Influence of Damping Materials on Blasting Vibration of Cylindrical Pool
-
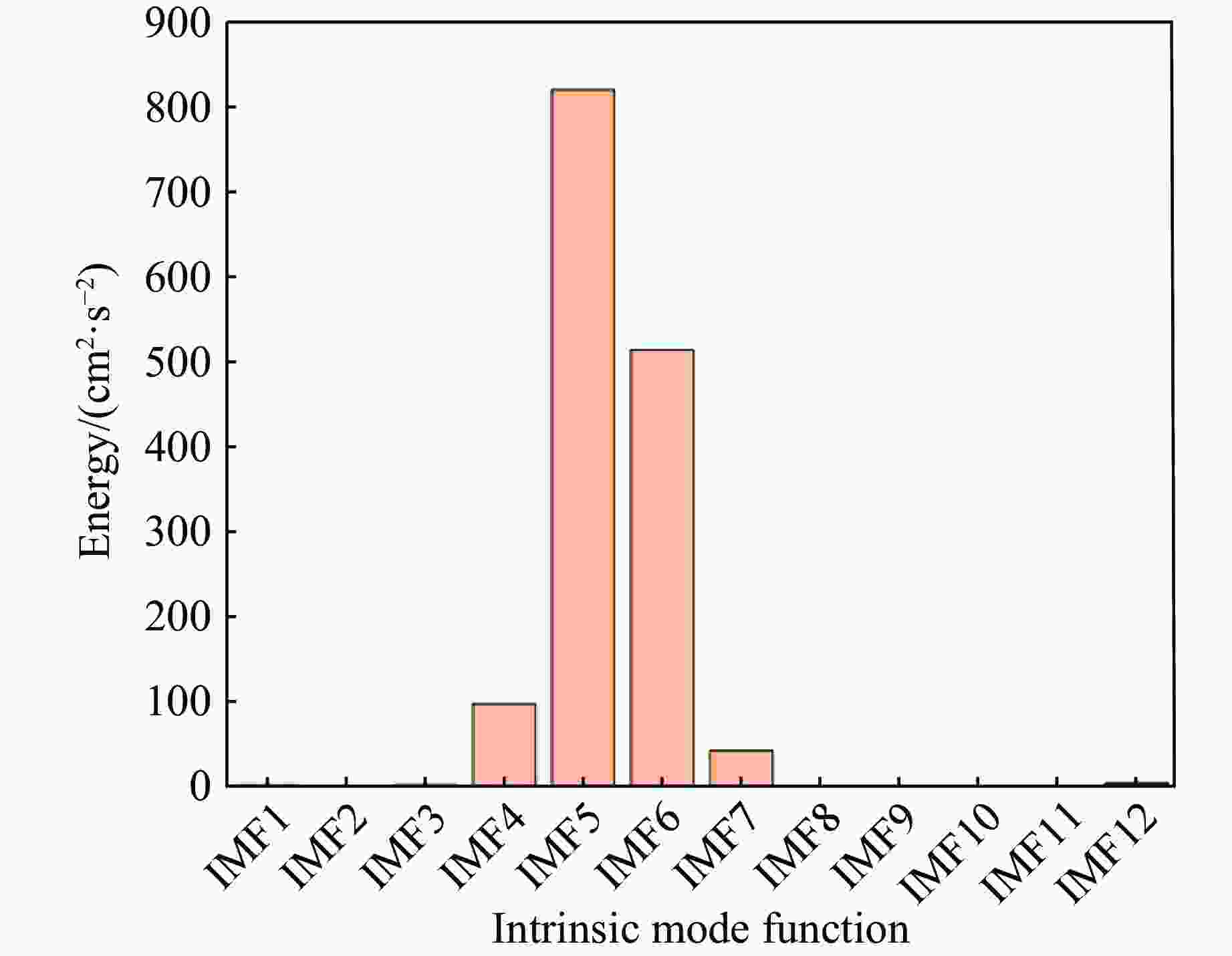
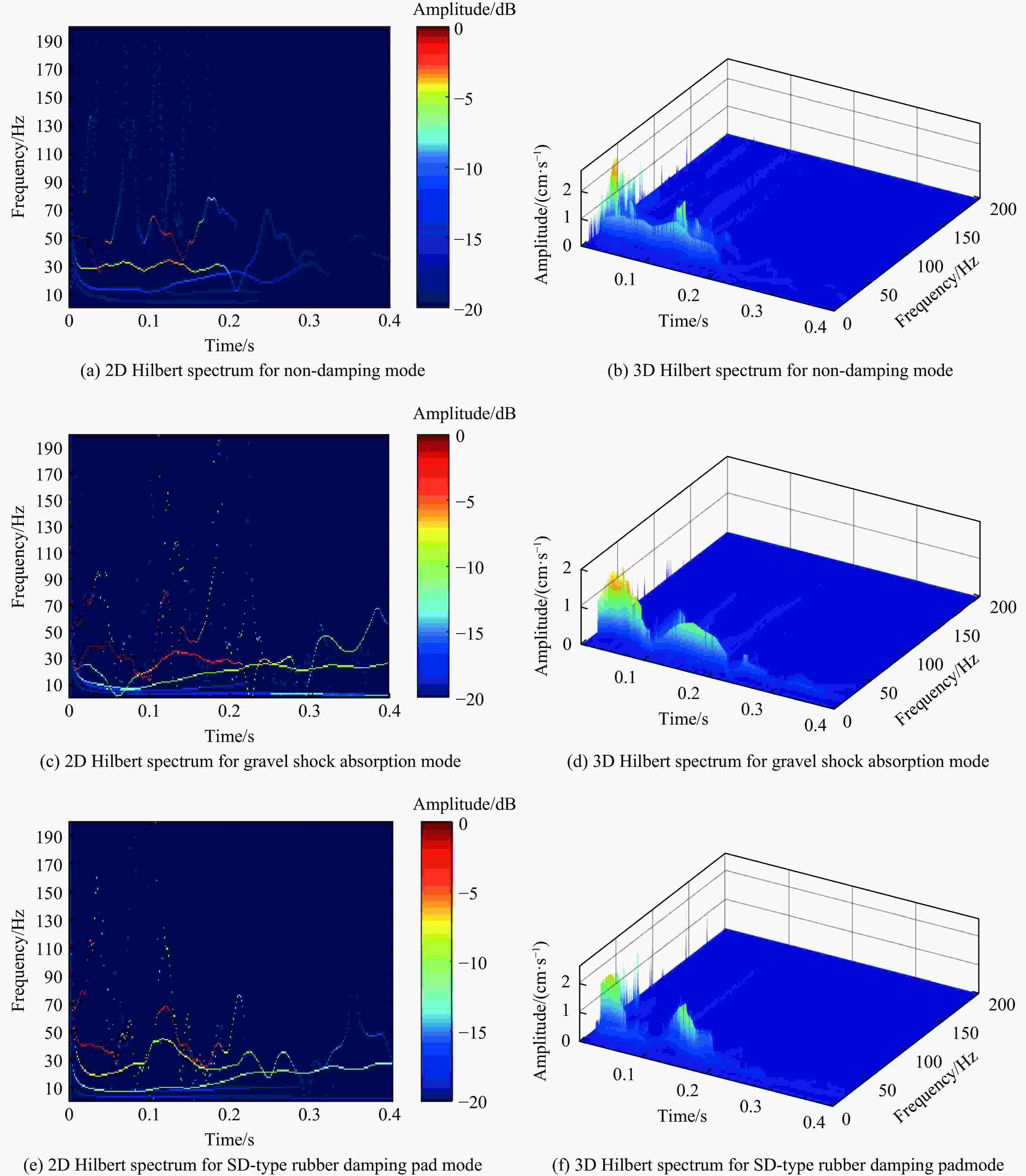
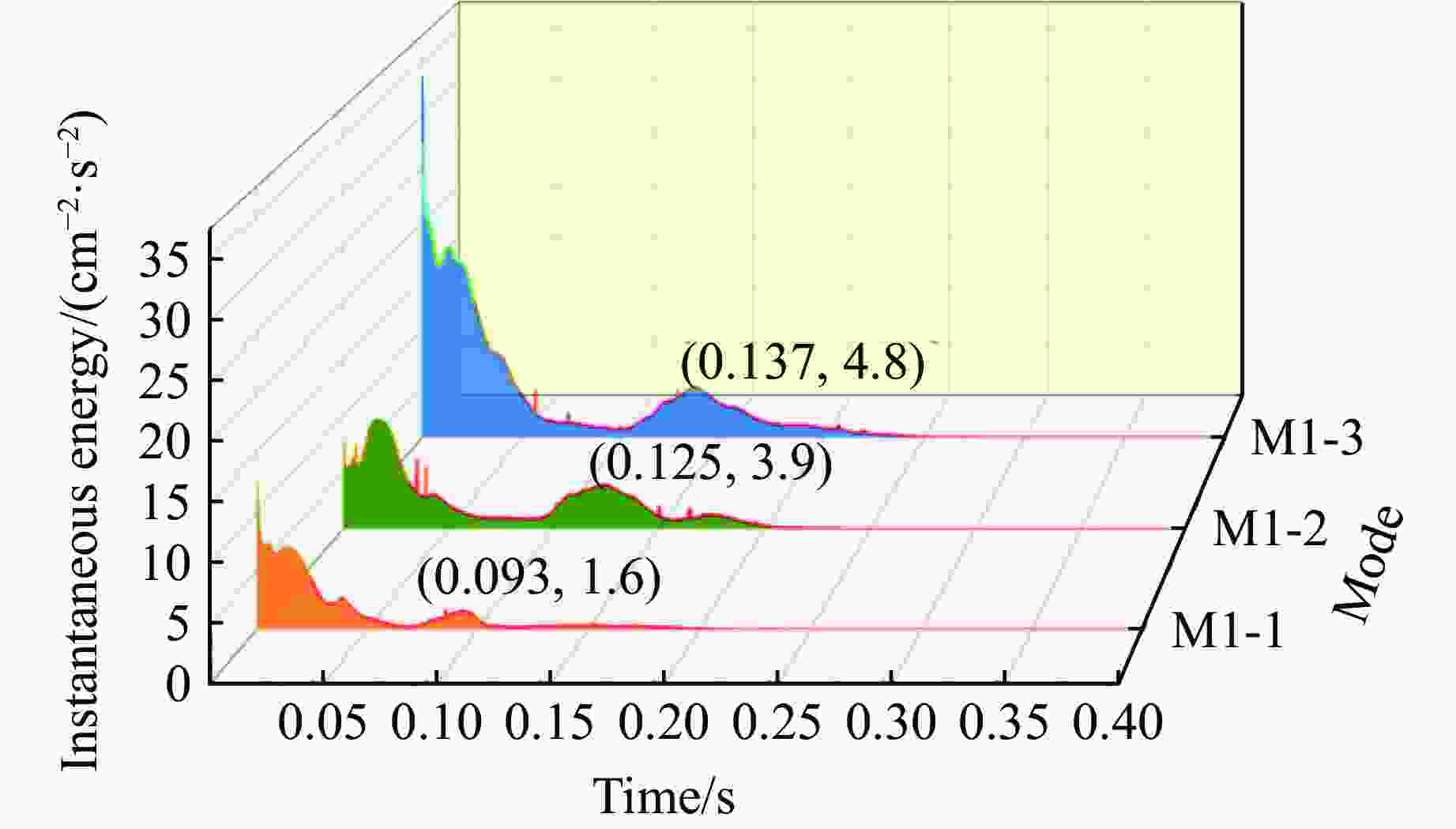
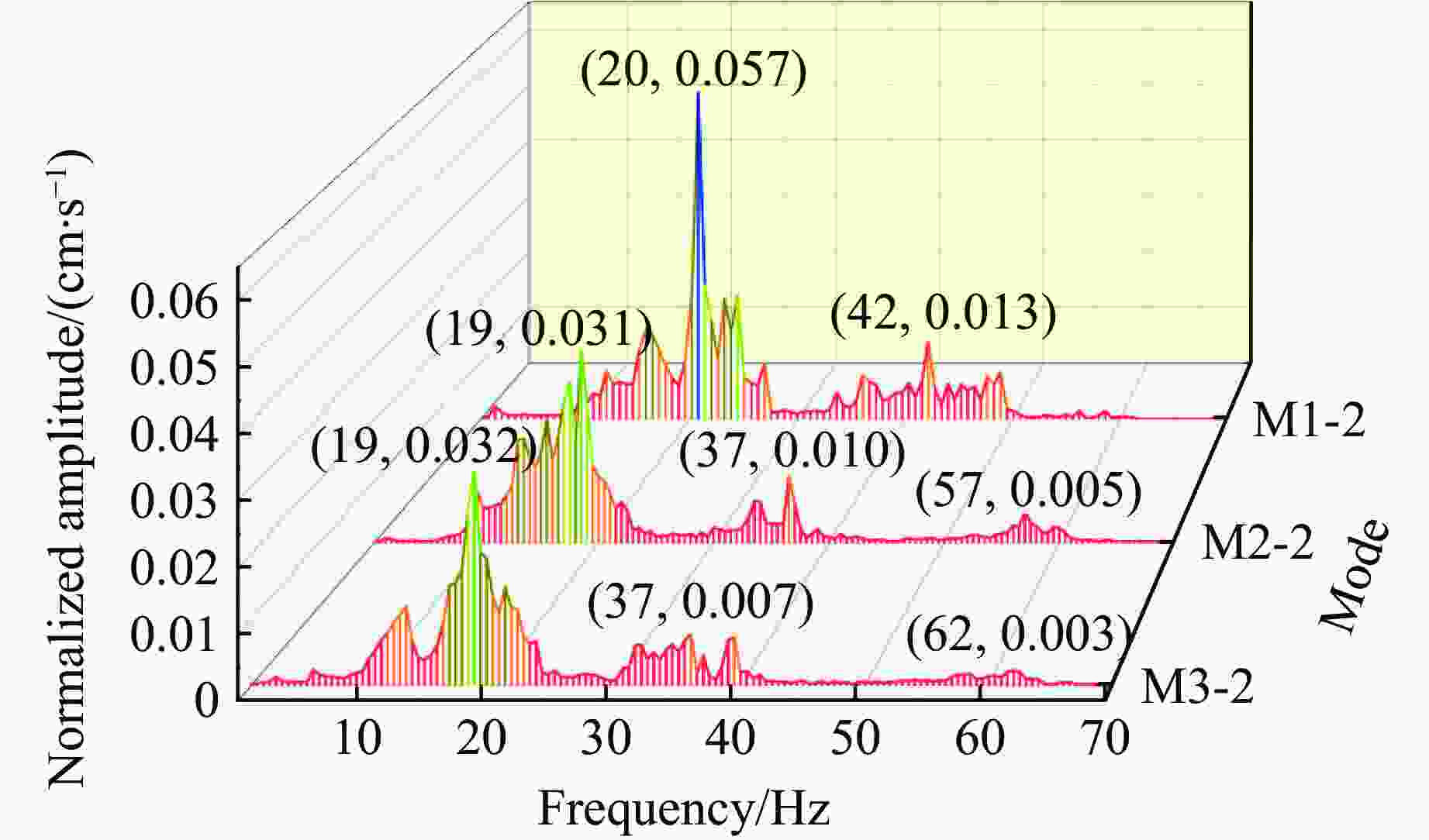
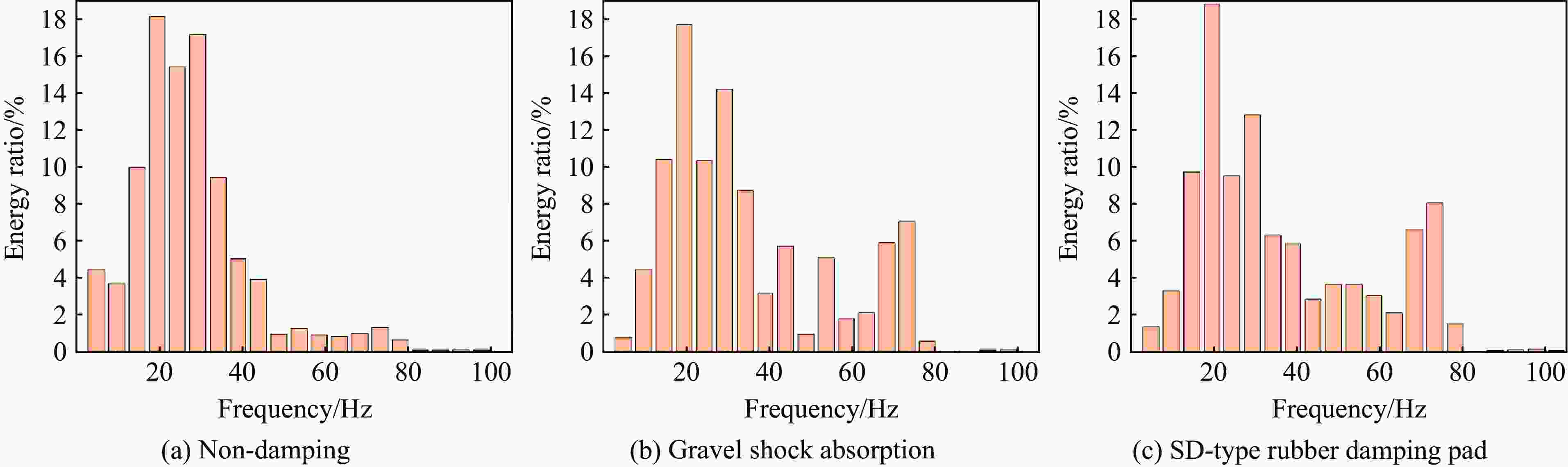
摘要: 在水下爆炸理论与技术的应用研究中,爆炸水池是十分重要的基础试验装置。研究爆炸水池爆破振动效应和减振对于圆柱形爆炸水池使用过程中的振动控制具有指导意义。为研究圆柱形水池内部装药爆炸对周围地面产生的爆破振动并寻求合适的减振材料,选取了建筑碎石、SD型橡胶垫2种减振材料,在小型爆炸水池中进行了单药包在无减振、建筑碎石和SD型橡胶垫减振3种模式下的爆炸试验,对采集到的爆破振动信号进行峰值振速分析、EEMD-HHT(ensemble empirical mode decomposition-Hilbert-Huang transform)处理及小波包分析。结果表明:爆炸水池周围地面的爆破振动包含爆炸冲击波导致的振动、水池跳动导致的触地振动,通过Hilbert瞬时能量分析可以有效识别水池产生的跳动;碎石减振和SD型橡胶减振垫模式下的振速较无减振模式下的振速分别降低53.0%和43.1%,振动能量分别降低64.9%和57.4%;3种减振模式下爆破振动信号的频率主要分布在10~80 Hz区间;无减振、建筑碎石减振、SD型橡胶垫3种减振模式下10~40 Hz频带的能量占比分别为79%、69%、66%,40~80 Hz频带的能量占比分别为11%、29%、31%。碎石和SD型橡胶垫具有吸能、减少低频成分和增加高频成分的效果,可有效降低近处测点的峰值振速。碎石减振模式下振动信号频带的能量分布较SD型橡胶垫模式下的能量分布更加均匀。Abstract: In the application research of underwater explosion theory and technology, an explosion tank is a very important basic experimental device. The research on the blasting vibration effect and vibration damping of the explosion tank is of guiding significance for the vibration control and the selection of vibration damping materials during the blasting of the cylindrical water tank. In order to explore the impact of explosive vibration caused by the internal charge explosion on the surrounding ground of the cylindrical pool, and to seek effective vibration reduction methods, two kinds of vibration reduction materials, construction gravel and SD-type rubber vibration reduction pad, were selected, and explosion tests were carried out in a small explosive pool under three modes, single charge without vibration reduction, with SD-type rubber vibration reduction pad and with gravel vibration reduction. The collected blasting vibration signals were analyzed by peak particle velocity, EEMD-HHT (ensemble empirical mode decomposition-Hilbert-Huang transform) processing and wavelet packet analysis. The results showed that the vibration signals include the blasting vibration caused by the explosion shock wave and the ground vibration caused by the pool jumping, and the the ground vibration caused by the pool jumping can be effectively identified by Hilbert instantaneous energy analysis. Compared to the single charge without vibration reduction, the vibration velocity and vibration energy under the gravel layer modes are reduced by 53.0% and 43.1%, the vibration velocity and vibration energy for SD-type rubber cushion modes are reduced by 64.9% and 57.4%. The frequency of blasting vibration signal for the three vibration reduction modes is mainly distributed in the range of 10–80 Hz. The energy proportions for the frequency range of 10–40 Hz under the three operating modes are 79%, 69% and 66%, respectively, and the energy proportions for the frequency range of 40–80 Hz are 11%, 29% and 31%, respectively. The gravel and SD-type rubber have the effect of absorbing energy and reducing low-frequency components, and increasing high-frequency components, which can effectively reduce the peak vibration velocity of nearby measurement points. Compared to the effect of the two kinds of vibration absorbing materials, the construction gravel results more uniform energy distribution of the vibration signal frequency band than that of the SD-type rubber.
-
Key words:
- underwater explosion /
- blasting vibration /
- damping material /
- time-frequency analysis
-
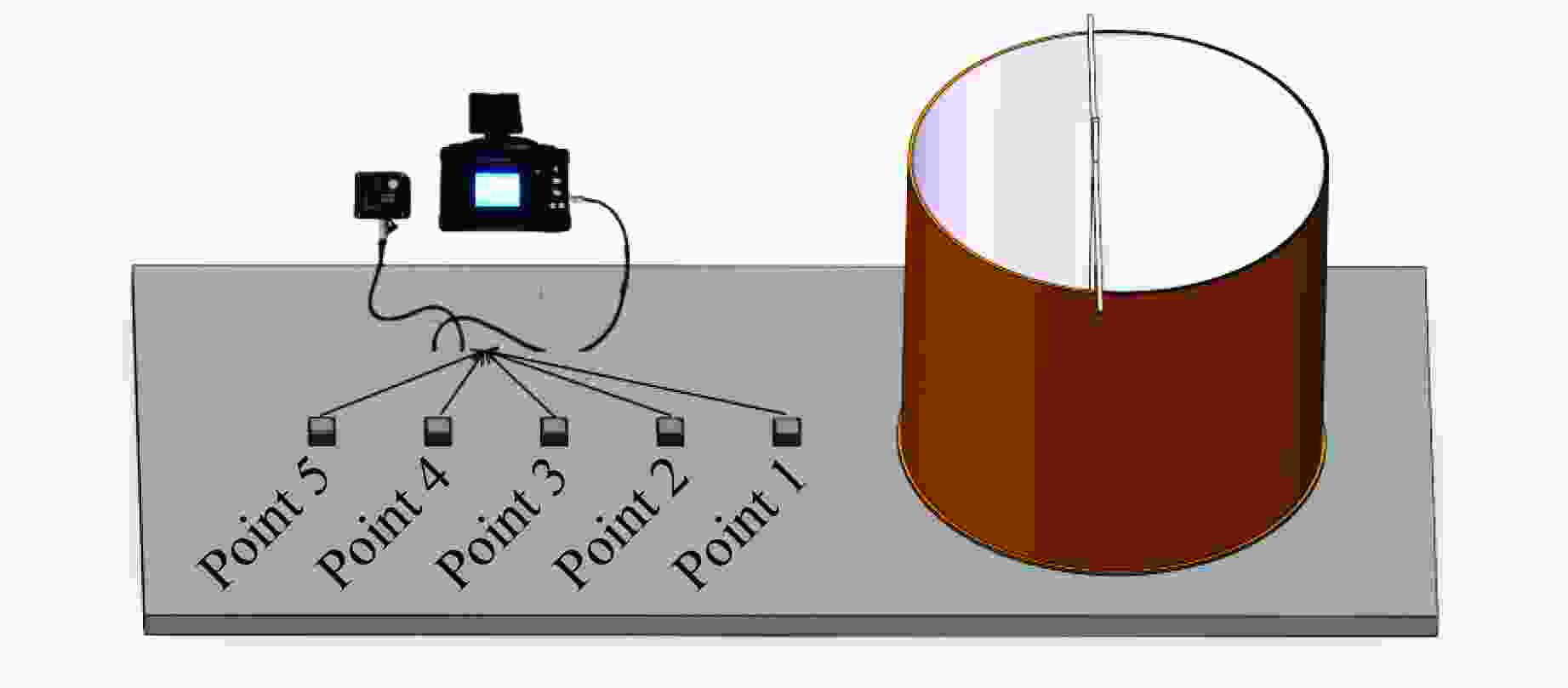
表 1 试验用爆炸水池的参数
Table 1. Test explosion pool’s parameters
Diameter/m Wall thickness/mm Height/m m0/t mt/t 1.6 16 1.4 1.19 4.00 表 2 不同模式下垂直振动速度峰值
Table 2. Vertical PPV under different test modes
Test mode Damping material Test No. Charge weight/g PPV/(cm∙s-1) l=2 m l=3 m l=4 m l=5 m l=6 m Ⅰ Non-damping M1-1 1 1.31 2.81 1.28 1.08 0.98 M1-2 2 2.35 3.81 1.98 1.62 1.53 M1-3 3 3.00 4.59 2.38 2.08 1.87 Ⅱ Gravel M2-1 1 1.14 1.32 0.93 0.78 0.67 M2-2 2 1.94 2.35 1.72 1.46 1.15 M2-3 3 2.54 3.13 2.35 1.88 1.43 Ⅲ SD-type rubber damping pad M3-1 1 1.43 1.60 0.75 0.60 0.64 M3-2 2 2.69 2.72 1.20 1.16 1.03 M3-3 3 2.81 3.76 1.72 1.34 1.15 表 3 水池爆破振动信号的总能量
Table 3. Total energy of pool blasting vibration signal
Test No. Test mode Total energy/(103 cm2·s−2) l=3 m l=4 m l=5 m M1-2 Ⅰ 3.85 1.04 0.94 M2-2 Ⅱ 1.35 0.57 0.51 M3-2 Ⅲ 1.63 0.77 0.64 -
[1] 曹祖贵, 郭子如, 姚笛. 小水池水下爆炸震动传播的测试 [J]. 煤矿爆破, 2010, 28(4): 12–14.CAO Z G, GUO Z R, YAO D. Ground vibration tests of underwater explosion in small pool [J]. Coal Mine Blasting, 2010, 28(4): 12–14. [2] 马晨阳, 吴立, 孙苗. 自由面数量对水下钻孔爆破振动信号能量分布及衰减规律的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(1): 015201. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0436MA C Y, WU L, SUN M. Influence of free surface numbers on the energy distribution and attenuation of vibration signals of underwater drilling blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(1): 015201. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0436 [3] 邵蔚, 王长柏. 水下爆破振动特征及衰减规律研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2018, 24(5): 15–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2018.05.003SHAO W, WANG C B. Study on vibration characteristics and attenuation law of under water blasting [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2018, 24(5): 15–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2018.05.003 [4] 王璞, 刘桐, 杨帆, 等. 水下爆破软土地基远区振动效应预测 [J]. 工程爆破, 2022, 28(3): 137–142. doi: 10.19931/j.EB.20220082WANG P, LIU T, YANG F, et al. Prediction of remote area vibration effect by underwater blasting of soft soil foundation [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2022, 28(3): 137–142. doi: 10.19931/j.EB.20220082 [5] 孙苗, 吴立, 袁青, 等. 基于CEEMDAN的爆破地震波信号时频分析 [J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(3): 76–82. doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.190179SUN M, WU L, YUAN Q, et al. Time-frequency analysis of blasting seismic signal based on CEEMDAN [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(3): 76–82. doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.190179 [6] 汤有富, 汪泉, 朱恺波, 等. 基于HHT变换的小水池水下爆炸振动分析 [J]. 工程爆破, 2017, 23(1): 29–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2017.01.006TANG Y F, WANG Q, ZHU K B, et al. Underwater explosion vibration analysis based on HHT transform in small pond [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2017, 23(1): 29–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2017.01.006 [7] PENG Y X, SU Y, WU L, et al. Study on the attenuation characteristics of seismic wave energy induced by underwater drilling and blasting [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019: 4367698. doi: 10.1155/2019/4367698 [8] 汪泉, 汤有富, 李志敏, 等. 有机玻璃-空气层结构对爆炸水池水下爆炸地基振动的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(2): 024201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20170611WANG Q, TANG Y F, LI Z M, et al. Influence of plexiglass-air interlayer structure on foundation vibration of small pool underwater explosion [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(2): 024201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20170611 [9] 张声辉, 刘连生, 钟清亮, 等. 露天边坡爆破地震波能量分布特征研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(7): 224–232. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.07.032ZHANG S H, LIU L S, ZHONG Q L, et al. Energy distribution characteristics of blast seismic wave on open pit slope [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(7): 224–232. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.07.032 [10] 石长岩, 赵兴柱, 姜洪波, 等. 爆破震动信号频带能量分布特征 [J]. 金属矿山, 2014, 43(8): 6–10.SHI C Y, ZHAO X Z, JIANG H B, et al. Frequency band energy distribution characteristics of blasting vibration signals [J]. Metal Mine, 2014, 43(8): 6–10. [11] 韦啸, 高文学, 王林台, 等. 基于EEMD的地铁隧道爆破振动信号分析与应用研究 [J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2019, 39(8): 1293–1300. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.2096-4498.2019.08.010WEI X, GAO W X, WANG L T, et al. Analysis and application of metro tunnel blasting vibration signal based on EEMD [J]. Tunnel Construction, 2019, 39(8): 1293–1300. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.2096-4498.2019.08.010 [12] 赵永玲. 隔振橡胶特性表征与橡胶悬架结构优化 [D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016.ZHAO Y L. Vibration isolation rubber characterization and rubber suspension structural optimization [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016. [13] 肖源杰, 王萌, 于群丁, 等. 振动荷载下级配碎石颗粒运动及其能量特征试验研究 [J]. 土木工程学报, 2023, 56(3): 78–89. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.21121208XIAO Y J, WANG M, YU Q D, et al. Laboratory investigation on meso-scale particle motion and kinematic energy characteristics of unbound aggregate base materials subjected to vibratory loading [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2023, 56(3): 78–89. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.21121208 [14] 赵明生, 梁开水, 罗元方, 等. EEMD在爆破振动信号去噪中的应用 [J]. 爆破, 2011, 28(2): 17–20, 59. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2011.02.005ZHAO M S, LIANG K S, LUO Y F, et al. Application of EEMD in blasting vibration signal de-noising [J]. Blasting, 2011, 28(2): 17–20, 59. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2011.02.005 [15] 孙苗. 爆破地震波信号处理HHT改进算法及应用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2021.SUN M. Improved HHT algorithm for blasting seismic wave signal processing and its application [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2021. [16] LI X F, LI H B, ZHANG G K. Damage assessment and blast vibrations controlling considering rock properties of underwater blasting [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 121: 104045. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.06.004 [17] 高启栋, 卢文波, 冷振东, 等. 考虑爆源特征的岩石爆破诱发地震波的波型与组分分析 [J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(10): 2830–2844. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.0108GAO Q D, LU W B, LENG Z D, et al. Analysis of wave-type and seismic component induced by rock blasting considering source characteristics [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(10): 2830–2844. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.0108 [18] 宋肖龙, 高文学, 季金铭, 等. 基于EEMD-HHT变换的爆破损伤分析方法 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(8): 2887–2896. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.08.033SONG X L, GAO W X, JI J M, et al. Blasting damage analysis method based on EEMD-HHT transform [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(8): 2887–2896. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.08.033 [19] 李丹丹. 基于集合经验模态分析的滚动轴承故障特征提取 [D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2013.LI D D. Rolling bearing’s breakdown feature extraction technology based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2013. [20] WU Z, HUANG N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise assisted data analysis method [J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis. 2009, 1(1): 1–41. [21] 闫大洋, 胡坤伦, 叶图强, 等. 小水池中延时爆破对地表振动的测试与分析 [J]. 爆破器材, 2014, 43(4): 42–46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2014.04.009YAN D Y, HU K L, YE T Q, et al. Test and analysis of ground surface vibration during the delay blasting in small pool [J]. Explosive Materials, 2014, 43(4): 42–46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2014.04.009 -






 下载:
下载: