Close-Range Blast Resistance and Analytical Methods of Polyurea Coated Masonry Infill Walls with Built-in Tie Reinforcement
-
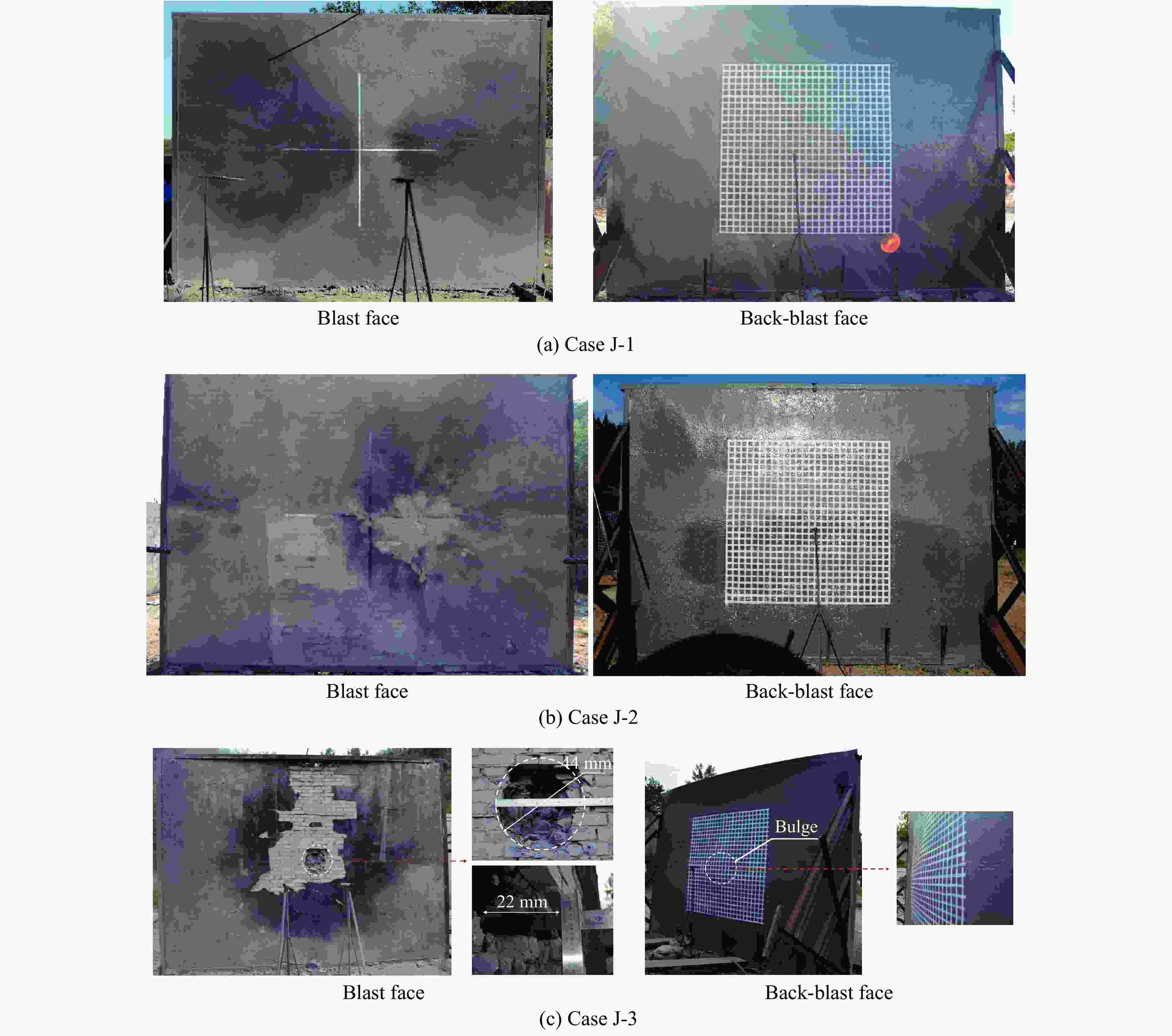
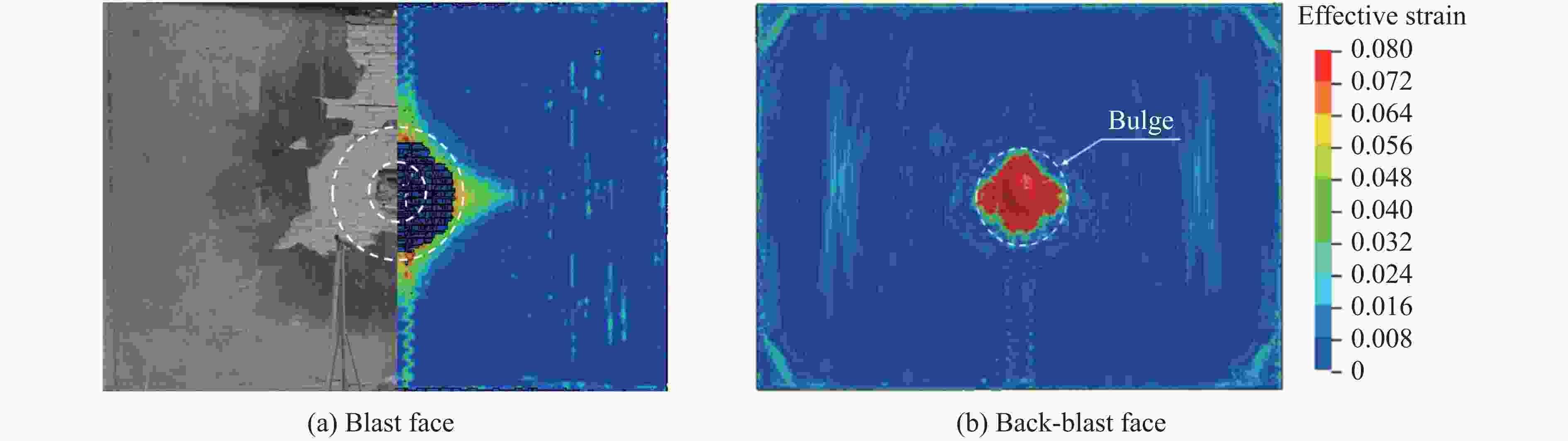
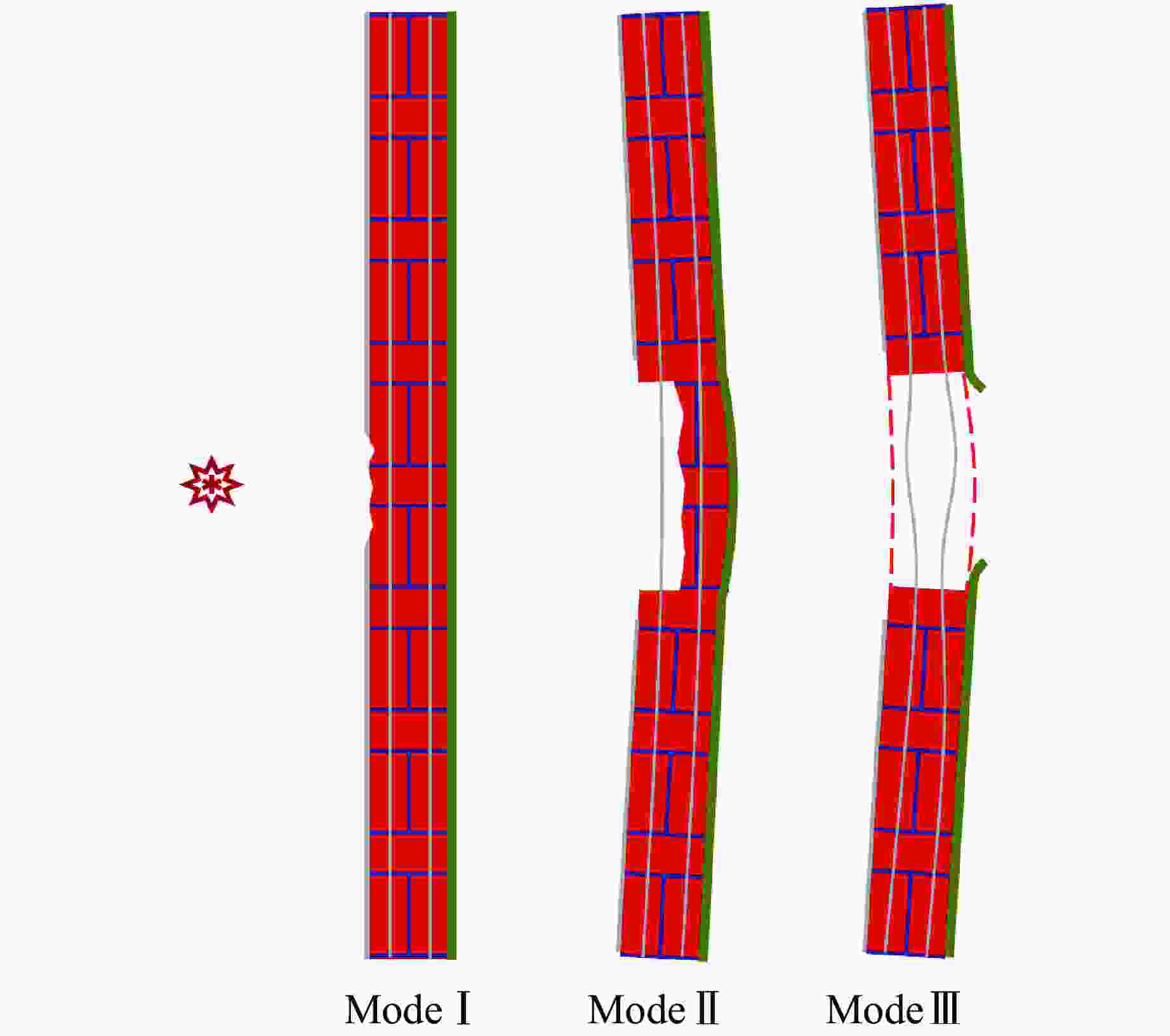
摘要: 为研究在近距离爆炸载荷作用下内置拉结筋聚脲涂覆砌体填充墙的动力响应过程、毁伤特征和破坏模式,对不同聚脲涂覆方式和涂覆厚度的砌体墙进行了近距离空爆试验,结合LS-DYNA软件开展了数值模拟研究,基于砖墙、钢筋和聚脲涂层的抗力函数建立了改进的等效单自由度理论计算模型。等效单自由度模型可以准确地描述内置拉结筋涂覆聚脲加固墙体在近场爆炸载荷作用下的位移响应过程。在近场爆炸工况下,根据墙体的面外响应特征,总结出3种近场爆炸破坏模式:表面砂浆层损伤、开坑位错及背面鼓包、贯穿损伤。随着拉结筋数量的增加,墙体的抗爆性能增强,临界贯穿破坏装药量增多。Abstract: In order to investigate the dynamic response process, damage characteristics and damage mode of polyurea coated masonry infill walls with built-in tie reinforcement under close-range explosion load, a series of close-range explosion tests were performed on masonry wall with different polyurea coating methods and thicknesses. Additionally, numerical studies were carried out using the LS-DYNA software. Based on the resistance function of the brick wall, steel bar and polyurea coating, an improved equivalent single degree of freedom (ESDOF) theoretical calculation model was established. This model can accurately describe the displacement response of the polyurea coated masonry infill walls with built-in tie reinforcement under close-range explosion load. Three damage modes: surface mortar layer damage, open pit dislocation with back bulge, and penetration damage were identified according to the wall’s out-of-face response characteristics during close-range explosion load. With the increase of the number of tension reinforcement, the anti-explosion performance of the wall improves and the critical penetration damage charge increases.
-
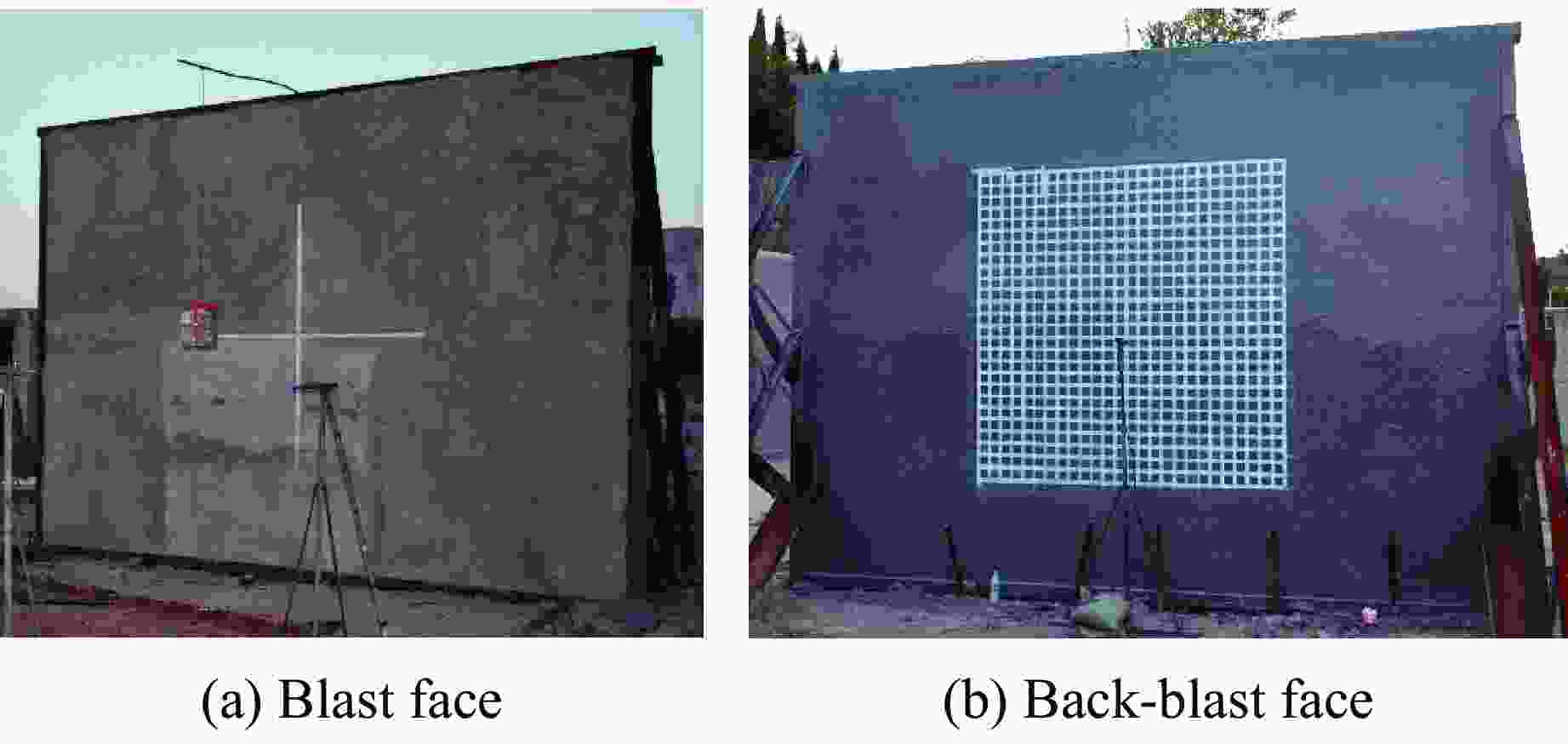
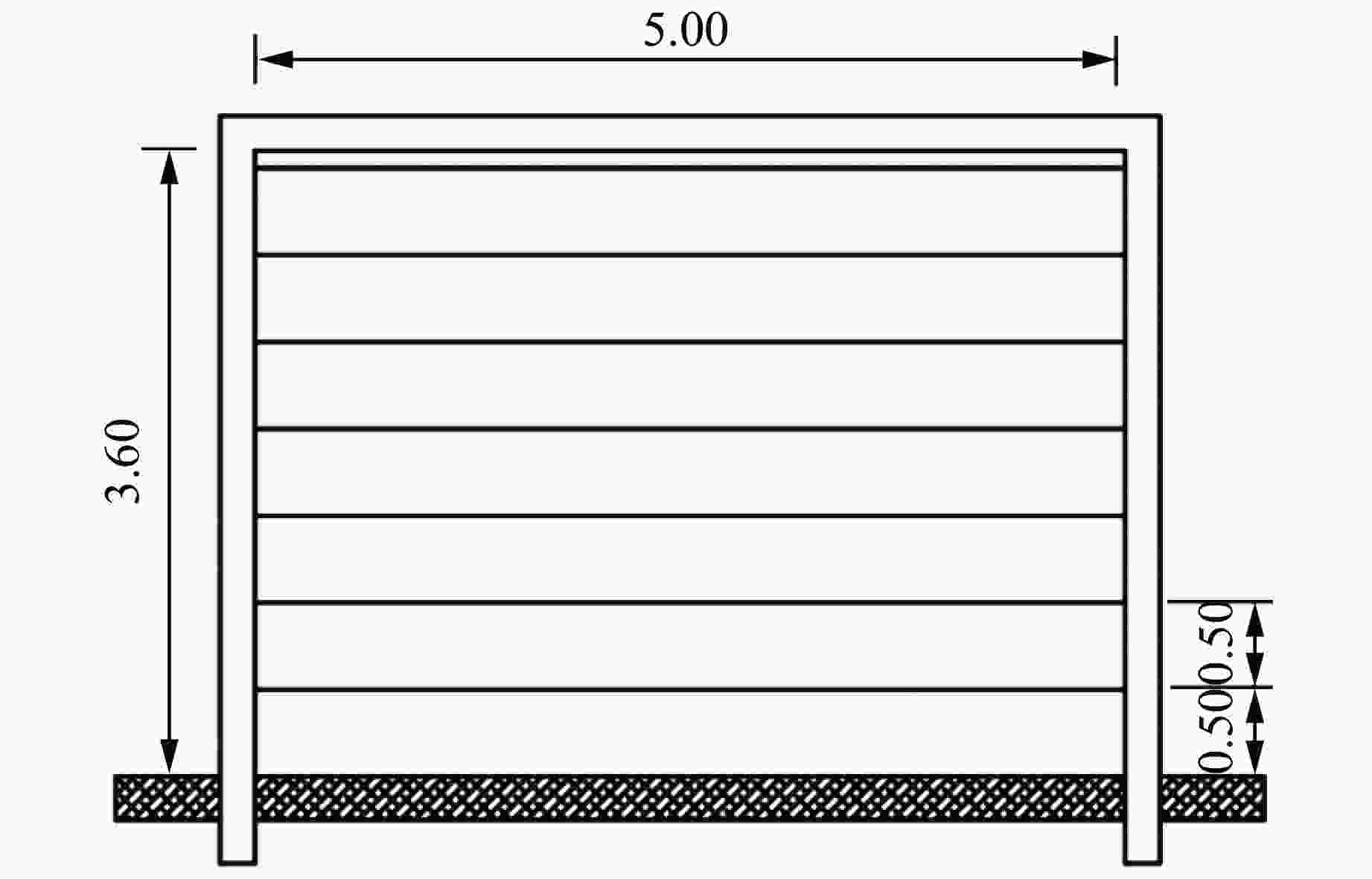
表 1 试验工况
Table 1. Test conditions
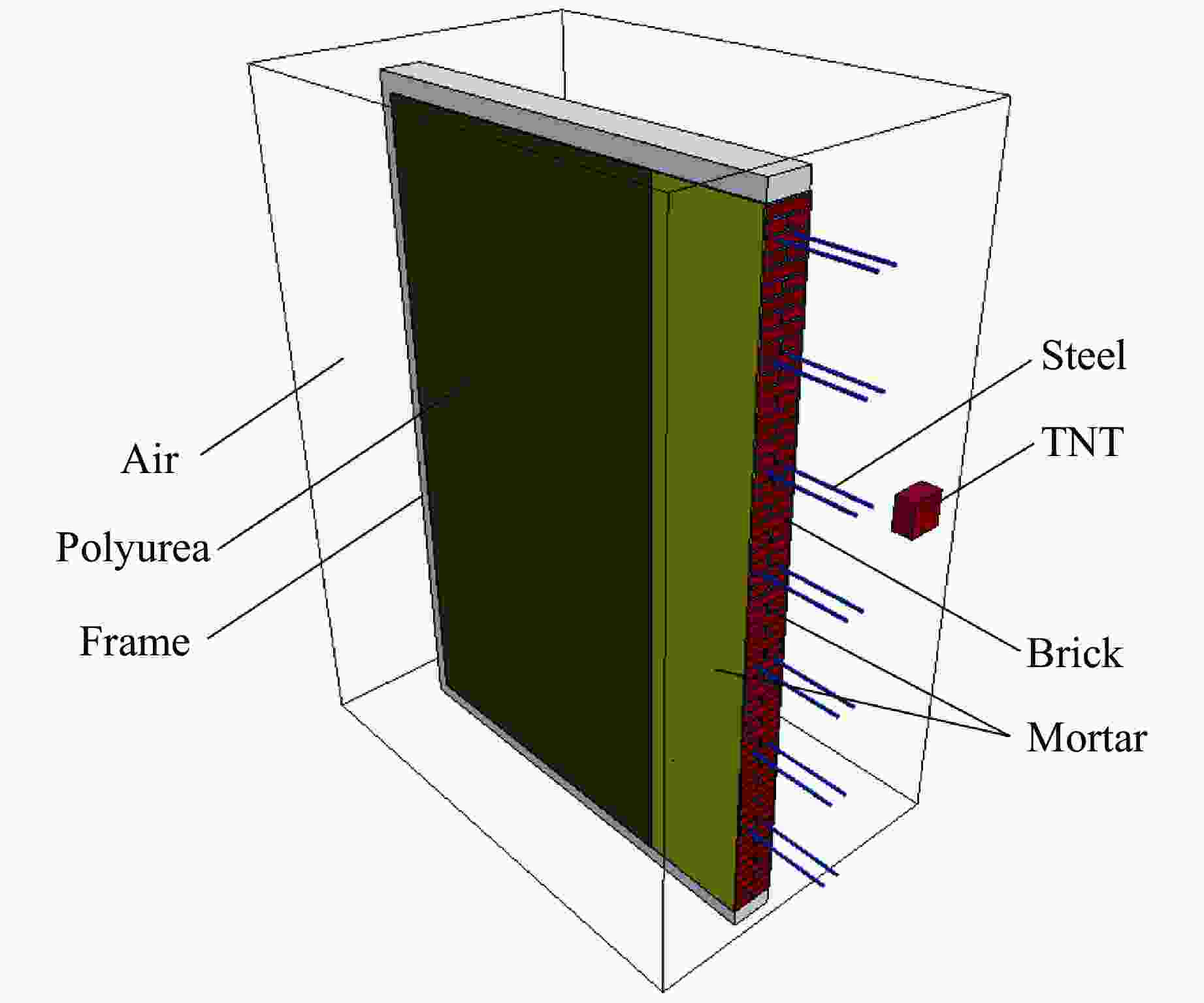
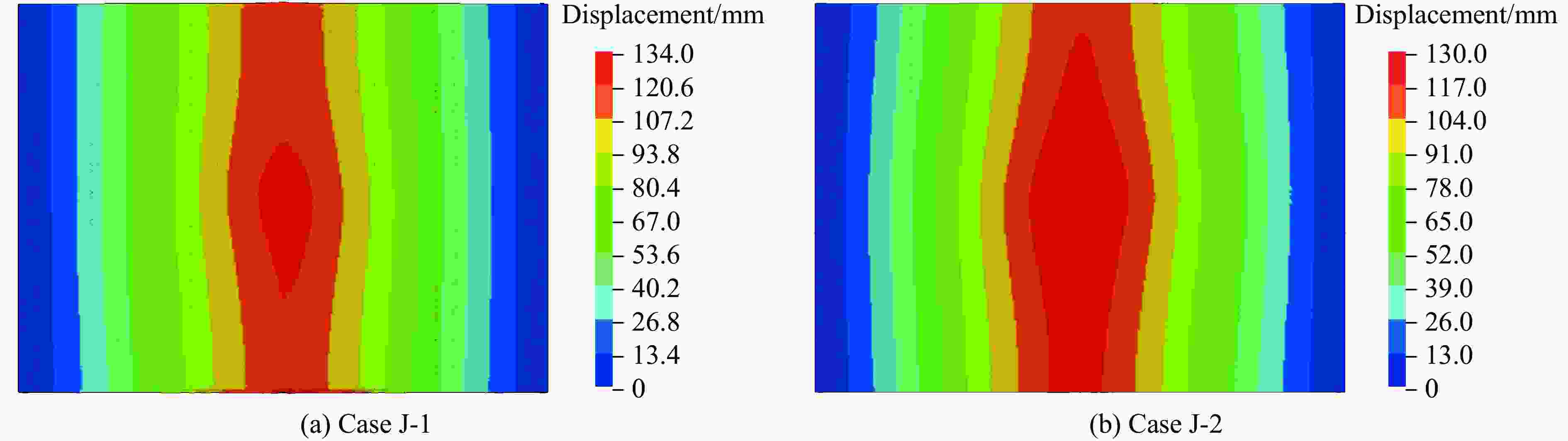
Test Rebar pieces Polyurea layer thickness/mm TNT mass/kg Blast distance/m Blast face Back-blast face J-1 14 3 3 14 1.4 J-2 14 0 5 14 1.4 J-3 14 0 5 14 1.0 表 2 聚脲材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of polyurea
$E/{\text{MPa}}$ $ \nu $ $ \rho /(\text{g}\cdot {\text{cm}}^{{-3}}) $ $ \sigma\mathrm{_Y}/\text{MPa} $ ${E_{\rm t}}/{\text{MPa}}$ 230 0.4 1.19 1.38 3.5 表 3 砖块材料参数
Table 3. Material parameters of brick
$ \rho /(\text{g}\cdot {\text{cm}}^{{-3}}) $ $ E/{\text{MPa}} $ $ \nu $ $ \sigma_{\mathrm{bc} {\rm}}/\text{MPa} $ $ R_{\mathrm{m} {\rm}}/\text{MPa} $ 1.8 8200 0.16 15.5 0.775 表 4 水泥砂浆材料参数
Table 4. Material parameters of mortar
$ \rho /(\text{g}\cdot {\text{cm}}^{{-3}}) $ $ E/{\text{MPa}} $ $ \nu $ $ \sigma\mathrm{_{bc}}/\text{MPa} $ $ R_{\mathrm{m}}/\text{MPa} $ 2.1 4100 0.21 4.9 0.245 表 5 HRB400钢筋材料参数
Table 5. Material parameters of HRB400 rebar
$ \rho/(\text{kg}\cdot\text{m}^{-3}) $ $ E/{\text{GPa}} $ $ \nu $ $ \sigma_{\mathrm{Y}}/\text{MPa} $ $ E\mathrm{_t}/\text{MPa} $ $ f\mathrm{_s} $ 7800 207 0.3 400 1100 0.092 表 6 试验与数值模拟结果对比
Table 6. Comparison of test and simulation results
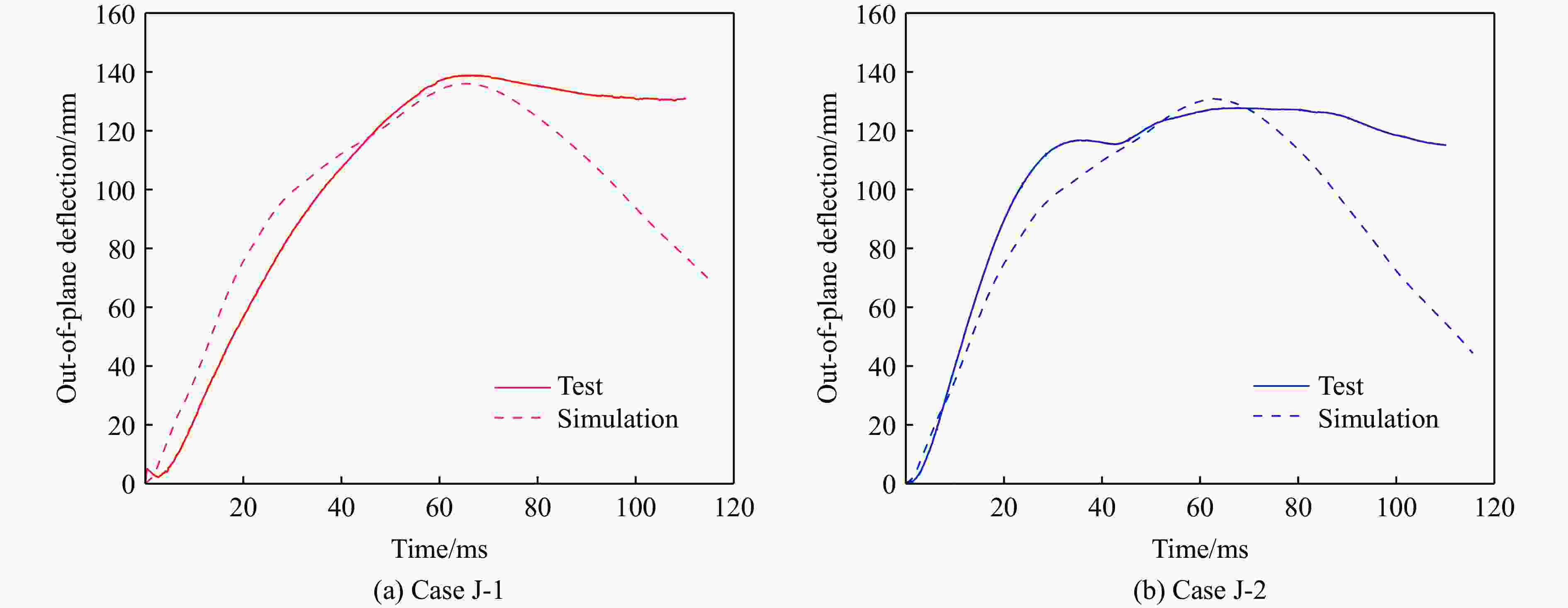
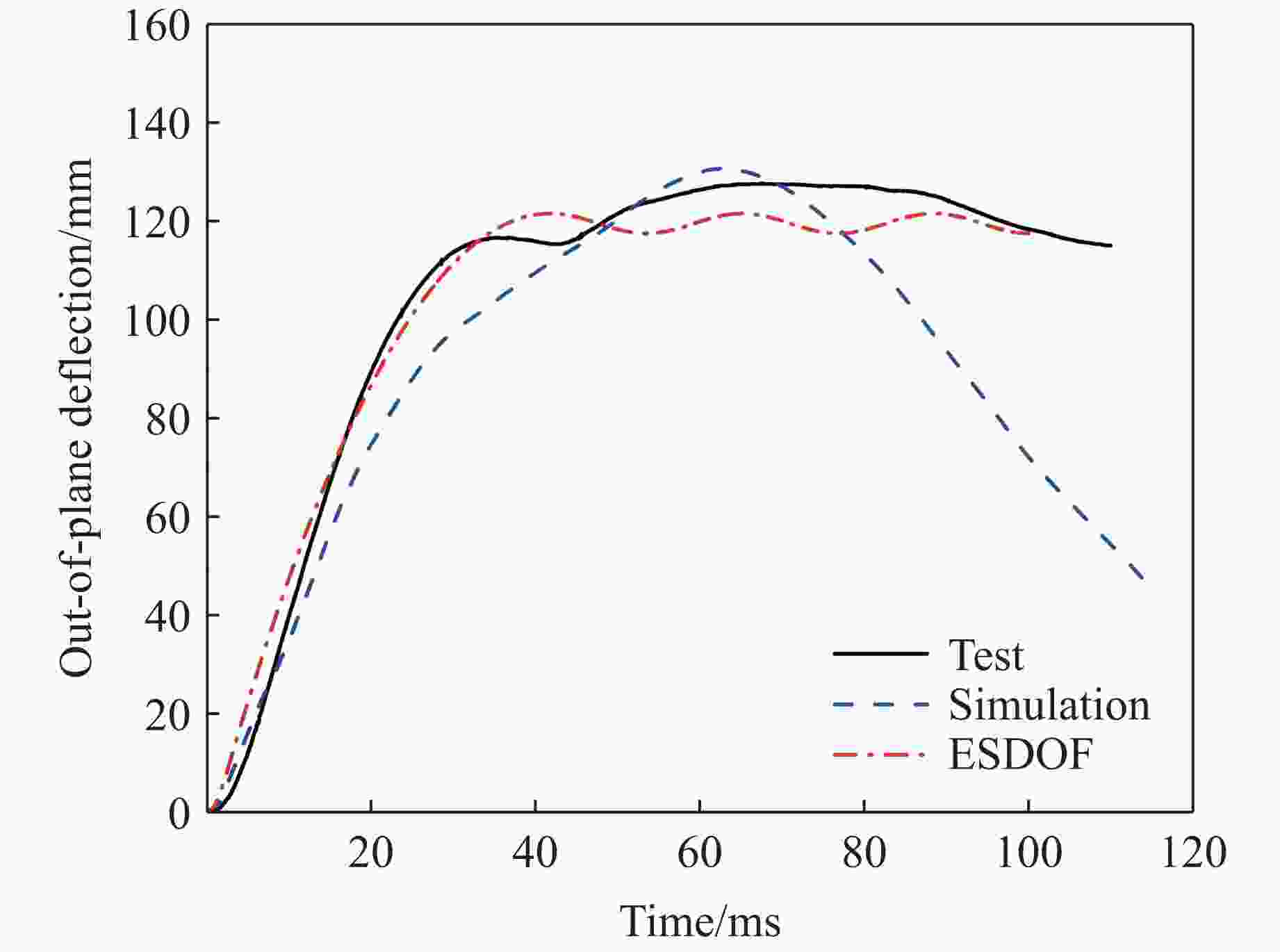
Case Maximum displacement Pit diameter Test/mm Simulation/mm Error/% Test/mm Simulation/mm Error/% J-1 138 134 3.6 J-2 127 130 2.4 J-3 44 42 4.5 表 7 等效质量系数、等效载荷系数及等效质量载荷系数
Table 7. Equivalent mass, load and mass loading factor
Boundary conditions and load forms Responsive KM KL KLM 
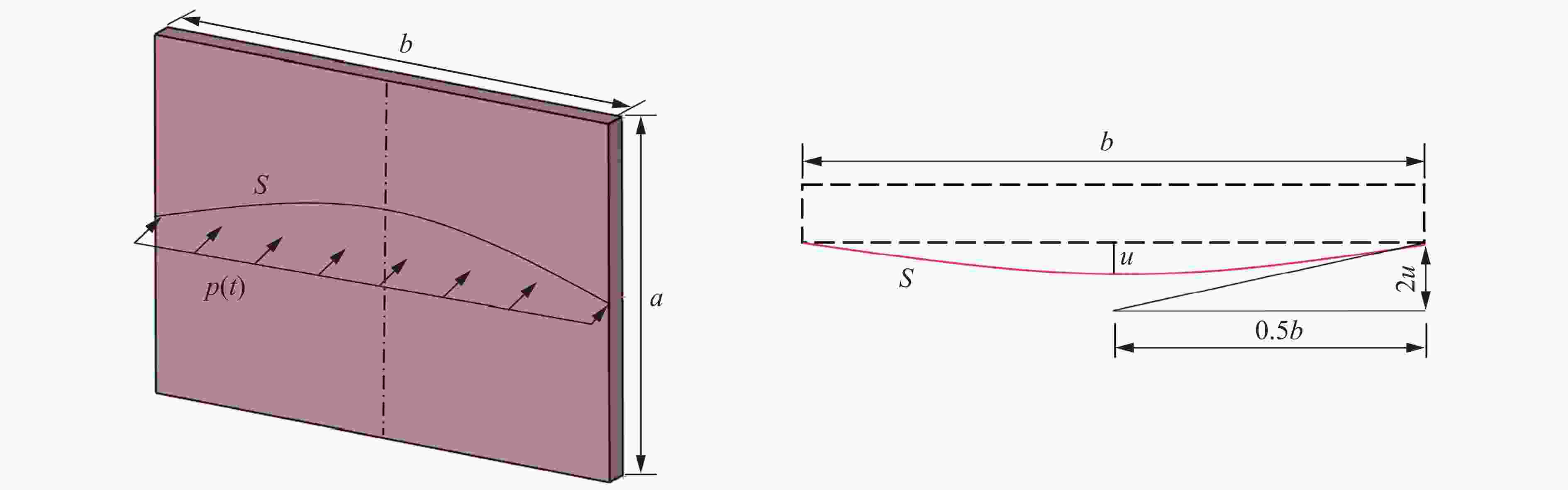
Elasticity 0.50 0.64 0.78 Plasticity 0.33 0.50 0.66 
Elasticity 0.41 0.53 0.77 Elastoplastic 0.50 0.64 0.78 Plasticity 0.33 0.50 0.66 表 8 数值模拟结果
Table 8. Numerical simulation results
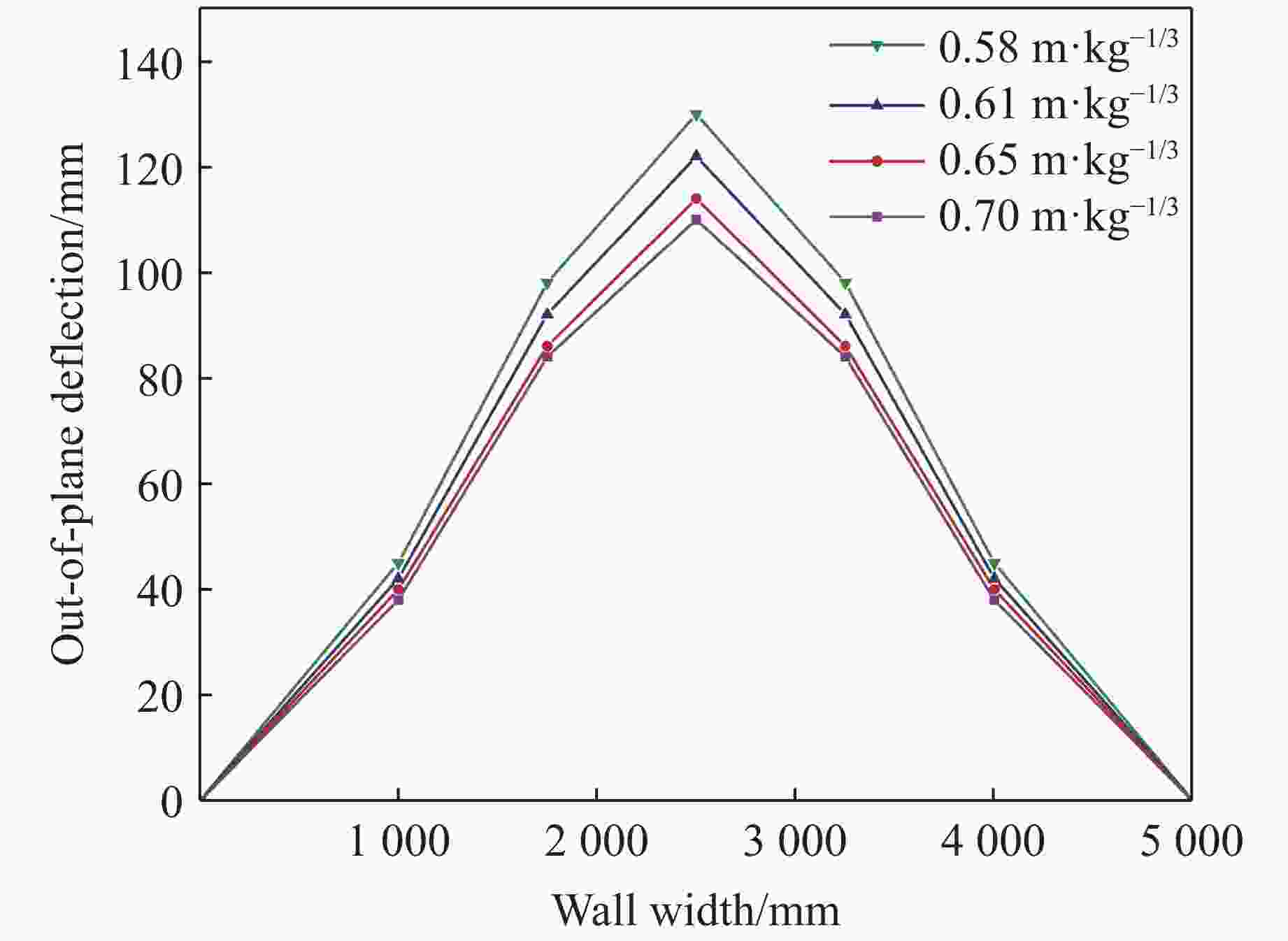
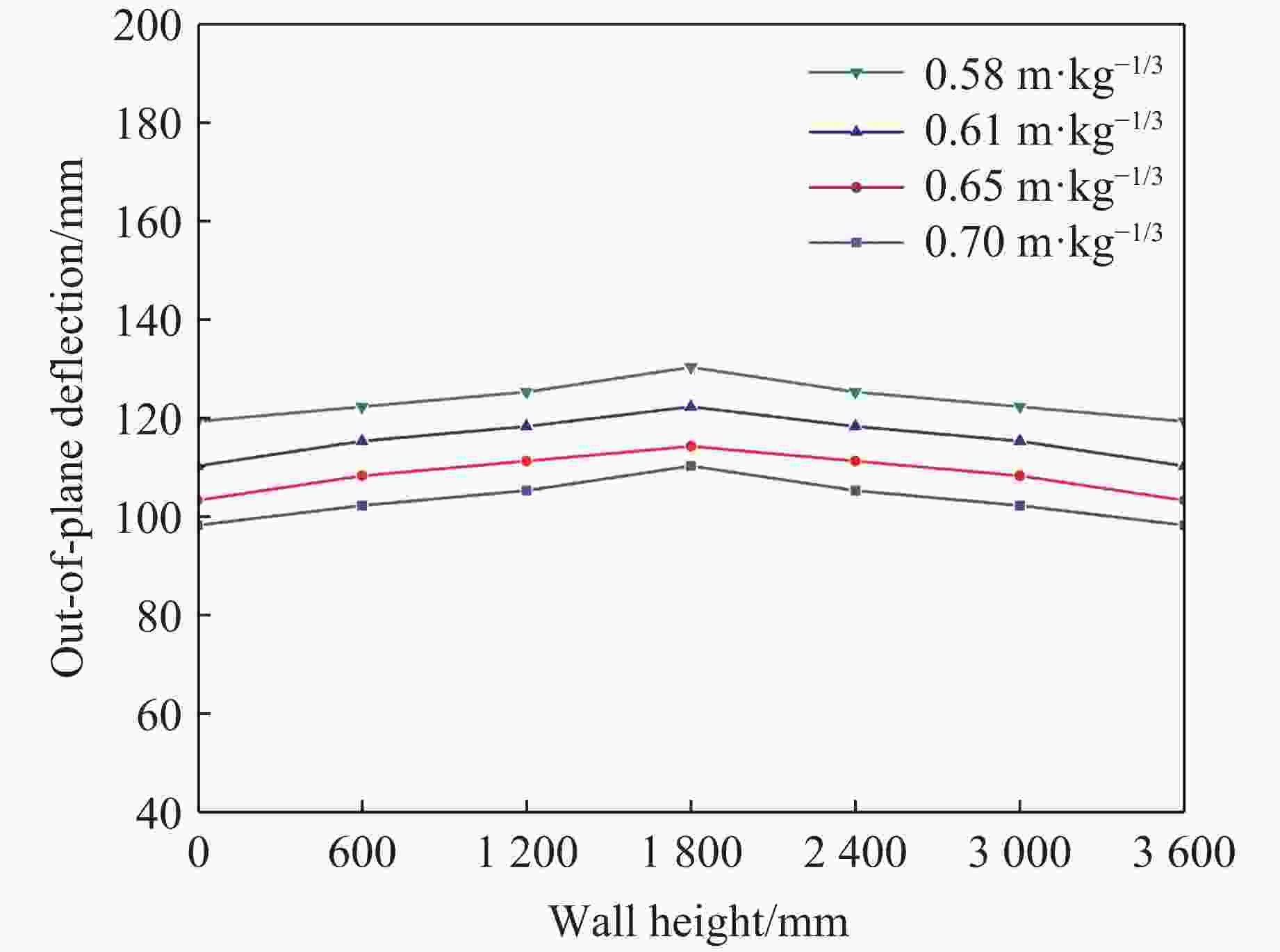
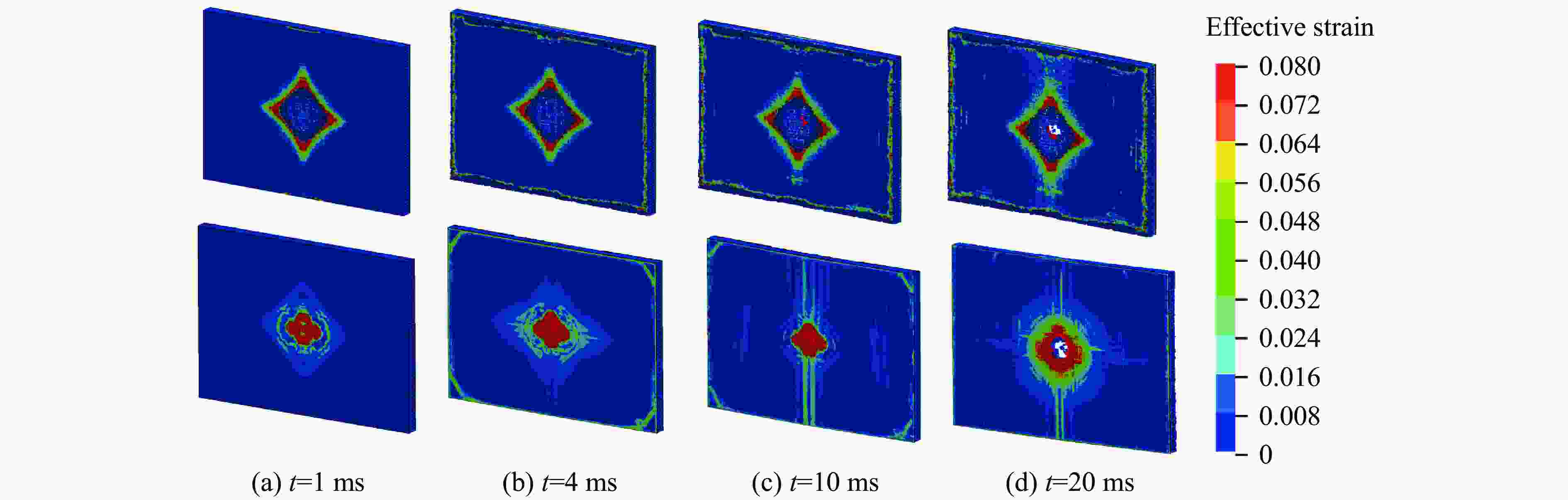
Case Blast distance/m TNT mass/kg Scaled distance/(m·kg−1/3) Back polyurea thickness/mm Damage mode JF-1 1.0 10 0.4642 5 Ⅰ JF-2 1.0 12 0.4368 5 Ⅰ JF-3 1.0 14 0.4149 5 Ⅱ JF-4 1.0 16 0.3969 5 Ⅱ JF-5 1.0 18 0.3816 5 Ⅲ JF-6 1.0 20 0.3684 5 Ⅲ 表 9 工况设置及数值模拟结果
Table 9. Test conditions and simulation results
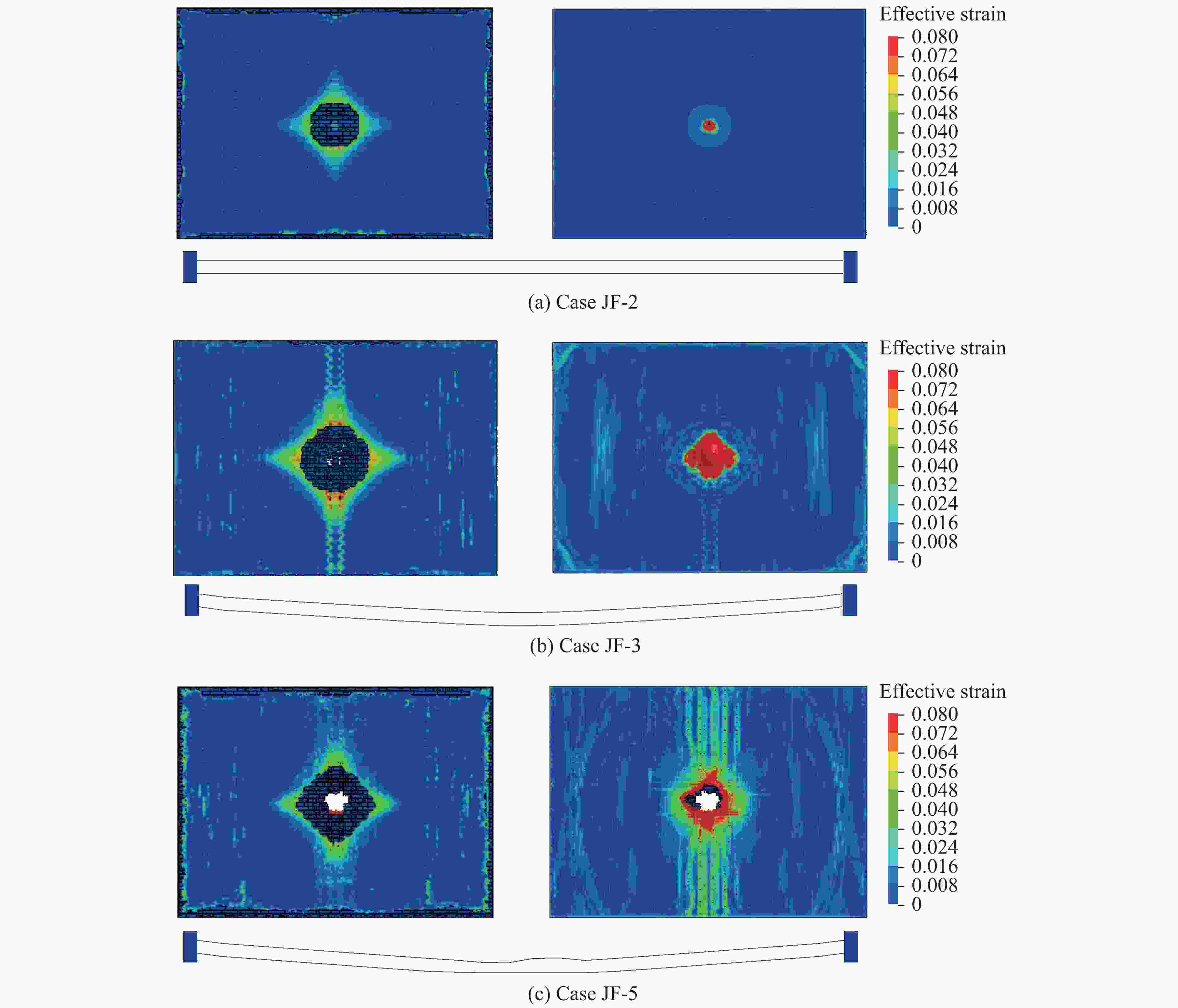
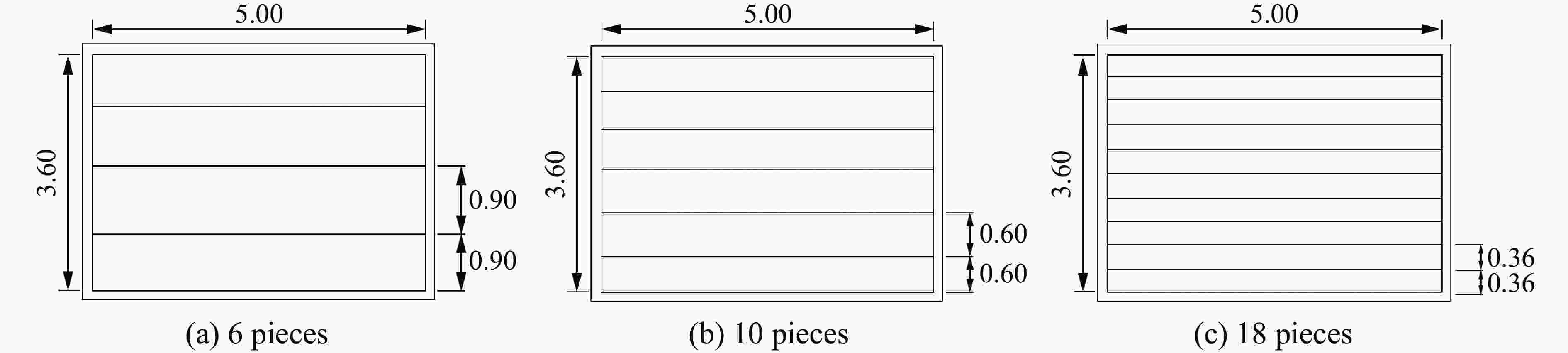
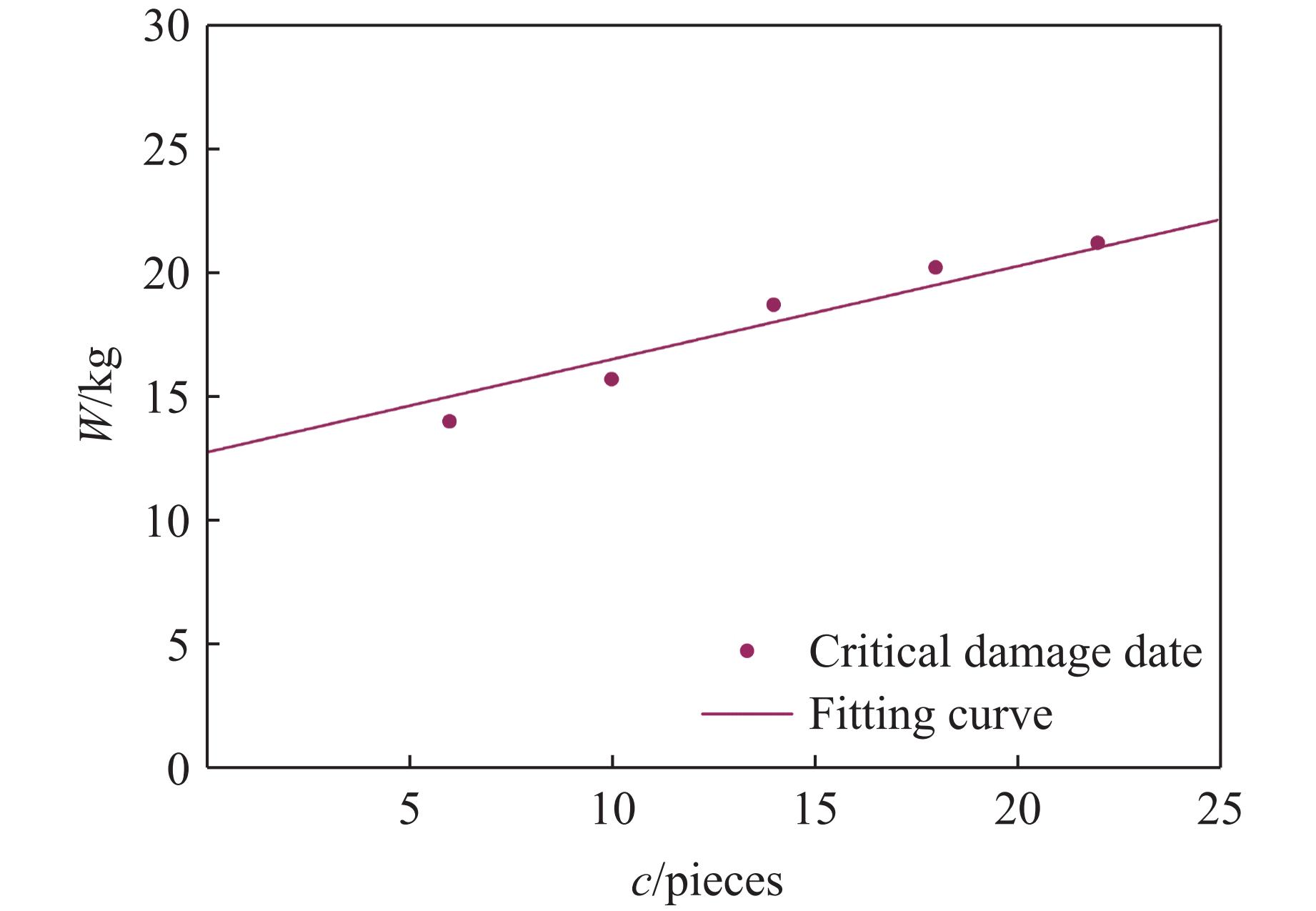
Case Blast distance/m TNT mass/kg Rebar/pieces Back polyurea thickness/mm Damage mode 1 1.0 14.0 6 5 Ⅱ 2 1.0 15.0 6 5 Ⅲ 3 1.0 15.5 10 5 Ⅱ 4 1.0 16.5 10 5 Ⅲ 5 1.0 18.0 10 5 Ⅲ 6 1.0 17.0 14 5 Ⅱ 7 1.0 18.0 14 5 Ⅲ 8 1.0 18.5 18 5 Ⅱ 9 1.0 19.0 18 5 Ⅱ 10 1.0 19.5 18 5 Ⅲ 11 1.0 20.0 22 5 Ⅱ 12 1.0 21.0 22 5 Ⅲ -
[1] 李利莎, 杜建国, 张洪海, 等. 爆炸冲击震动对砖墙破坏作用的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(4): 459–466. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)04-0459-08LI L S, DU J G, ZHANG H H, et al. Numerical simulation of damage of brick wall subjected to blast shock vibration [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(4): 459–466. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)04-0459-08 [2] 曾繁, 肖桂仲, 冯晓伟, 等. 砌体结构长脉宽爆炸荷载损伤等级评估方法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(10): 127–137. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0399ZENG F, XIAO G Z, FENG X W, et al. A damage assessment method for masonry structures subjected to long duration blast loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(10): 127–137. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0399 [3] WANG W, WEI G S, WANG X, et al. Structural damage assessment of RC slab strengthened with POZD coated steel plate under contact explosion [J]. Structures, 2023, 48: 31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.12.090 [4] WANG W, YANG G R, YANG J C, et al. Experimental and numerical research on reinforced concrete slabs strengthened with POZD coated corrugated steel under contact explosive load [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 166: 104256. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104256 [5] CHEN D, WU H, FANG Q, et al. A nonlinear visco-hyperelastic model for spray polyurea and applications [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 167: 104265. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104265 [6] CHEN D, WU H, WEI J S, et al. Nonlinear visco-hyperelastic tensile constitutive model of spray polyurea within wide strain-rate range [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 163: 104184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104184 [7] WANG J G, REN H Q, WU X Y, et al. Blast response of polymer-retrofitted masonry unit walls [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2017, 128: 174–181. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.02.044 [8] ZHU H J, WANG X, WANG Y T, et al. Damage behavior and assessment of polyurea sprayed reinforced clay brick masonry walls subjected to close-in blast loads [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 167: 104283. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104283 [9] ZHU H J, LUO X N, JI C, et al. Strengthening of clay brick masonry wall with spraying polyurea for repeated blast resistance [J]. Structures, 2023, 53: 1069–1091. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2023.05.004 [10] ZHANG Y, HU J H, ZHAO W D, et al. Numerical simulation of the blast resistance of SPUA retrofitted CMU masonry walls [J]. Buildings, 2023, 13(2): 446. doi: 10.3390/buildings13020446 [11] SANTOS A P, CHIQUITO M, CASTEDO R, et al. Experimental and numerical study of polyurea coating systems for blast mitigation of concrete masonry walls [J]. Engineering Structures, 2023, 284: 116006. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.116006 [12] CHEN D, WU H, FANG Q. Simplified micro-model for brick masonry walls under out-of-plane quasi-static and blast loadings [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 174: 104529. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104529 [13] Methodology manual for the single degree of freedom blast effects design spreadsheets [R]. PDC-TR 06-01, US Army Corps of Engineers, 2008. [14] Structures to resist the effects of accidental explosions [R]. UFC 3-340-02, Washington DC: US Department of Defence, 2008. [15] 许林峰, 陈力, 李展, 等. 聚脲加固砖填充墙抗爆性能的试验和分析方法研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(7): 126–137. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0332XU L F, CHEN L, LI Z, et al. Experimental and analytical study on blast resistance performance of brick infill walls strengthened with polyuria [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(7): 126–137. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0332 [16] YANG C Z, JIA X, HUANG Z X, et al. Damage of full-scale reinforced concrete beams under contact explosion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 163: 104180. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104180 [17] RAMAN S, NGO T, LU J H, et al. Experimental investigation on the tensile behavior of polyurea at high strain rates [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 50: 124–129. [18] 汪维. 钢筋混凝土构件在爆炸载荷作用下的毁伤效应及评估方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2014.WANG W. Study on damage effects and assessments method of reinforced concrete structural members under blast loading [D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014. [19] 陈力, 方秦, 还毅, 等. 爆炸荷载作用下钢筋混凝土梁板结构的面力效应 [J]. 工程力学, 2010, 27(8): 156–163.CHEN L, FANG Q, HUAN Y, et al. Membrane action on reinforced concrete beam-slab structures subjected to blast loads [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2010, 27(8): 156–163. [20] WU G, JI C, WANG X, et al. Blast response of clay brick masonry unit walls unreinforced and reinforced with polyurea elastomer [J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(4): 643–662. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.03.004 -






 下载:
下载: