Applications of High-Pressure Solution Device for Synchrotron Radiation Small Angle X-Ray Scattering Method
-
摘要: 高压作为一种重要的热力学变量,可用于引发软物质系统中的各种结构变化。小角X射线散射具有高空间分辨能力,可用于蛋白质折叠动力学、核酸结构稳定机制研究,在生命科学领域具有广阔的应用前景。然而,目前国内尚缺少用于高压溶液散射的专用装置,为此,在上海光源BL19U2线站设计开发了一种专用于溶液X射线散射的高压原位样品装置和手动加压系统,实现了在0.1~250 MPa范围内静水压测量。该装置可实现X射线窗口在整个测量过程中保留在原位,有助于准确扣除背景散射,实现高信噪比测量,为食品科学、药理学、结构生物学等研究领域提供重要的研究平台。Abstract: High pressure is one of the fundamental thermodynamic parameters, which can induce the structural changes in soft matter systems. By combining the spatial resolution of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), this technique can be employed to explore the dynamics of protein folding and the mechanisms of nucleic acid structural stability. Moreover, it has promising and broad applications in the field of life sciences. Currently, the specialized equipment for high-pressure solution scattering is still lacking in China. For this purpose, a high-pressure in-situ sample device and a manual pressurization system for specialized solution X-ray scattering have been developed at BL19U2 beamline at SSRF, which can complete the hydrostatic pressure measurements from 0.1 to 250 MPa. More important, the apparatus can keep the X-ray window in the same place throughout the experiment, which can help to subtract the accurate background scattering and achieve the measurements with high signal-to-noise ratio. This will provide a valuable research platform for wide range of areas, including food science, pharmacology, and structural biology.
-
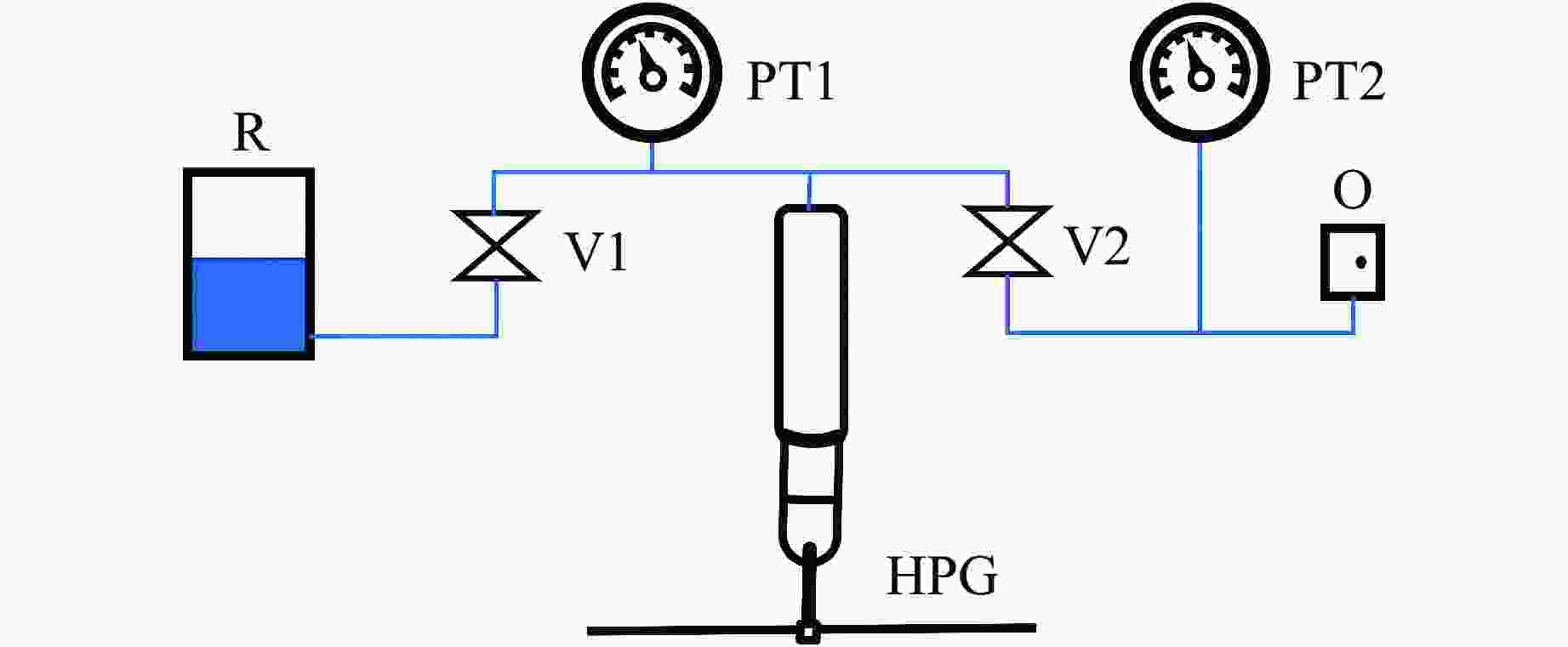
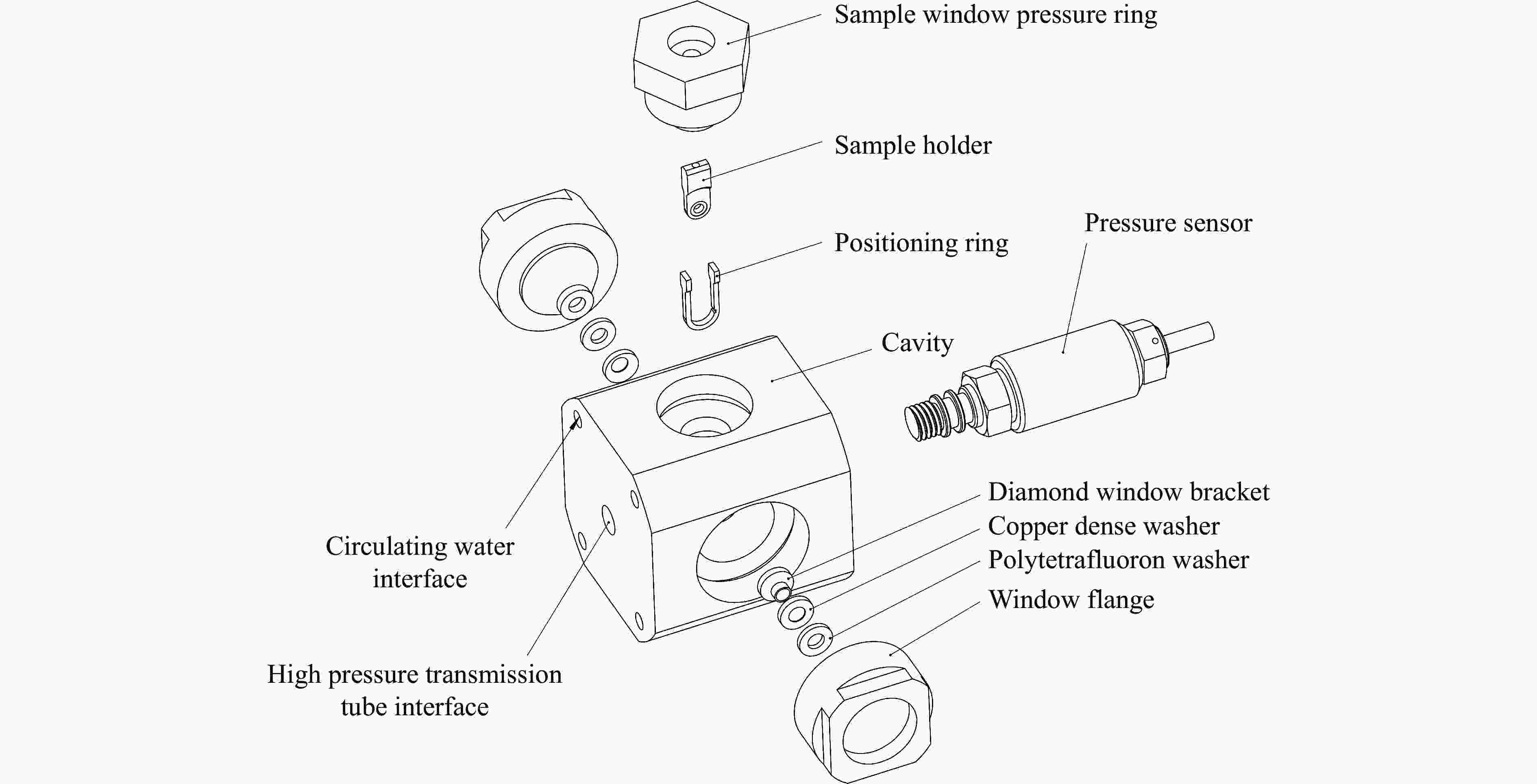
图 3 加压装置结构示意图(HPG为手动加压泵,V1和V2为高压针阀,PT1和PT2为压力表,R为传压介质存储罐,O为压力出口)
Figure 3. Structural diagram of the pressurized device(HPG is the manual pressure pump; V1 and V2 are the high pressure needle valves; PT1 and PT2 are the pressure gauges; R is the pressure transmission medium storage tank; O is the pressure outlet.)
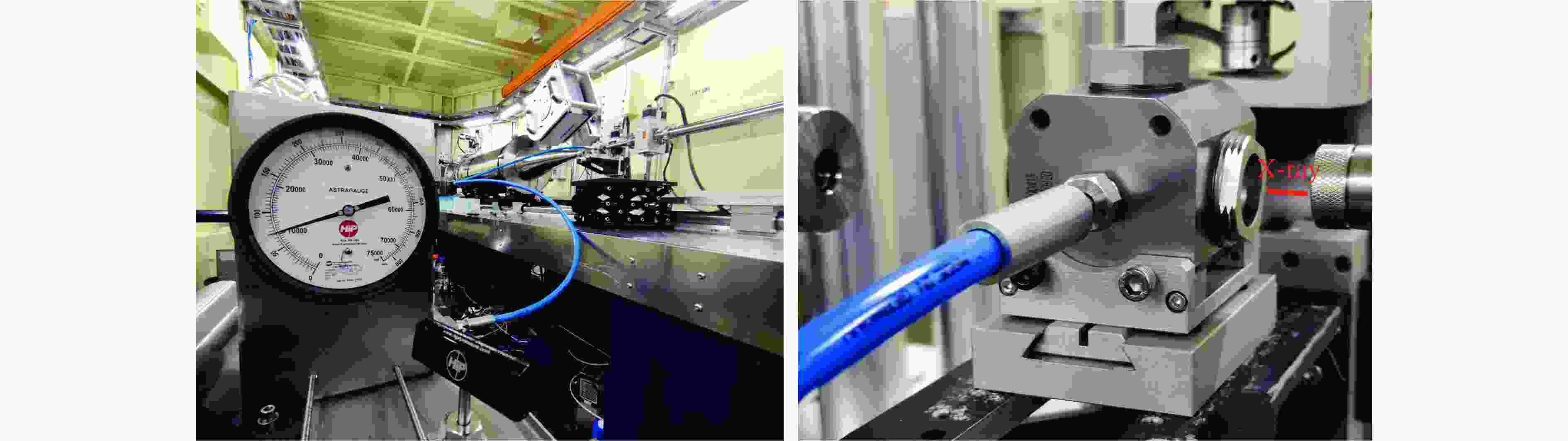
图 4 高压散射实验现场照片(加压泵站与压腔通过高压管线(蓝色)连接,压腔通过专用的底座安装于位移平台)
Figure 4. Photos of high pressure scattering experiment (The pump station is connected with the pressure chamber through the high pressure pipeline (blue), and the pressure chamber is installed on the displacement platform through a special base.)
-
[1] SILVA J L, OLIVEIRA A C, VIEIRA T C R G, et al. High-pressure chemical biology and biotechnology [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(14): 7239–7267. doi: 10.1021/cr400204z [2] SCHROER M A, PAULUS M, JEWORREK C, et al. High-pressure SAXS study of folded and unfolded ensembles of proteins [J]. Biophysical Journal, 2010, 99(10): 3430–3437. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.09.046 [3] BROOKS N J, SEDDON J M. High pressure X-ray studies of lipid membranes and lipid phase transitions [J]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 2014, 228(10/11/12): 987–1004. doi: 10.1515/zpch-2014-0602 [4] KRZYŻANIAK A, BARCISZEWSKI J, FÜRSTE J P, et al. A-Z-RNA conformational-changes effected by high-pressure [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 1994, 16(3): 159–162. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(94)90044-2 [5] OTAKE T, TANIGUCHI T, FURUKAWA Y, et al. Stability of amino acids and their oligomerization under high-pressure conditions: implications for prebiotic chemistry [J]. Astrobiology, 2011, 11(8): 799–813. doi: 10.1089/ast.2011.0637 [6] BLANCHET C E, SVERGUN D I. Small-angle X-ray scattering on biological macromolecules and nanocomposites in solution [J]. Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, 2013, 64: 37–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-040412-110132 [7] KÖNIG N, PAULUS M, JULIUS K, et al. Antibodies under pressure: a small-angle X-ray scattering study of immunoglobulin G under high hydrostatic pressure [J]. Biophysical Chemistry, 2017, 231: 45–49. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2017.05.016 [8] SOMKUTI J, SMELLER L. High pressure effects on allergen food proteins [J]. Biophysical Chemistry, 2013, 183: 19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2013.06.009 [9] 李晓东, 袁清习, 徐伟, 等. 第四代高能同步辐射光源HEPS及高压相关线站建设 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(5): 050101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200554LI X D, YUAN Q X, XU W, et al. Introduction of fourth-generation high energy photon source HEPS and the beamlines for high-pressure research [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(5): 050101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200554 [10] 杨科, 蒋升, 闫帅, 等. 上海同步辐射光源高压相关线站概述 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(5): 050102. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200584YANG K, JIANG S, YAN S, et al. Application of Shanghai synchrotron radiation source in high pressure research [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(5): 050102. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200584 [11] KUNZ M, MACDOWELL A A, CALDWELL W A, et al. A beamline for high-pressure studies at the Advanced Light Source with a superconducting bending magnet as the source [J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2005, 12(5): 650–658. doi: 10.1107/S0909049505020959 [12] LI X D, LI H, LI P S, et al. A high-pressure single-crystal-diffraction experimental system at 4W2 beamline of BSRF [J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2017, 24(3): 699–706. doi: 10.1107/S1600577517003393 [13] ROTHKIRCH A, GATTA G D, MEYER M, et al. Single-crystal diffraction at the extreme conditions beamline P02.2: procedure for collecting and analyzing high-pressure single-crystal data [J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2013, 20(5): 711–720. doi: 10.1107/S0909049513018621 [14] HIRAO N, KAWAGUCHI S I, HIROSE K, et al. New developments in high-pressure X-ray diffraction beamline for diamond anvil cell at SPring-8 [J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5(1): 018403. doi: 10.1063/1.5126038 [15] PRESSL K, KRIECHBAUM M, STEINHART M, et al. High pressure cell for small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1997, 68(12): 4588–4592. doi: 10.1063/1.1148436 [16] ANDO N, CHENEVIER P, NOVAK M, et al. High hydrostatic pressure small-angle X-ray scattering cell for protein solution studies featuring diamond windows and disposable sample cells [J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2008, 41(1): 167–175. doi: 10.1107/S0021889807056944 [17] BROOKS N J, GAUTHE B L L E, TERRILL N J, et al. Automated high pressure cell for pressure jump X-ray diffraction [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2010, 81(6): 064103. doi: 10.1063/1.3449332 [18] CINAR S, AL-AYOUBI S, STERNEMANN C, et al. A high pressure study of calmodulin-ligand interactions using small-angle X-ray and elastic incoherent neutron scattering [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(5): 3514–3522. doi: 10.1039/C7CP07399B [19] LEHOFER B, GOLUB M, KORNMUELLER K, et al. Structural effects of high hydrostatic pressure on human low density lipoprotein revealed by small angle X-ray and neutron scattering [J]. Biophysical Journal, 2016, 110(3): 255a–256a. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.11.1403 [20] ABE H, HAMAYA N, KOYAMA Y, et al. Long periodic structure of a room-temperature ionic liquid by high-pressure small-angle X-ray scattering and wide-angle X-ray scattering: 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [J]. ChemPhysChem, 2018, 19(12): 1441–1447. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201701273 [21] LI Y W, LIU G F, WU H J, et al. BL19U2: small-angle X-ray scattering beamline for biological macromolecules in solution at SSRF [J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2020, 31(12): 117. doi: 10.1007/s41365-020-00825-3 [22] ORTORE M G, SPINOZZI F, MARIANI P, et al. Combining structure and dynamics: non-denaturing high-pressure effect on lysozyme in solution [J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2009, 6(Suppl 5): S619–S634. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0163.focus [23] SONG X T, ZHENG Y X, ZHU L, et al. Development of robust and facile purification process for production of recombinant human ferritin heavy chain nanoparticle from Escherichia coli [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2021, 104: 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2021.02.014 [24] WANG Q, ZHANG C, LIU L P, et al. High hydrostatic pressure encapsulation of doxorubicin in ferritin nanocages with enhanced efficiency [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 254: 34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.05.025 -






 下载:
下载: