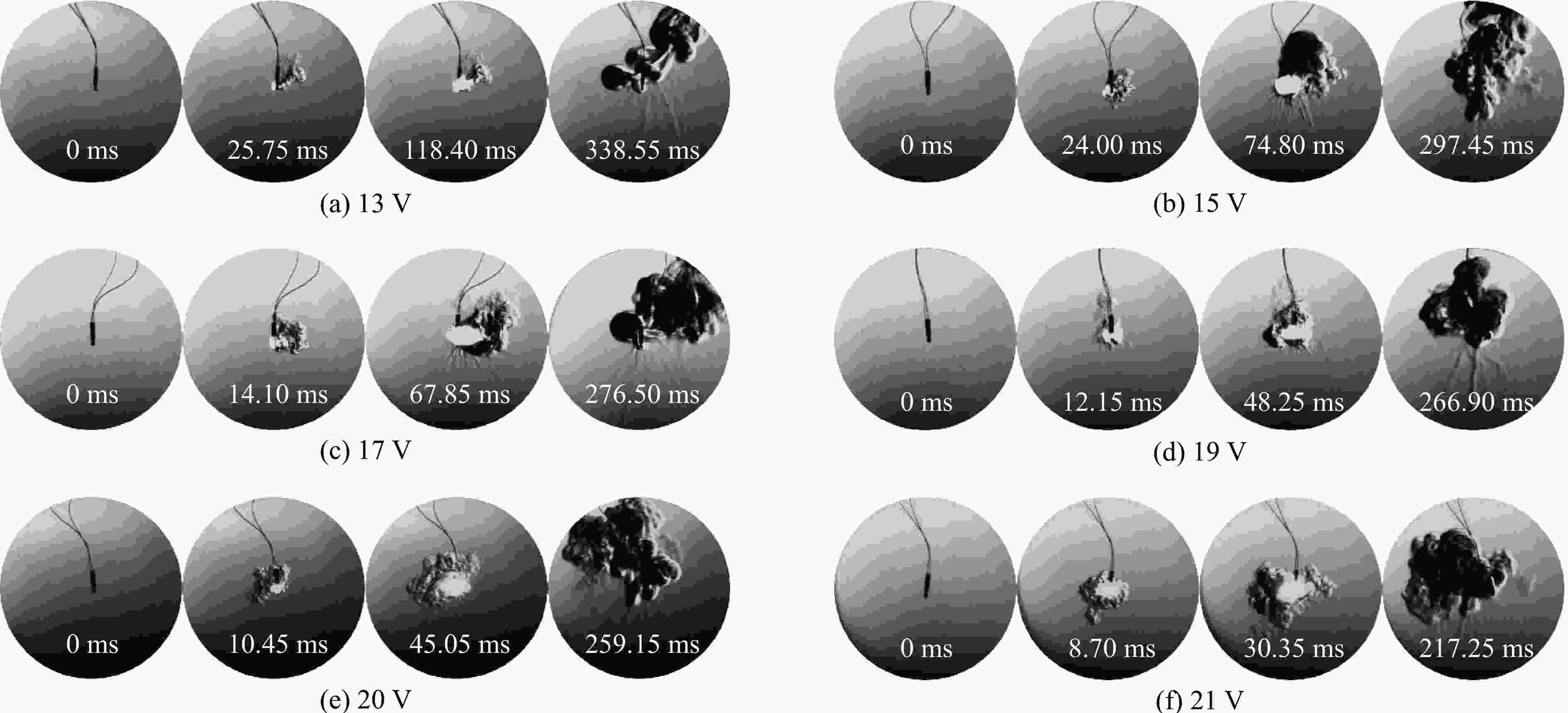
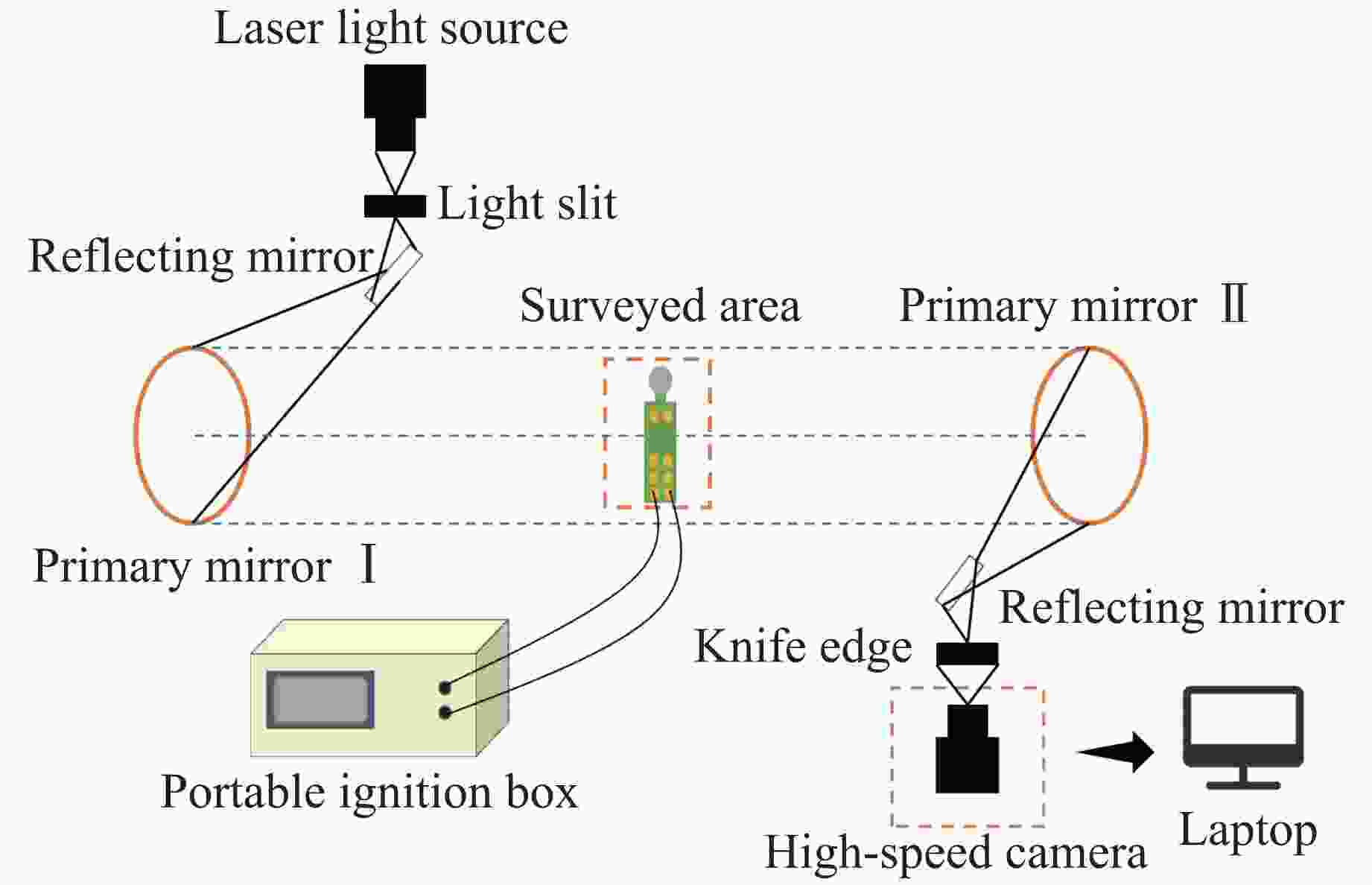
Experimental Study on Ignition Time of Industrial Electronic Detonator Ignition Head under Different Ignition Voltages
-
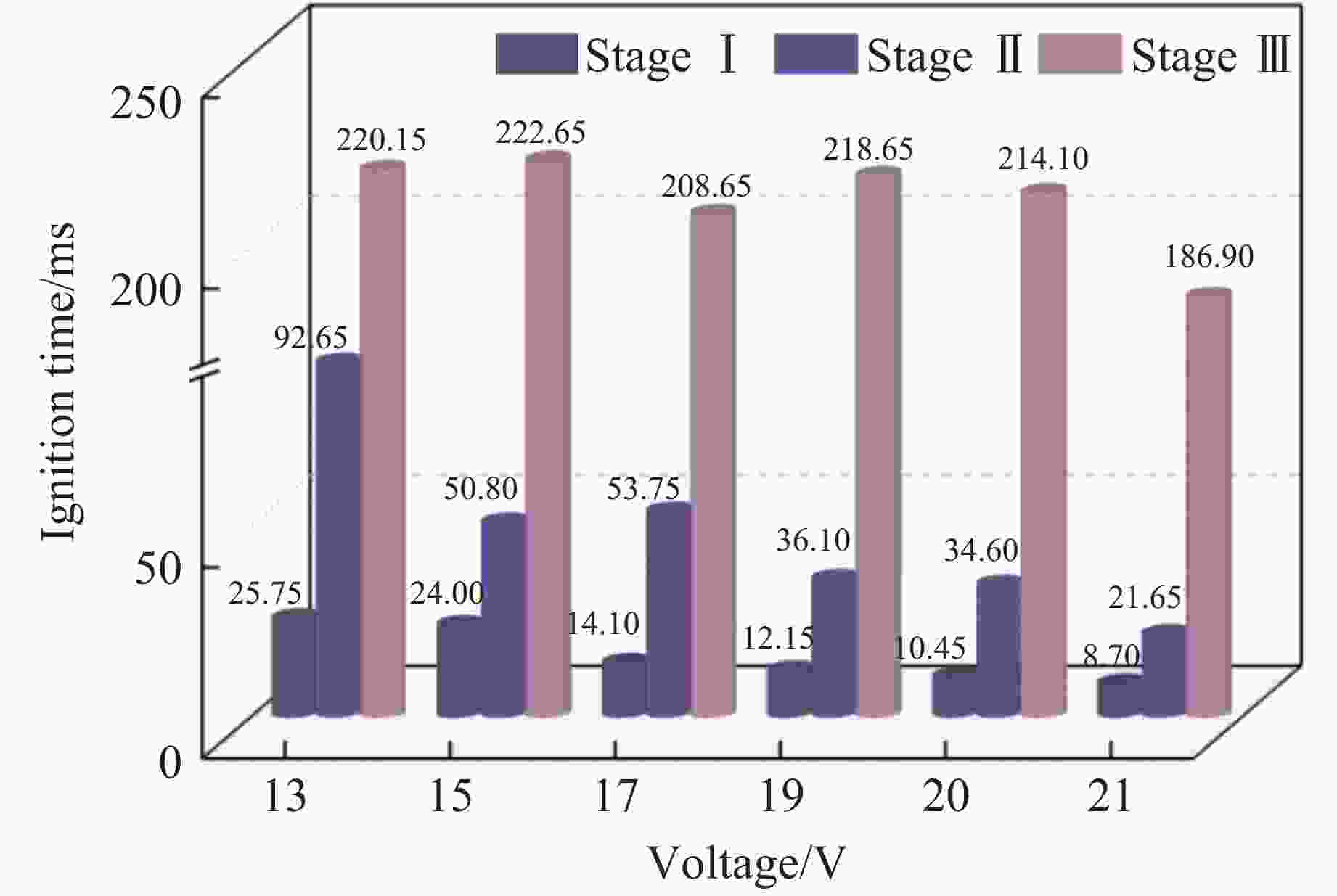
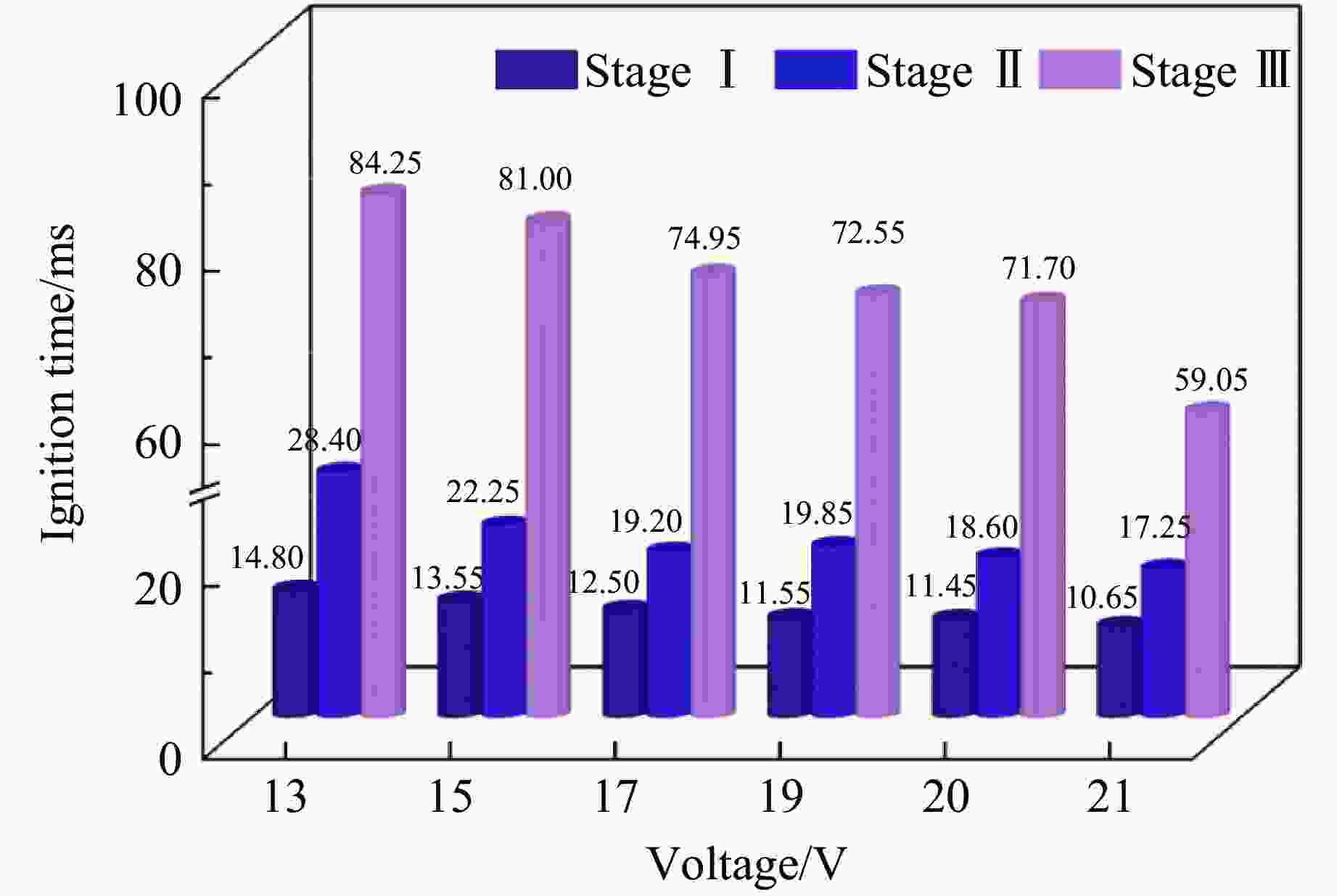
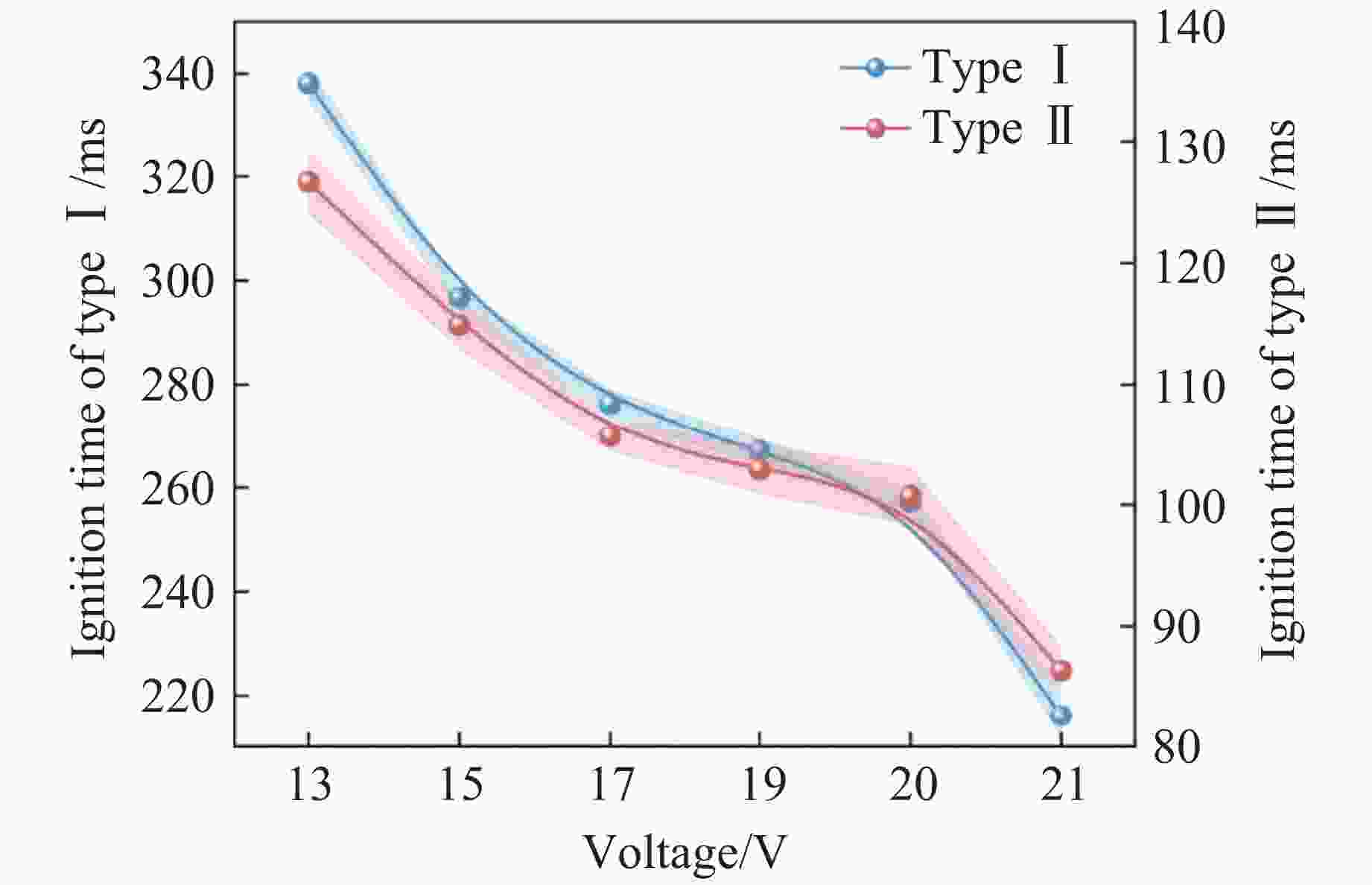
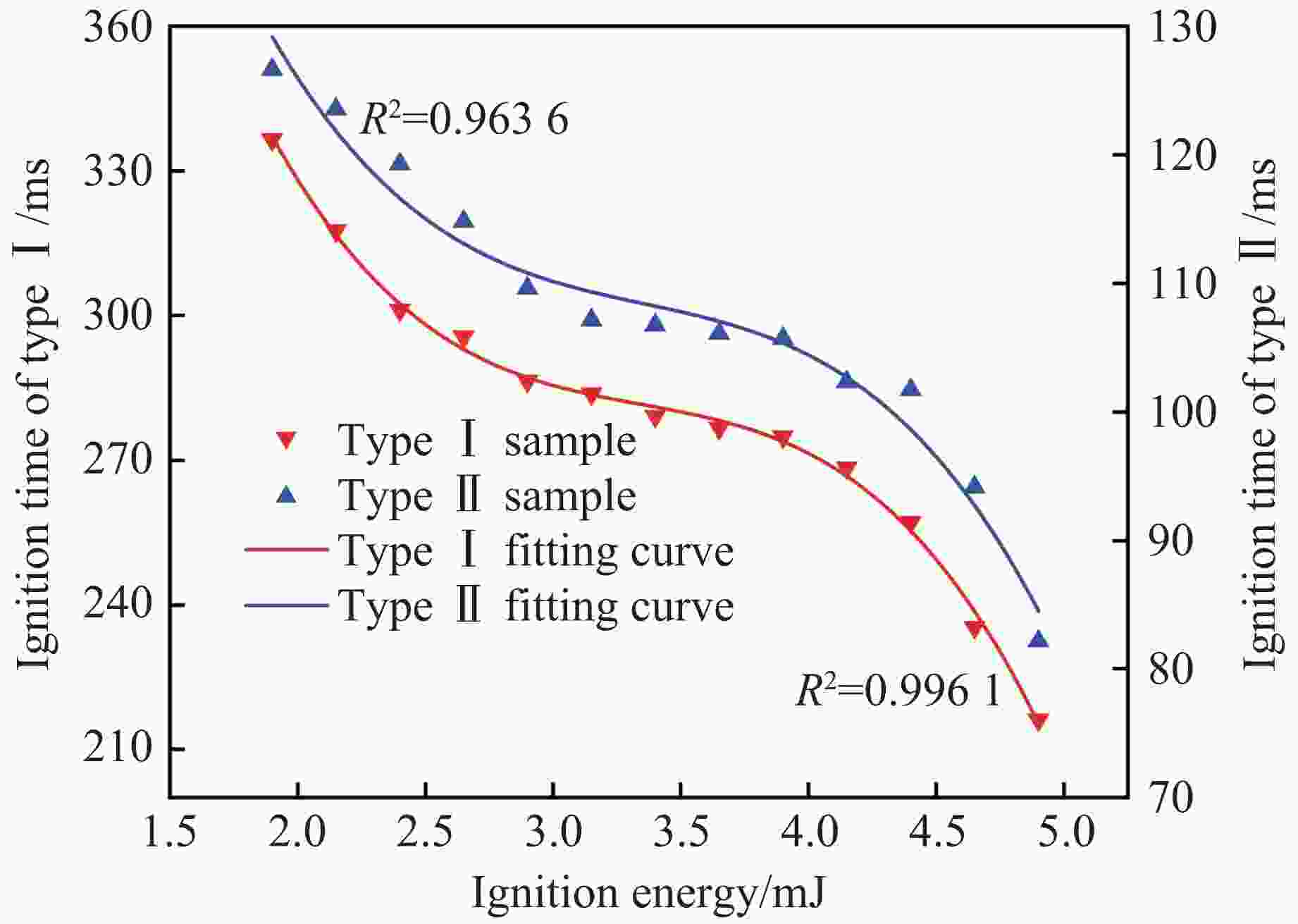
摘要: 针对电子雷管发火电容受冲击后出现掉电可能导致其因发火能量不足而无法可靠起爆这一工程实际问题,通过高速纹影测试系统,研究了不同发火电压下金属桥膜型及桥丝型引火药头的发火时间,明确输入引火药头的初始能量对其热分解阶段、火焰增长期、火焰持续期时间的影响,得到了2种引火药头发火总时间与发火电压、发火能量的关系。结果表明:13~21 V区间内,引火药头的发火总时间随电压的变化率呈先减小后增大的趋势;随着发火电压的增大,金属桥膜型引火药头的热分解期、火焰增长期、火焰持续期的时间降幅分别为66.2%、76.6%、15.0%,桥丝型引火药头在3个阶段的时间降幅分别为28.0%、39.2%、30.0%,且金属桥膜型引火药头各阶段的发火时间较桥丝型短;当发火电容剩余能量处于1.9~4.9 mJ时,金属桥膜型和桥丝型引火药头的发火一致性及发火精度受到影响;当剩余能量小于1.9 mJ时,金属桥膜型引火药头因发火能量不足导致瞎火。研究结果将为电子雷管发火裕度设计提供依据,有助于降低小孔距爆破中电子雷管的拒爆率。Abstract: In response to the practical engineering problem that the firing capacitor of electronic detonators may lose power after being impacted, which subsequently lead to insufficient firing energy and unreliable detonation, the firing time of metal bridge and bridge-wire ignition heads under different firing voltages were studied through the high-speed schlieren testing system. The influence of the initial energy input to the ignition head on the thermal decomposition stage, flame growth period, and flame duration was clarified, and the relationship between the total ignition time and the ignition voltage and ignition energy for two types ignition heads was obtained. The results show that within the range of 13−21 V, the rate of change of the total firing time of the ignition heads with voltage decreases first and then increases. As the firing voltage increases, the time reduction rates of the thermal decomposition, flame growth period, and flame duration of the metal bridge model ignition heads are 66.2%, 76.6%, and 15.0% respectively. The time reduction rates of the three stages of the bridge-wire ignition heads are 28.0%, 39.2%, and 30.0% respectively, and the firing time of each stage of the metal bridge model ignition head is shorter than that of the bridge-wire. When the ignition energy is between 1.9 and 4.9 mJ, the firing consistency and accuracy of the metal bridge model and bridge-wire ignition head will be affected. When the ignition energy is less than 1.9 mJ, the metal bridge mode ignition heads will fail to fire due to insufficient firing energy. This study provides a basis for the design of the firing margin of electronic detonators, which will reduce the misfire rate of electronic detonators in small-hole blasting.
-
Key words:
- industrial electronic detonator /
- ignition head /
- ignition time /
- ignition energy
-
表 1 不同电压对应的引火药头发火能量
Table 1. Ignition energy of ignition corresponding to different voltages
Ignition voltage/V Ignition energy/mJ Ignition time of type Ⅰ/ms Ignition time of type Ⅱ/ms 13.14 1.90 336.51 126.62 13.98 2.15 317.61 123.54 14.77 2.40 301.16 119.29 15.52 2.65 295.63 114.81 16.24 2.90 286.45 109.63 16.92 3.15 283.82 107.15 17.58 3.40 279.15 106.76 18.22 3.65 276.69 106.12 18.83 3.90 274.95 105.73 19.42 4.15 268.46 102.35 20.00 4.40 257.17 101.75 20.56 4.65 235.42 94.16 21.11 4.90 216.07 82.16 -
[1] 孙金梦. 数码电子雷管点火模块的研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2023.SUN J M. Study on ignition module of digital electronic detonator [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2023. [2] 杨文, 岳彩新, 宋家良, 等. 工业电子雷管抗冲击性能试验研究 [J]. 火工品, 2022(2): 16–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2022.02.004YANG W, YUE C X, SONG J L, et al. Experimental research on the impact resistance of industrial electronic detonators [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2022(2): 16–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2022.02.004 [3] TEVEROVSKY A. Effect of mechanical stresses on characteristics of chip tantalum capacitors [J]. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 2007, 7(3): 399–406. doi: 10.1109/TDMR.2007.907289 [4] 王家乐, 李洪伟, 王小兵, 等. 冲击载荷作用下钽电容的电压瞬变特性及微观机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(4): 043101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0232WANG J L, LI H W, WANG X B, et al. Voltage transient characteristics and microscopic mechanism of tantalum capacitors under impact load [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(4): 043101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0232 [5] LENG Z D, FAN Y, LU W B, et al. Failure mechanisms of electronic detonators subjected to high impact loading in rock drilling and blasting [J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 2025, 12(1): 10. doi: 10.1007/s40789-025-00749-6 [6] REN D M, HOU J H, DUAN J R, et al. Failure mode analysis of electronic detonator under high overload condition [J]. FirePhysChem, 2022, 2(2): 199–205. doi: 10.1016/j.fpc.2022.02.001 [7] 杨文. 工业电子雷管抗冲击性能研究 [D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2022.YANG W. Research on impact resistance performance of industrial electronic detonator [D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2022. [8] 孙金梦, 卫延安, 武寿昌. 灼热桥丝式电点火药头的发火时间变化规律研究 [J]. 爆破器材, 2022, 51(6): 27–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2022.06.005SUN J M, WEI Y A, WU S C. Ignition time variation of hot bridge-wire electric fusehead [J]. Explosive Materials, 2022, 51(6): 27–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2022.06.005 [9] 杨刚, 彭星新, 孙热, 等. 桥丝式电点火头发火时间一致性试验研究 [J]. 爆破器材, 2024, 53(4): 23–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2024.04.004YANG G, PENG X X, SUN R, et al. Experimental study on consistency of ignition time of the bridge wire fuse head [J]. Explosive Materials, 2024, 53(4): 23–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2024.04.004 [10] 杨霖, 李洪伟, 梁昊, 等. 爆炸冲击作用对电子雷管引火药头损伤及发火时间的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2025, 39(6): 065301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240945YANG L, LI H W, LIANG H, et al. Effect of explosive impact on ignition head damage and ignition time of electronic detonator [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2025, 39(6): 065301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240945 [11] 马健行, 黄寅生, 毛立. 两种电子雷管用点火元件的制备及研究 [J]. 火工品, 2022(1): 15–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2022.01.004MA J X, HUANG Y S, MAO L. Preparation and research of two kinds of electric matchhead for electronic detonator [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2022(1): 15–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2022.01.004 [12] 任泰昌, 裴霈, 朱方杰. 硫氰酸铅在电子引火元件中的应用探究 [J]. 化工管理, 2019(22): 146–147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4800.2019.22.092REN T C, PEI P, ZHU F J. Application of lead thiocyanate in electronic ignition components [J]. Chemical Enterprise Management, 2019(22): 146–147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4800.2019.22.092 [13] 郑星, 黄海莹, 毛勇建, 等. 基于高速纹影技术的爆炸冲击波图像测量研究 [J]. 光学精密工程, 2022, 30(18): 2187–2194. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2187ZHENG X, HUANG H Y, MAO Y J, et al. Research on image measurement of explosion shock wave based on high speed schlieren technology [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(18): 2187–2194. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2187 [14] GRÜNINGER M, TOEDTER O, KOCH T. Optical analysis of ignition sparks and inflammation using background-oriented schlieren technique [J]. Energies, 2024, 17(6): 1274. doi: 10.3390/en17061274 [15] JÓZSA V, MALÝ M, FÜZESI D, et al. Schlieren analysis of non-mild distributed combustion in a mixture temperature-controlled burner [J]. Energy, 2023, 273: 127230. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.127230 [16] 焦清介, 赵婉君, 常英珂, 等. 电爆桥膜换能元设计研究 [J]. 火工品, 2023(6): 14–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2023.06.003JIAO Q J, ZHAO W J, CHANG Y K, et al. Research on the design of exploding bridge film energy convertor [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2023(6): 14–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2023.06.003 [17] 王家乐. 电子雷管电容的冲击失效规律及失效机理 [D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2024.WANG J L. Impact failure law and failure mechanism of electronic detonator capacitors [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2024. [18] 李洪伟, 王家乐, 梁昊, 等. 爆炸冲击对电子雷管发火电容释能特性的影响 [J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(3): 240221. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0221LI H W, WANG J L, LIANG H, et al. Effect of explosion shock on the energy release characteristics of ignition capacitance of electronic detonator [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(3): 240221. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0221 -






 下载:
下载: