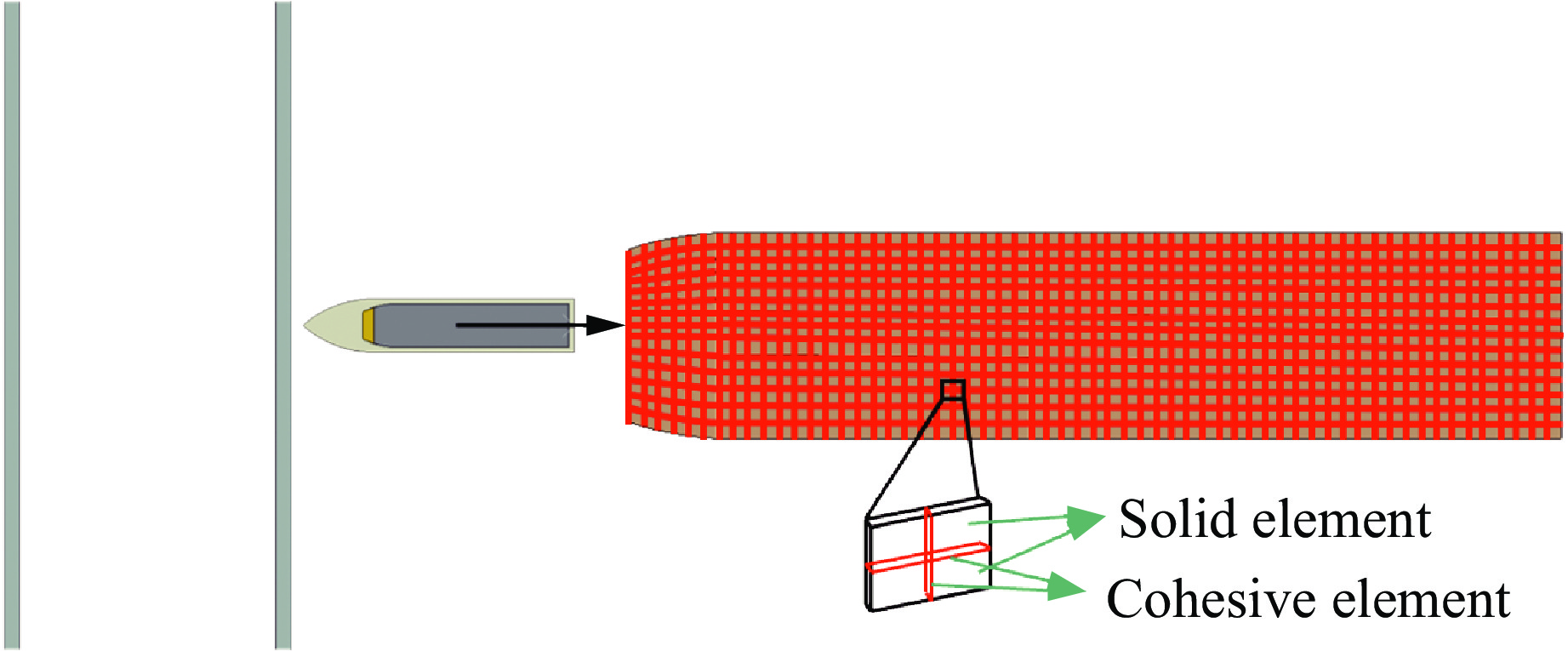
Numerical Simulation Study on Macro-Microscopic Damage of PBX Charge during Penetration of Double-Layer Targets
-
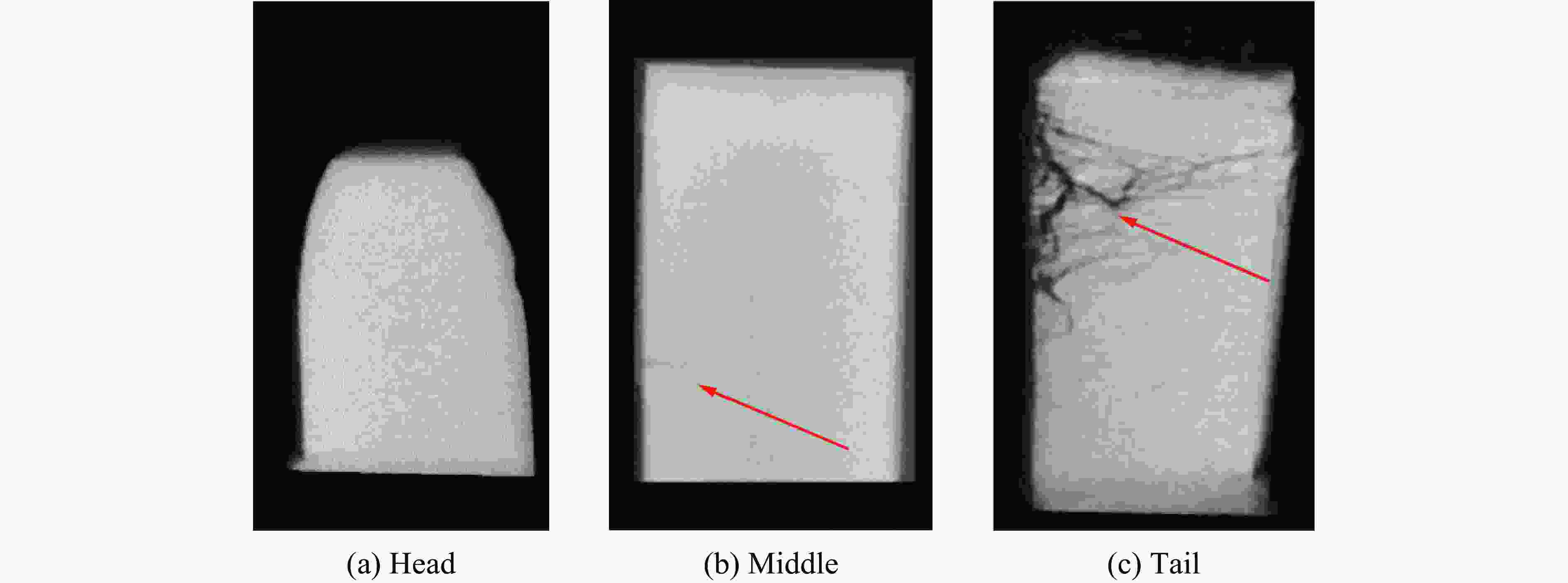
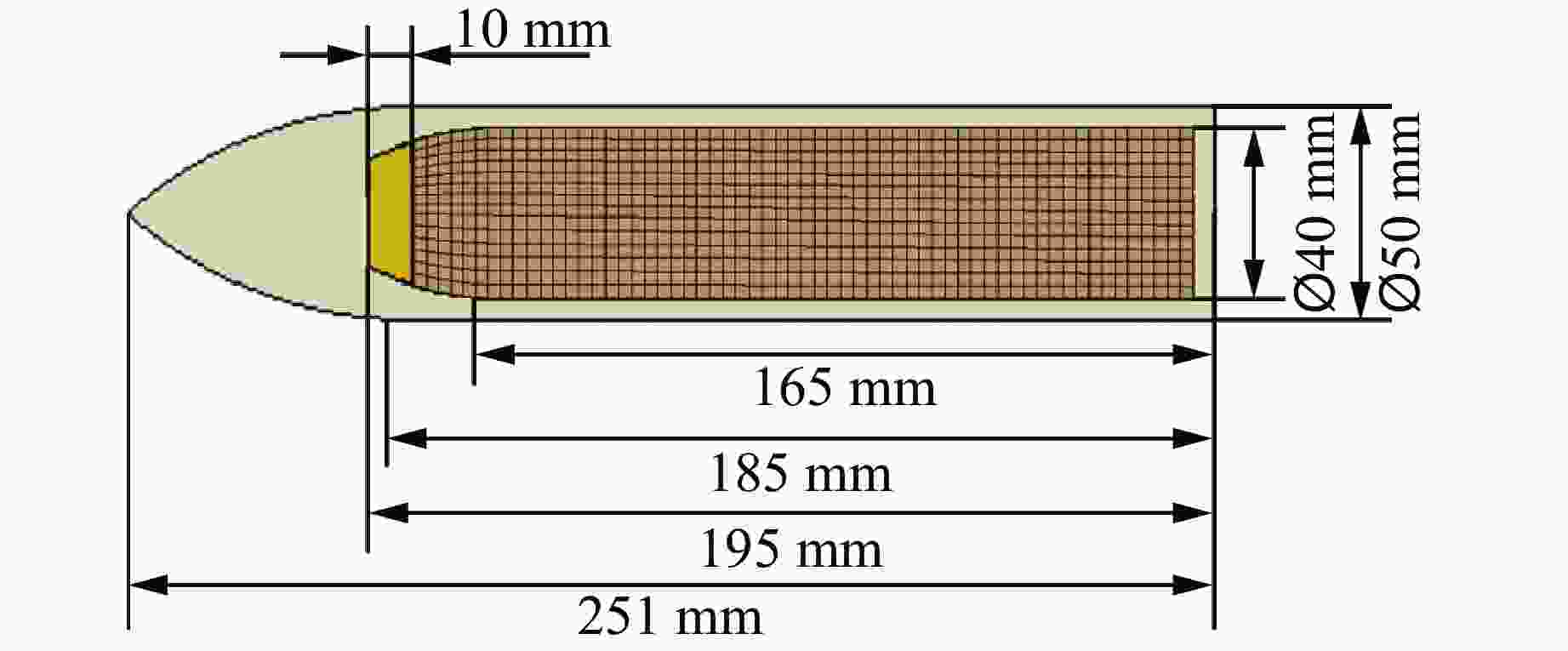
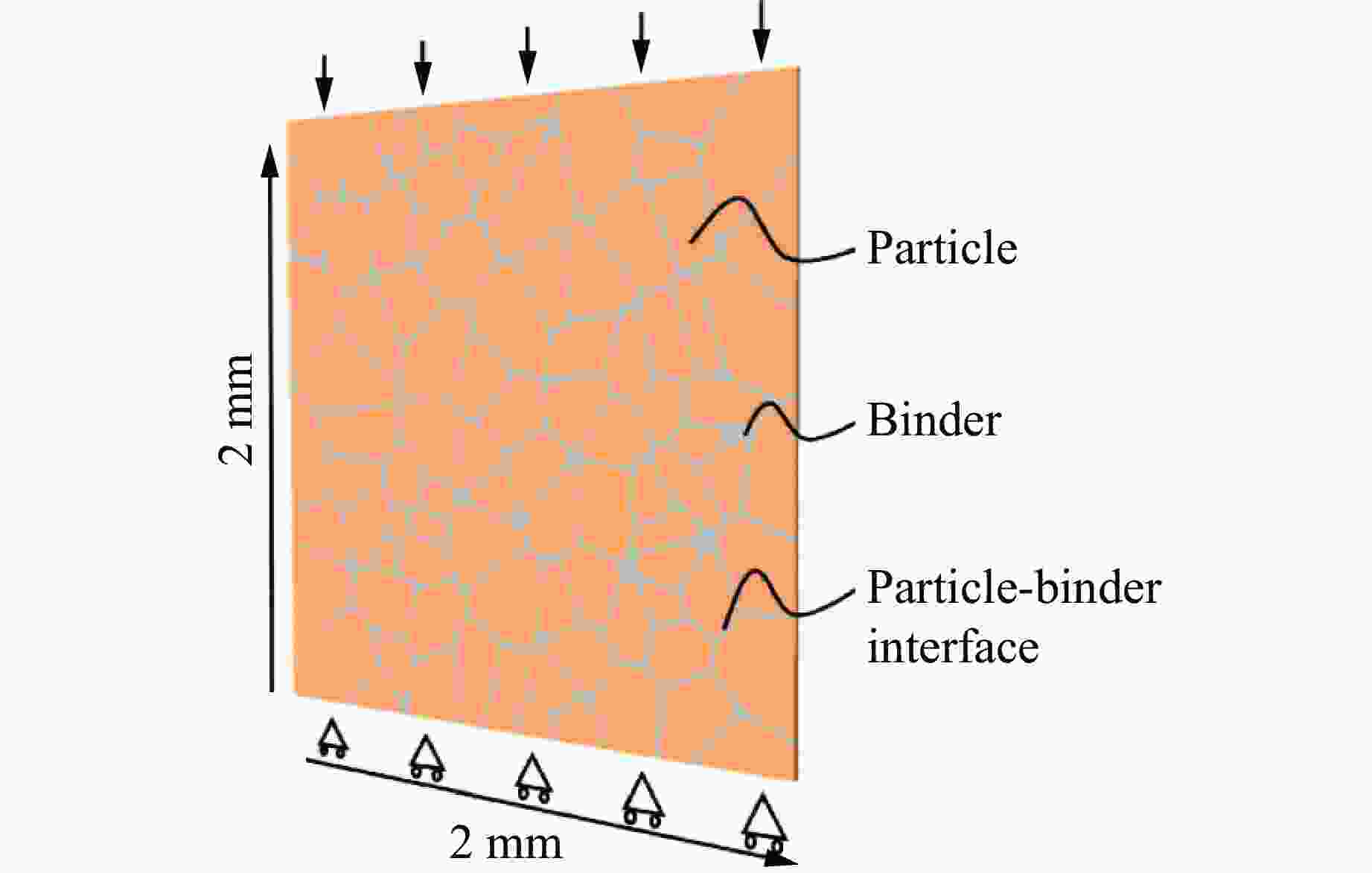
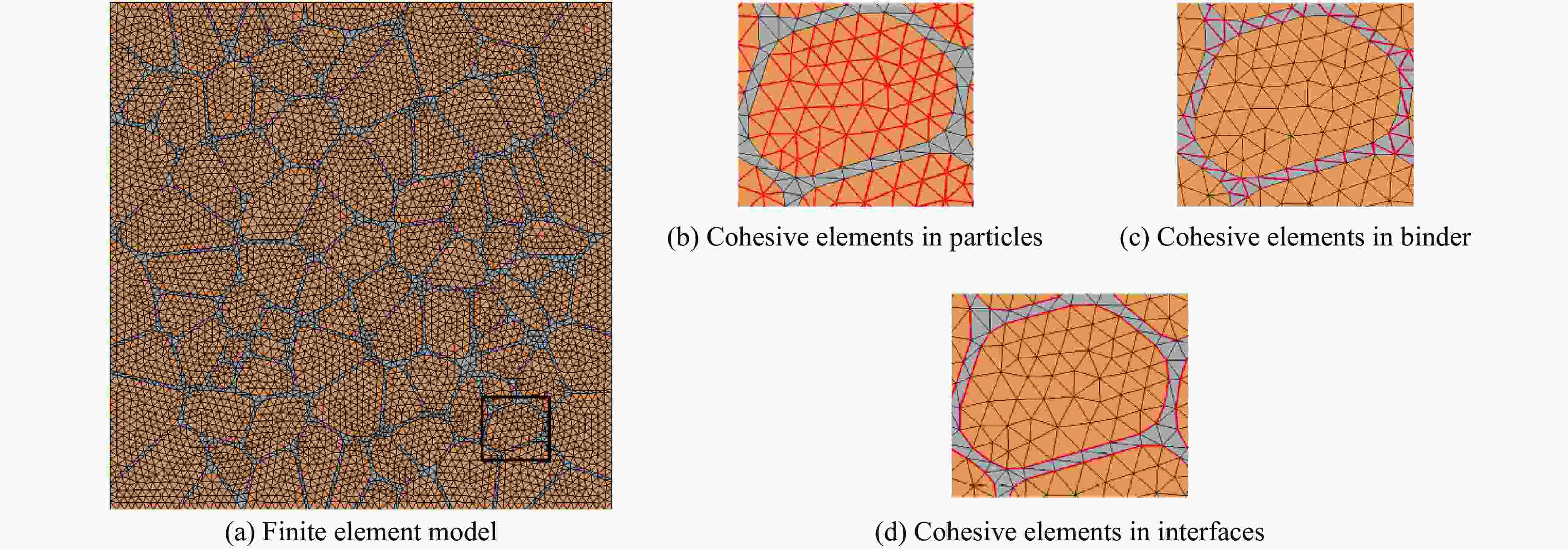
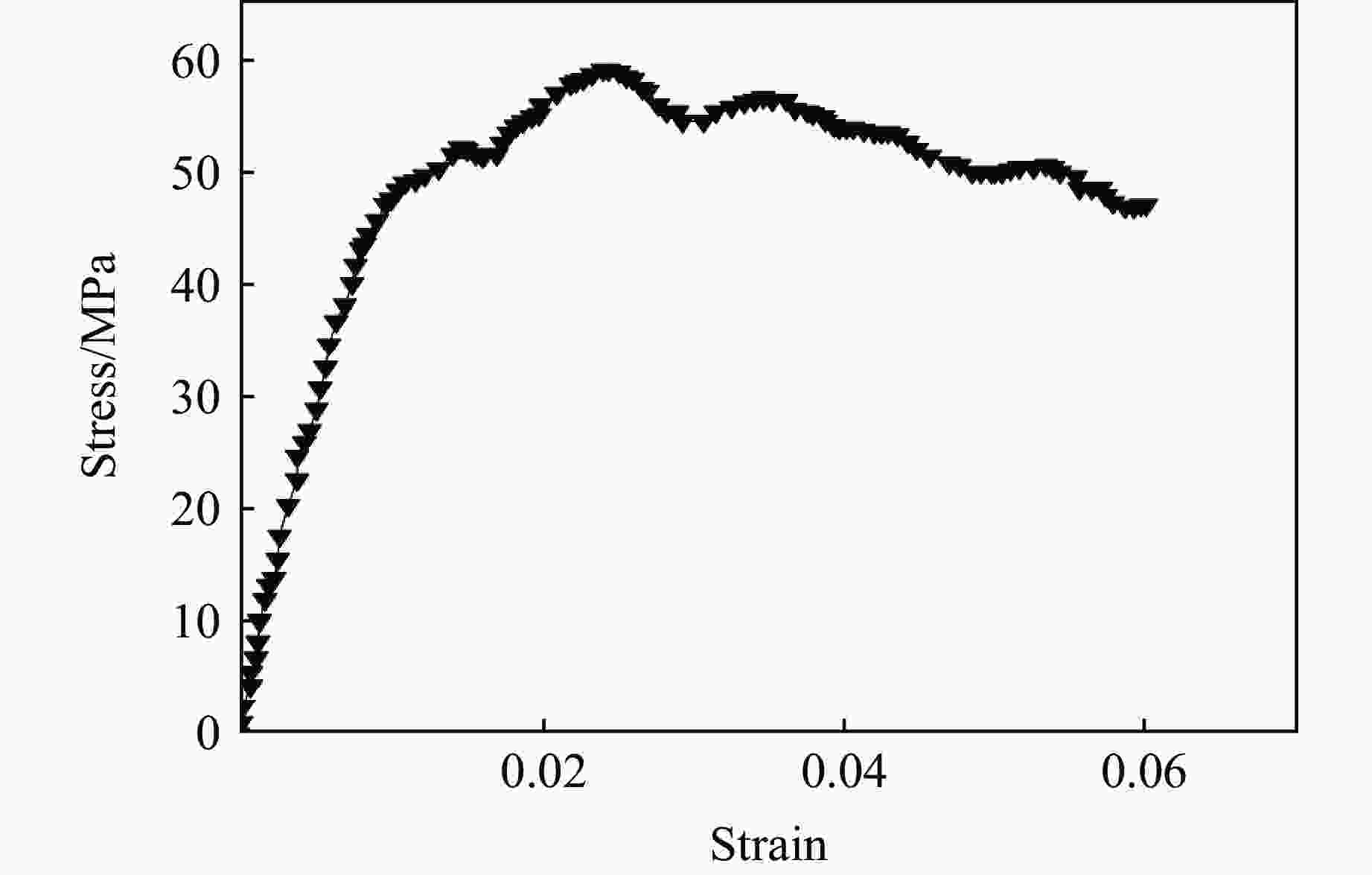
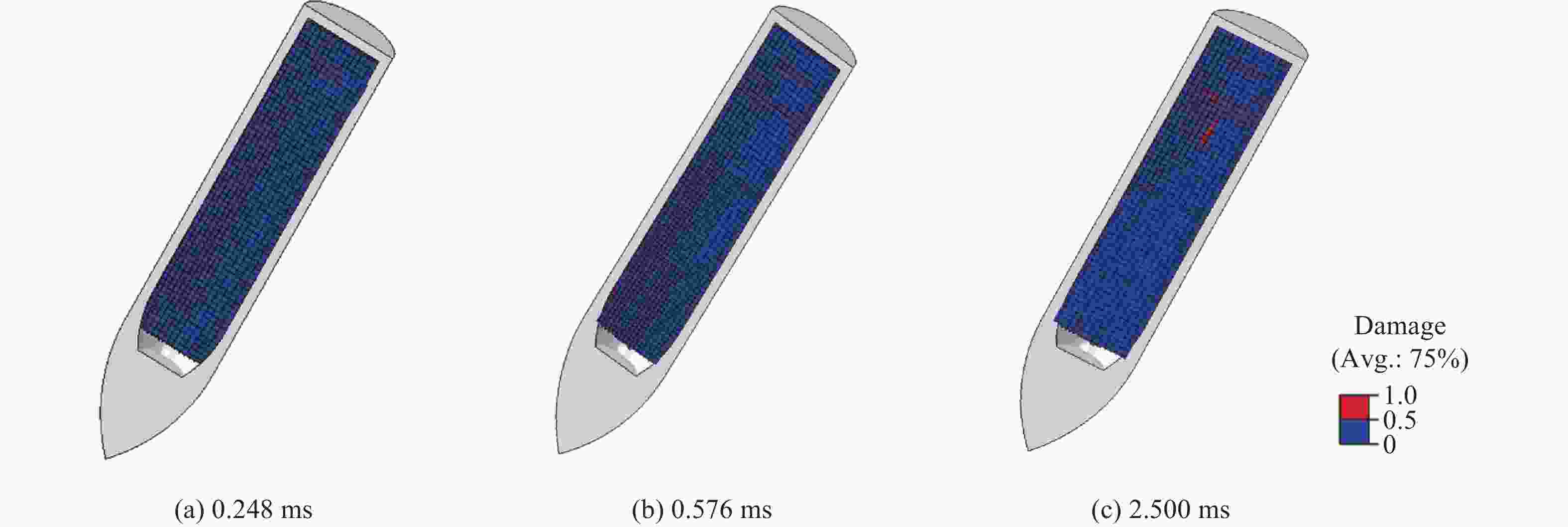
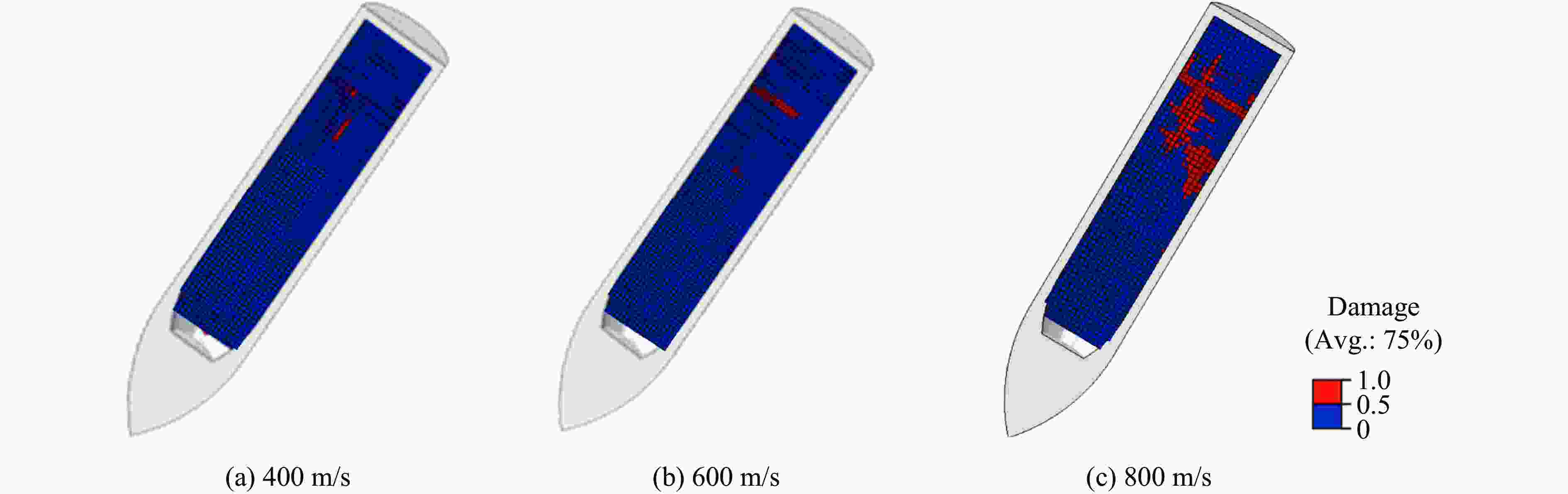
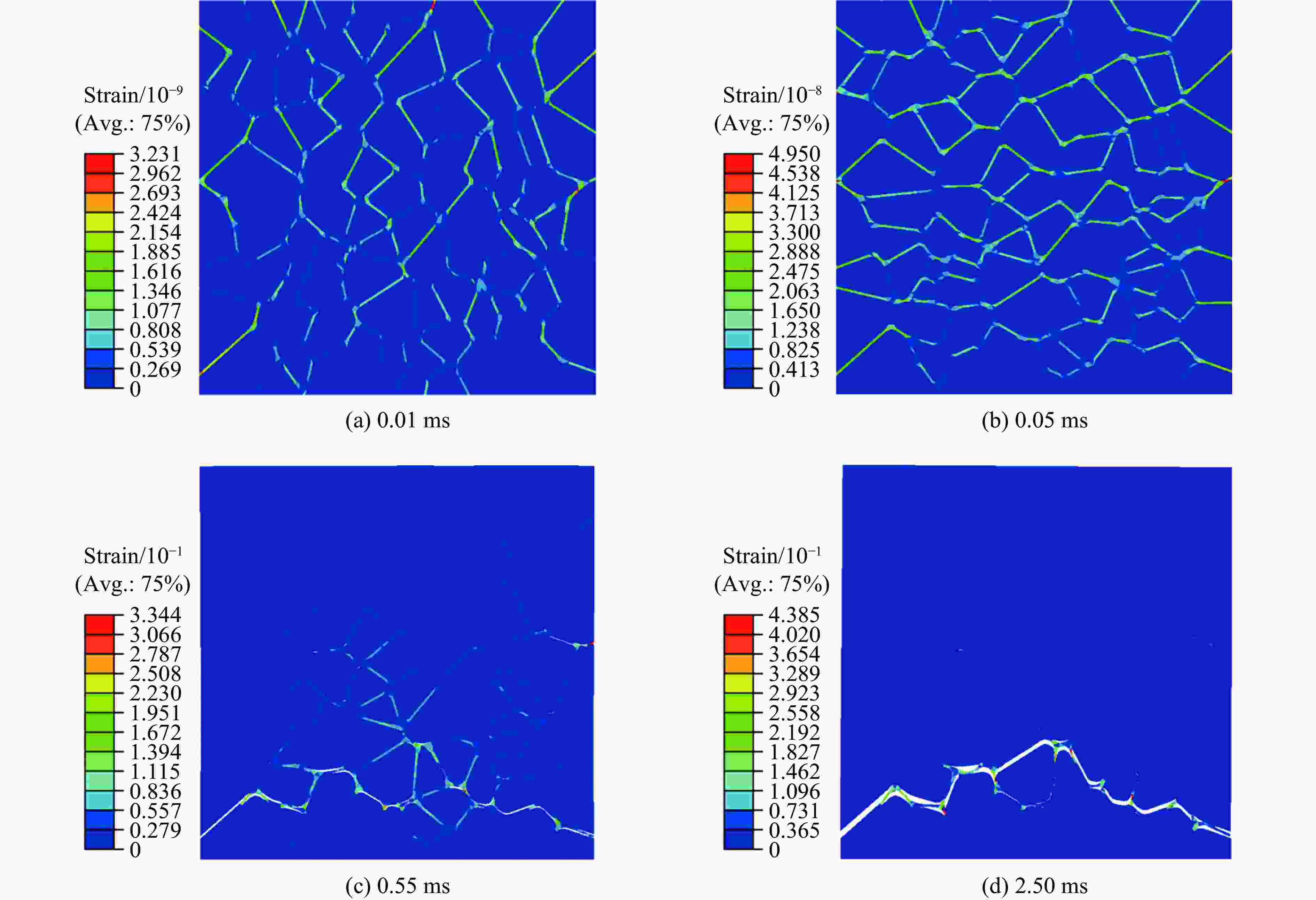
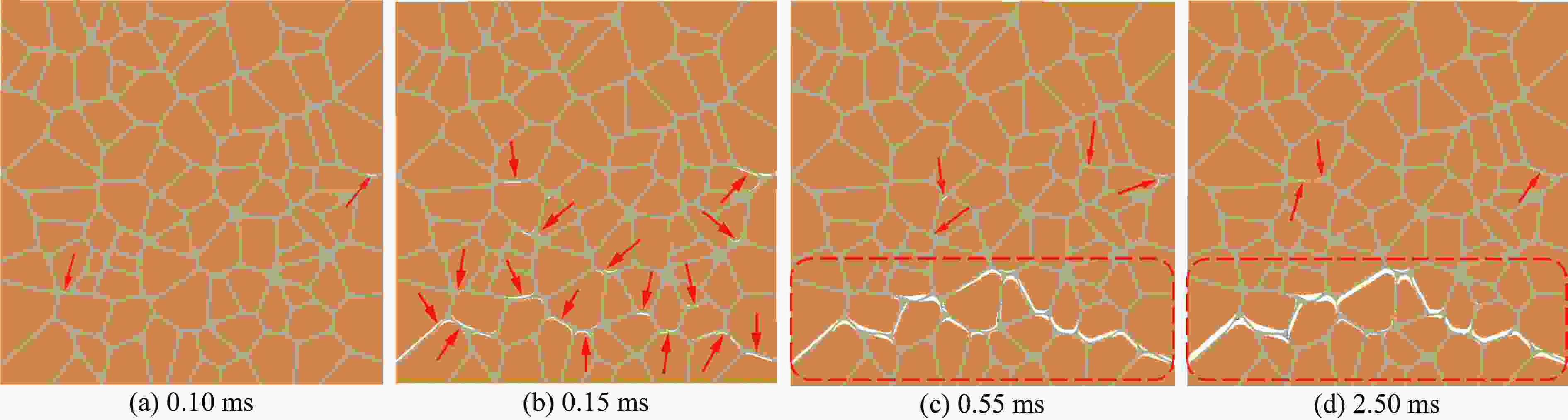
摘要: 针对高速战斗部侵彻双层目标时装药的损伤问题,基于内聚力模型开展了PBX装药战斗部侵彻双层靶板的数值模拟研究。采用内聚力模型计算装药损伤的出现与演化,分析了侵彻速度与损伤发生的关系,通过损伤比对侵彻结束后PBX装药的损伤进行了量化,建立了PBX装药细观损伤仿真模型,研究了侵彻双层靶板过程中PBX装药细观损伤机制。结果表明:当弹体垂直侵彻双层靶板时,在压-拉反复作用下,装药尾部形成了垂直于加载方向的贯穿裂纹,且装药的损伤程度随着侵彻速度的增大而增大;在侵彻双层靶板过程中,PBX装药的主要损伤模式是界面脱粘,微裂纹最先出现在颗粒边角处,并且逐渐增多,最终界面微裂纹失稳扩展并汇聚为连续的主裂纹。Abstract: To study the charge damage evolution process when a high-velocity warhead penetrated a double-layer target, a numerical simulation study was conducted using a cohesive zone model to investigate the penetration of double-layer target. The cohesive zone model was utilized to calculate the occurrence and evolution of PBX damage, as well as to analyze the relationship between the penetration velocity and damage evolution. The quantification of damage was conducted by means of the damage ratio. Furthermore, a micro-damage finite element model for PBX was established to examine the microscopic damage mechanisms during penetration into a double-layer target. The results show that when the projectile penetrates the target plate vertically, the extent of damage of the charge increases with the increase of penetration velocity. From a microscopic perspective, it was observed that cyclic tensile and compressive loads induced the formation of vertical cracks perpendicular to the loading direction. The primary mechanism of damage in PBX charge penetration into double-layer target is interface debonding. Additionally, the microcracks destabilize, propagate, and converge into a continuous main crack.
-
表 1 弹壳、靶板和缓冲层的材料参数
Table 1. Parameters of projectile shell, target, and buffer layer
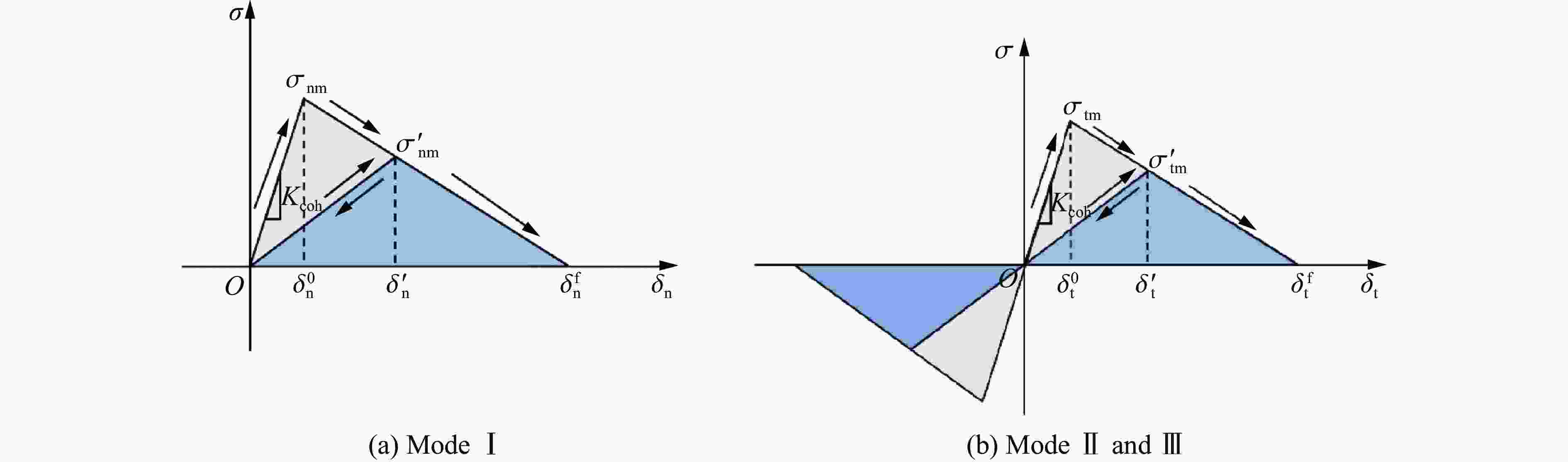
Material $ \rho $/(kg·m−3) μ E/GPa A/MPa B/MPa n C m $ {\dot \varepsilon _0} $/s−1 35CrMnSi steel 7830 0.30 204 1440 1501 0.4403 0.039 0.404 10−3 45 steel 7830 0.33 210 496 434 0.2600 0.014 1.030 1.0 Polycarbonate 1190 0.38 3.6 84 3228 3.1456 0.089 1.010 0.1 表 2 PBX装药的内聚力单元参数
Table 2. Cohesive elements parameters of PBX charge
Kcoh/(GPa·m−1) $ \sigma $/MPa G/(kN·m−1) 1700 23 0.17 表 3 PBX装药颗粒、黏结剂和界面内聚力单元参数
Table 3. Cohesive elements parameters of particle, binder and interface
Cohesive element Kcoh/(GPa·m−1) $ \sigma $/MPa G/(kN·m−1) Particle 1800 6.00 0.010 Binder 900 7.50 0.150 Particle-binder interface 800 2.75 0.012 -
[1] 李媛媛, 高立龙, 李巍, 等. 抗过载炸药装药侵彻安全性试验研究 [J]. 含能材料, 2010, 18(6): 702–705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2010.06.021LI Y Y, GAO L L, LI W, et al. Experiment research on security of insensitive explosive charge during penetration [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2010, 18(6): 702–705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2010.06.021 [2] 陈文, 张庆明, 胡晓东, 等. 侵彻过程冲击载荷对装药损伤实验研究 [J]. 含能材料, 2009, 17(3): 321–325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2009.03.017CHEN W, ZHANG Q M, HU X D, et al. Experimental study on damage to explosive charge by impact load in the process of penetration [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2009, 17(3): 321–325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2009.03.017 [3] LI X, LIU Y Z, SUN Y. Dynamic mechanical damage and non-shock initiation of a new polymer bonded explosive during penetration [J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(6): 1342. doi: 10.3390/polym12061342 [4] 李晓. 侵彻过程中PBX装药的损伤与点火机制研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.LI X. Investigations on damage and initiation mechanism of PBX charge during penetration [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. [5] 赵生伟, 初哲, 李明. 抗侵彻过载战斗部装药安定性实验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2010, 31(Suppl 1): 284–287.ZHAO S W, CHU Z, LI M. Experiment investigation on stability of explosive in anti-overload warhead [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2010, 31(Suppl 1): 284–287. [6] 成丽蓉, 汪德武, 贺元吉. 侵彻单层和多层靶时战斗部装药损伤及热点生成机理研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(1): 32–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.01.004CHENG L R, WANG D W, HE Y J. Research on the damage and hot-spot generation in explosive charges during penetration into single- or multi-layer target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(1): 32–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.01.004 [7] 毕超, 郭翔, 屈可朋, 等. 斜侵彻靶板过程中装药损伤的数值模拟 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2022, 45(3): 383–387. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202201009BI C, GUO X, QU K P, et al. Numerical simulation of charge damage during oblique penetration [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2022, 45(3): 383–387. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202201009 [8] 崔云霄. 冲击载荷作用下PBX炸药的损伤破坏研究 [D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2017.CUI Y X. Research on damage and destruction of PBX explosive under impact load [D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2017. [9] 石啸海, 戴开达, 陈鹏万, 等. 战斗部侵彻过程中PBX装药动态损伤数值模拟 [J]. 中国测试, 2016, 42(10): 138–142. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2016.10.026SHI X H, DAI K D, CHEN P W, et al. Numerical simulation of dynamic damage of PBX charge during the warhead penetration process [J]. China Measurement & Test, 2016, 42(10): 138–142. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2016.10.026 [10] 石啸海, 余春祥, 戴开达, 等. 侵彻过程中弹头形状对PBX炸药损伤的影响 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2019, 39(3): 81–85, 89. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2019.03.019SHI X H, YU C X, DAI K D, et al. The influence of nose shape to dynamic damage of PBX charge during the penetration process [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2019, 39(3): 81–85, 89. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2019.03.019 [11] 张学伦, 汪衡, 谭正军, 等. 混凝土靶边界效应与弹丸长径比关联性的研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2018, 39(4): 11–13, 18. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.04.003ZHANG X L, WANG H, TAN Z J, et al. Relevance between aspect ratio of projectile and boundary effect of concrete target [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2018, 39(4): 11–13, 18. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.04.003 [12] 孙宝平, 段卓平, 万经伦, 等. 基于Visco-SCRAM模型的侵彻装药点火研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(5): 689–695. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)05-0689-07SUN B P, DUAN Z P, WAN J L, et al. Investigation on ignition of an explosive charge in a projectile during penetration based on Visco-SCRAM model [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(5): 689–695. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)05-0689-07 [13] 李硕. 强冲击载荷下35CrMnSi动态力学行为与断裂机理研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2015.LI S. Study on dynamic mechanical behavior and fracture mechanism of 35CrMnSi under impact loads [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2015. [14] 赵丽俊, 郝永平, 黄晓杰, 等. 杆式射流侵彻45钢靶数值分析及试验研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2023, 44(8): 147–153. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.08.021ZHAO L J, HAO Y P, HUANG X J, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental research on jetting projectile charge penetrating 45 steel target [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2023, 44(8): 147–153. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.08.021 [15] 于鹏. 航空聚碳酸酯动态力学性能及本构关系研究 [D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014.YU P. Investigation on the dynamic characteristics and constitutive model of polycarbonate of aircraft [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014. [16] XIAO Y C, ZHANG Q, FAN C Y, et al. Numerical analysis of the damage and failure behavior of polymer-bonded explosives using discrete element method [J]. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2024, 11(2): 579–598. doi: 10.1007/s40571-023-00640-8 [17] XIAO Y C, ZHANG Q, GONG T Y, et al. Experimental analysis and multi-scale simulation of the fracture behavior of polymer-bonded explosives based on the dynamic notched semi-circular bend method [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2024, 291: 112690. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2024.112690 [18] BI C, GUO X, WANG A H, et al. Strain-rate-dependent cohesive zone modelling of charge damage behavior when a projectile penetrates multilayered targets [J]. Acta Mechanica, 2023, 234(7): 2869–2887. doi: 10.1007/s00707-023-03541-2 [19] XIAO Y C, GONG T Y, ZHANG X W, et al. Multiscale modeling for dynamic compressive behavior of polymer bonded explosives [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2023, 242: 108007. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.108007 [20] YANG Z, KANG G, LIU R, et al. Predicting the mechanical behaviour of highly particle-filled polymer composites using the nonlinear finite element method [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 286: 115275. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115275 [21] BARUA A, KIM S, HORIE Y, et al. Prediction of probabilistic ignition behavior of polymer-bonded explosives from microstructural stochasticity [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(18): 184907. doi: 10.1063/1.4804251 [22] HARDIN D B, ZHOU M. Effect of viscoplasticity on ignition sensitivity of an HMX based PBX [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1793(1): 080005. doi: 10.1063/1.4971611 [23] CHEN X, DENG X M, SUTTON M A, et al. An inverse analysis of cohesive zone model parameter values for ductile crack growth simulations [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2014, 79: 206–215. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.12.006 [24] AIROLDI A, DÁVILA C G. Identification of material parameters for modelling delamination in the presence of fibre bridging [J]. Composite Structures, 2012, 94(11): 3240–3249. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.05.014 [25] VALOROSO N, SESSA S, LEPORE M, et al. Identification of mode-Ⅰ cohesive parameters for bonded interfaces based on DCB test [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2013, 104: 56–79. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2013.02.008 [26] YAMAKOV V, SAETHER E, GLAESSGEN E H. Multiscale modeling of intergranular fracture in aluminum: constitutive relation for interface debonding [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43(23/24): 7488–7494. doi: 10.1007/s10853-008-2823-7 [27] XU Y J, ZHAO S, JIN G H, et al. Ductile fracture of solder-Cu interface and inverse identification of its interfacial model parameters [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2017, 114: 279–292. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2017.08.013 [28] FENG T, XU J S, HAN L, et al. Modeling and simulation of the debonding process of composite solid propellants [J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 220: 012020. [29] CUI J Y, QIANG H F, WANG J X. Experimental and simulation research on microscopic damage of HTPB propellant under tension-shear loading [J]. AIP Advances, 2022, 12(8): 085214. doi: 10.1063/5.0101388 [30] CUI H R, SHEN Z B, LI H Y. A novel time dependent cohesive zone model for the debonding interface between solid propellant and insulation [J]. Meccanica, 2018, 53(14): 3527–3544. doi: 10.1007/s11012-018-0894-3 [31] 胡静. Janus粒子对硅胶类热力学不相容体系相容性的影响及其应用研究 [D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2021.HU J. The effect and application of Janus particles on the compatibility of inherent immiscible blends composed of silicone rubber [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2021. -






 下载:
下载: