Accelerating Finite Element Analysis of Dynamic Impact Response of TiN/Ti Multilayer Coatings Based on Small Sample Machine Learning
-
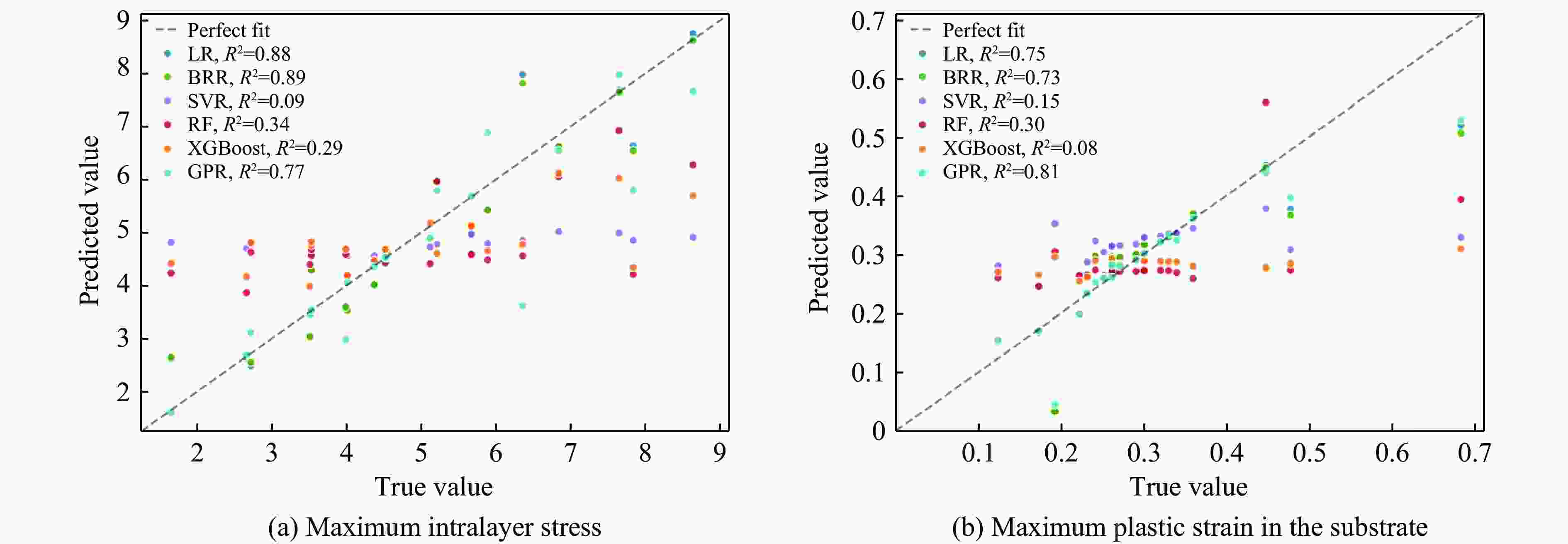
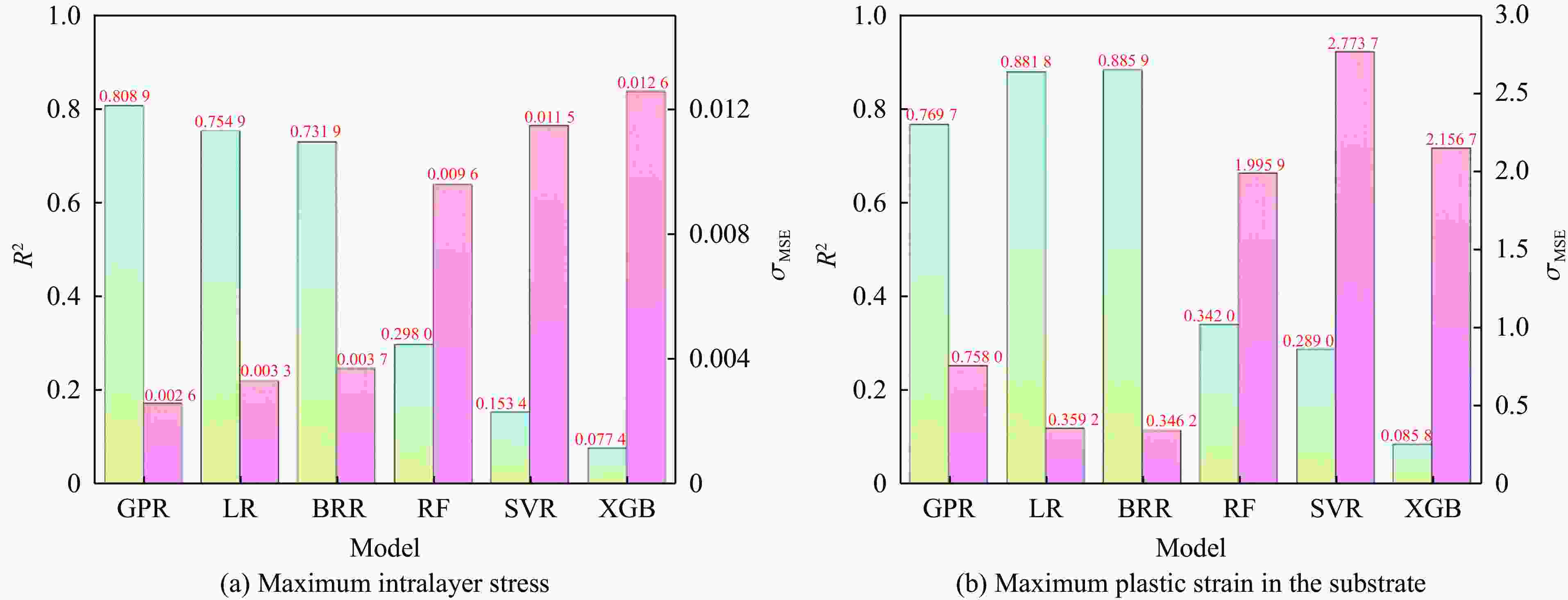
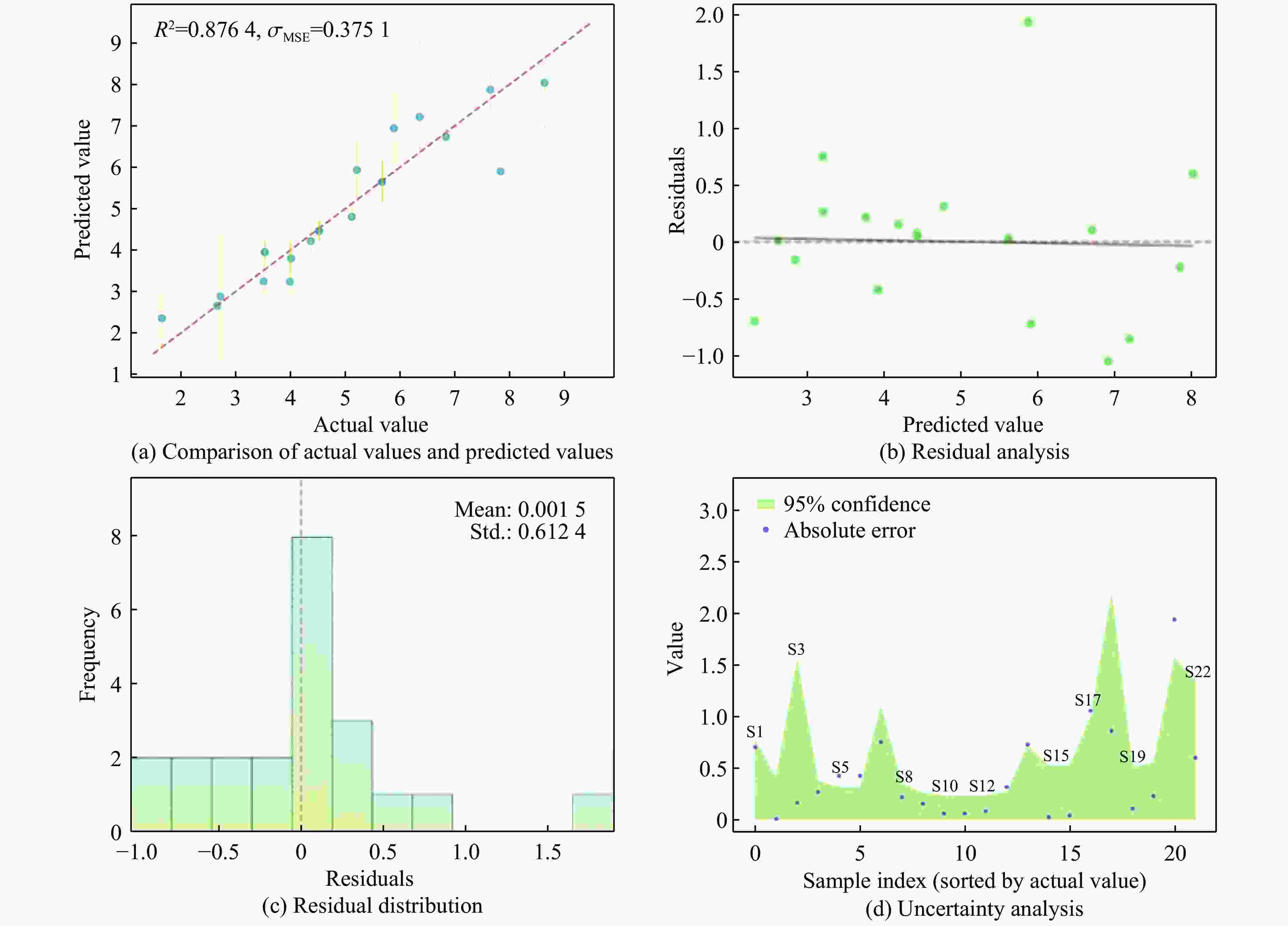
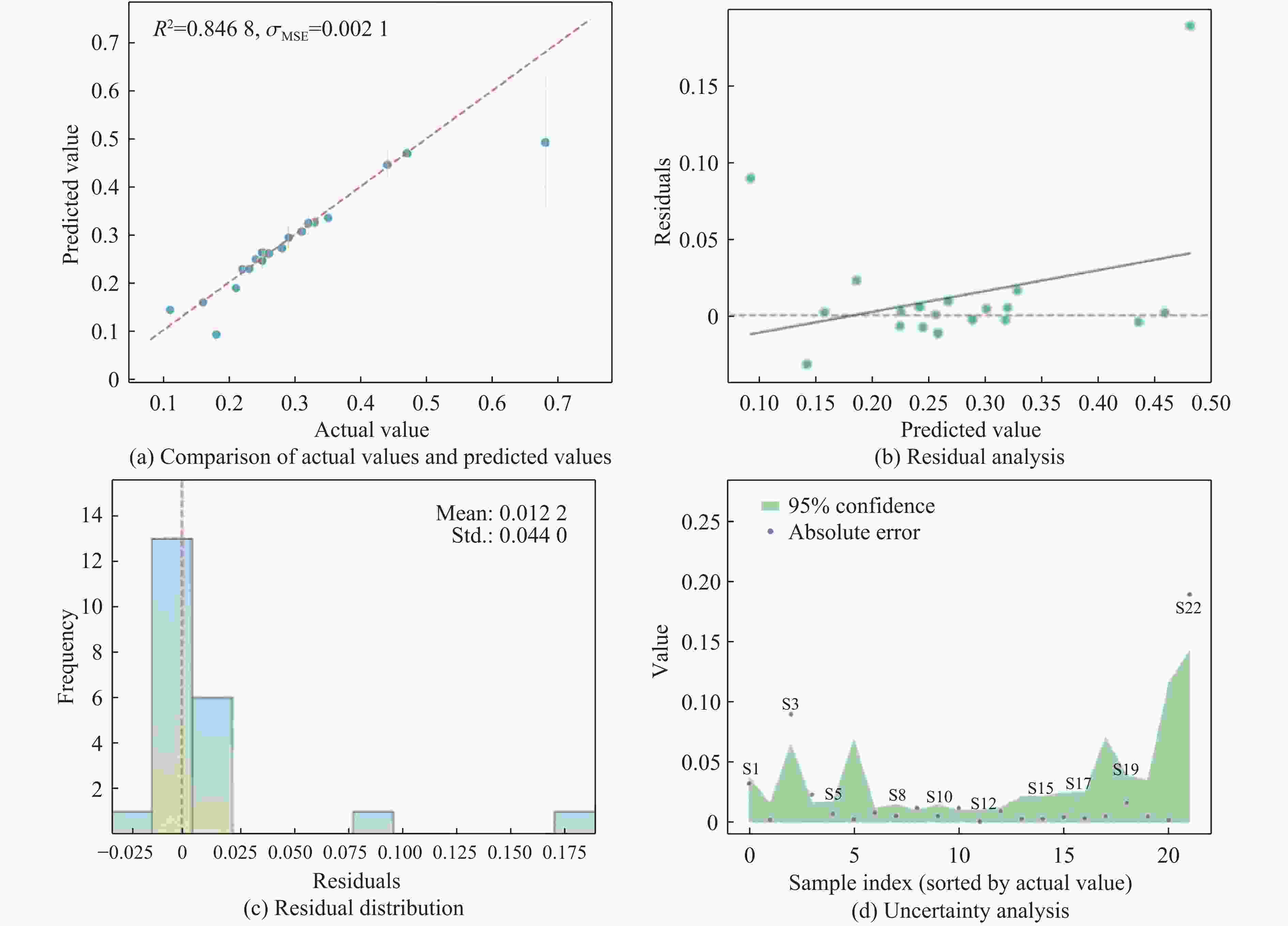
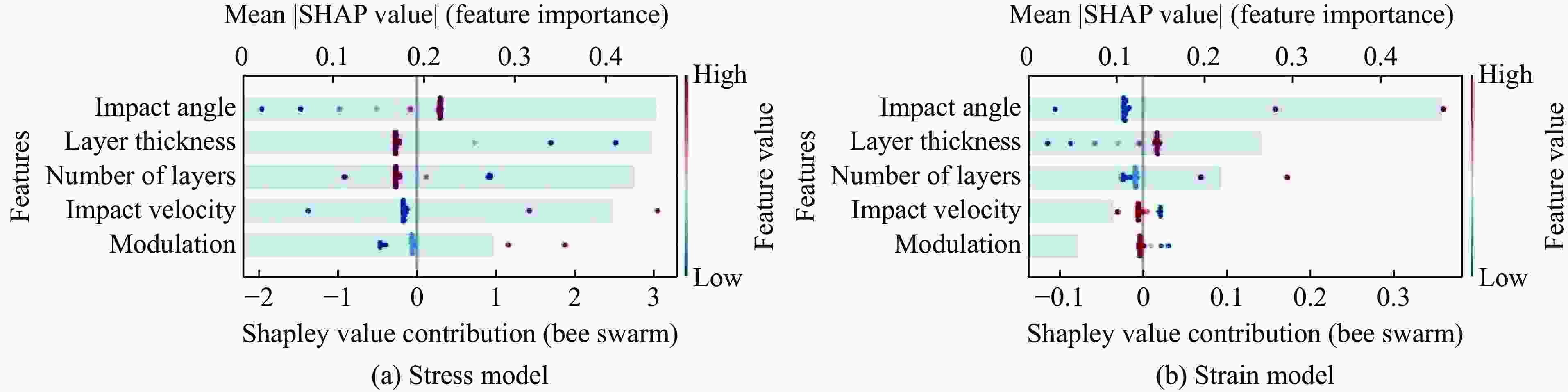
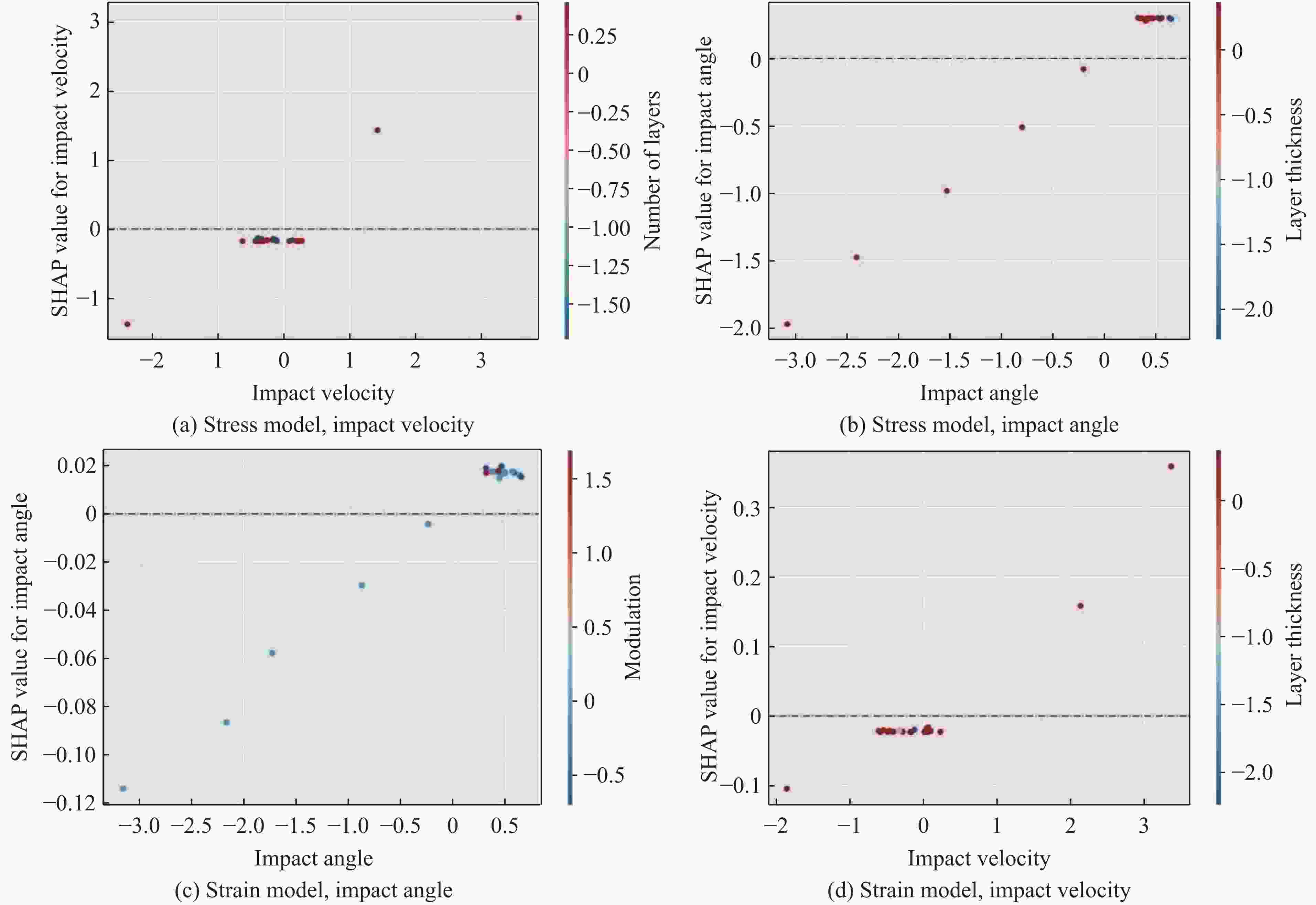
摘要: 服役于极端环境下的发动机高压涡轮叶片,因长期承受高温燃气携带的沙尘颗粒的高速撞击,使役寿命会大幅降低。TiN/Ti多层涂层凭借其高硬、高韧的特性成为叶片表面涂层的首选材料。然而,其抗冲蚀性能与其结构参数紧密相关,传统的实验试错法与有限元模拟往往耗时耗力。为了解决这一困境,提出了一个基于小样本机器学习(machine learning,ML)与有限元分析融合的TiN/Ti多层涂层设计框架。评估了多种回归算法,并优选出高斯过程回归模型,实现了涂层在动态冲击下的层内最大应力与基体最大塑性应变的高精度预测(决定系数R2分别为0.88和0.85)。结合残差与不确定性分析,进一步强化了模型的拟合能力。此外,通过SHAP(shapley additive explanations)模型分析揭示各特征对目标的影响。最终设计了8种新的结构与冲击条件下的涂层仿真模型,并验证了ML模型预测结果的准确性。该框架为高维参数空间下涂层抗冲击设计提供了数据高效、计算经济的解决方案。
-
关键词:
- TiN/Ti多层涂层 /
- 机器学习 /
- 有限元分析 /
- 动态冲击
Abstract: Engine high-pressure turbine blades operating in extreme environments, such as deserts, are subjected to long-term high-velocity impacts from sand particles carried by hot combustion gases, significantly reducing their service life. Owing to its high hardness and toughness, the TiN/Ti multilayer coating has emerged as a preferred surface coating material for such blades. However, its erosion resistance is highly dependent on structural parameters, and traditional experimental trial-and-error methods and finite element simulations are often time-consuming and labor-intensive. To address this challenge, this study proposes a TiN/Ti multilayer coating design framework that integrates small-sample machine learning (ML) with finite element analysis. Multiple regression algorithms were evaluated, and Gaussian process regression (GPR) was selected for its superior performance, enabling high-accuracy prediction of the maximum intralayer stress and the maximum plastic strain in the substrate under dynamic impact conditions (with R2 values of 0.88 and 0.85, respectively). The modelʼs fitting capability was further enhanced through residual and uncertainty analyses. Moreover, shapley additive explanations (SHAP) analysis was employed to elucidate the contribution of each feature to the target variables. Finally, eight new coating structures under varying impact conditions were designed and simulated to validate the predictive accuracy of the ML model. This framework offers a data-efficient and computationally economical solution for impact-resistant coating design in high-dimensional parameter spaces.-
Key words:
- TiN/Ti multilayer coating /
- machine learning /
- finite element analysis /
- dynamic impact
-
表 1 原始数据集
Table 1. Original dataset
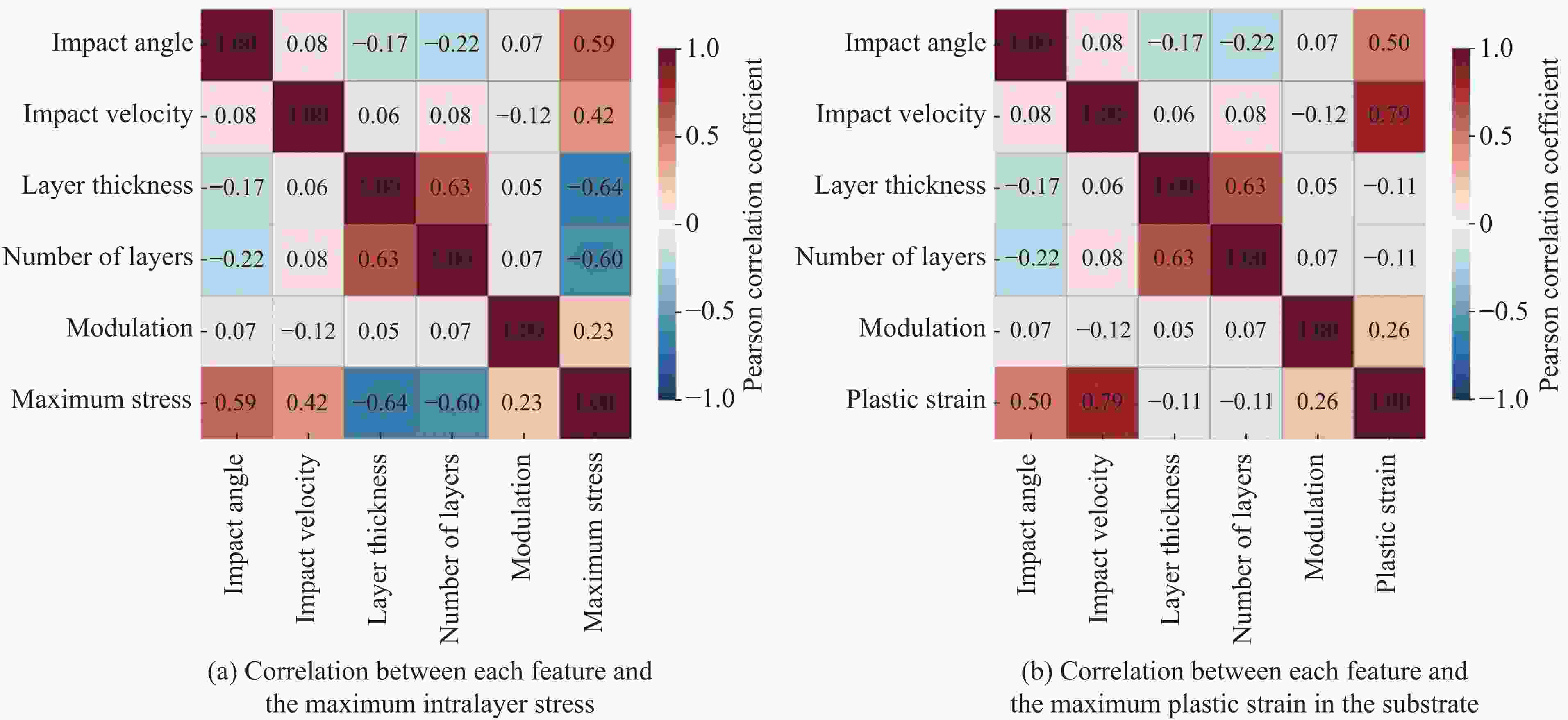
Feature Target α/(°) v/(m·s−1) h/μm N $ \lambda $ σmax/GPa εmax 15 100 24 8 4 1.65 0.11 30 100 24 8 4 2.66 0.16 45 100 24 8 4 3.51 0.21 60 100 24 8 4 4.01 0.22 75 100 24 8 4 4.37 0.24 90 100 24 8 4 4.54 0.25 90 75 24 8 2 2.72 0.18 90 100 24 8 2 3.53 0.25 90 125 24 8 2 5.21 0.44 90 150 24 8 2 7.84 0.68 90 100 12 2 4 8.64 0.33 90 100 16 2 4 7.65 0.32 90 100 20 2 4 6.84 0.31 90 100 24 2 4 5.68 0.29 90 100 24 2 4 5.67 0.29 90 100 24 6 4 5.12 0.28 90 100 24 8 4 4.52 0.25 90 100 24 12 4 3.99 0.23 90 100 24 8 2 3.53 0.25 90 100 24 8 4 4.52 0.26 90 100 24 8 11 5.89 0.35 90 100 24 8 19 6.36 0.47 表 2 TiN/Ti多层涂层有限元建模结构参数及冲击条件设定
Table 2. Finite element modeling of TiN/Ti multilayer coating structural parameters and impact condition settings
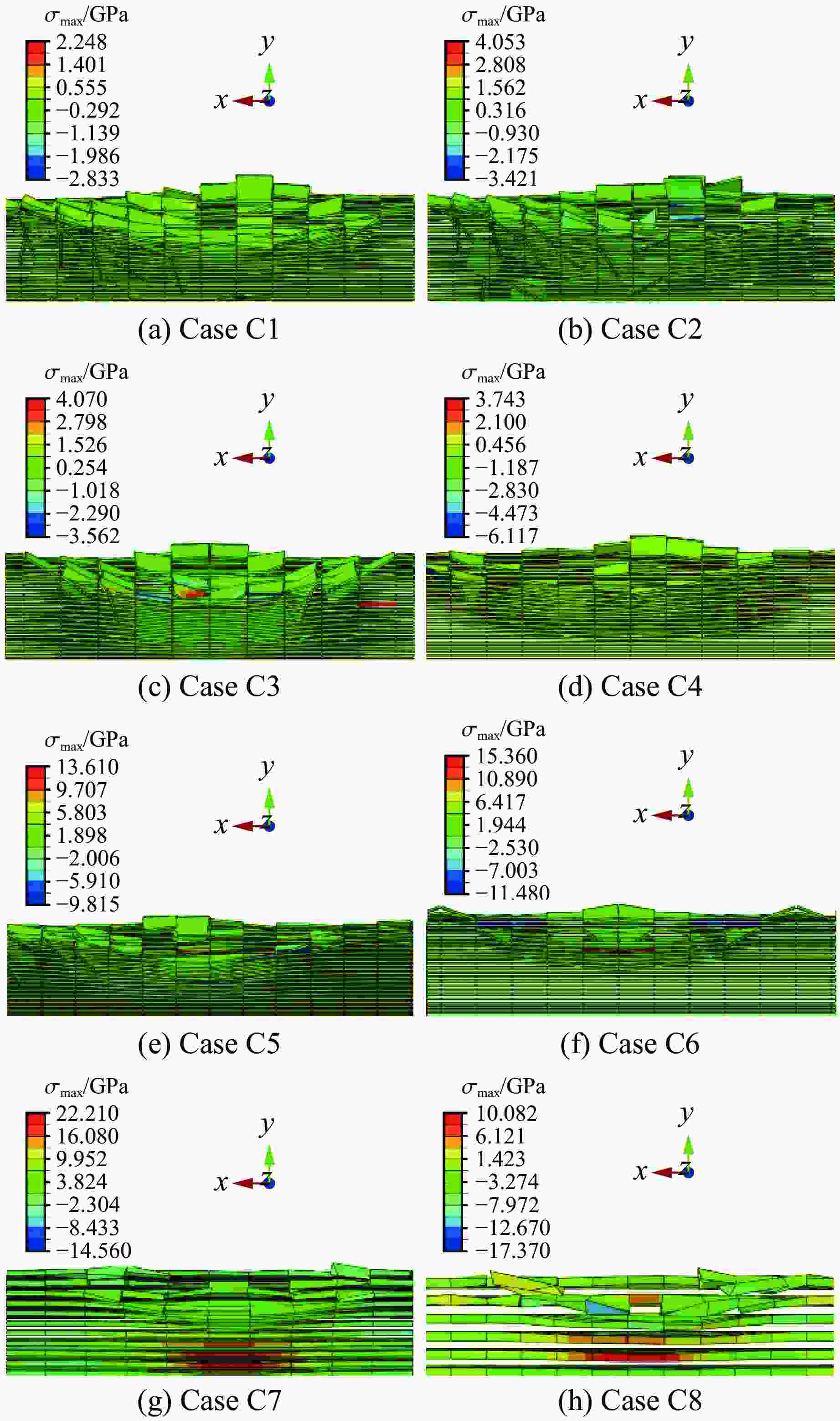
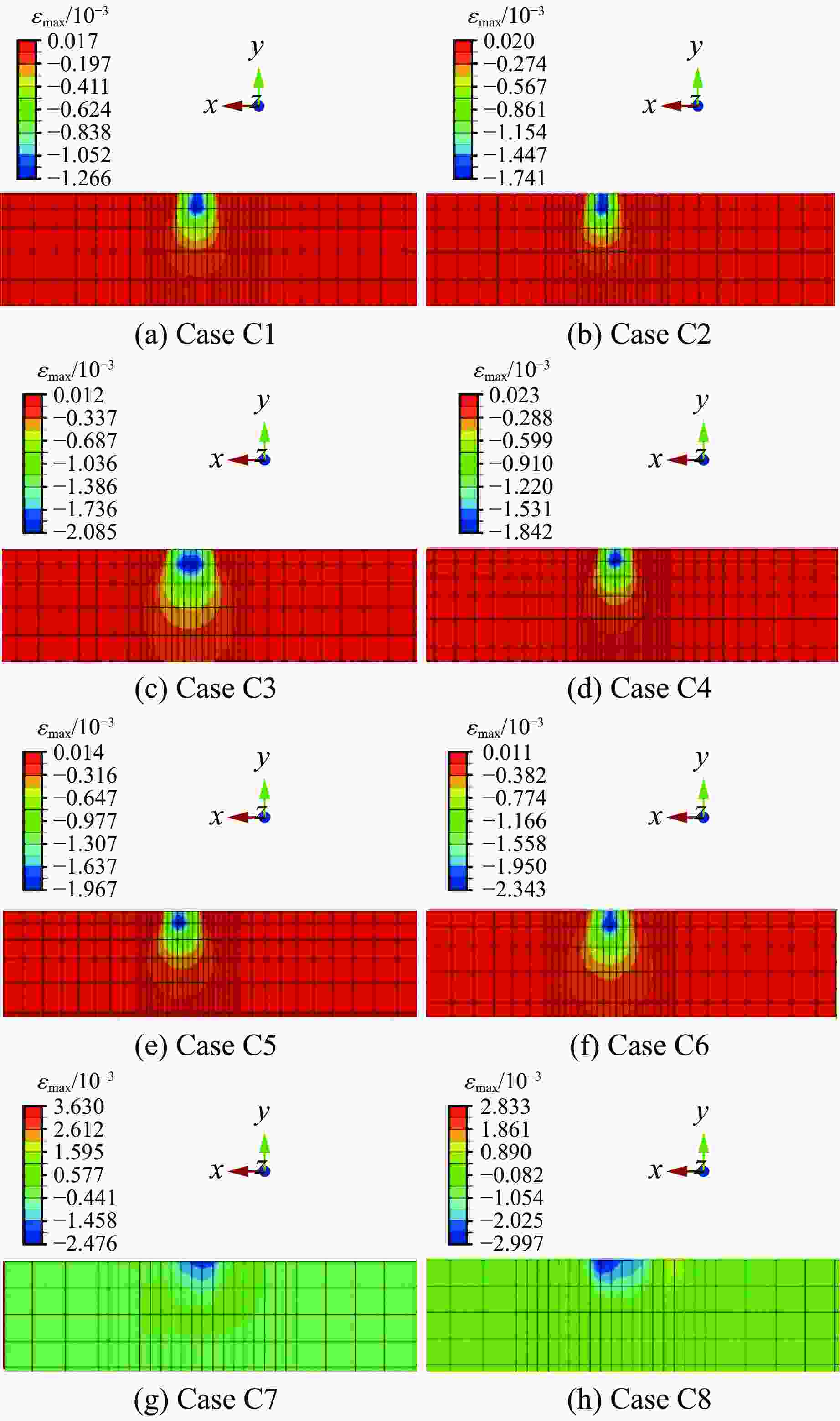
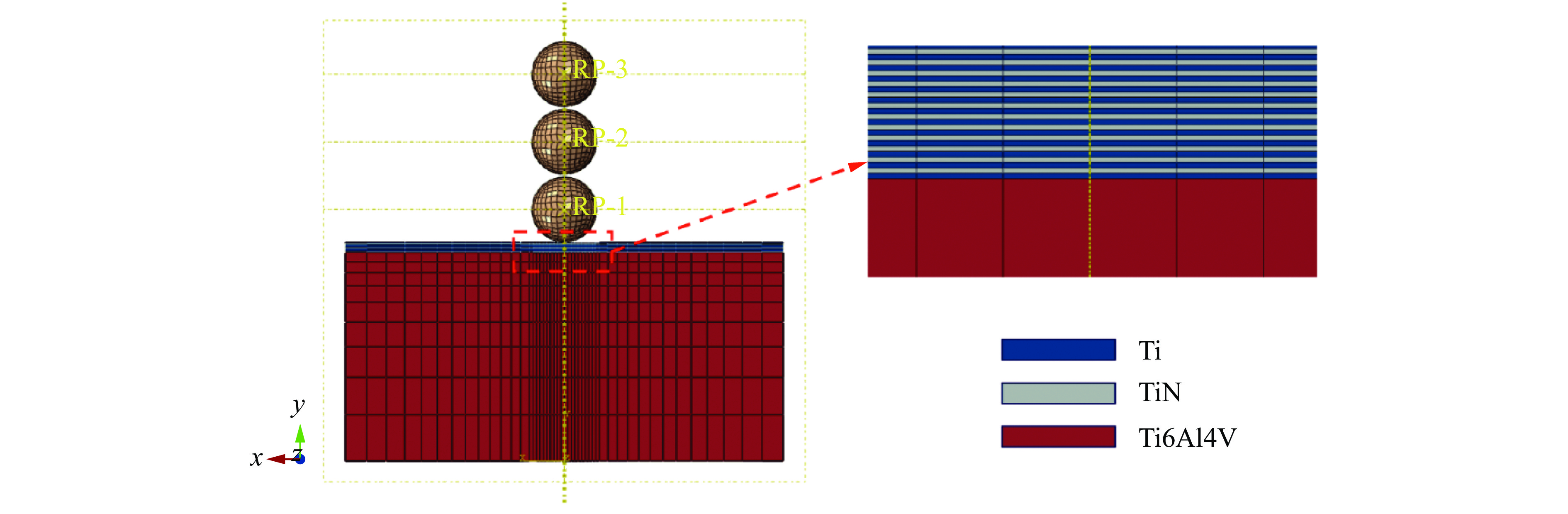
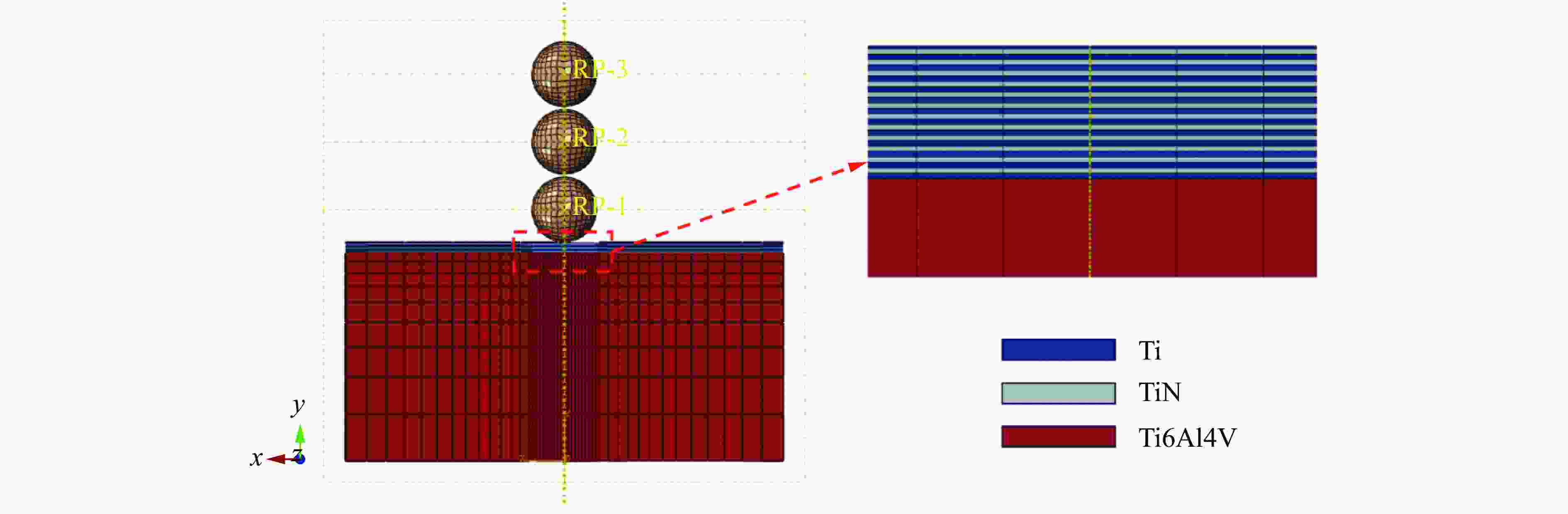
Case α/(°) v/(m·s−1) h/μm N $ \lambda $ C1 30 100 24 48 2 C2 60 100 24 48 2 C3 90 100 24 48 2 C4 30 200 24 48 2 C5 60 200 24 48 2 C6 90 200 24 48 2 C7 90 200 24 24 2 C8 90 200 24 12 2 表 3 Ti6Al4V、TiN、Ti和Al2O3的基本参数
Table 3. Basic parameters of Ti6Al4V, TiN, Ti, and Al2O3
Material ρ/(kg·m−3) E/GPa ν Ti6Al4V 4 428 113.8 0.34 TiN 5 400 480.0 0.27 Ti 4 500 110.0 0.33 Al2O3 3 970 344.0 0.20 表 4 基体Ti6Al4V与Ti的J-C本构参数
Table 4. J-C constitutive parameters of the matrix Ti6Al4V and Ti
Material A/MPa B/MPa n0 C $ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0} $/s–1 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 Ti6Al4V 1 098 1 092 0.93 0.014 1 –0.090 0.27 0.48 0.014 3.87 Ti 309 80 0.16 0.060 1 0.145 0.33 0.48 0.004 3.90 表 5 8组涂层层内最大应力与基体最大塑性应变的真实值与预测值对比结果
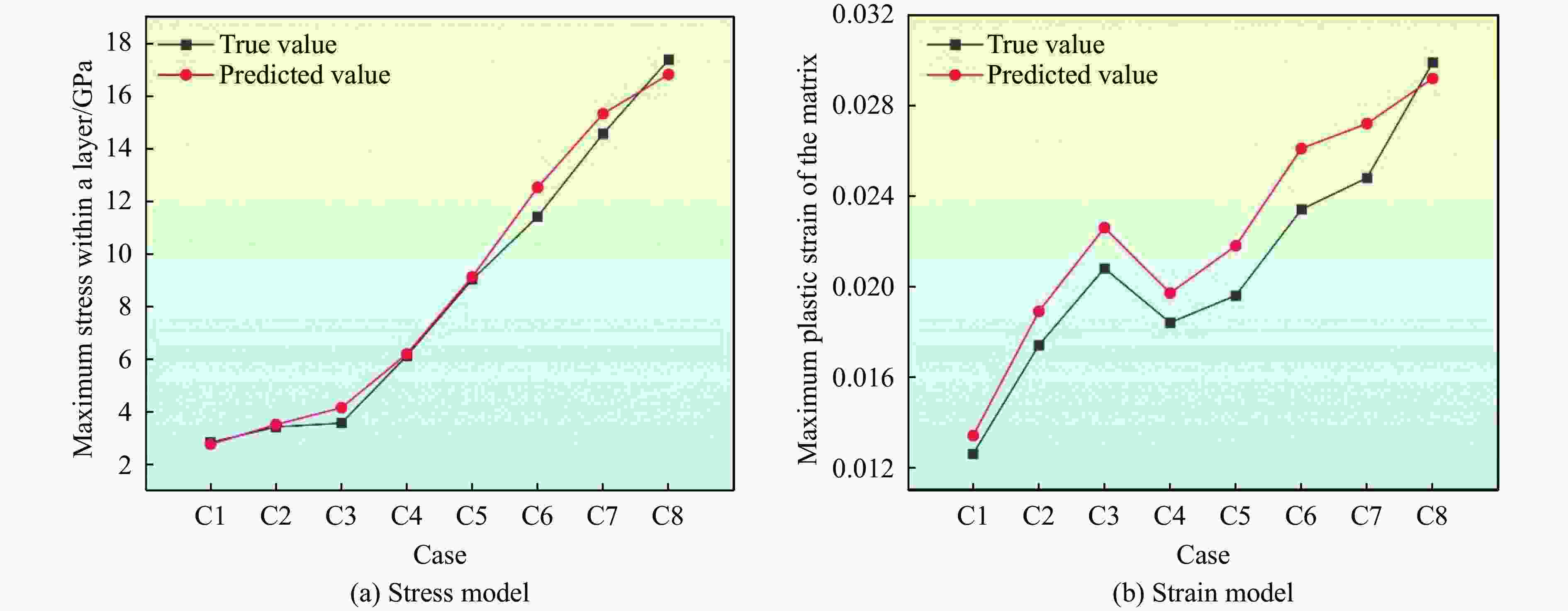
Table 5. Comparison between the predicted and actual values of the maximum intralayer stress and the maximum plastic strain in the substrate for eight coating groups
Case σmax/GPa εmax True value Predicted value True value Predicted value C1 2.83 2.76 0.012 6 0.013 4 C2 3.42 3.51 0.017 4 0.018 9 C3 3.56 4.15 0.020 8 0.022 6 C4 6.12 6.19 0.018 4 0.019 7 C5 9.02 9.12 0.019 6 0.021 8 C6 11.41 12.52 0.023 4 0.026 1 C7 14.56 15.32 0.024 8 0.027 2 C8 17.37 16.81 0.029 9 0.030 3 -
[1] 李德顺, 梁恩培, 李银然, 等. 风力机叶片涂层风沙冲蚀磨损特性的风洞试验研究 [J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43(6): 196–203. doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2020-1032LI D S, LIANG E P, LI Y R, et al. Wind tunnel experimental study on erosion and wear characteristics of wind turbine blade coating [J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43(6): 196–203. doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2020-1032 [2] 张福生. 风沙环境下风力机叶片磨损特性分析与研究 [D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2022.ZHANG F S. Analysis and research on wear characteristics of wind turbine blade in wind-blown sand environment [D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2022. [3] 王健, 杜国正, 张永, 等. 运行状态下风力机叶片涂层沙蚀磨损研究 [J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(4): 177–180. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20060234WANG J, DU G Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Research on sand erosion wear of wind turbine blade coating in operation state [J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(4): 177–180. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20060234 [4] 王成泽. 风沙环境下风力机叶片的冲蚀磨损特性研究 [D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2016.WANG C Z. Research on erosion characteristics of wind turbine blades under sand-wind environment [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016. [5] HE G Y, SUN D Y, CHEN J, et al. Key problems affecting the anti-erosion coating performance of aero-engine compressor: a review [J]. Coatings, 2019, 9(12): 821. doi: 10.3390/coatings9120821 [6] PEPI M, SQUILLACIOTI R, PFLEDDERER L, et al. Solid particle erosion testing of helicopter rotor blade materials [J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2012, 12(1): 96–108. doi: 10.1007/s11668-011-9531-3 [7] NASH D, LEISHMAN G, MACKIE C, et al. A staged approach to erosion analysis of wind turbine blade coatings [J]. Coatings, 2021, 11(6): 681. doi: 10.3390/coatings11060681 [8] WANG D, LIN S S, DUAN D Y, et al. Thermal shock resistance of Cr/CrN/Cr/CrAlN multilayer anti-erosion coating [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2023, 470: 129776. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2023.129776 [9] LIU R, PAN Y, CHEN A H, et al. Study on the influence of surface roughness on the erosion characteristics of compressor blades [J]. Powder Technology, 2023, 430: 119037. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2023.119037 [10] BONU V, JEEVITHA M, TIZZILE J S J, et al. Energy absorbing nano-porous Ti layers assisted erosion-corrosion resistant Ti/TiN multi-layered coatings for gas turbine compressor blades [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2024, 479: 130526. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.130526 [11] YUAN Z W, HAN Y T, ZANG S L, et al. Damage evolution behavior of TiN/Ti multilayer coatings under high-speed impact conditions [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 426: 127807. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127807 [12] RUAN H T, WANG Z Y, WANG L, et al. Designed Ti/TiN sub-layers suppressing the crack and erosion of TiAlN coatings [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 438: 128419. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128419 [13] COTO B, MENDIZABAL L, PAGANO F, et al. Role of surface finishing and interfacial lacquer layer on particle erosion mechanisms of Ti/TiN multilayer PVD coatings for carbon fibre reinforced polymer substrates protection [J]. Materials Letters, 2021, 285: 129187. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.129187 [14] ZHOU K, LIU D X, YANG Z Q, et al. Effect of TiN/Ti multilayer coatings with different microstructure on wear, corrosion, and fatigue performance of high strength steel [J]. Ceramics International, 2025, 51(18): 25990–26002. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2025.03.282 [15] KRELLA A K. Cavitation erosion resistance of Ti/TiN multilayer coatings [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 228: 115–123. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.04.016 [16] CHEN J, HE G Y, HAN Y T, et al. Structural toughness and interfacial effects of multilayer TiN erosion-resistant coatings based on high strain rate repeated impact loads [J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(19): 27660–27667. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.06.190 [17] CAO X, HE W F, LIAO B, et al. Sand particle erosion resistance of the multilayer gradient TiN/Ti coatings on Ti6Al4V alloy [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019, 365: 214–221. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.08.066 [18] ZHANG Z L, YANG M L, HE G Y. Structure, mechanical, and sand erosion behavior of TiN/Ti coating deposited at various temperature [J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(11): 16786–16795. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.02.039 [19] LIU W, SHEN Q, YANG M, et al. High hardness and toughness potential TiN/TiSiN gradient nano-multilayer coating structure by finite element study [J]. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(6): 9034–9046. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.12.217 [20] SHARMA L K, SHARMA N K, RANA A S. Finite element simulations of thermal properties of multilayer coatings [C]//Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Materials and Thermophysical Properties. Jaipur: Springer, 2025: 445−452. [21] ISLAM M J, BAKR M A, FARHAN M, et al. Impact response and optimization of reinforced concrete slabs under dynamic loading: a finite element analysis study [J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2025, 178: 105200. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2025.105200 [22] AMMAR Y B, AOUADI K, BESNARD A, et al. Exploring the effect of layer thickness on the elastoplastic properties of the constituent materials of CrN/CrAlN multilayer coatings: a nanoindentation and finite element-based investigation [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2024, 808: 140581. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2024.140581 [23] SOHAIL Y, ZHANG C L, XUE D Z, et al. Machine-learning design of ductile FeNiCoAlTa alloys with high strength [J]. Nature, 2025, 643(8070): 119–124. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09160-2 [24] XU B Q, PAN Y W, PENG J, et al. Stacking machine learning models for predicting hardness and modulus in refractory metal high-entropy nitride coatings [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2025, 132: 107243. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2025.107243 [25] WANG J J, XU B Q, LEE K, et al. Machine learning assisted CALPHAD framework for thermodynamic analysis of CVD SiOxNy thin films [J]. Calphad, 2025, 88: 102806. doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2025.102806 [26] BUTLER K T, DAVIES D W, CARTWRIGHT H, et al. Machine learning for molecular and materials science [J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7715): 547–555. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0337-2 [27] PENG J, YAMAMOTO Y, HAWK J A, et al. Coupling physics in machine learning to predict properties of high-temperatures alloys [J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2020, 6(1): 141. doi: 10.1038/s41524-020-00407-2 [28] SONG B, ZHOU R, AHMED F. Multi-modal machine learning in engineering design: a review and future directions [J]. Journal of Computing Information Science in Engineering, 2024, 24(1): 010801. doi: 10.1115/1.4063954 [29] POLLA A, FRULLA G, CESTINO E, et al. Coupled thermo-mechanical numerical modeling of CFRP panel under high-velocity impact [J]. Aerospace, 2023, 10(4): 367. doi: 10.3390/aerospace10040367 [30] GREENHILL S, RANA S, GUPTA S, et al. Bayesian optimization for adaptive experimental design: a review [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 13937–13948. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2966228 [31] SETTLES B. Active learning literature survey [M]. San Rafael: Morgan & Claypool Publishers, 2012. [32] SHAHRIARI B, SWERSKY K, WANG Z Y, et al. Taking the human out of the loop: a review of Bayesian optimization [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(1): 148–175. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2494218 [33] KERMOUCHE G, GRANGE F, LANGLADE C. Local identification of the stress–strain curves of metals at a high strain rate using repeated micro-impact testing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 569: 71–77. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.01.020 [34] 史文龙. TiN/Ti多层涂层多颗粒冲击损伤与承载响应模拟研究 [D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2024.SHI W L. Simulation study on multi particle impact damage and load-bearing response of TiN/Ti multilayer coatings [D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2024. [35] PEARSON K. Ⅶ. note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1895, 58(347/348/349/350/351/352): 240−242. [36] PEARSON K. Ⅲ. contributions to the mathematical theory of evolution [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Ohysical and Engineering Sciences, 1894, 185: 71–110. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1894.0003 [37] TIBSHIRANI R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso [J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 1996, 58(1): 267–288. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x [38] TIPPING M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine [J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1: 211–244. doi: 10.1162/15324430152748236 [39] DRUCKER H, BURGES C J C, KAUFMAN L, et al. Support vector regression machines [C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver: MIT Press, 1996: 155−161. [40] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system [C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco: Association for Computing Machinery, 2016: 785−794. [41] RASMUSSEN C E, WILLIAMS C K I. Gaussian processes for machine learning [M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2005. [42] BREIMAN L. Random forests [J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [43] STONE M. Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions [J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 1974, 36(2): 111–133. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1974.tb00994.x [44] RUDIN C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead [J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(5): 206–215. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0048-x [45] SHAPLEY L S. A value for n-person games [M]//KUHN H W, TUCKER A W. Contributions to the Theory of Games. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1953. [46] BISWAS S, CENNA A, WILLIAMS K, et al. Subsurface behavior of ductile material by particle impacts and its influence on wear mechanism [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 90: 160–165. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.830 [47] DERINGER V L, BARTÓK A P, BERNSTEIN N, et al. Gaussian process regression for materials and molecules [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(16): 10073–10141. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00022 -






 下载:
下载: