Dynamic Response of Nacre-Like Voronoi Brick and Mortar Structure under Explosive Load
-
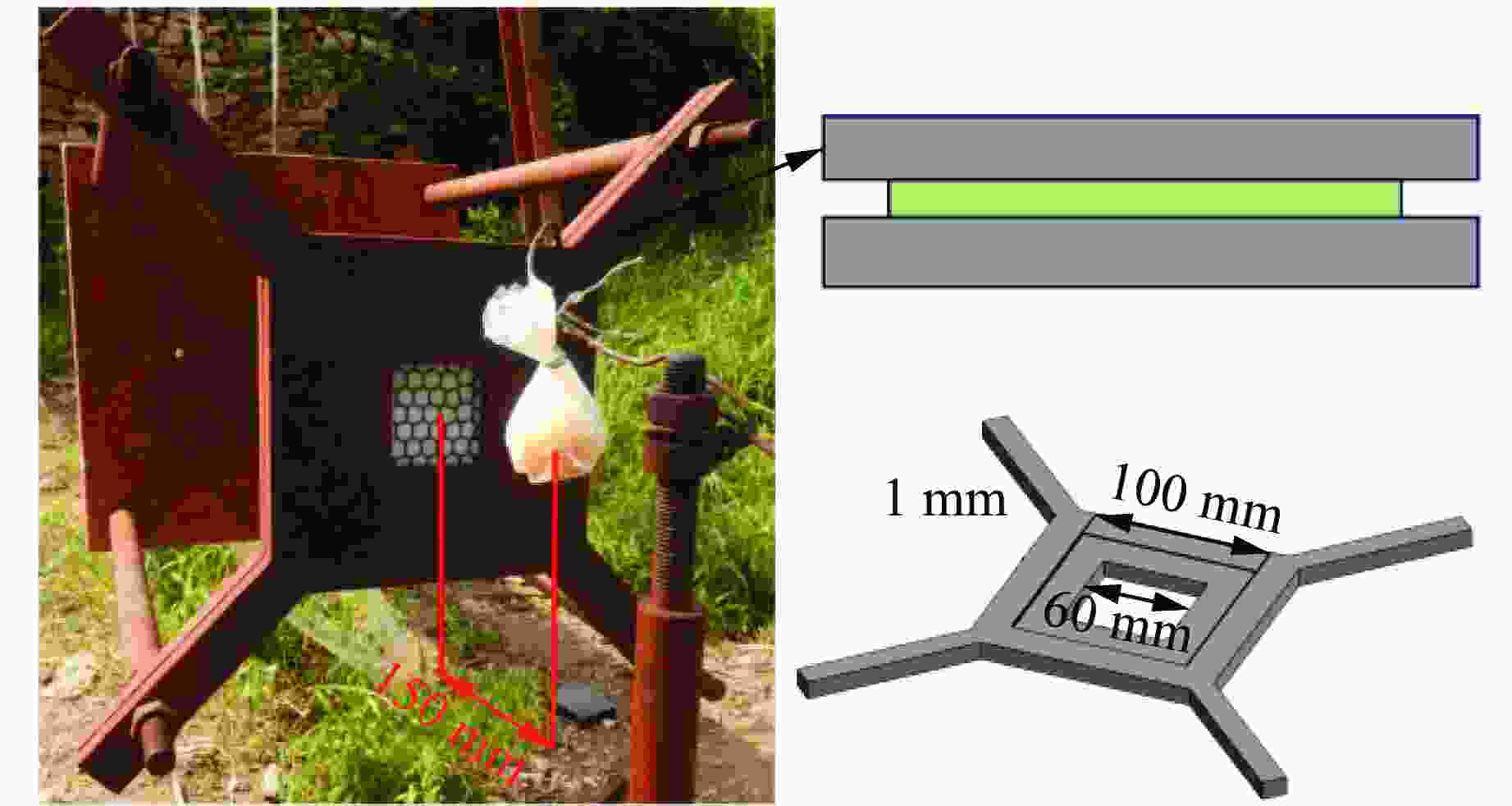
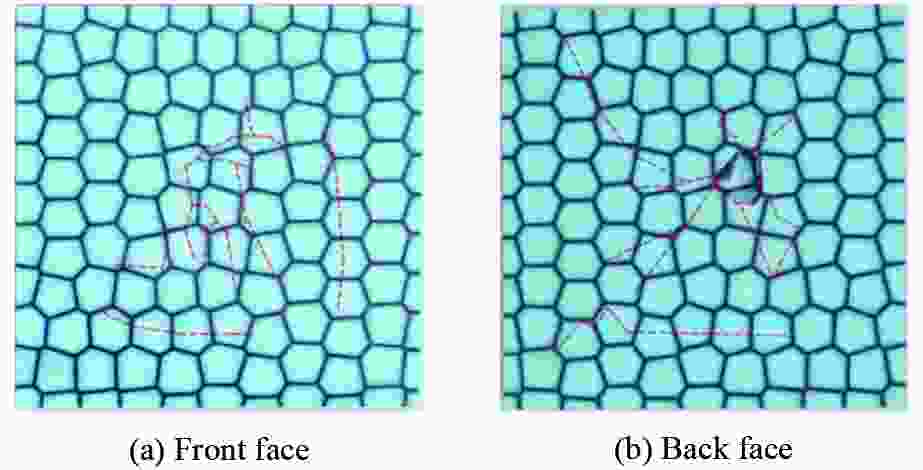
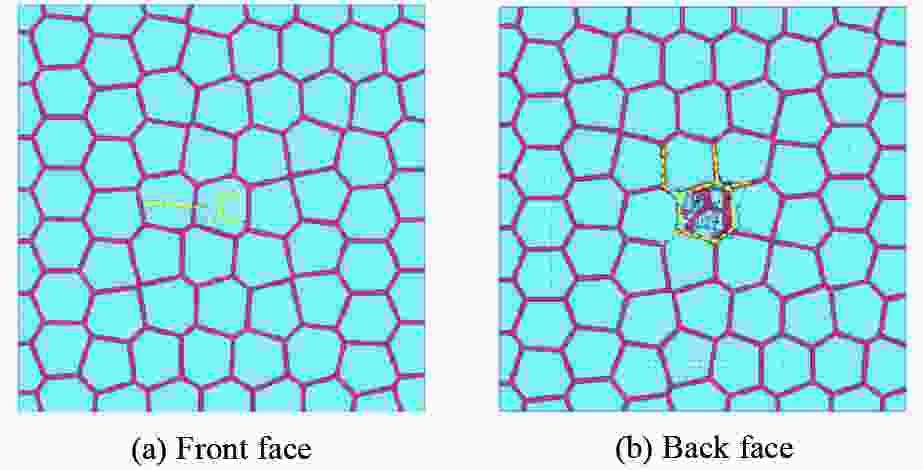
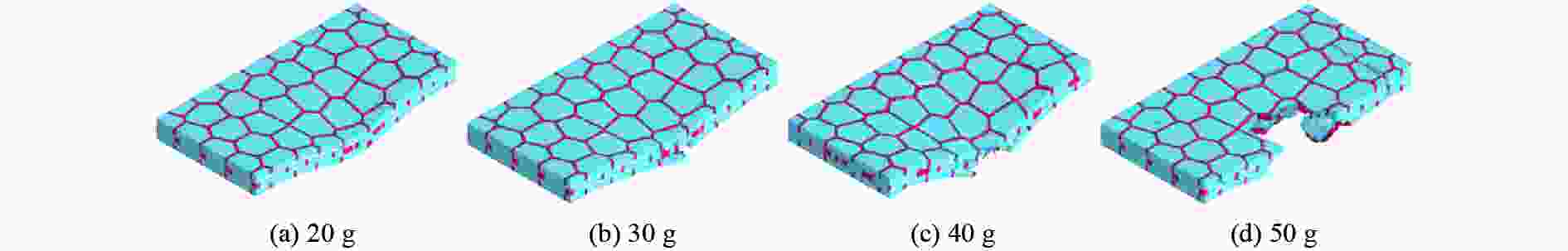
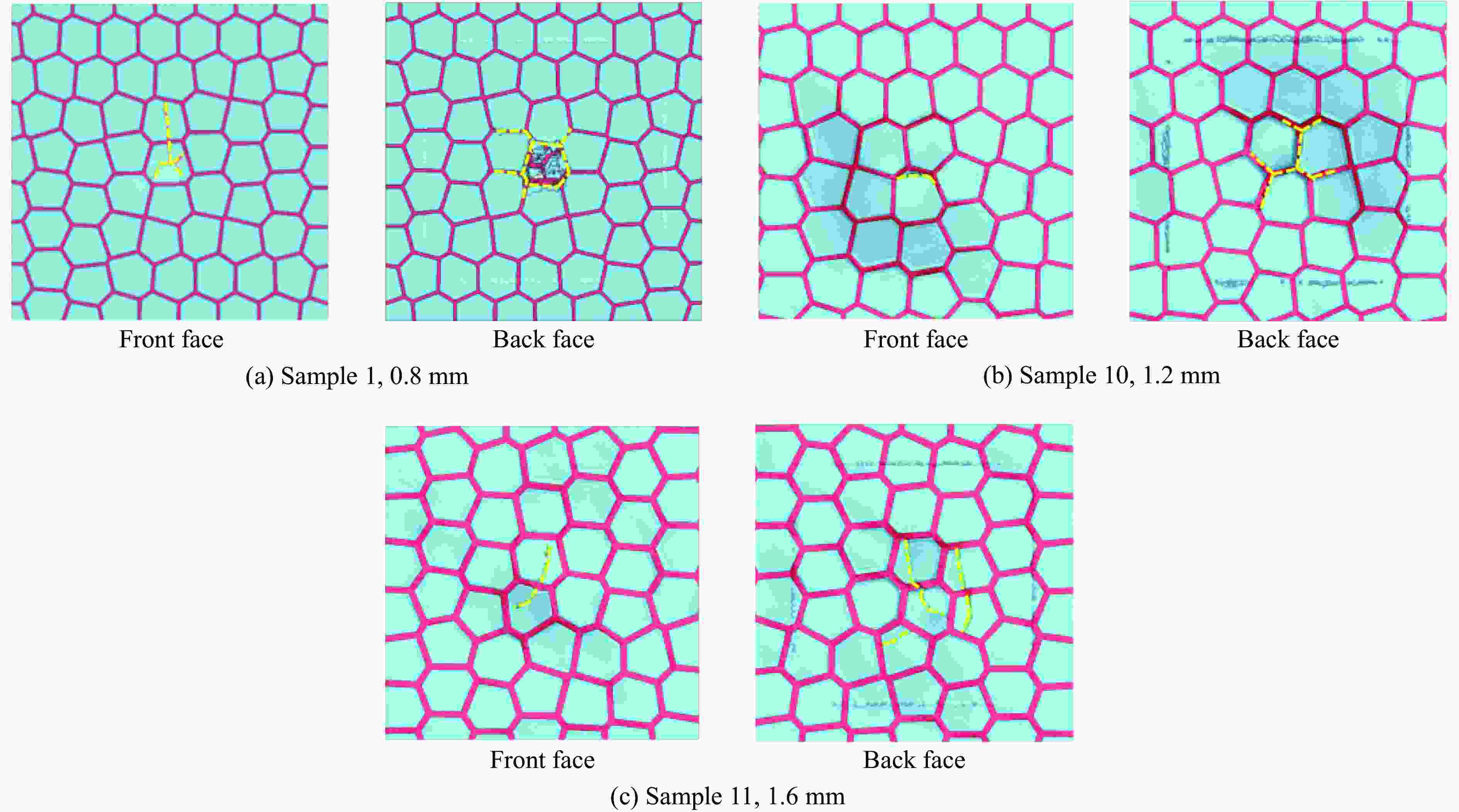
摘要: 基于贝壳多尺度、多层级的砖泥结构,构建仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构。通过将3D打印、爆炸实验和数值模拟相结合,探索仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构在爆炸载荷下的动力学响应,研究Voronoi单元尺寸和层内软材料厚度对结构变形破坏模式和能量吸收的影响。实验结果表明:在40 g球形乳化炸药作用下,仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构的前面板中心处出现了向四周蔓延的径向裂纹,后面板出现小块材料脱落。在此基础上,建立了有限元模型,并验证了其有效性。随着药量的增加,仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构主要分为塑性变形、前后面板裂纹、小块材料脱落、结构整体贯穿破坏伴随夹持端剪切破坏4种破坏模式。研究发现:仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构中硬材料的水平正应力远大于垂直正应力,层间软材料的剪应变大于层内软材料的剪应变。层间软材料的比吸能远大于硬材料的比吸能,约为硬材料的1.8~2.3倍;随着Voronoi单元尺寸的增大,层内软材料的比吸能增大了45.6%;随着层内软材料厚度增加,层内软材料的比吸能增大了31.1%,允许结构进一步的塑性变形。研究结果为仿生结构设计提供了一定的技术依据。
-
关键词:
- 仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构 /
- 爆炸实验 /
- 动力学响应 /
- 比吸能
Abstract: Inspired by the brick and mortar structure of multi-scale and multi-hierarchy, a nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structure was created. Afterwards, the dynamic response of nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structure under explosive load was explored by combining 3D printing, explosion experiments, and numerical simulations. The influence of the Voronoi unit cell size and the thickness of the intralaminar soft material on the damage mode as well as the energy absorption of the structure was analyzed. Under the spherical emulsion explosive charge of 40 g, the radial cracks appeared on the front face of the nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structure and then spread around, while small pieces of fragments fell off the back panel. A finite element model was built and showed good agreement with the experimental results. The damage modes of nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structures under different explosive charges include plastic deformation, cracks occurred on the front and back face, small pieces of material falling off, damage of whole structure accompanied with shear failure at the gripper end. The horizontal normal stress of the stiff material is much larger than the vertical normal stress. Meanwhile, the shear strain in the interlaminar soft material is much larger than that in the intralaminar soft material. The specific energy absorption is 1.8−2.3 times larger in the interlaminar soft material than that in the stiff material. With the increase of the Voronoi unit cell size, the specific energy absorption of the interlaminar soft material increases by 45.6%. As the thickness of the intralaminar soft material increases, the specific energy absorption of the intralaminar soft material increases by 31.1%. This study may provide some definite reference for the design of biologically inspired structures. -
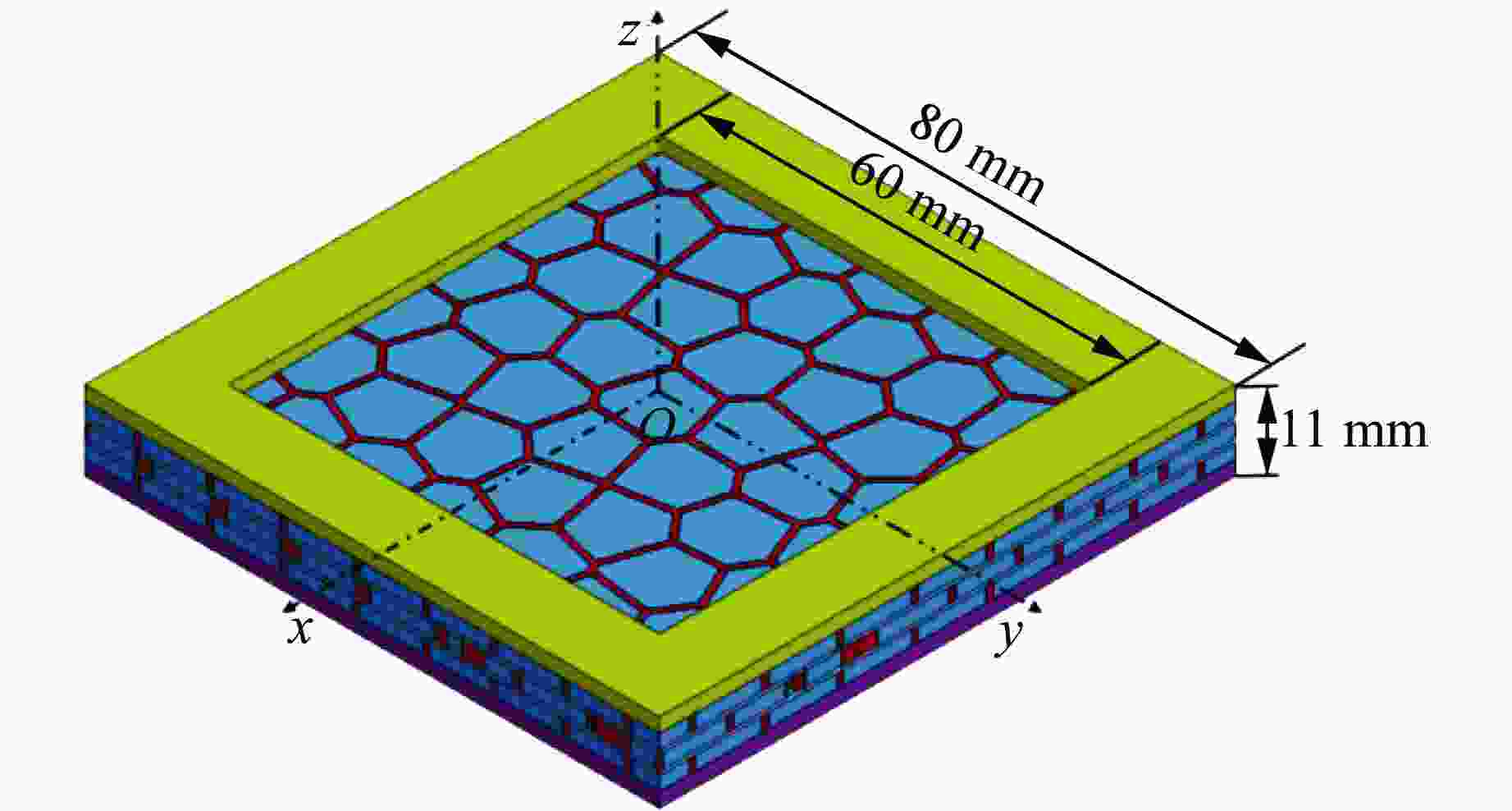
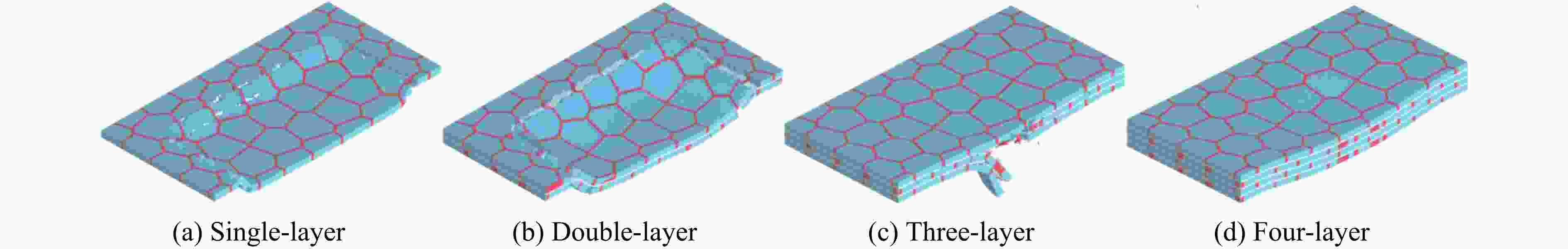
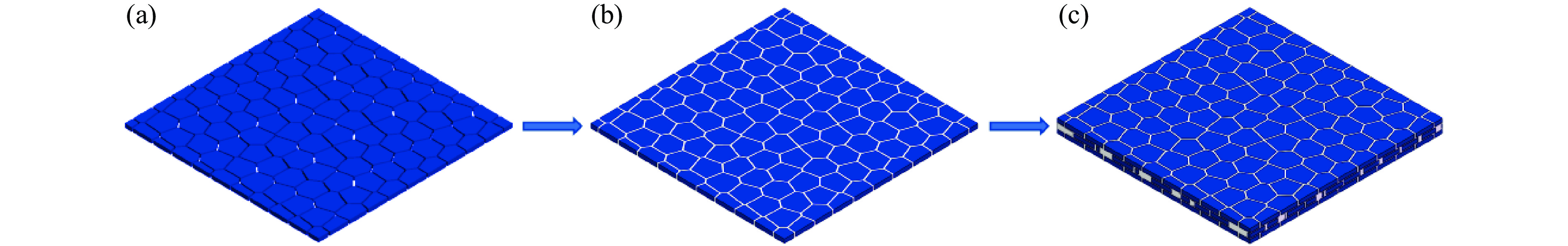
图 1 仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构的构建流程:(a) 单层硬材料,(b) 单层仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构,(c) 3层仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构
Figure 1. Construction flowchart of nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structures: (a) single layer of stiff material; (b) single layer of nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structure; (c) three layers of nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structure
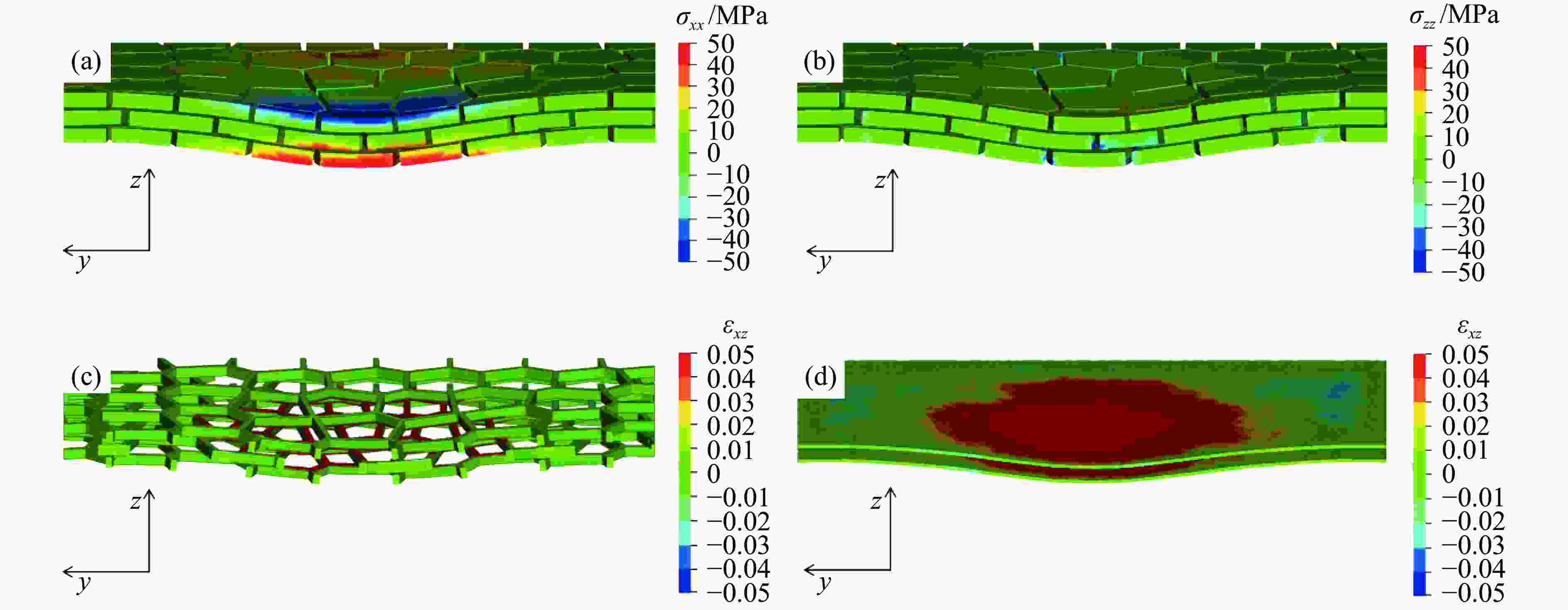
图 7 仿贝壳Voronoi砖泥结构的应力和应变云图:(a) 硬材料水平正应力,(b) 硬材料垂直正应力,(c) 层间软材料的剪切应变,(d) 层内软材料的剪切应变
Figure 7. Stress and strain contour plots of nacre-like Voronoi brick and mortar structure: (a) horizontal normal strain of the stiff material; (b) vertical normal stress of the stiff material; (c) shear strain of the interlaminar soft material; (d) shear strain of the intralaminar soft material
表 1 试样的几何参数
Table 1. Geometrical parameters of samples
Sample No. Voronoi cell
size/mmSoft material
thickness/mmNumber of plies Mass of emulsion
explosive/gVolume fraction of
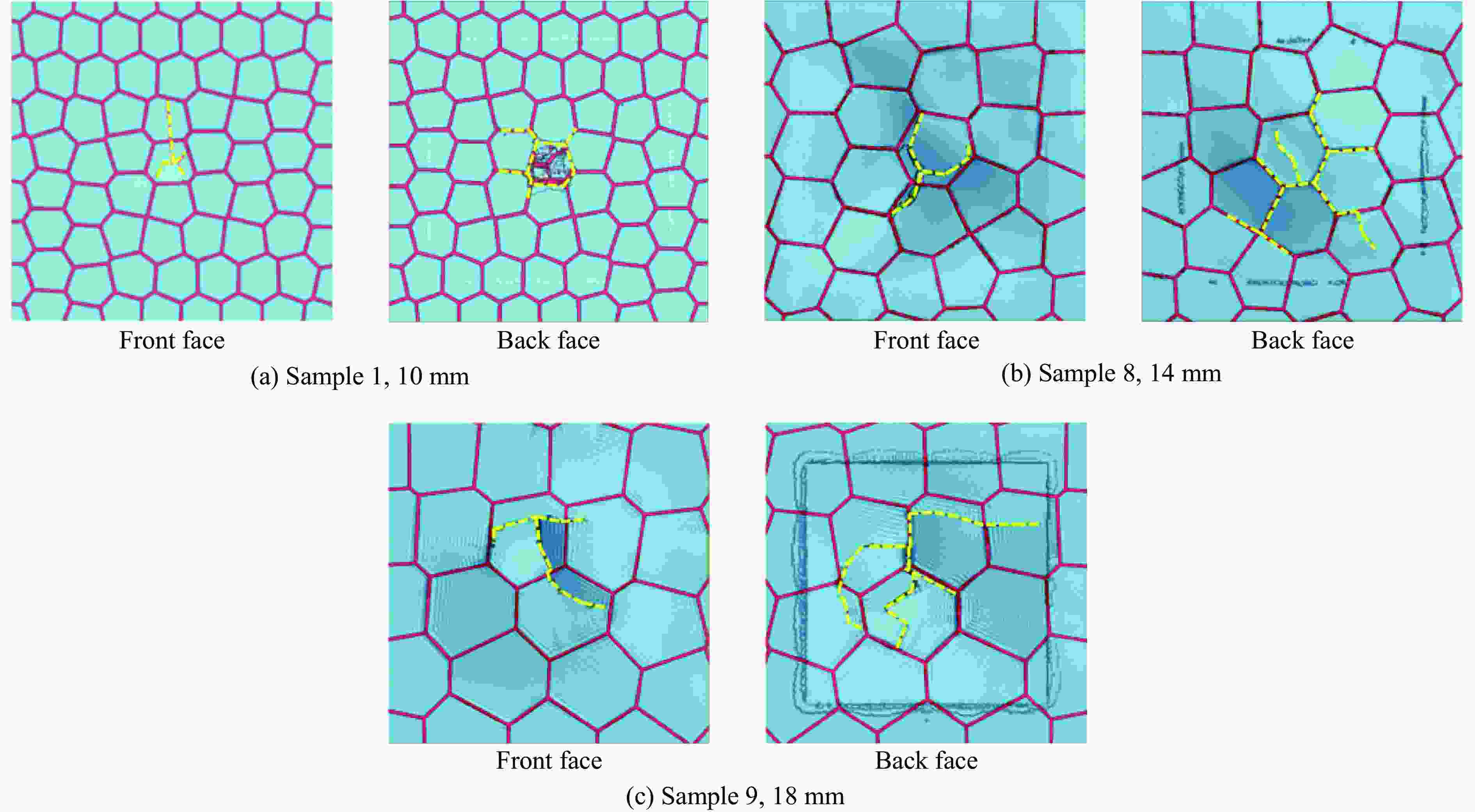
soft material/%1 10 0.8 3 40 27.3 2 10 0.8 3 20 27.3 3 10 0.8 3 30 27.3 4 10 0.8 3 50 27.3 5 10 0.8 1 40 11.9 6 10 0.8 2 40 21.7 7 10 0.8 4 40 25.4 8 14 0.8 3 40 22.8 9 18 0.8 3 40 20.1 10 10 1.2 3 40 29.9 11 10 1.6 3 40 35.5 表 2 不同单元尺寸、层内软材料厚度的3层砖泥结构各组分的比吸能
Table 2. $E_{\mathrm{SA}} $ of each component of 3-layer structure with different element size and soft material thickness
Cell size/mm Soft material thickness/mm Volume fraction of
soft material/%ESA of interlaminar soft material/(J·kg–1) ESA of intralaminar soft material/(J·kg–1) ESA of stiff material/(J·kg–1) 10 0.8 27.3 138.1 37.9 63.7 12 0.8 24.6 138.5 43.5 61.6 14 0.8 22.8 138.5 44.9 61.0 16 0.8 22.1 138.5 46.2 60.9 18 0.8 20.1 141.1 55.2 60.9 10 1.0 29.6 124.6 46.5 63.0 10 1.2 29.9 124.2 47.8 65.6 10 1.4 34.3 125.6 49.7 70.9 10 1.6 35.5 122.5 52.3 66.4 -
[1] RKHALAF M, SUNESARA A, ASHRAFI B, et al. Toughness by segmentation: fabrication, testing and micromechanics of architectured ceramic panels for impact applications [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2019, 158: 52–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2018.08.025 [2] LIU P, ZHU D J, YAO Y M, et al. Numerical simulation of ballistic impact behavior of bio-inspired scale-like protection system [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 99: 201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.040 [3] DIMAS L S, BRATZEL G H, EYLON I, et al. Tough composites inspired by mineralized natural materials: computation, 3D printing, and testing [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(36): 4629–4638. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201300215 [4] GRUNENFELDER L K, SUKSANGPANYA N, SALINAS C, et al. Bio-inspired impact-resistant composites [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(9): 3997–4008. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.03.022 [5] GU G X, TAKAFFOLI M, HSIEH A J, et al. Biomimetic additive manufactured polymer composites for improved impact resistance [J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2016, 9: 317–323. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2016.09.006 [6] BARTHELAT F. Nacre from mollusk shells: a model for high-performance structural materials [J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2010, 5(3): 035001. doi: 10.1088/1748-3182/5/3/035001 [7] CORNI I, HARVEY T J, WHARTON J A, et al. A review of experimental techniques to produce a nacre-like structure [J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2012, 7(3): 031001. doi: 10.1088/1748-3182/7/3/031001 [8] 赵赫威, 郭林. 仿贝壳珍珠母层状复合材料的制备及应用 [J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(6): 576–589. doi: 10.1360/N972016-00754ZHAO H W, GUO L. Synthesis and applications of layered structural composites inspired by nacre [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(6): 576–589. doi: 10.1360/N972016-00754 [9] GU G X, SU I, SHARMA S, et al. Three-dimensional-printing of bio-inspired composites [J]. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 2016, 138(2): 021006. doi: 10.1115/1.4032423 [10] 刘英志, 雷建银, 王志华. 冲击载荷下仿贝壳砖泥结构的动态响应 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(1): 014202. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210790LIU Y Z, LEI J Y, WANG Z H. Dynamic response of narce-like brick and mortar structure under impact load [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(1): 014202. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210790 [11] PADOLE M, GHARDE S, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Three-dimensional printing of molluscan shell inspired architectures via fused deposition modeling [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(34): 46356–46366. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09799-6 [12] YADAV R, GOUD R, DUTTA A, et al. Biomimicking of hierarchal molluscan shell structure via layer by layer 3D printing [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(32): 10832–10840. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.8b01738 [13] WU K J, ZHENG Z J, ZHANG S S, et al. Interfacial strength-controlled energy dissipation mechanism and optimization in impact-resistant nacreous structure [J]. Materials & Design, 2019, 163: 107532. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.12.004 [14] GU G X, TAKAFFOLI M, BUEHLER M J. Hierarchically enhanced impact resistance of bioinspired composites [J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(28): 1700060. doi: 10.1002/adma.201700060 [15] WU X D, MENG X S, ZHANG H G. An experimental investigation of the dynamic fracture behavior of 3D printed nacre-like composites [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2020, 112: 104068. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.104068 [16] RITCHIE R O. The conflicts between strength and toughness [J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10(11): 817–822. doi: 10.1038/nmat3115 [17] TRAN P, NGO T D, GHAZLAN A, et al. Bimaterial 3D printing and numerical analysis of bio-inspired composite structures under in-plane and transverse loadings [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2017, 108: 210–223. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.09.083 [18] WU K J, SONG Y H, ZHANG X, et al. A prestressing strategy enabled synergistic energy-dissipation in impact-resistant nacre-like structures [J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(6): 2104867. doi: 10.1002/advs.202104867 [19] WANG J, HU D Y, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Anti-impact performance of bionic tortoiseshell-like composites [J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 303: 116315. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116315 [20] KO K, JIN S, LEE S E, et al. Impact resistance of nacre-like composites diversely patterned by 3D printing [J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 238: 111951. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.111951 [21] KO K, LEE S, HWANG Y K, et al. Investigation on the impact resistance of 3D printed nacre-like composites [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2022, 177: 109392. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.109392 [22] WEI Z Q, XU X H. Gradient design of bio-inspired nacre-like composites for improved impact resistance [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 215: 108830. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108830 [23] 李志洋, 雷建银, 刘志芳. 爆炸载荷下仿贝壳结构的动态响应 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(8): 083101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0145LI Z Y, LEI J Y, LIU Z F. Dynamic response of nacre-like structure under explosion load [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(8): 083101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0145 [24] CHEN B C, ZOU M, LIU G M, et al. Experimental study on energy absorption of bionic tubes inspired by bamboo structures under axial crushing [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 115: 48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.01.005 -






 下载:
下载: