Discrete Element Analysis on the Influence of Block Shape and Spatial Arrangement on Shielding Performance
-
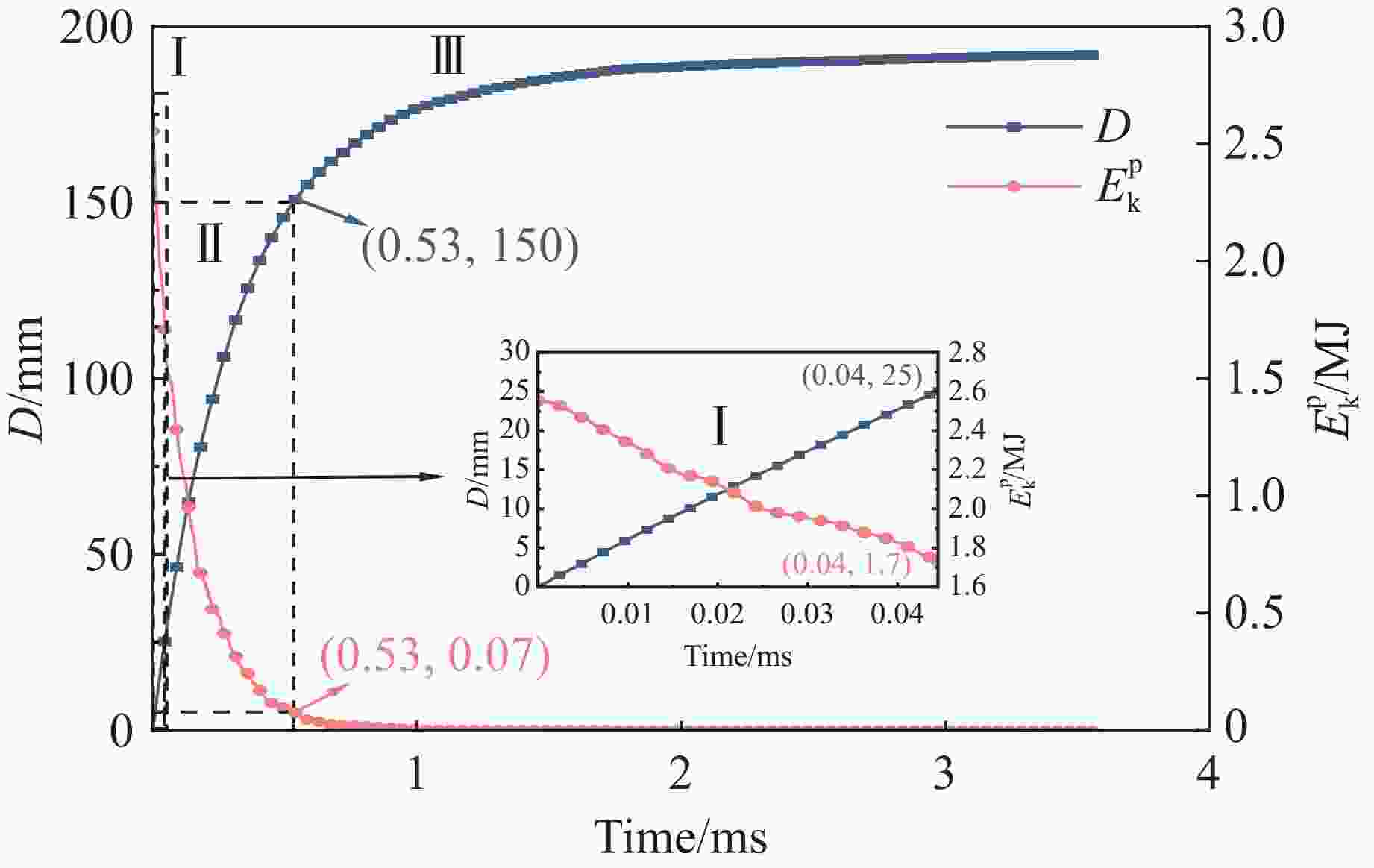
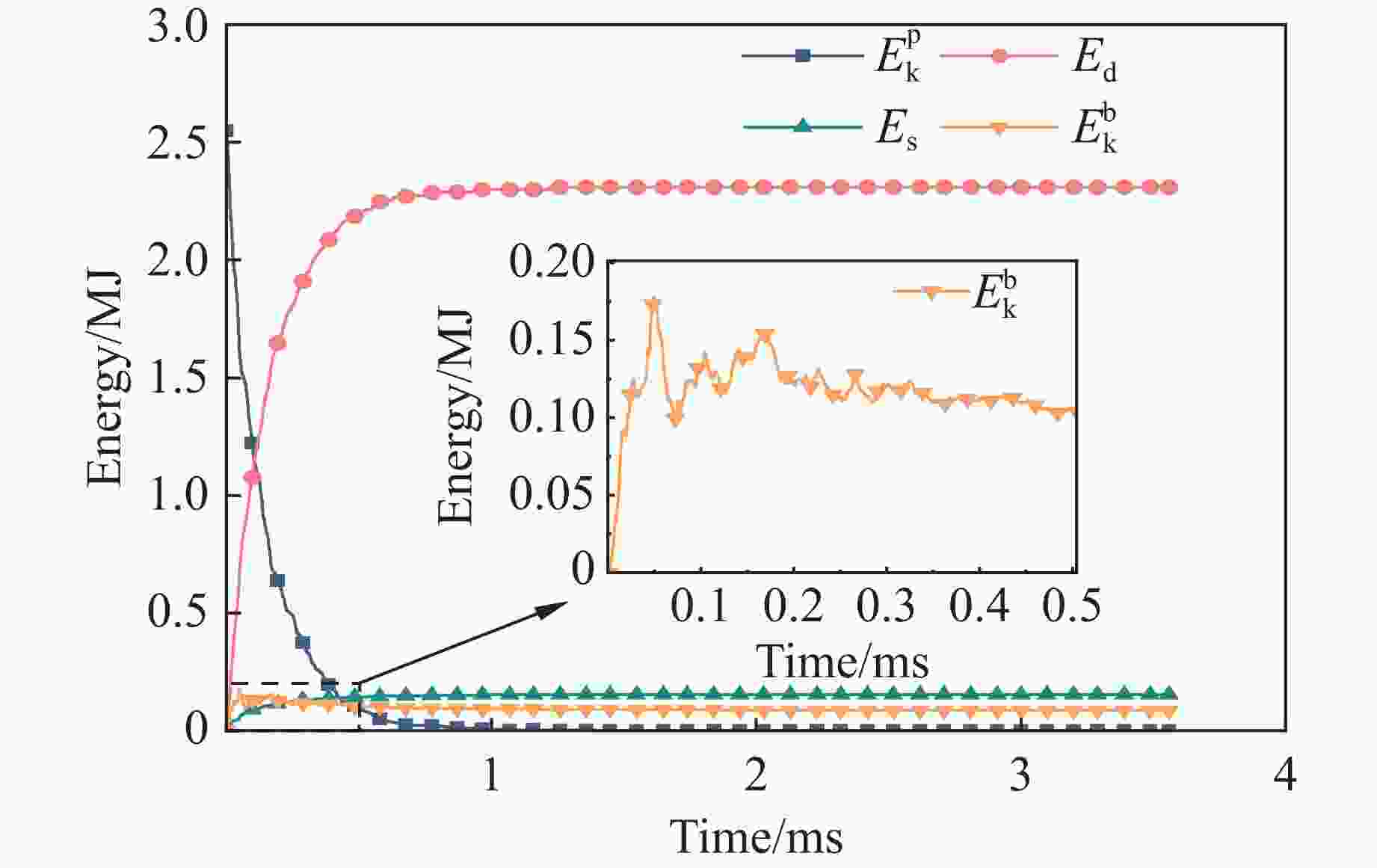
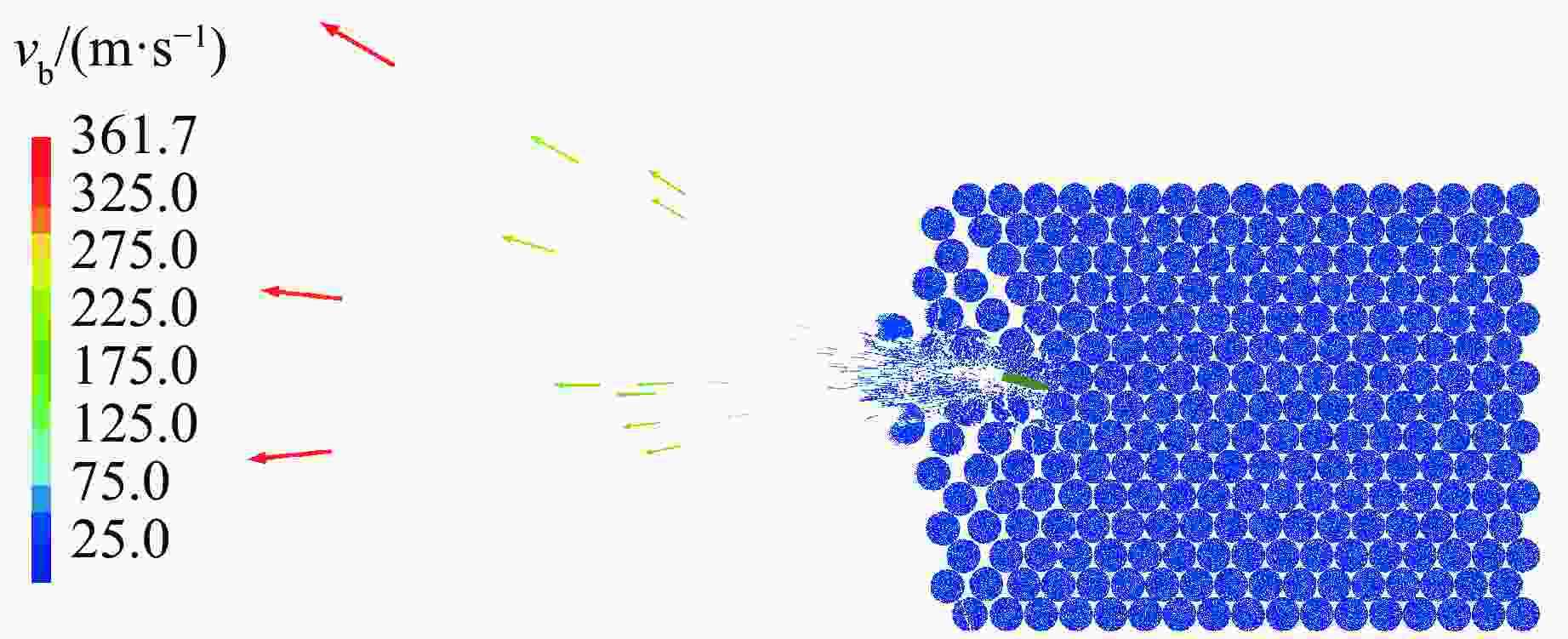
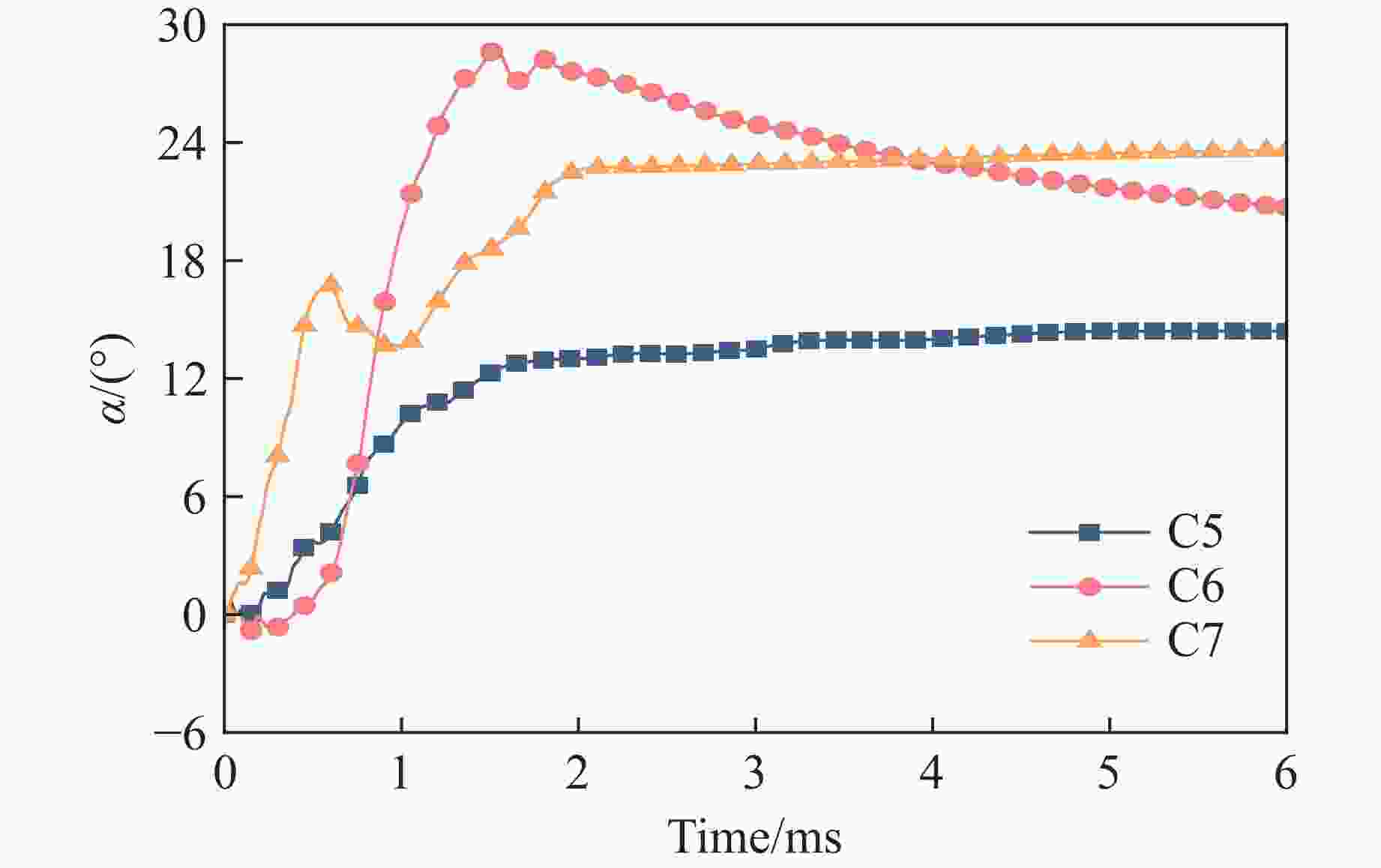
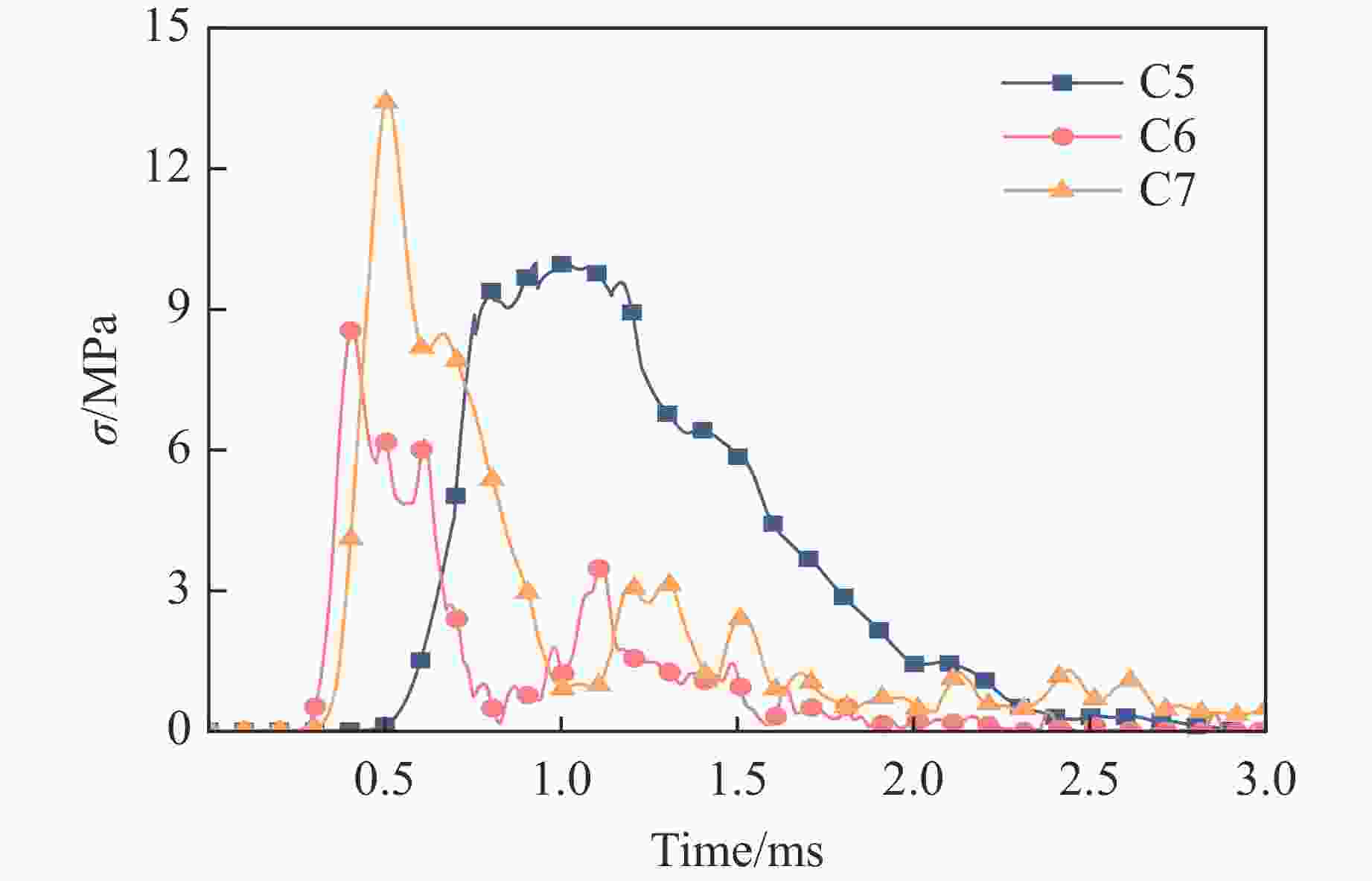
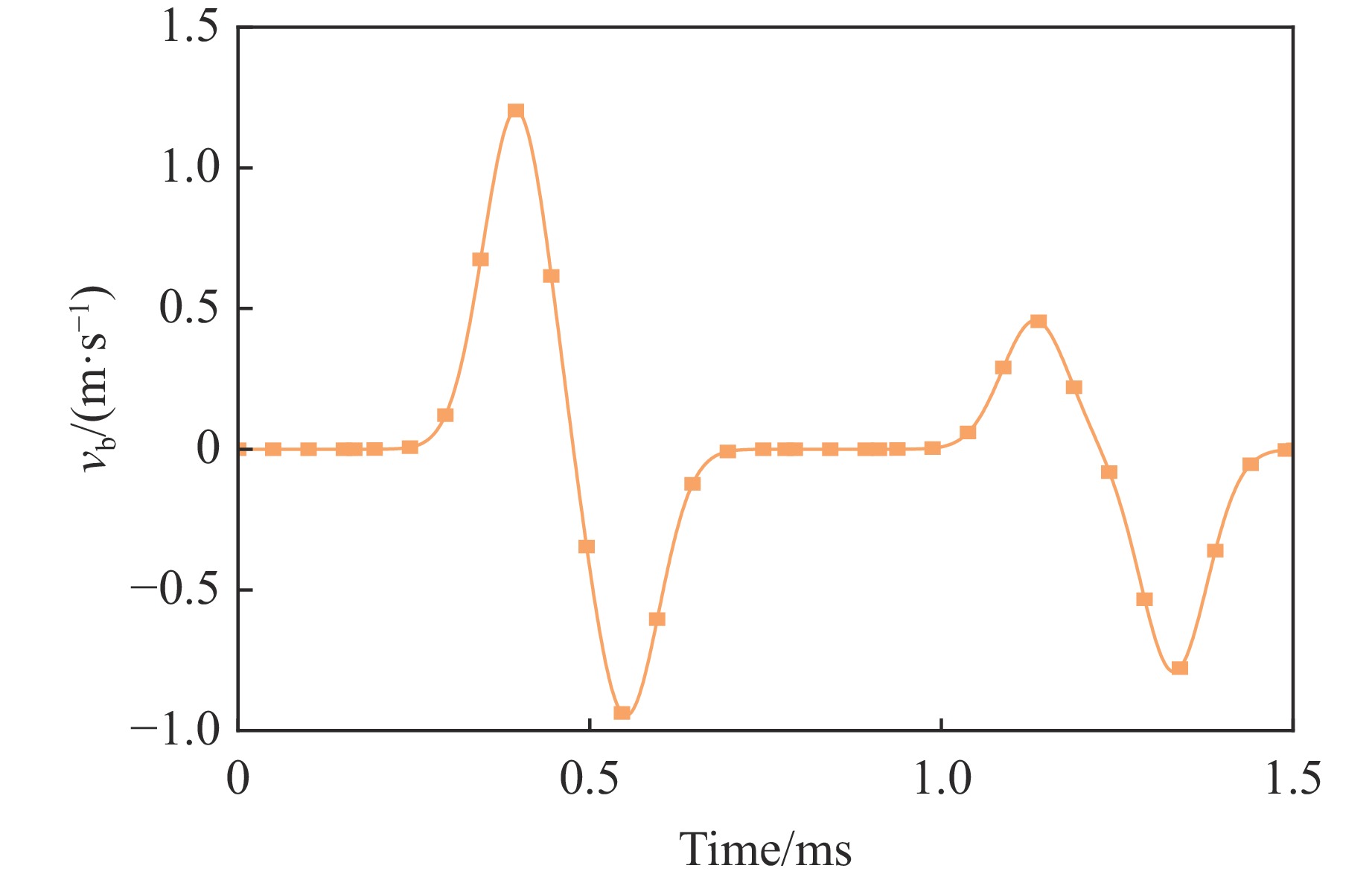
摘要: 遮弹层作为现代军事防御体系的关键组成部分,可为后方重要目标提供防护。块石作为遮弹层的常用堆筑材料,其遮弹机理及性能优化研究具有重要意义。采用离散元球体单元和黏结破碎模型,模拟了块石在弹体冲击载荷下的破碎现象,并对刚性弹正侵彻密实堆积的块石结构进行了数值模拟,探讨了块石粒径、形状及空间排布特性对其抗侵彻性能的影响。结果表明:在侵彻过程中,块石通过碰撞和滑移耗散了90%以上的弹体动能;块石破碎数量与块石粒径呈负相关,与块石长短轴比呈正相关;采用单粒径块石多层位错排布时,弹体侵彻深度主要取决于侵彻阻力峰值,粒径为120 mm的圆形块石工况的侵彻阻力最大且侵彻深度最小;采用块石粒径沿迎弹面方向梯度递减的分层排布时,不能有效提高结构体的遮弹效果。研究结果可为理解块石遮弹机理提供参考。Abstract: Shelter layers, recognized as a critical component in modern military defense systems, are designed to protect strategically important rear assets. Given the prevalent application of block stones as primary filling materials in these protective structures, comprehensive investigations into their fundamental ballistic resistance mechanisms and practical performance optimization have become increasingly crucial for defense engineering. Therefore, the dynamic fragmentation behavior of block stones under high-velocity projectile impact was systematically simulated using discrete element spherical particles and bonded particle model (BPM) in this paper. The process of rigid projectile vertical penetration into densely packed block stone structure was numerically simulated, with the influences of block stone particle size, shape, and spatial arrangement characteristics on its anti-penetration performance being explored. The results revealed two primary energy dissipation mechanisms governing the shelter layer performance: over 90% of the kinetic energy of the projectile was dissipated through the combined effects of inter-block collisions and sliding friction during the penetration process. Meanwhile, the number of break block stones is found to be negatively correlated with the block stone particle size and positively correlated with the aspect ratio (long-to-short axis) of the block stones. Moreover, when single-sized block stones are used in a multi-layer staggered arrangement, the penetration depth of the projectile is primarily determined by the magnitude of the peak penetration resistance. Specifically, the maximum penetration resistance and the minimum penetration depth are exhibited by the scenario with circular block stones of 120 mm particle size. However, when a layered arrangement with block stone particle size gradiently decreasing along the direction of the impact face is employed, the overall blast-resistant effect of the structure is not effectively enhanced. Finally, the results of the study can provide a reference for understanding the underlying mechanism of the shielding effect of block stone structure.
-
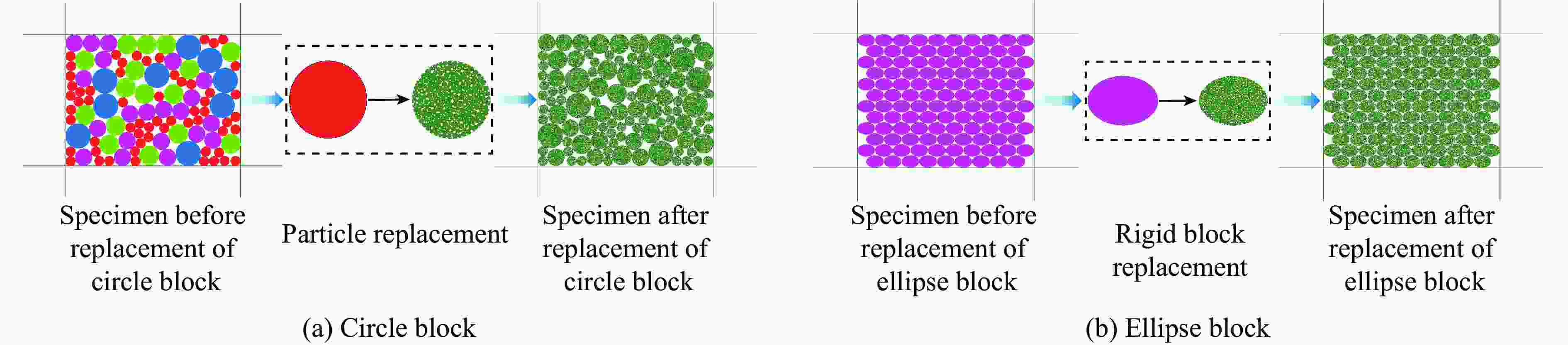
表 1 块石柔性簇模板
Table 1. Block cluster template
Block cluster template Diameter/mm Aspect ratio Np Nc Z 
70 1.0 227 600 5.29 
120 1.0 884 2 006 4.54 
138 1.0 1 166 2 662 4.57 
175 1.0 1 879 4 362 4.64 
120 1.4 608 1 297 4.27 
120 2.0 442 925 4.19 表 2 数值模拟细观参数
Table 2. Meso-parameters of numerical simulation
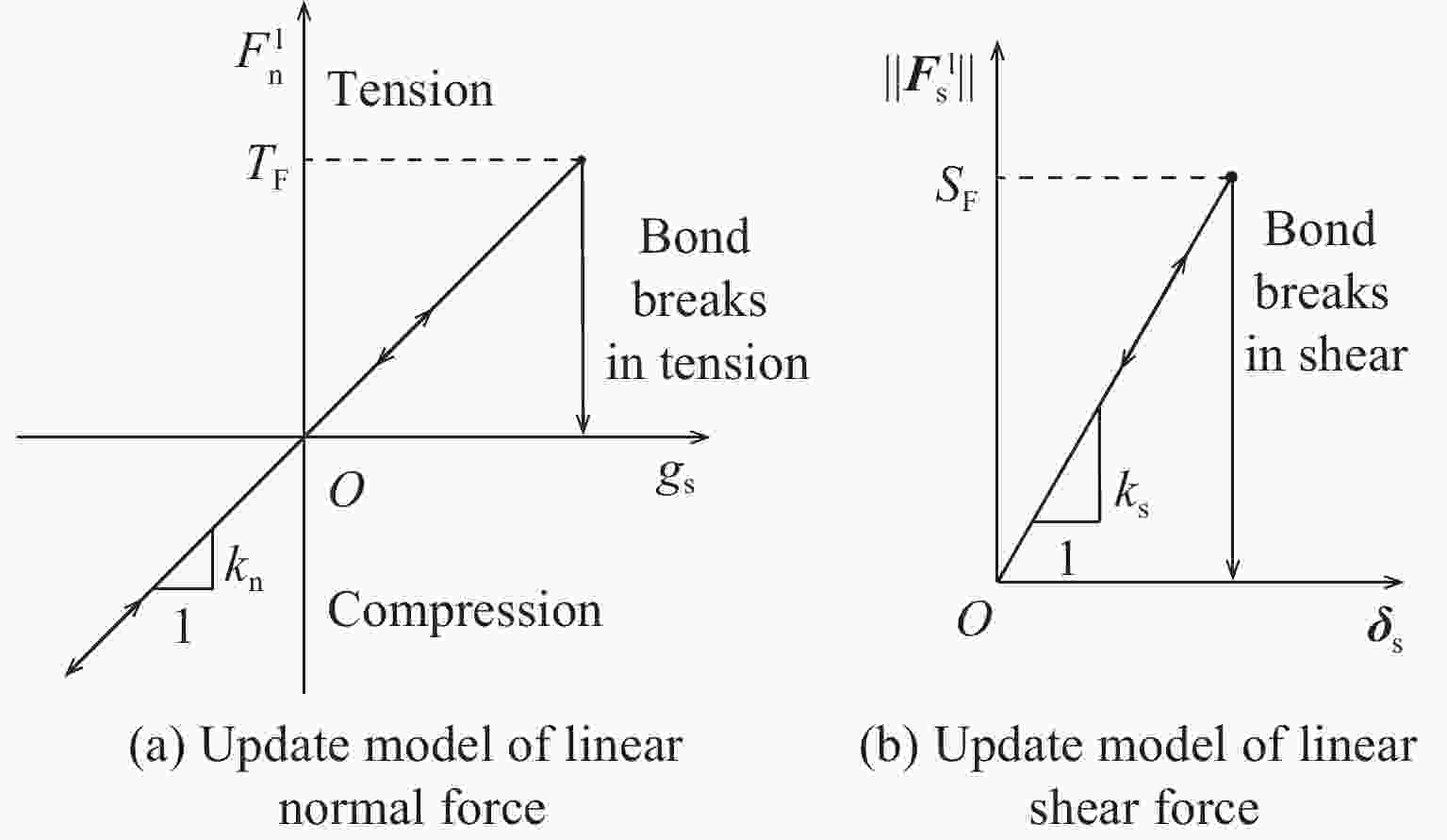
Rmin/mm Rmax/mm ρ/(kg·m−3) kn/(N·m−1) ks/(N·m−1) $\sigma_{\rm{n}} $/MPa $\sigma_{\rm{t}} $/MPa 0.9 2.7 2 685 99×109 49.5×109 215±50 215±50 表 3 计算工况
Table 3. Calculated cases
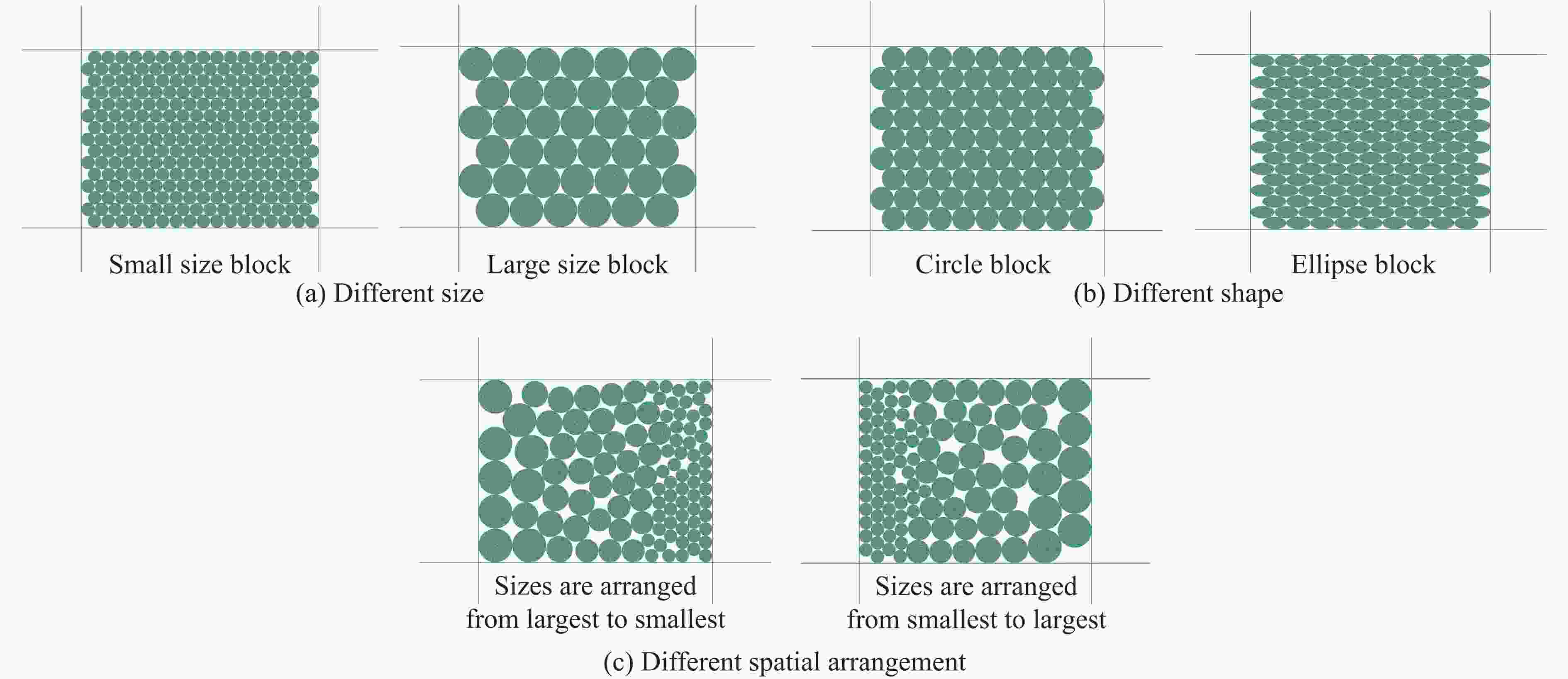
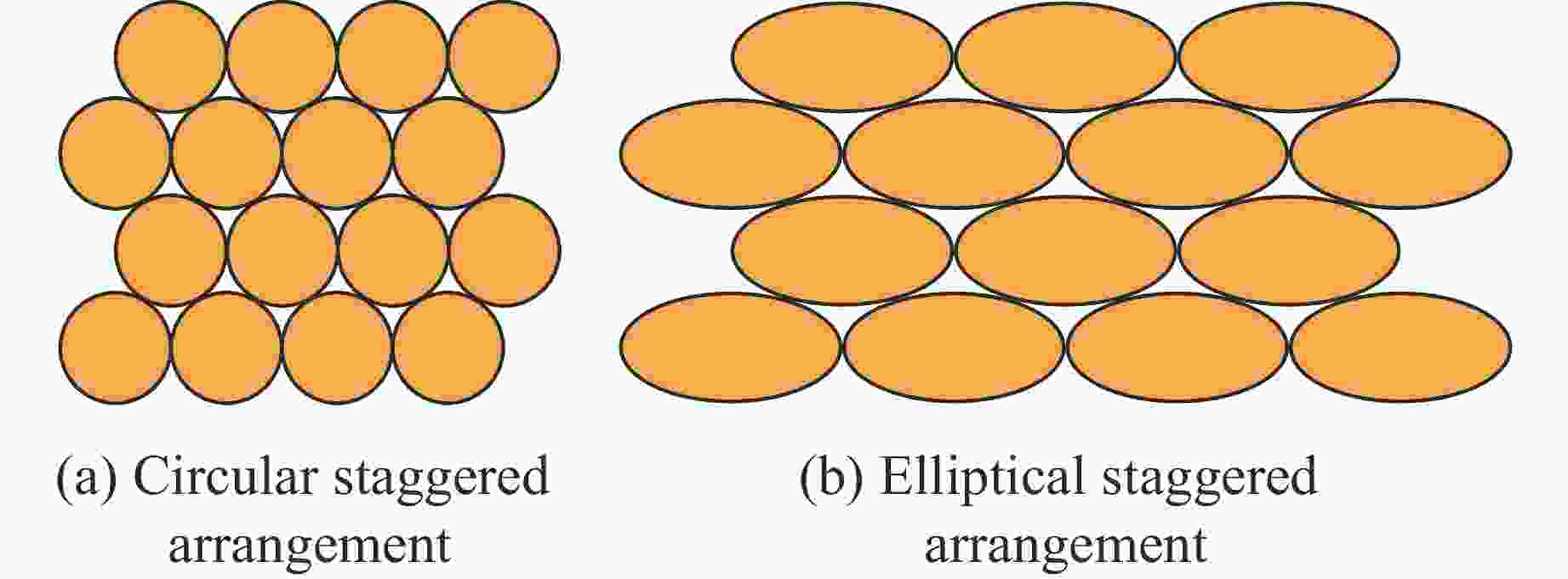
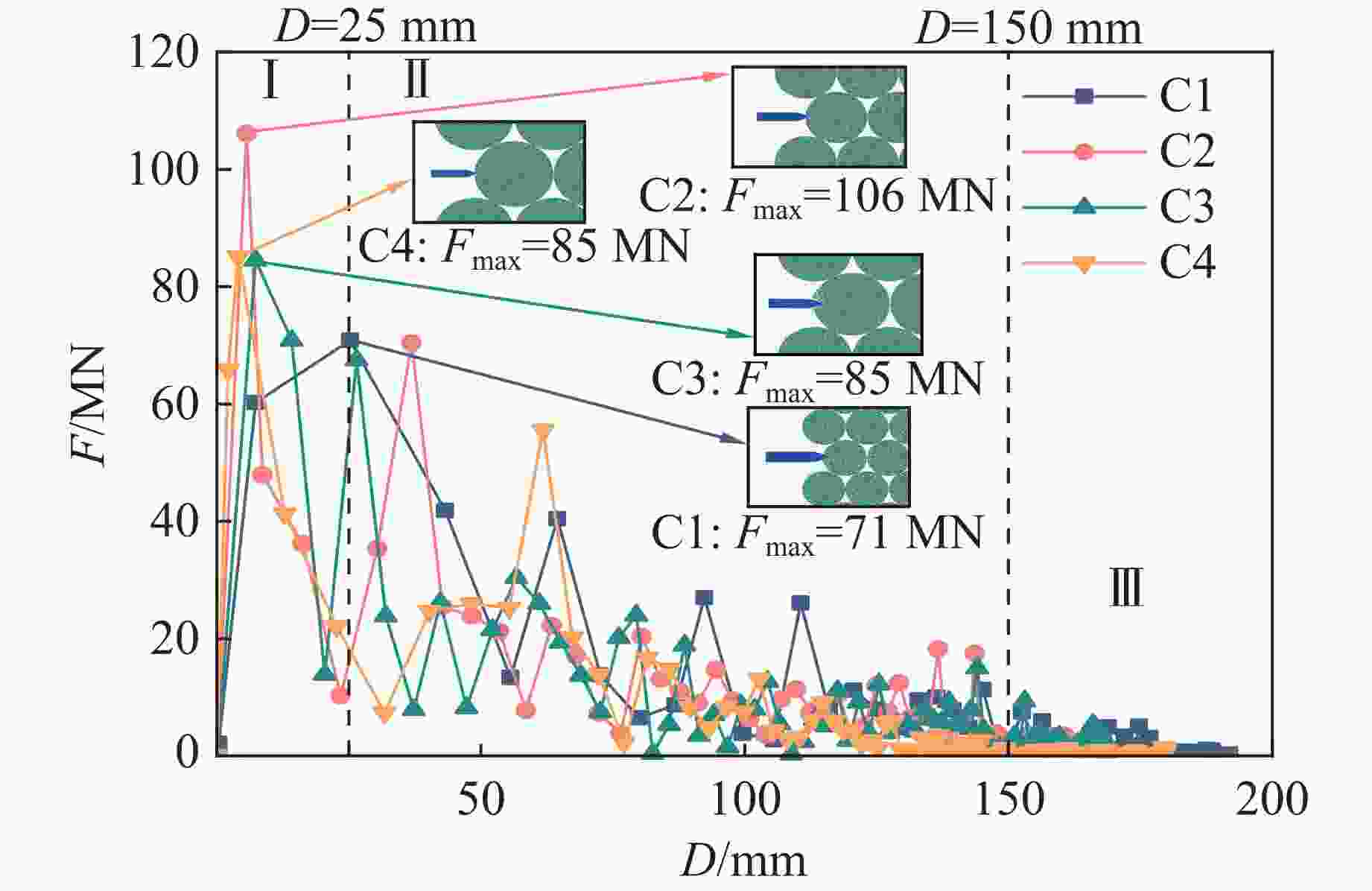
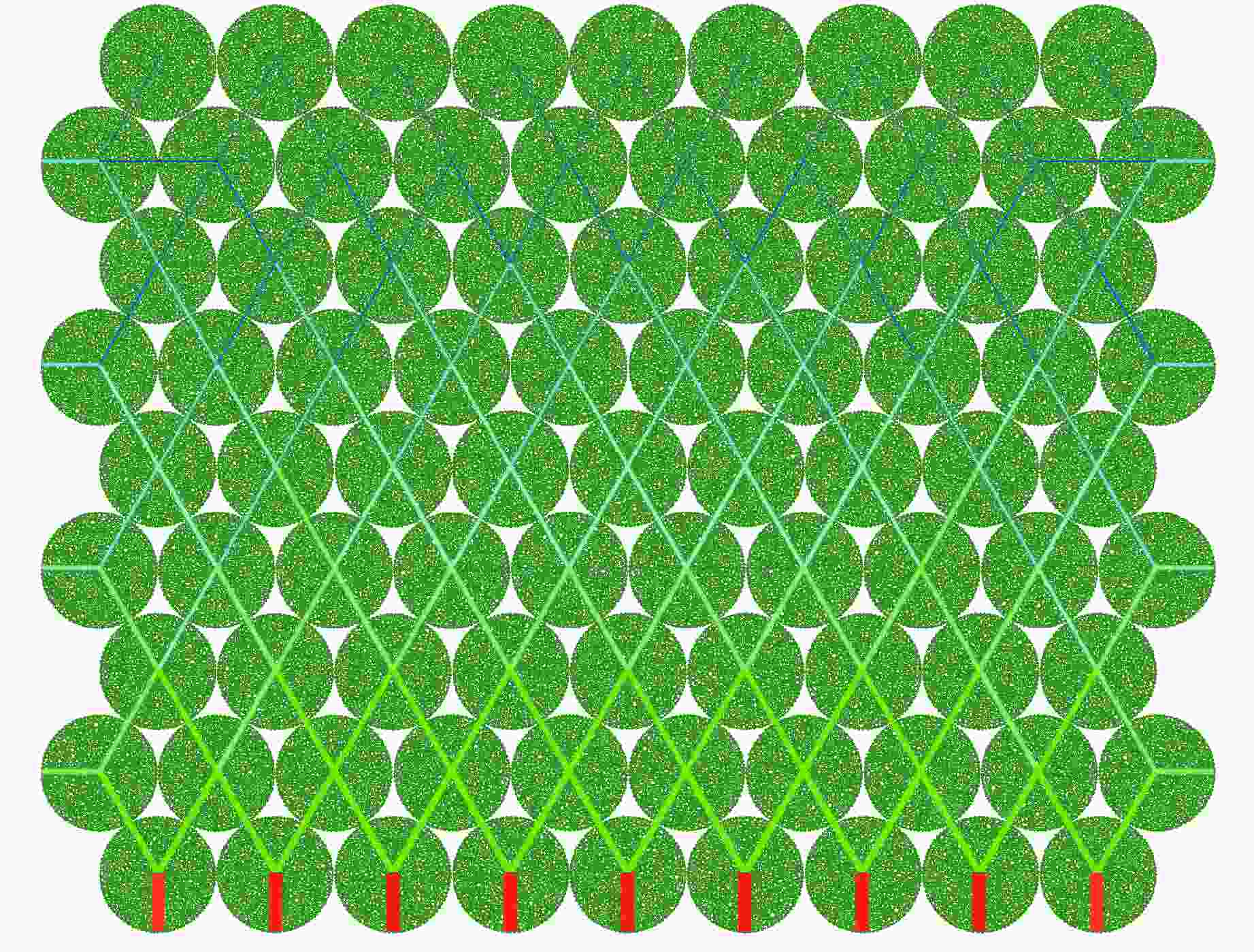
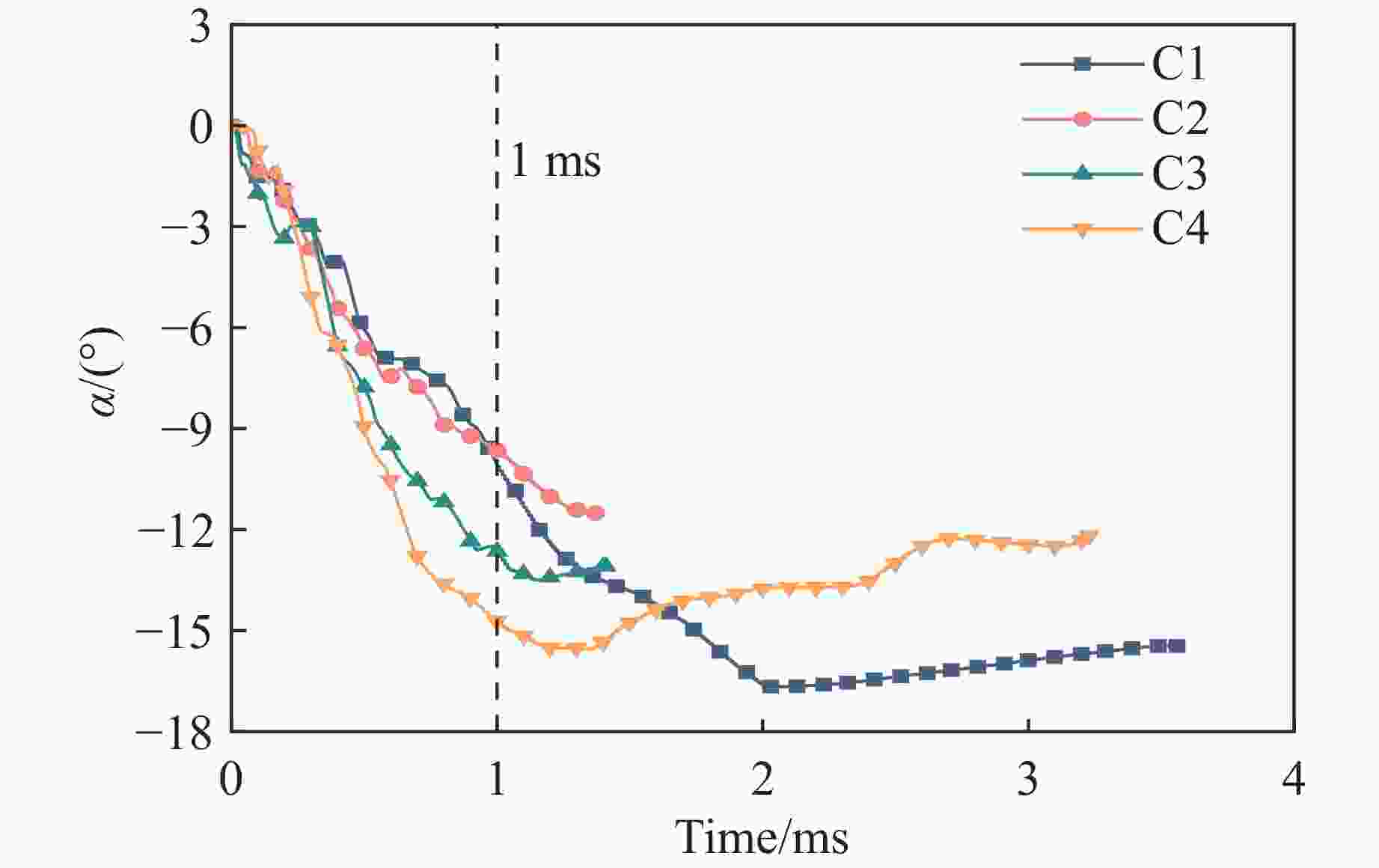
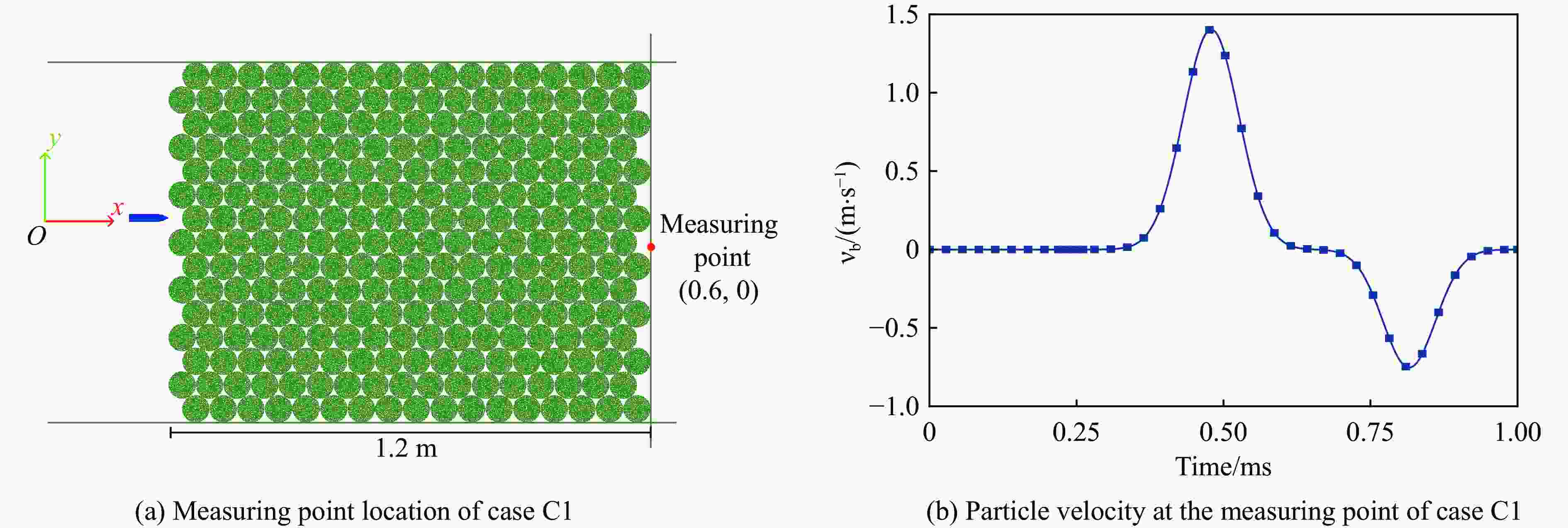
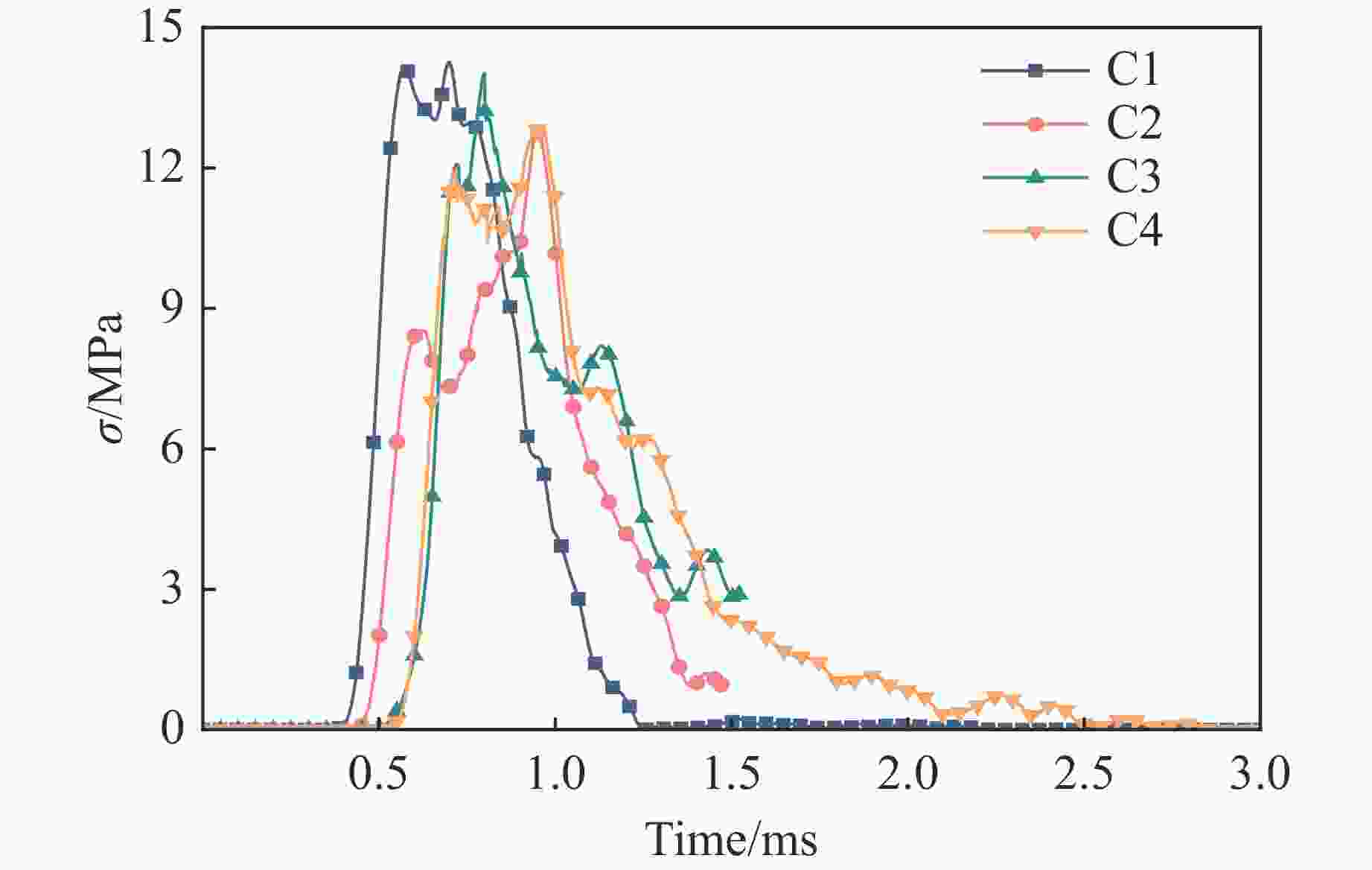
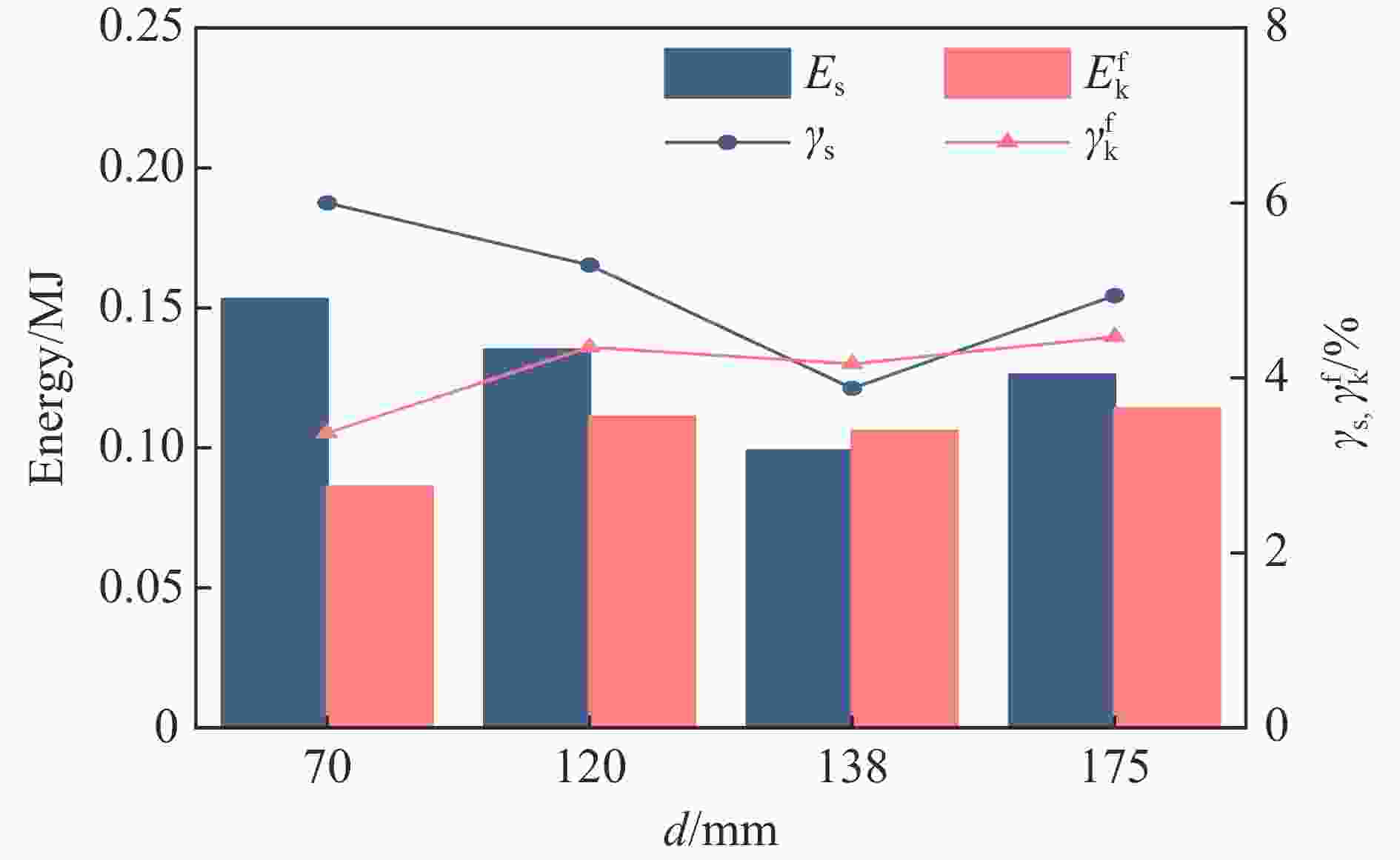
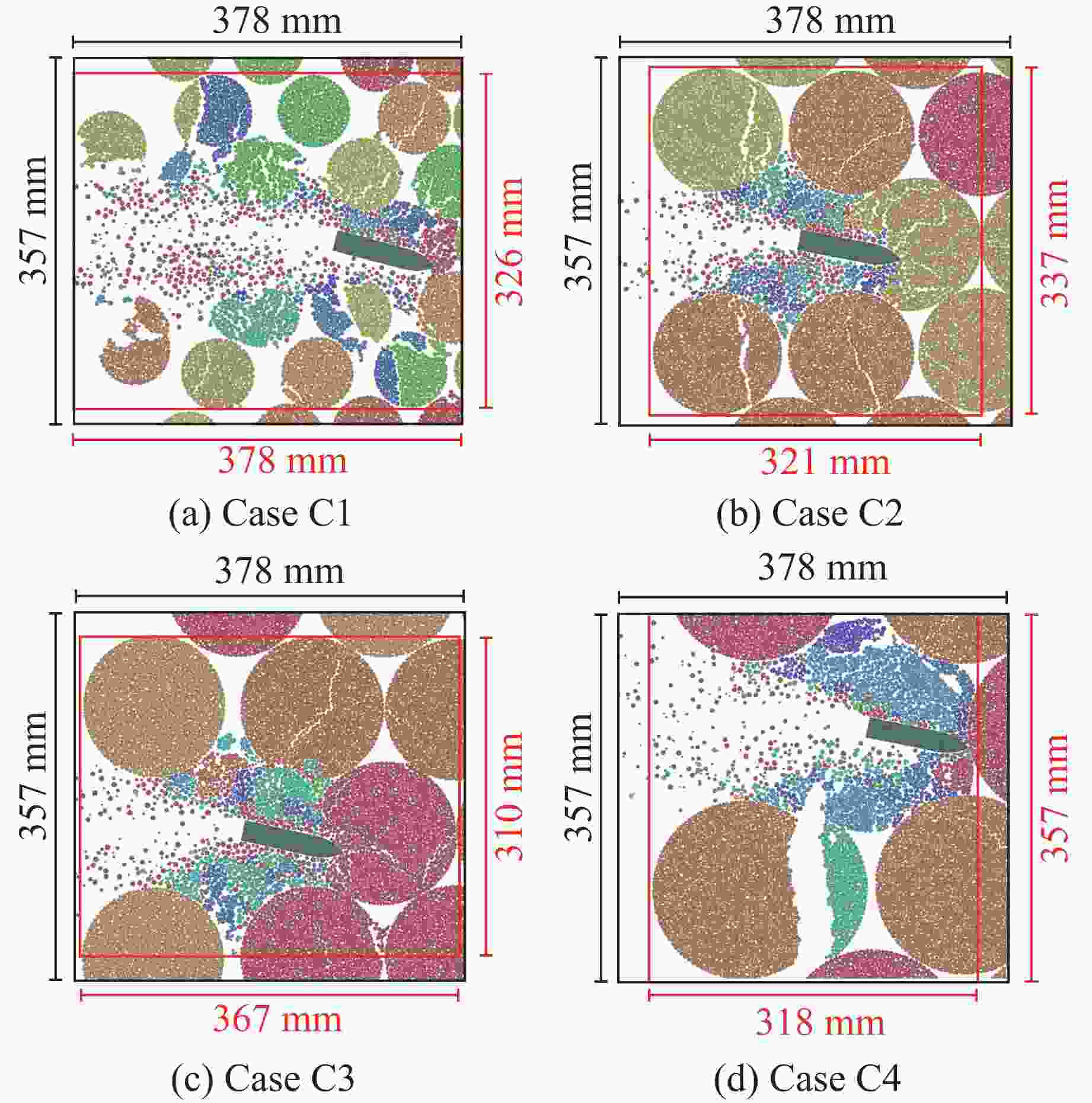
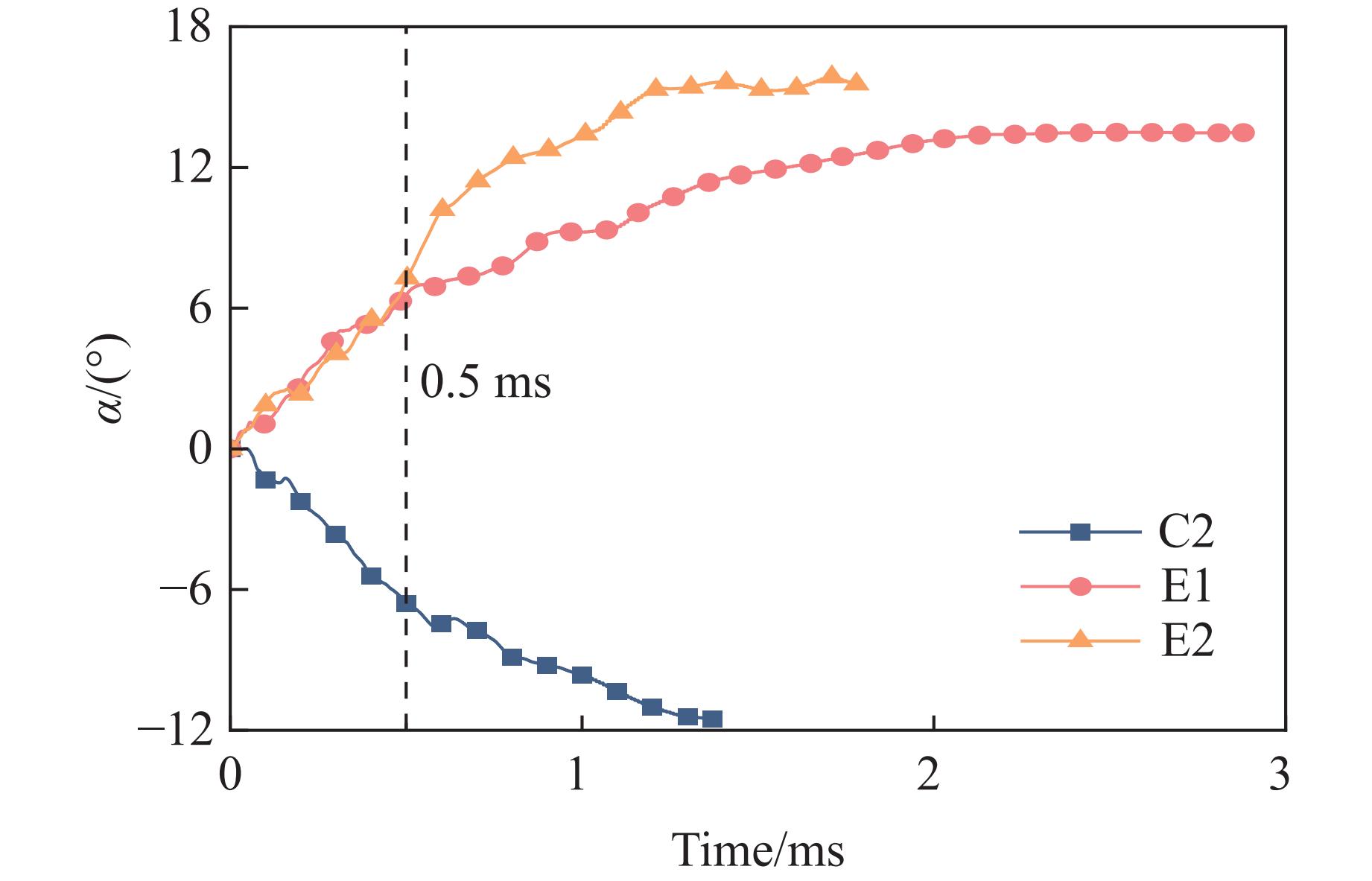
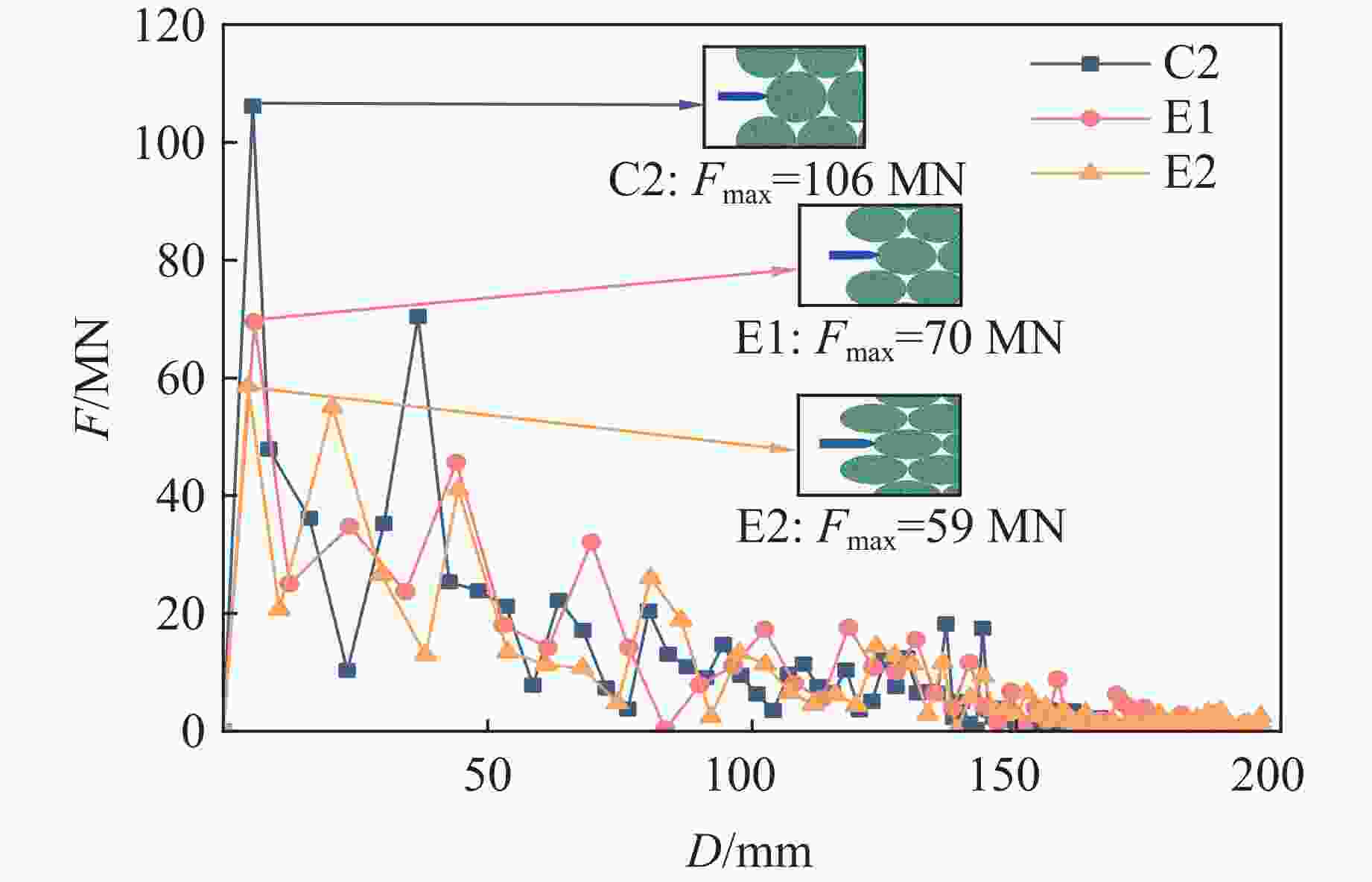
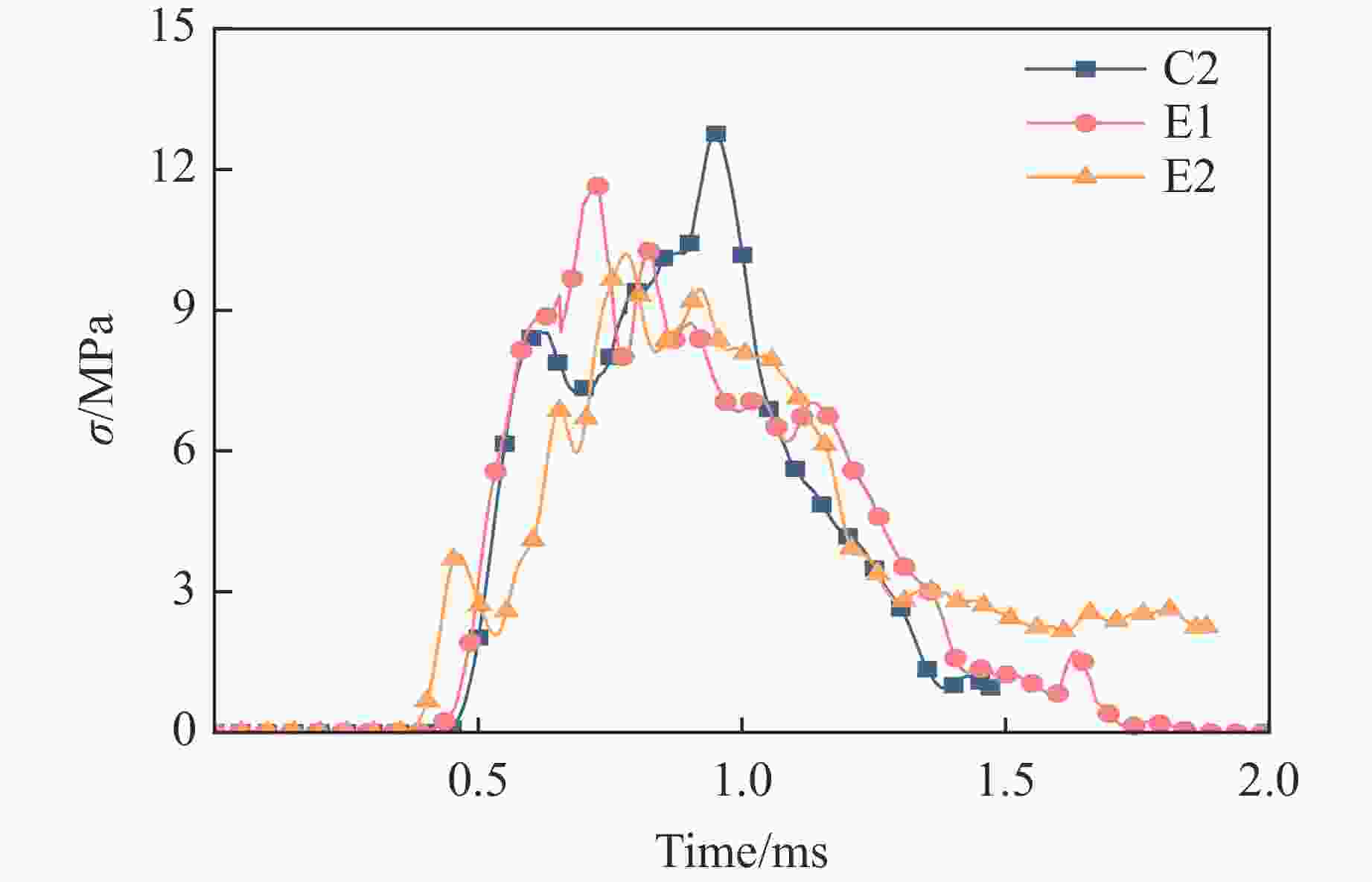
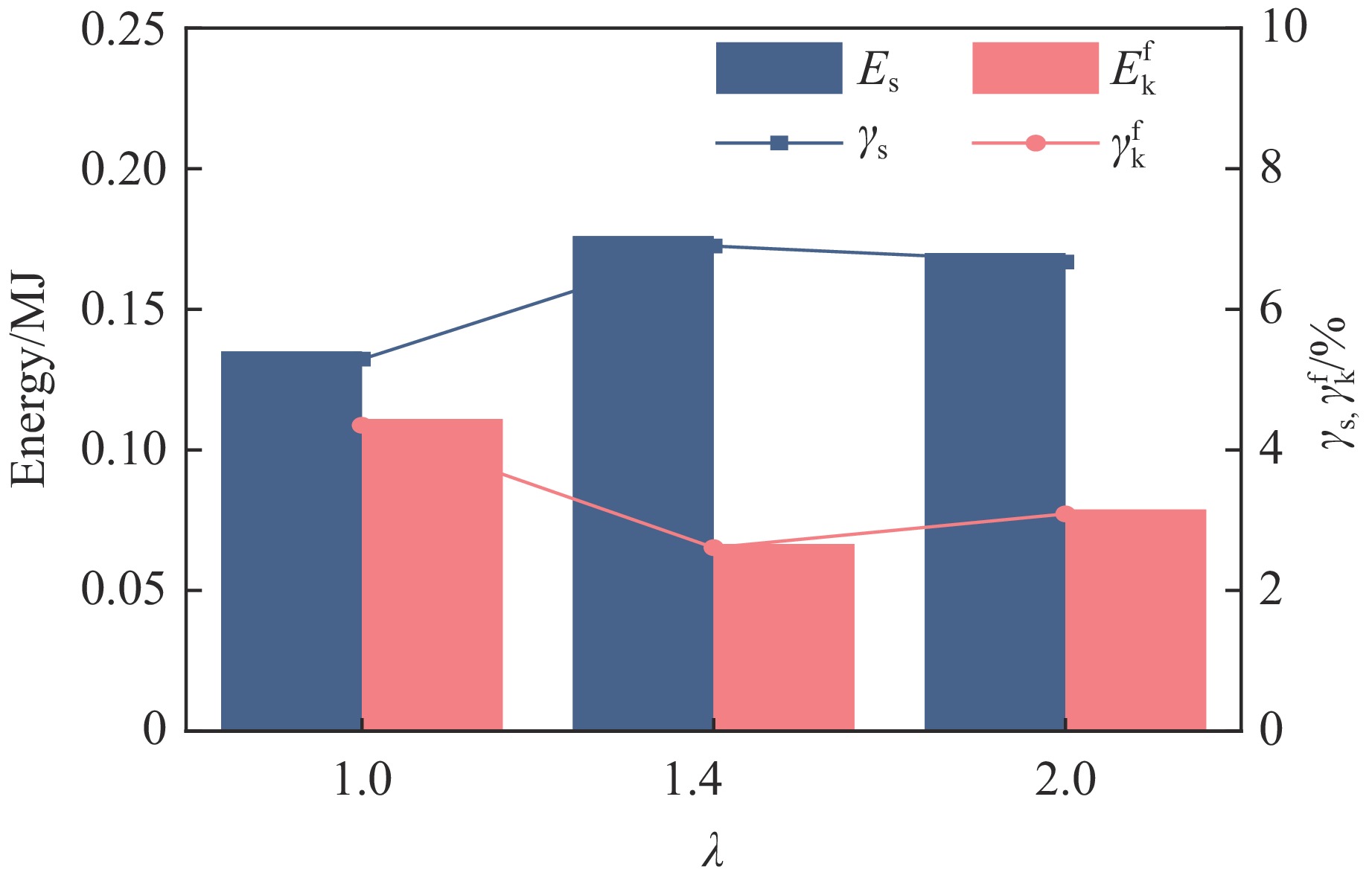
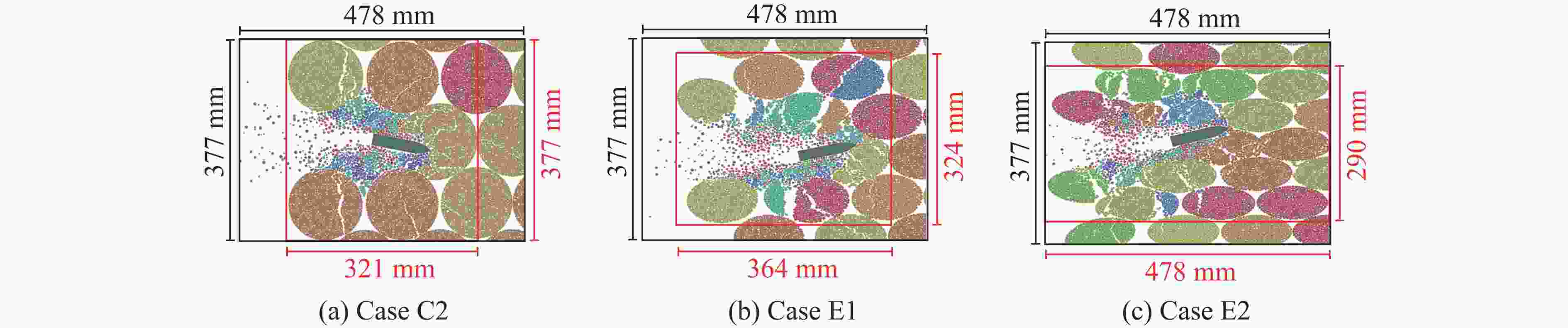
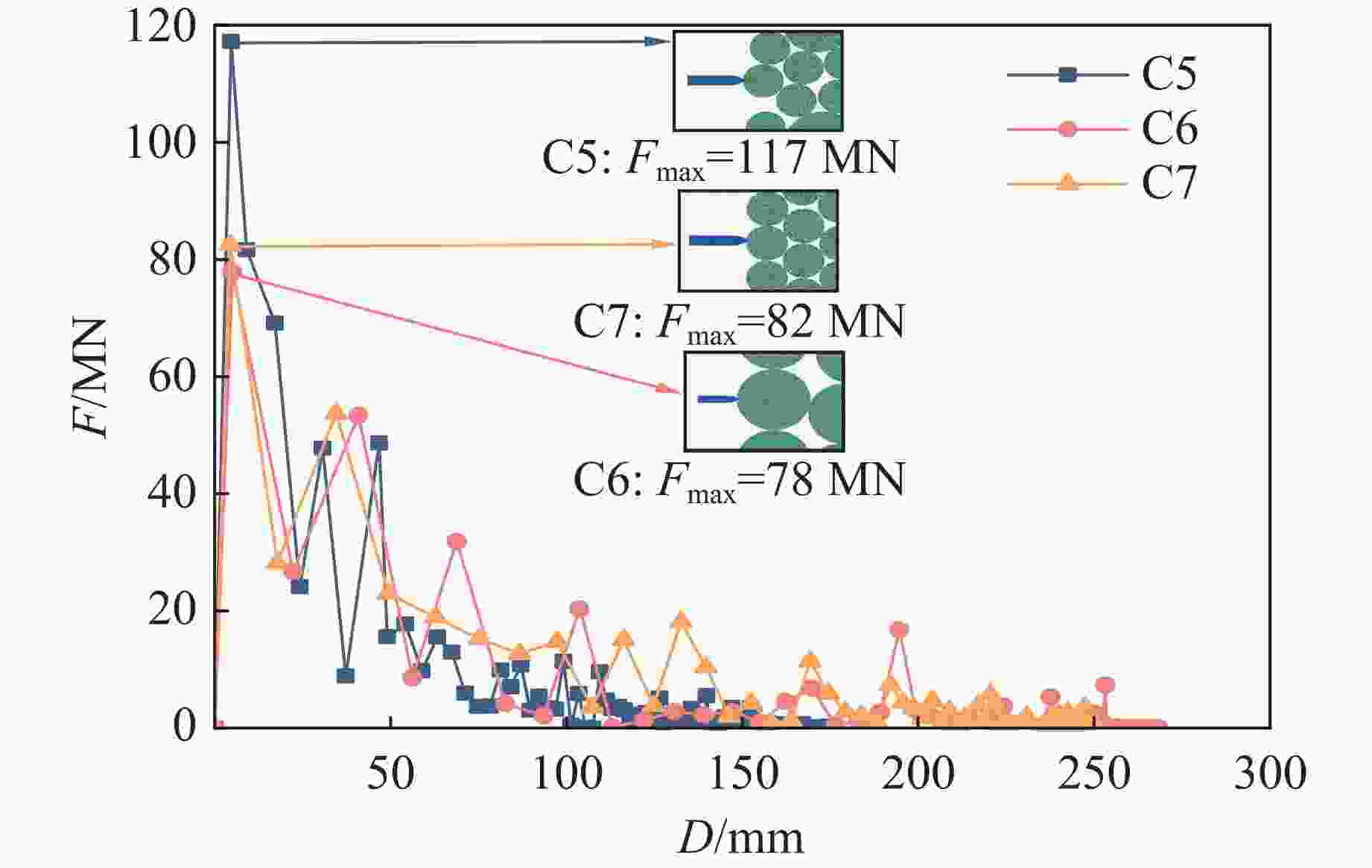
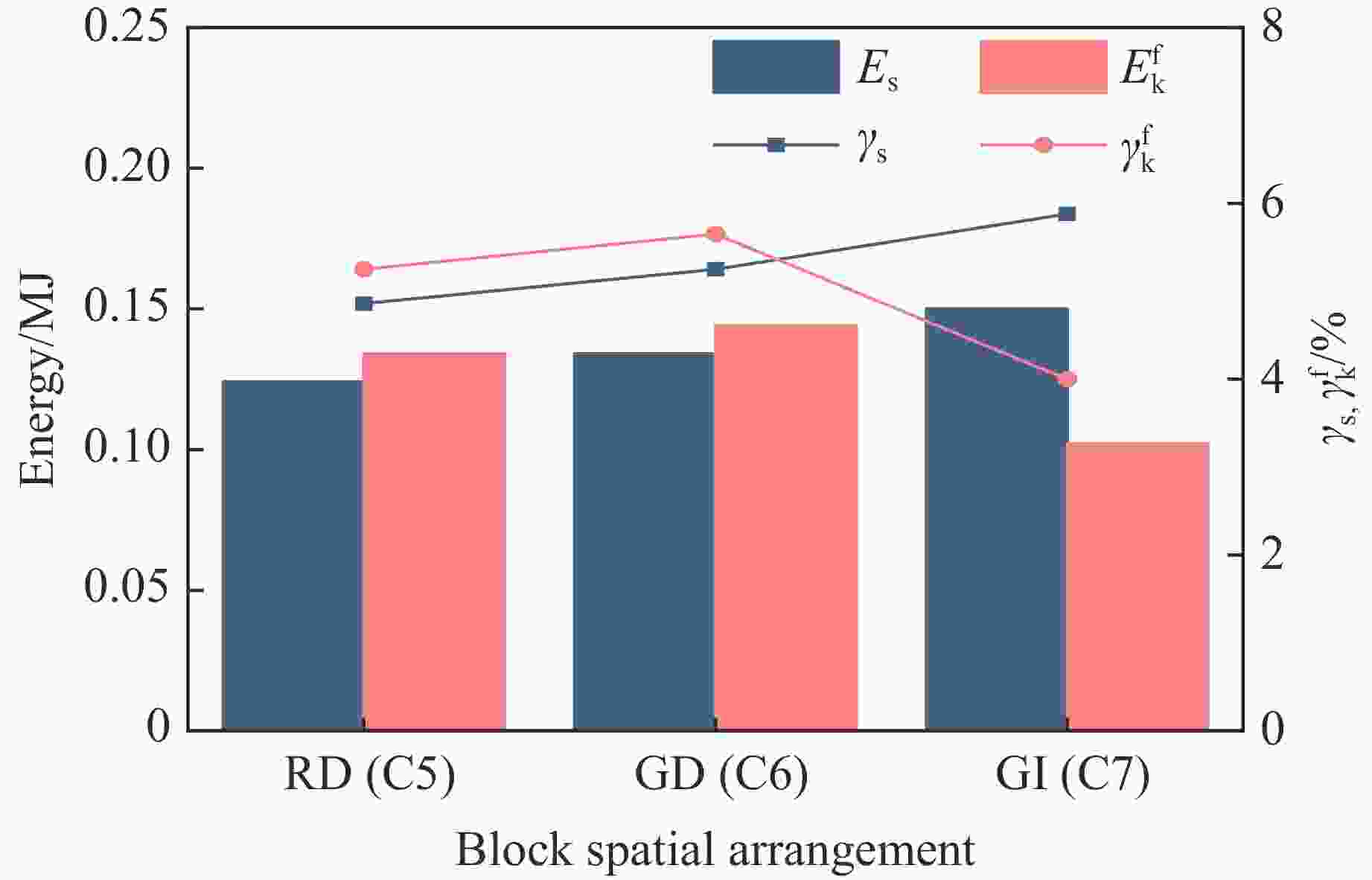
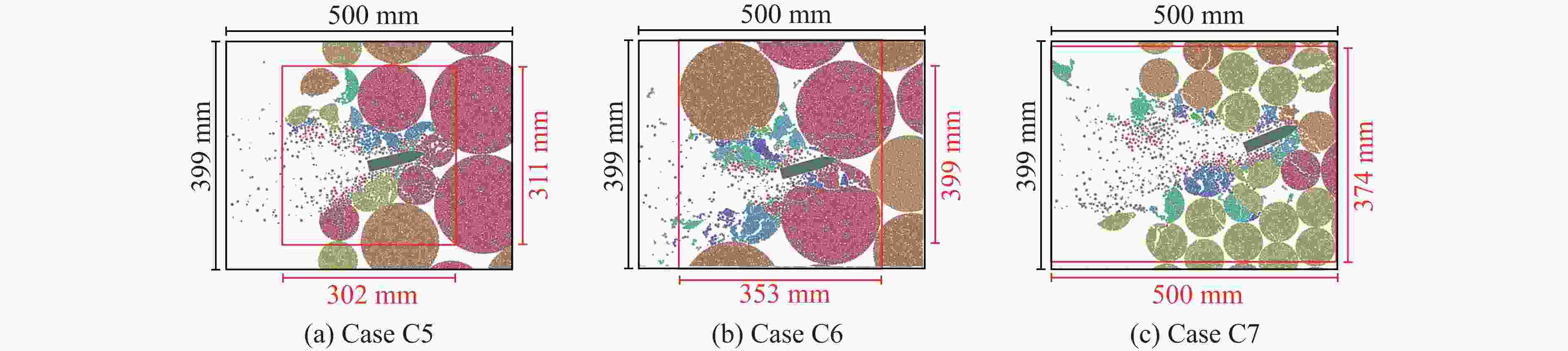
Case Block stone shape Block stone diameter/mm Spatial arrangement C1 Circle 70 Multi-layer staggered arrangement C2 Circle 120 Multi-layer staggered arrangement C3 Circle 138 Multi-layer staggered arrangement C4 Circle 175 Multi-layer staggered arrangement C5 Circle 70–175 Random distribution C6 Circle 70–175 Size gradient-decreasing C7 Circle 70–175 Size gradient-increasing E1 Ellipse with aspect ratio of 1.4 120 Multi-layer staggered arrangement E2 Ellipse with aspect ratio of 2.0 120 Multi-layer staggered arrangement -
[1] 穆朝民, 任辉启. 弹丸对钢筋混凝土中钢筋交汇处侵彻效应研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2010, 24(5): 351–358. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2010.05.006MU C M, REN H Q. Research on the effect of the projectile penetrating into the reinforced concrete targets at the intersection of the steel bar [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2010, 24(5): 351–358. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2010.05.006 [2] 邓旭辉, 王达锋. 近爆作用下中空夹层超高性能钢管混凝土柱的抗爆性能 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(6): 065201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200540DENG X H, WANG D F. Anti-blast performance of ultra-high performance concrete-filled double steel tubes under close in blast loading [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(6): 065201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200540 [3] AUSTIM C F, HALSEY C C, CLODT R L. Protection systems development: ESLTR339 [R]. Florida, USA: Tyndall Air Force Base, 1982. [4] GEBARA J M, PAN J B, ANDERSON J B. 浅埋结构块石防弹层的有限块法分析 [J]. 王承树, 译. 防护工程, 1994(1): 84–93.GEBARA J M, PAN J B, ANDERSON J B. Finite block method analysis of the ballistic protection layer of shallow buried structural blocks [J]. Translated by WANG C S. Protective Engineering, 1994(1): 84–93. [5] ZHANG M H, SHIM V P W, LU G, et al. Resistance of high-strength concrete to projectile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(7): 825–841. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.04.009 [6] WU H, FANG Q, CHEN X W, et al. Projectile penetration of ultra-high performance cement based composites at 510–1 320 m/s [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 741: 88–200. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.10.041 [7] WU H, FANG Q, GONG J, et al. Projectile impact resistance of corundum aggregated UHP-SFRC [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 84: 38–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.05.007 [8] 逄高伟, 方秦, 孔祥振, 等. WDU-34/B战斗部侵彻块石遮弹层的数值模拟研究 [J]. 防护工程, 2020, 42(4): 15–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2020.04.002PANG G W, FANG Q, KONG X Z, et al. Numerical simulation of WDU-34/B warhead penetrating into rubble burster layer [J]. Protective Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 15–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2020.04.002 [9] FANG Q, ZHANG J H. 3D numerical modeling of projectile penetration into rock-rubble overlays accounting for random distribution of rock-rubble [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 63: 118–128. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.08.010 [10] NIU Y Q, HUANG Z X, JIA X, et al. Research on the penetration performance of shaped charge jet into block stone concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 193: 105060. doi: 10.1016/J.IJIMPENG.2024.105060 [11] 郭虎, 何丽灵, 陈小伟, 等. 球形颗粒遮弹层对高速侵彻弹体的作用机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(10): 103301. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0428GUO H, HE L L, CHEN X W, et al. Penetration mechanism of a high-speed projectile into a shelter made of spherical aggregates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(10): 103301. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0428 [12] MANDAL J, GOEL M D, AGARWAL A K. Surface and buried explosions: an explorative review with recent advances [J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2021, 28(7): 4815–4835. doi: 10.1007/s11831-021-09553-2 [13] WANG G H, LU W B, YANG G D, et al. A state-of-the-art review on blast resistance and protection of high dams to blast loads [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 139: 103529. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103529 [14] POTYONDY D O, CUNDALL P A. A bonded-particle model for rock [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(8): 1329–1364. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011 [15] 张涛, 蔚立元, 鞠明和, 等. 基于PFC3D-GBM的晶体-单元体尺寸比对花岗岩动态拉伸特性影响分析 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(3): 468–478. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0303ZHANG T, YU L Y, JU M H, et al. Study on the effect of grain size-particle size ratio on the dynamic tensile properties of granite based on PFC3D-GBM [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(3): 468–478. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0303 [16] LI W Y, SHI C, ZHANG C. Numerical study on the effect of grain size on rock dynamic tensile properties using PFC-GBM [J]. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2024, 11(1): 481–489. doi: 10.1007/s40571-023-00634-6 [17] FAN R, LUO Y, GONG H L, et al. Dynamic damage and fracture characteristics of granite under cyclic impact simulated with coupled finite-difference and discrete element methods [J]. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials, 2023, 27(2): 469–487. doi: 10.1007/s11043-023-09597-w, [18] 鞠明和, 陶泽军, 蔚立元, 等. 钢粒子迟滞重复冲击破岩硬岩损伤破裂特征研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2024, 45(4): 1242–1255. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2023.0515JU M H, TAO Z J, YU L Y, et al. Damage and fracture characteristics of hard rocks caused by hysterisis and repeated impacts of steel particles [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2024, 45(4): 1242–1255. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2023.0515 [19] 高飞, 邓树新, 张国凯, 等. 缩比模型弹侵彻岩石靶尺寸效应试验研究与理论分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3601–3612. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0014GAO F, DENG S X, ZHANG G K, et al. Experimental study and theoretical analysis of the size effect for scale model projectile penetrating into rock target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(12): 3601–3612. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0014 [20] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, et al. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 465–476. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00048-F [21] 章涵, 向国梁, 王乐华, 等. 基于三维模型构建新方法的块石形状效应下S-RM宏细观剪切力学行为 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(10): 2030–2044. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0988ZHANG H, XIANG G L, WANG L H, et al. Effect of block form on the shear marco- and meso-mechanical behaviors of S-RM based on 3D novel modelling approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(10): 2030–2044. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0988 [22] 崔溦, 魏杰, 王超, 等. 考虑颗粒级配和形态的颗粒柱坍塌特性离散元模拟 [J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(12): 2230–2239. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202112009CUI W, WEI J, WANG C, et al. Discrete element simulation of collapse characteristics of particle column considering gradation and shape [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(12): 2230–2239. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202112009 [23] ZHOU Z L, ZHAO Y, JIANG Y H, et al. Dynamic behavior of rock during its post failure stage in SHPB tests [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(1): 184–196. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60021-9 [24] 赵婷婷, 冯云田. 大规模颗粒系统的精确缩尺和粗粒化离散元方法 [J]. 计算力学学报, 2022, 39(3): 365–372. doi: 10.7511/jslxCMGM202213ZHAO T T, FENG Y T. Exact scaling laws and coarse-grained discrete element modelling of large scale granular systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2022, 39(3): 365–372. doi: 10.7511/jslxCMGM202213 [25] FENG Y T, OWEN D R J. Discrete element modelling of large scale particle systems-Ⅰ: exact scaling laws [J]. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2014, 1(2): 159–168. doi: 10.1007/s40571-014-0010-y [26] 张杰, 王志华, 王志勇, 等. 骨料对刚性弹正侵彻混凝土过程的影响机理 [J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2021, 51(3): 272–280. doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0483ZHANG J, WANG Z H, WANG Z Y, et al. Impact mechanisms of aggregate on rigid projectile normal penetration into concrete target [J]. Scientia Sinica: Technologica, 2021, 51(3): 272–280. doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0483 [27] 徐飞. 普通混凝土骨料最小空隙率的探讨 [J]. 混凝土, 2004(3): 17–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2004.03.006XU F. The research of minimal fraction void of concrete aggregate [J]. Concrete, 2004(3): 17–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2004.03.006 [28] NASR A A, WANG B Z, CHEN S G, et al. Monitoring the flow patterns of high performance self-compacting concrete in the voids of sloped rock-filled concrete structures [J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2025, 16(3): 103313. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2025.103313 -






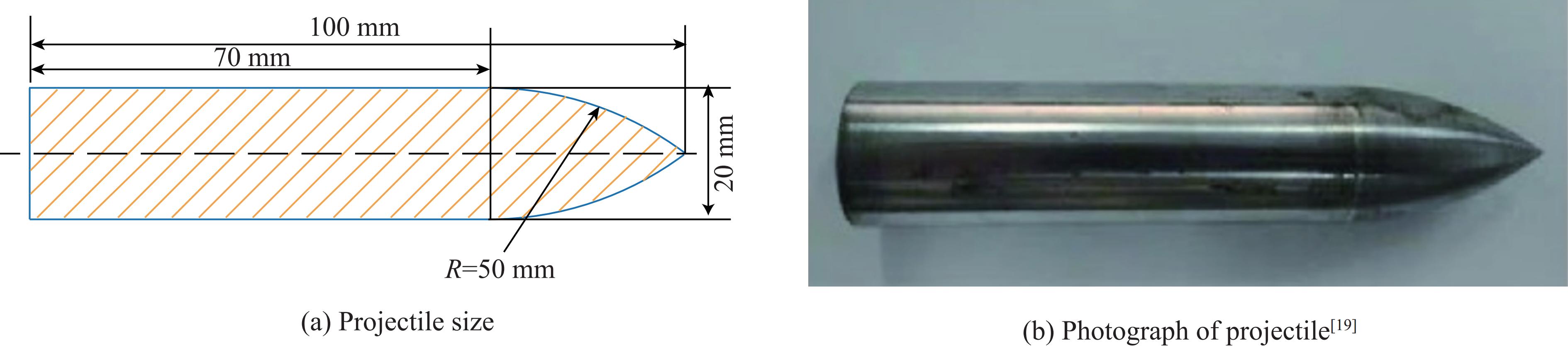
 下载:
下载: