv: 1804.05109. (2018-04-13)[2025-08-21]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.05109. [126] KONOPKOVA Z, EDMUND E, BALL O B, et al. Observation of body-centered cubic iron above 200 gigapascals [EB/OL]. arXiv: 2505.15397. (2025-05-21)[2025-08-21]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2505.15397. [127] LI Z, SCANDOLO S. Elasticity and viscosity of hcp iron at Earth’s inner core conditions from machine learning-based large-scale atomistic simulations [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(24): e2022GL101161. doi: 10.1029/2022GL101161 [128] NIKOLOV S, RAMAKRISHNA K, ROHSKOPF A, et al. Probing iron in Earth’s core with molecular-spin dynamics [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(51): e2408897121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2408897121 [129] GUBBINS D, SREENIVASAN B, MOUND J, et al. Melting of the Earth’s inner core [J]. Nature, 2011, 473(7347): 361–363. doi: 10.1038/nature10068 [130] TURNEAURE S J, SHARMA S M, GUPTA Y M. Crystal structure and melting of Fe shock compressed to 273 GPa: in situ X-ray diffraction [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(21): 215702. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.215702 [131] HE Y, SUN S C, KIM D Y, et al. Superionic iron alloys and their seismic velocities in Earth’s inner core [J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7896): 258–262. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04361-x [132] ZHANG Y J, LIN J F. Molten iron in Earth-like exoplanet cores [J]. Science, 2022, 375(6577): 146–147. doi: 10.1126/science.abn2051 [133] FISCHER R A. Melting of Fe alloys and the thermal structure of the core [M]//TERASAKI H, FISCHER R A. Deep Earth: Physics and Chemistry of the Lower Mantle and Core. Washington: American Geophysical Union (AGU), 2016: 1–12. [134] LI J, WU Q, LI J B, et al. Shock melting curve of iron: a consensus on the temperature at the Earth’s inner core boundary [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(15): e2020GL087758. doi: 10.1029/2020GL087758 [135] WU F L, WU S Q, WANG C Z, et al. Melting temperature of iron under the Earth’s inner core condition from deep machine learning [J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2024, 15(6): 101925. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2024.101925 [136] YIN Y, LIU C, ZHAI S M, et al. Lattice thermal conductivity of hcp Fe-Si alloys determined by machine learning potentials [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2025, 52(17): e2024GL111953. doi: 10.1029/2024GL111953 [137] LI Z, SCANDOLO S. Short-range order stabilizes a cubic iron alloy in Earth’s inner core [J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 7574. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62666-1 [138] TAHMASBI H, RAMAKRISHNA K, LOKAMANI M, et al. Machine learning-driven structure prediction for iron hydrides [J]. Physical Review Materials, 2024, 8(3): 033803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.8.033803 [139] ZHANG Y, WANG W Z, LI Y G, et al. Superionic iron hydride shapes ultralow-velocity zones at Earth’s core-mantle boundary [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(35): e2406386121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2406386121 [140] YUAN L, STEINLE-NEUMANN G. Hydrogen distribution between the Earth’s inner and outer core [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2023, 609: 118084. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2023.118084 [141] LIU T, JING Z C. Hydrogen and silicon are the preferred light elements in Earth’s core [J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2024, 5(1): 282. doi: 10.1038/s43247-024-01450-3 [142] ZHANG C, TANG L, SUN Y, et al. Deep machine learning potential for atomistic simulation of Fe-Si-O systems under Earth’s outer core conditions [J]. Physical Review Materials, 2022, 6(6): 063802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.6.063802 [143] ZHANG D, BI H R, DAI F Z, et al. Pretraining of attention-based deep learning potential model for molecular simulation [J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2024, 10(1): 94. doi: 10.1038/s41524-024-01278-7 [144] MO P H, ZHANG Y J, ZHAO Z Y, et al. High-speed and low-power molecular dynamics processing unit (MDPU) with ab initio accuracy [J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2024, 10(1): 253. doi: 10.1038/s41524-024-01422-3 -







 下载:
下载: