Deformation Mode and Energy Absorption of Modularized Cellular Structures
-
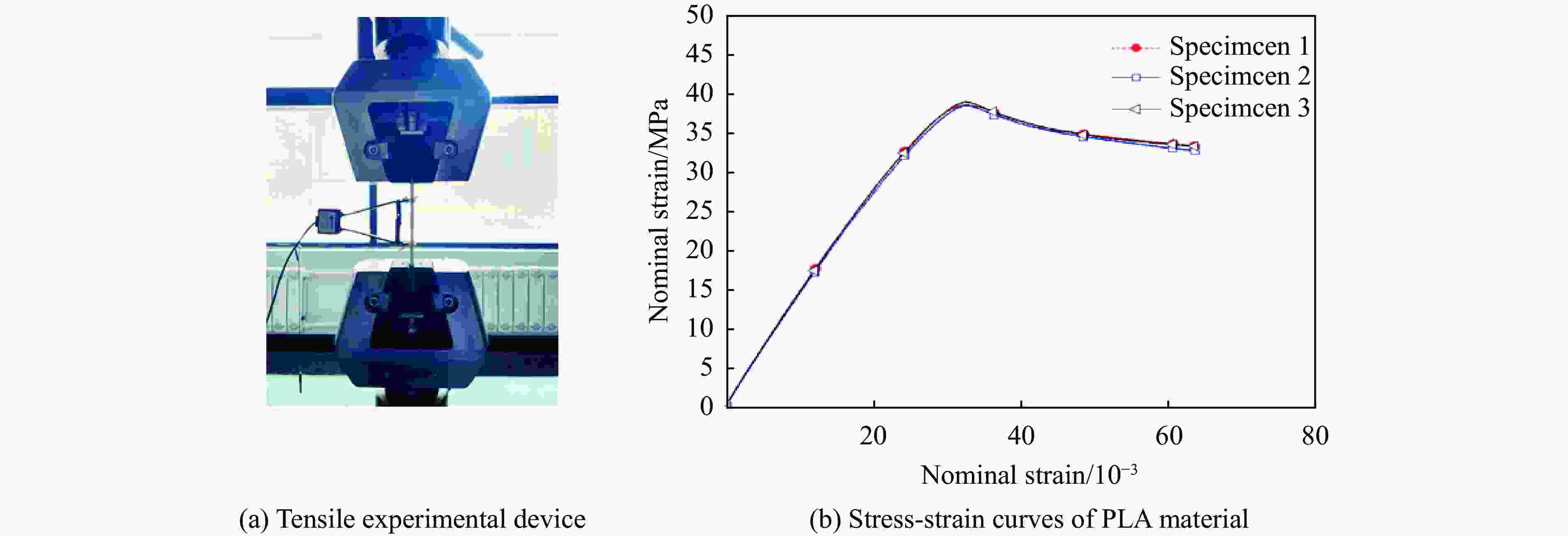
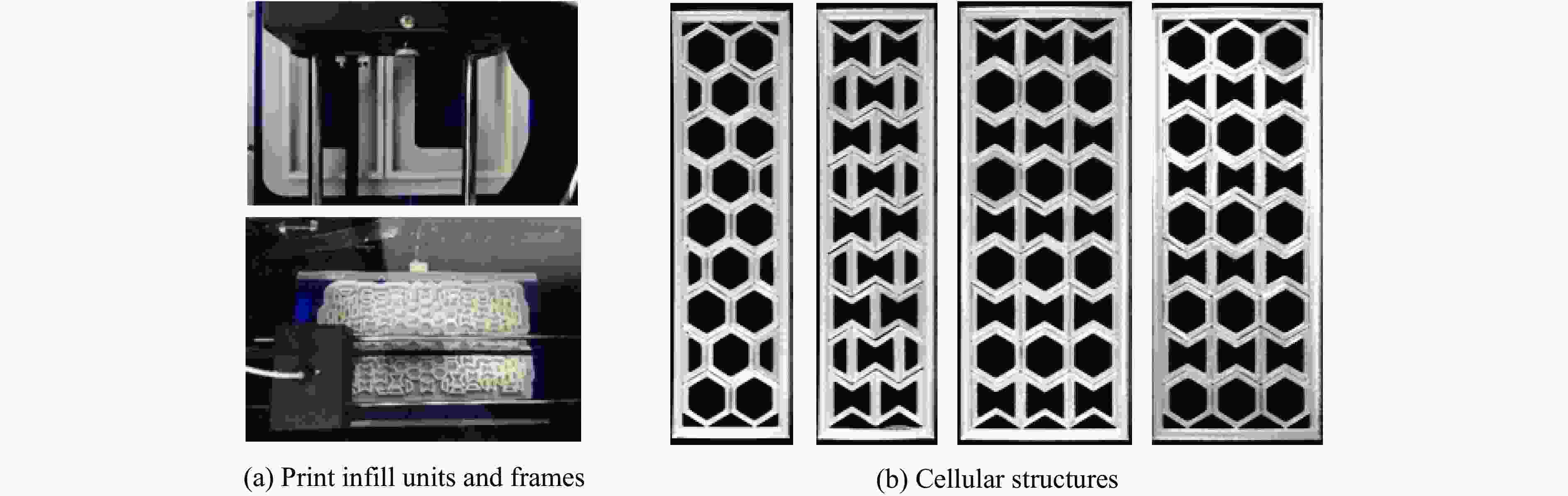
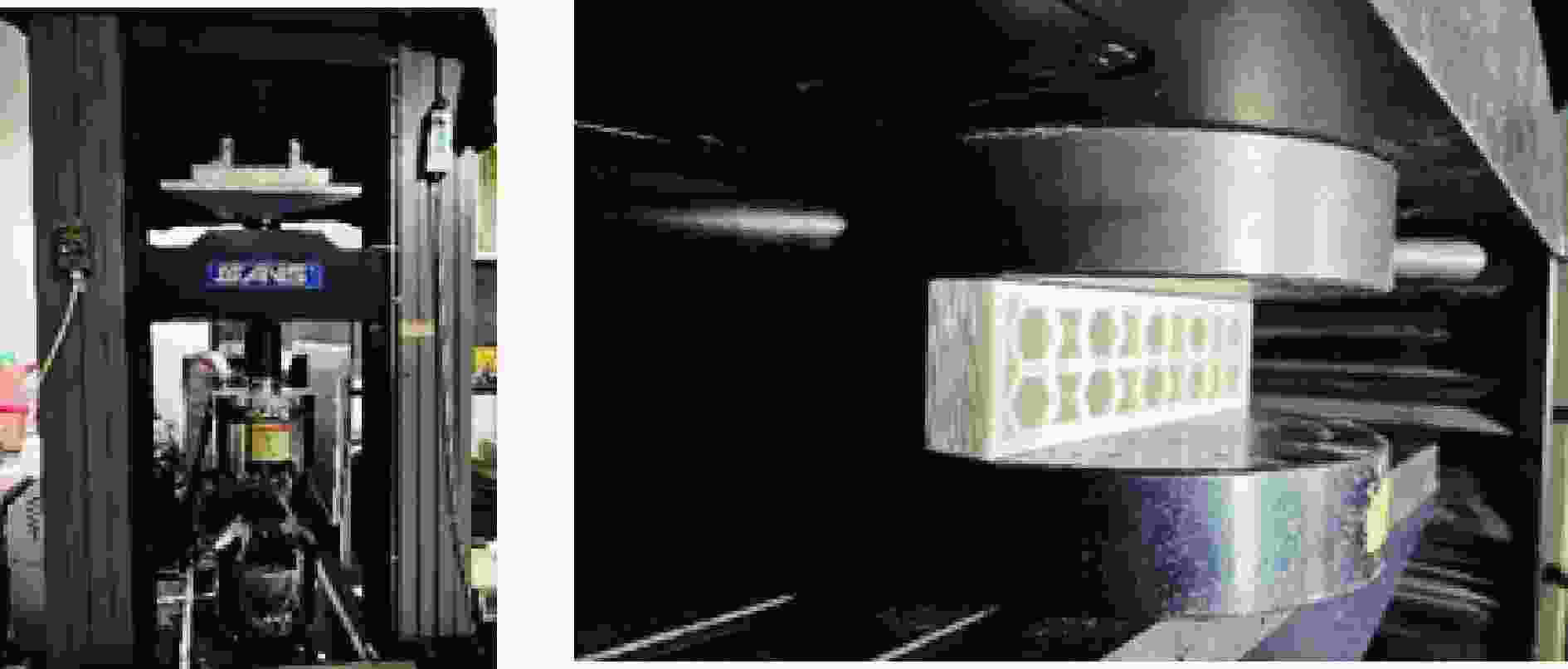
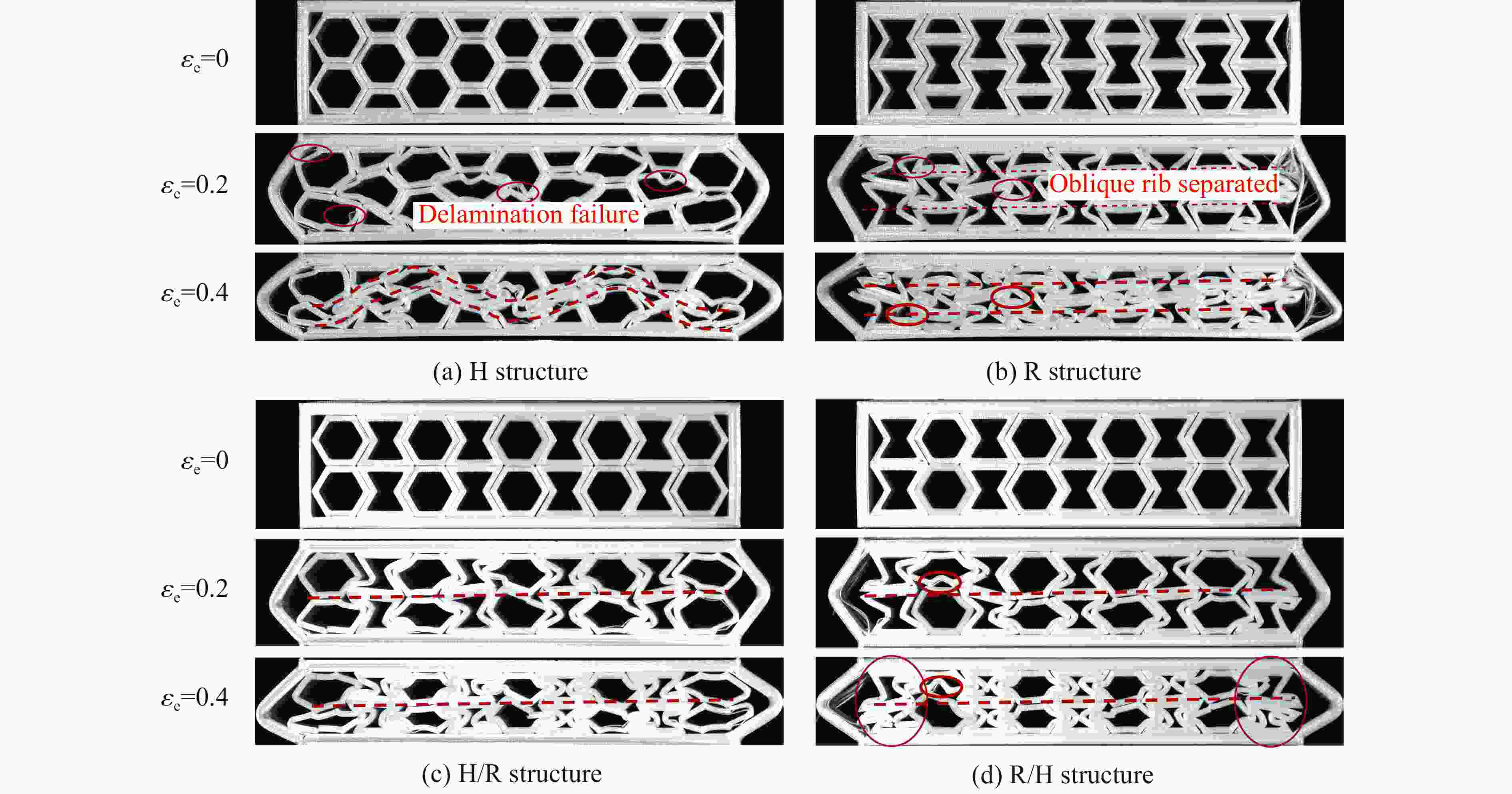
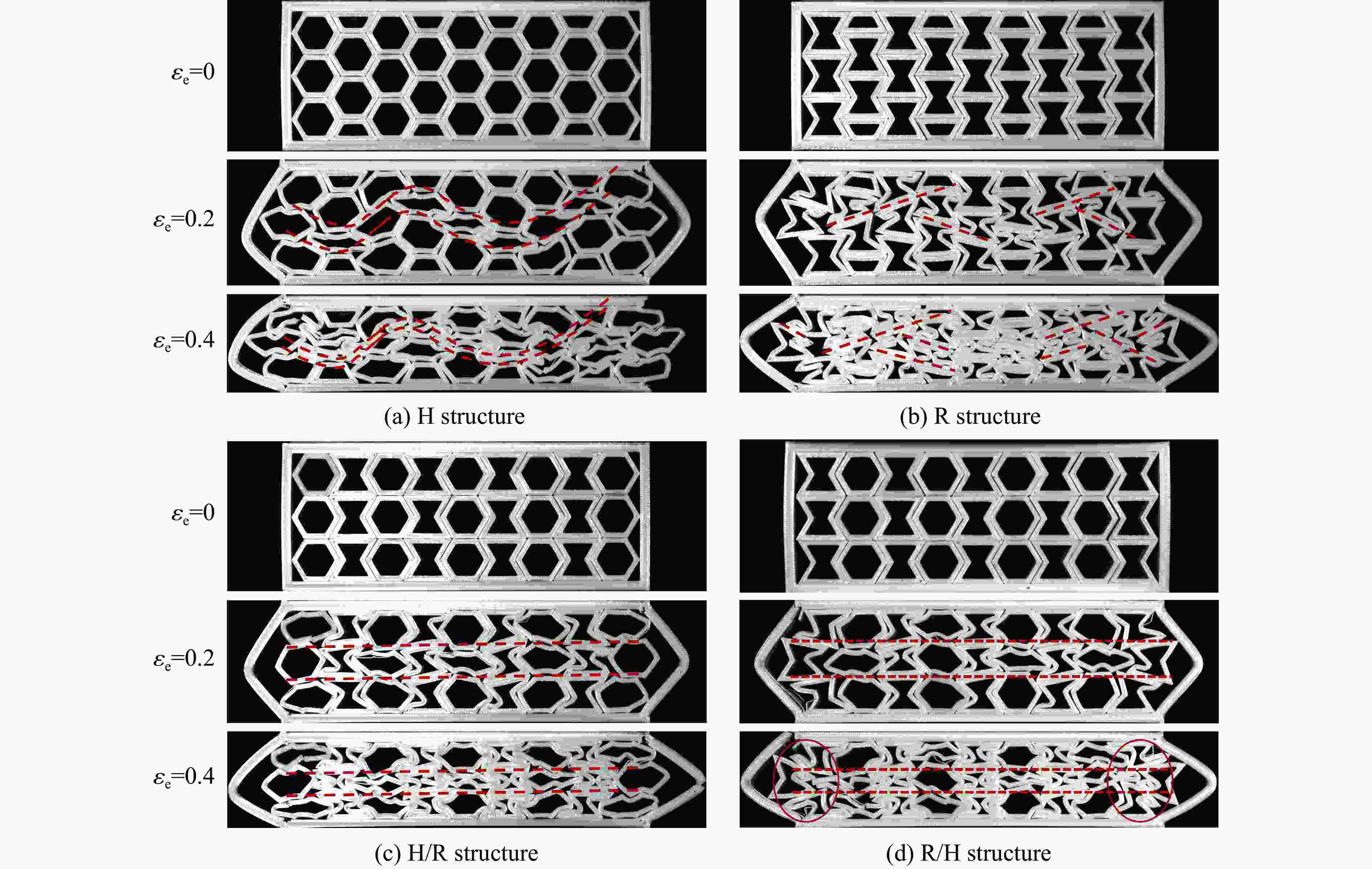
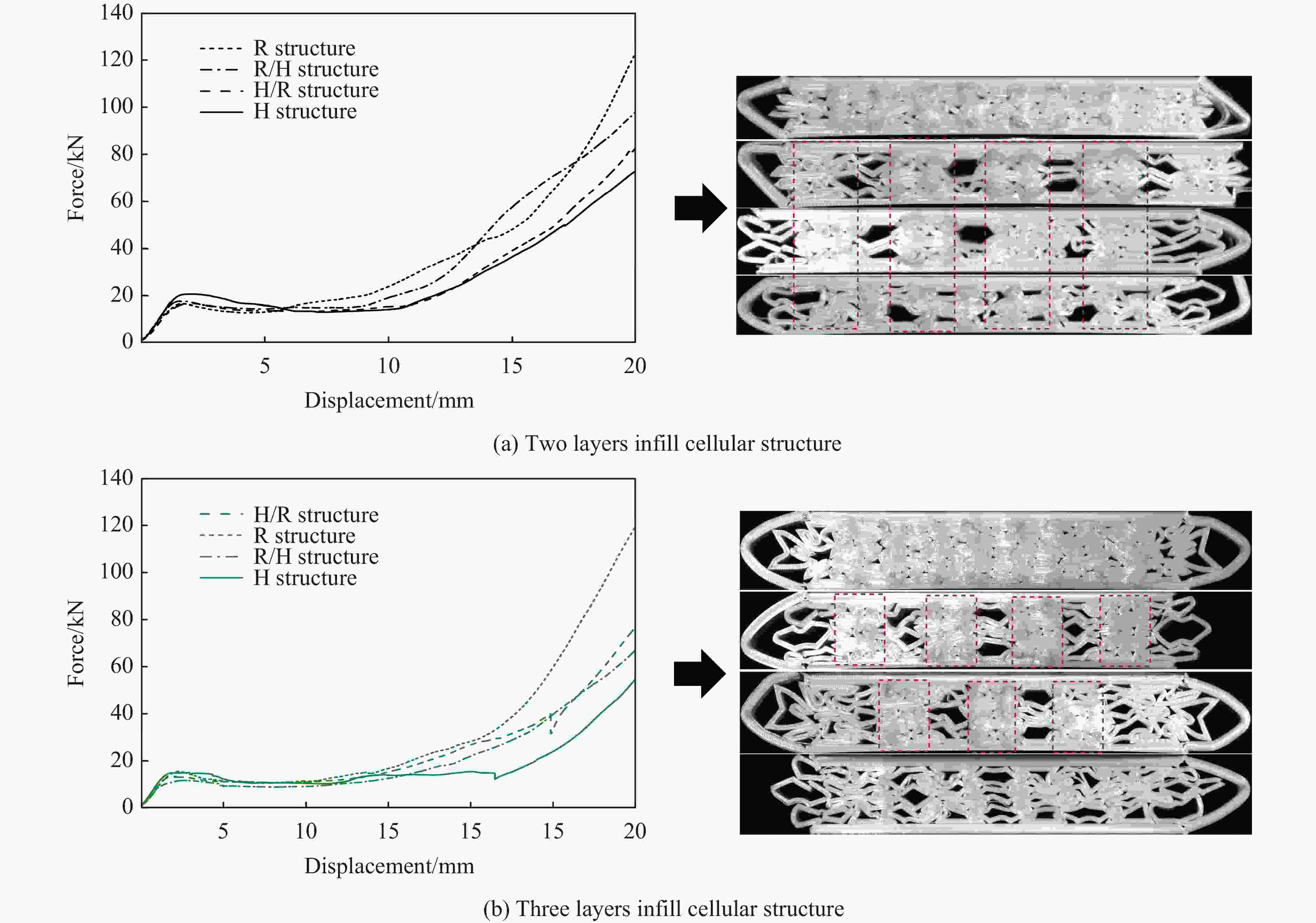
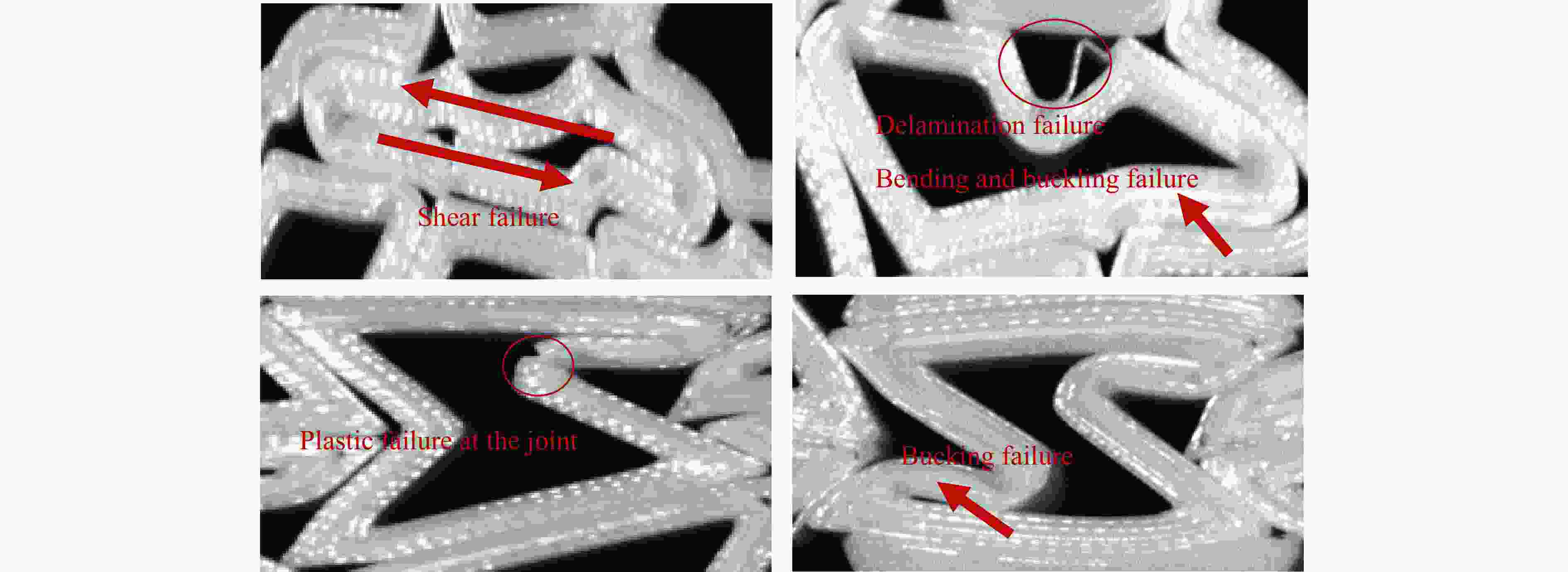
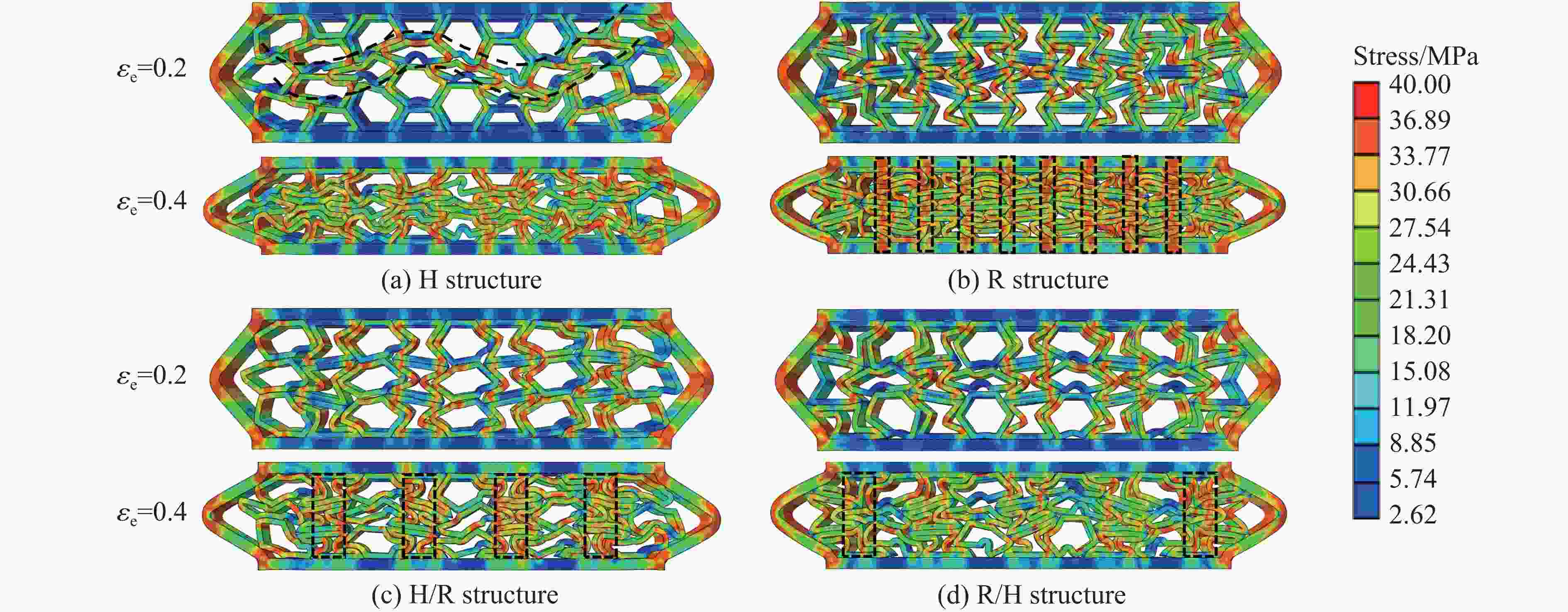
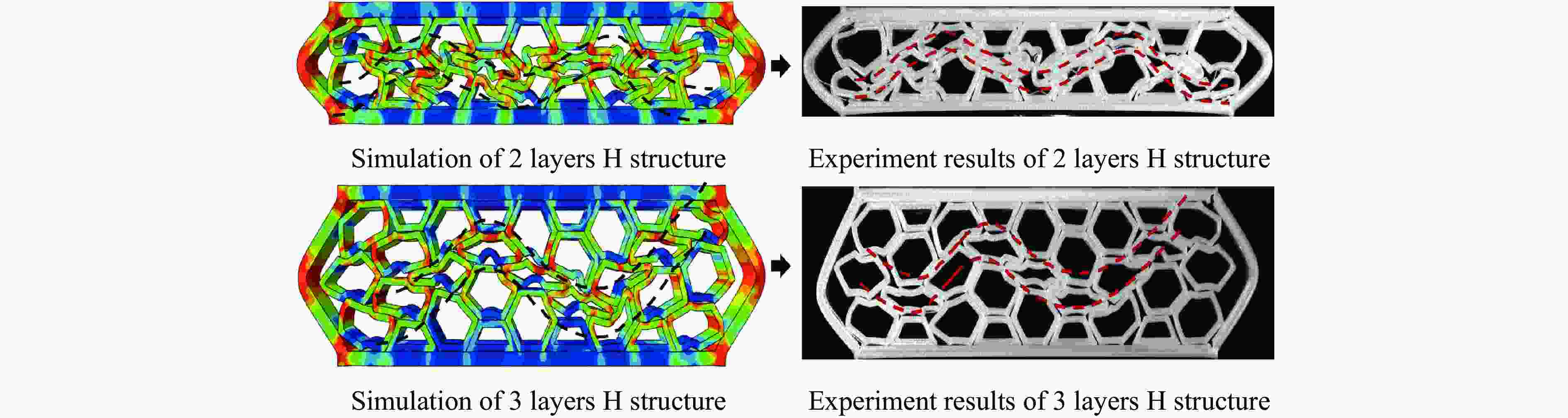
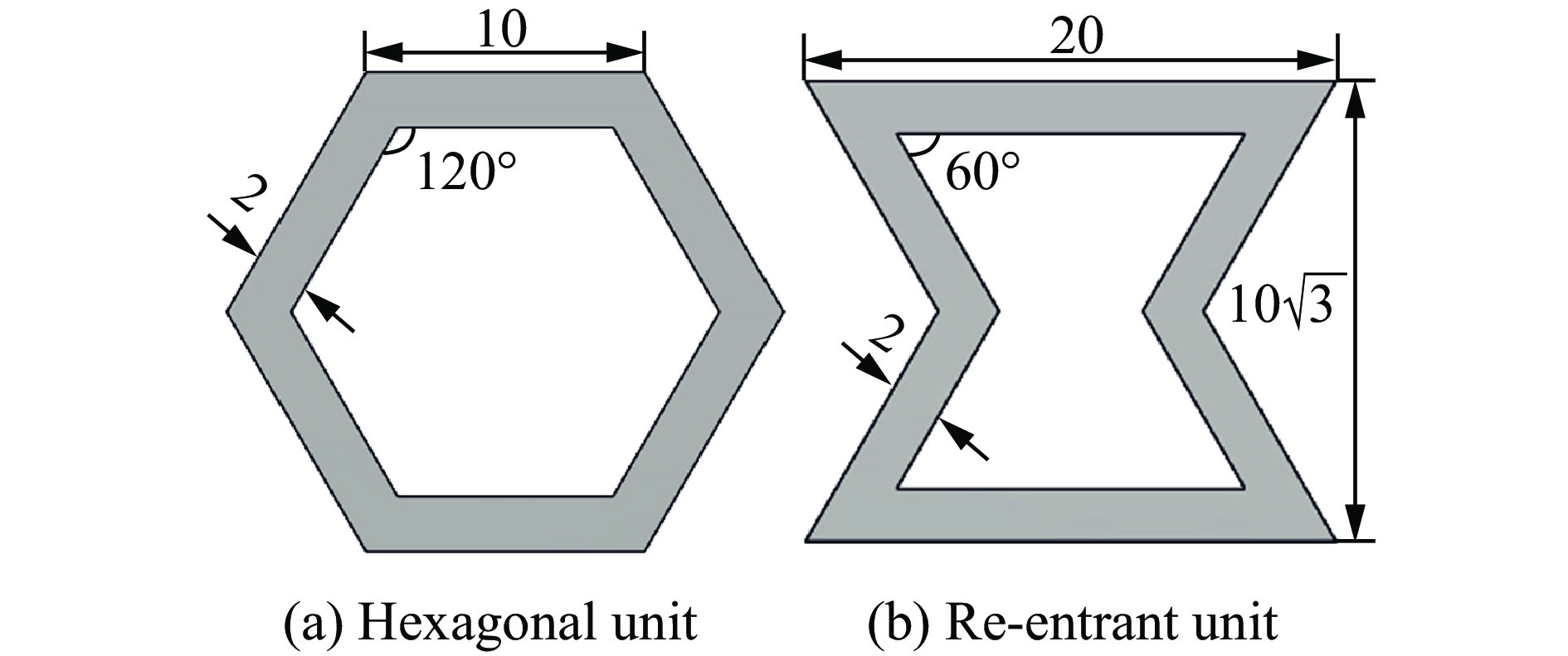
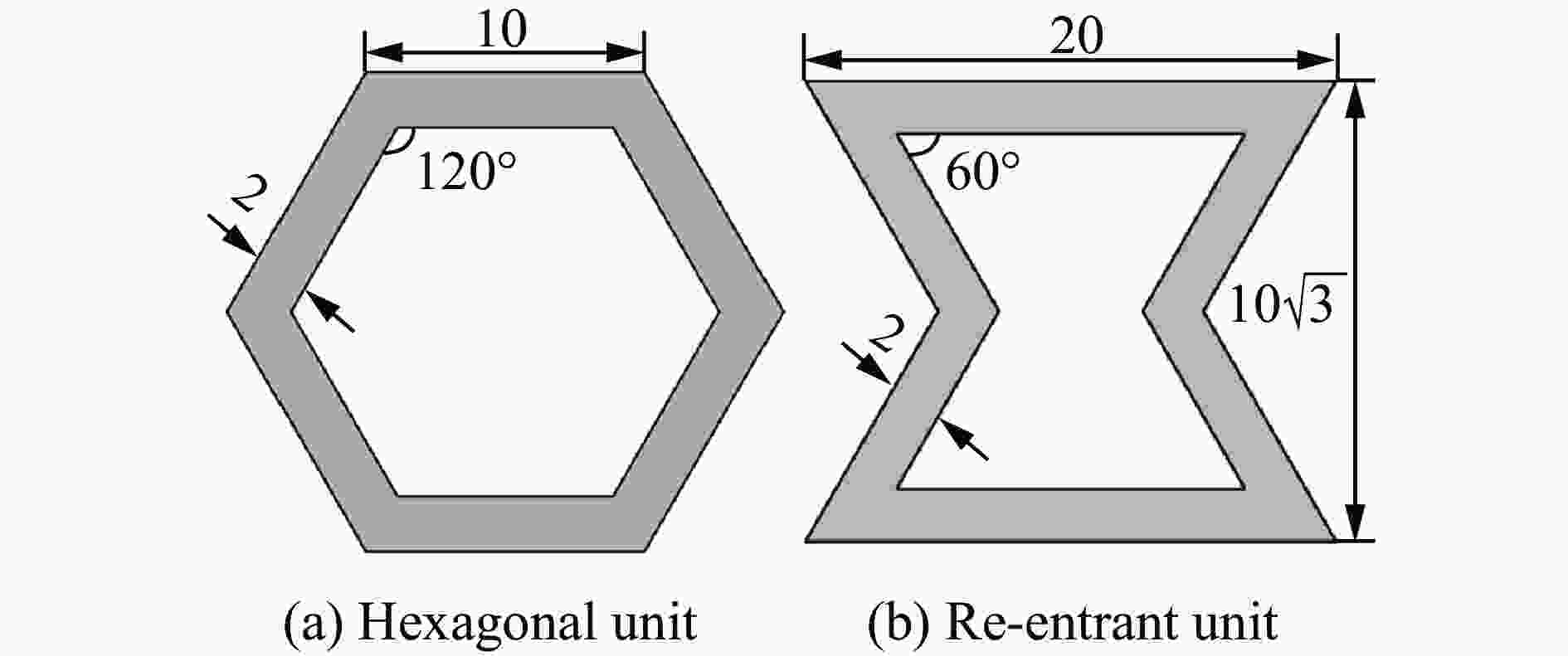
摘要: 模块化多孔结构相较于传统一体式结构能够更加灵活地满足装配需求,研究其变形模式和吸能特性,可为多孔结构在工程中的应用提供新思路。选用具有正泊松比效应的正六边形和具有负泊松比效应的内凹形作为模块化多孔结构的填充单元,共设计了8种结构,并进行了准静态压缩实验。实验结果与有限元模拟计算结果吻合良好。研究发现:不同填充方式的结构具有不同的变形模式,其中正六边形填充表现出明显的剪切破坏带,交替填充能较好地保持单元的初始形状;2层填充多孔结构的压缩力峰值均大于3层填充结构,2层结构的比吸能也大于对应的3层填充结构;正六边形填充结构的总吸能、平均压缩力和比吸能在4种填充方式中均最小;内凹形填充结构的总吸能和平均压缩力均最大,且其比吸能保持在稳定且较高的水平。Abstract: Compared with the traditional integrated structures, modularized cellular structures can meet the assembly requirements more flexibly. The deformation modes and energy absorption were studied to provide new ideas for the application of cellular structures in engineering, the regular hexagon with positive Poisson’s ratio effect and the re-entrant hexagon with negative Poisson’s ratio effect were selected as the infill units of the modularized cellular structures in this paper, and eight kinds of structures were designed for quasi-static compression experiments. The experimental results were in good agreement with the simulation results. The cellular structures with different infill approaches had different deformation modes under the compression experiments, in which the regular hexagon infill units showed obvious shear failure bands, and the alternate infill approaches can maintain the original units shape. The peak force of the two-layer infill cellular structures were greater than the three-layer infill structures, and the specific absorption energy were greater than the corresponding three-layer infill structures. The total absorption energy, average compression force and specific absorption energy of the hexagon infill structures were always the smallest among the four infill approaches, while the total absorption energy and average compression force of the re-entrant hexagon infill structures were always the largest and the specific absorption energy was kept at a stable and high level.
-
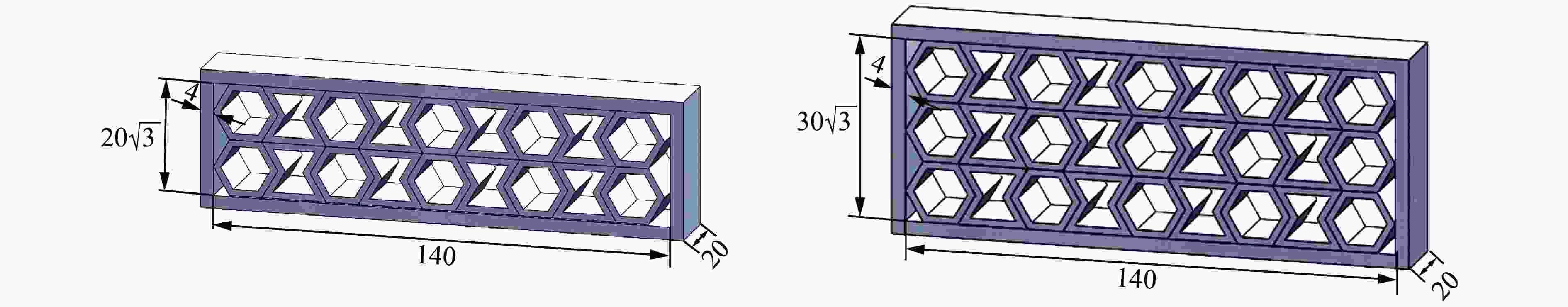
表 1 8种多孔结构的内部填充
Table 1. Internal infill of eight cellular structures
Layer number Structural style H R H/R R/H 2 



3 



表 2 8种多孔结构的吸能指标
Table 2. Energy absorption index of eight cellular structures
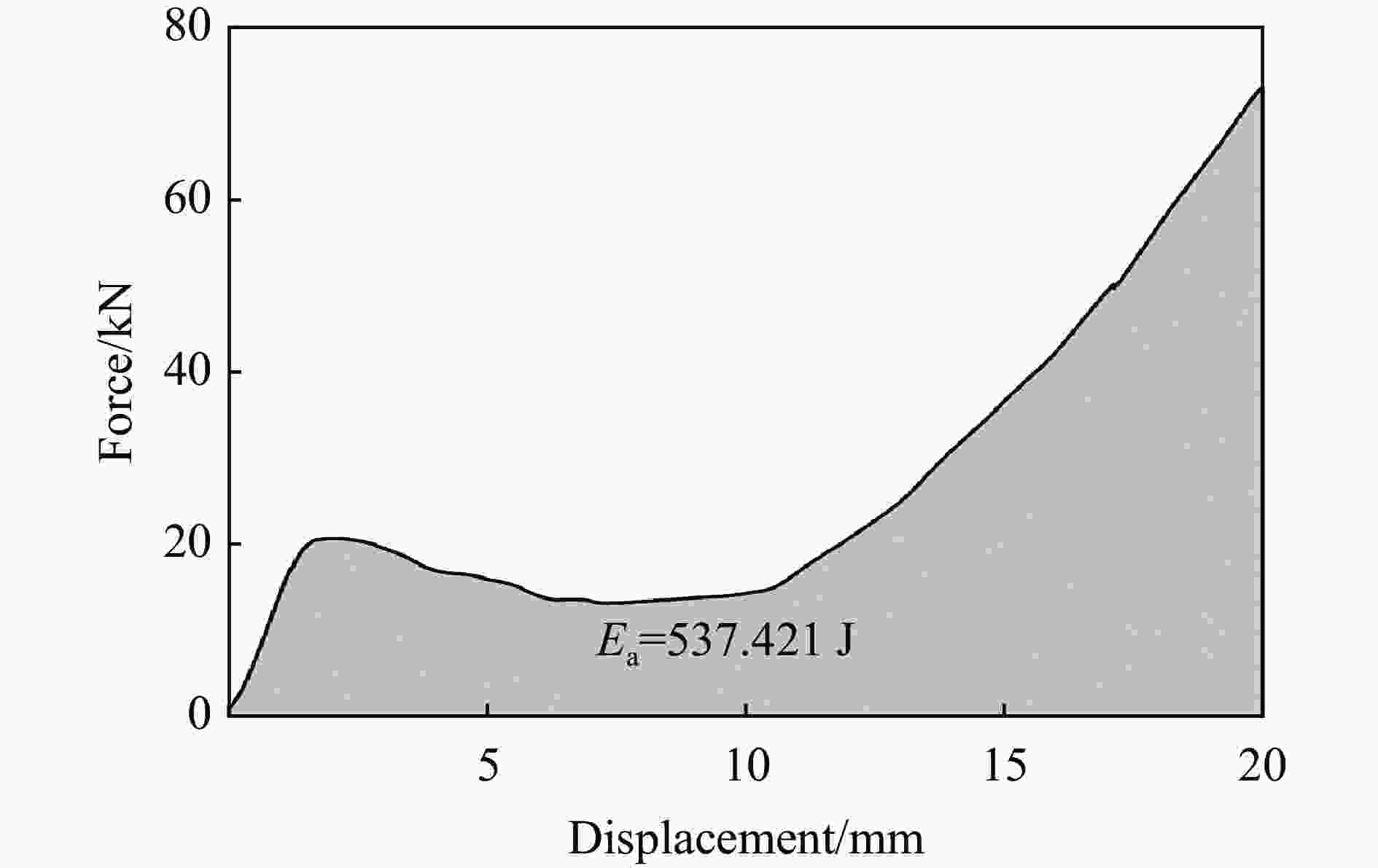
Structure Layer Ea/J Esa/(J·g−1) Fp/kN Fa/kN H 2 537.421 6.796 20.676 26.871 R 730.291 7.373 16.635 36.515 H/R 550.843 6.445 16.774 27.542 R/H 693.729 7.853 17.780 34.687 H 3 540.071 4.728 15.236 18.002 R 948.612 7.263 15.576 31.620 H/R 719.230 6.164 13.764 23.974 R/H 647.934 5.396 11.957 21.598 -
[1] BABAEI M, KIARASI F, ASEMI K, et al. Functionally graded saturated porous structures: a review [J]. Journal of Computational Applied Mechanics, 2022, 53(2): 297–308. doi: 10.22059/jcamech.2022.342710.719 [2] YANG B S, CHEN W H, XIN R L, et al. Pomelo peel-inspired 3D-printed porous structure for efficient absorption of compressive strain energy [J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2022, 19(2): 448–457. doi: 10.1007/s42235-021-00145-1 [3] AJAJ R M, PARANCHEERIVILAKKATHIL M S, AMOOZGAR M, et al. Recent developments in the aeroelasticity of morphing aircraft [J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2021, 120: 100682. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2020.100682 [4] CHOWDHURY S, YADAIAH N, PRAKASH C, et al. Laser powder bed fusion: a state-of-the-art review of the technology, materials, properties & defects, and numerical modelling [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 20: 2109–2172. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.121 [5] 张欣茹, 邓庆田, 李新波, 等. 预制裂纹参数及相对密度对平面多孔结构裂纹扩展的影响 [J]. 实验力学, 2023, 38(1): 68–80. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-22-057ZHANG X R, DENG Q T, LI X B, et al. Influences of prefabricated crack parameters and relative density on crack propagation in planar cellular structures [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2023, 38(1): 68–80. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-22-057 [6] ZHANG X R, DENG Q T, LI X B. Effects of damage mode on crack propagation pattern in additively manufactured honeycomb cellular panel [J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2023, 23(5): 2090–2104. doi: 10.1007/s11668-023-01749-x [7] SHIVARAM M J, ARYA S B, NAYAK J, et al. Role of porosity on electrochemical corrosion behavior of porous Ti-20Nb-5Ag alloy in simulated body fluid [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 33: 5257–5261. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.952 [8] 李振, 丁洋, 王陶, 等. 新型并联梯度蜂窝结构的面内力学性能 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(1): 155–163. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190417.003LI Z, DING Y, WANG T, et al. In-plane crushing behaviors of honeycombs with a novel parallel graded design [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(1): 155–163. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190417.003 [9] MA N F, DENG Q T, LI X B. Deformation behaviors and energy absorption of composite re-entrant honeycomb cylindrical shells under axial load [J]. Materials, 2021, 14(23): 7129. doi: 10.3390/ma14237129 [10] LI T, DENG Q T, LI X B. Energy absorption and deformation modes of several thin-walled tubes under dynamic compression [J]. Structures, 2023, 54: 890–897. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2023.05.099 [11] 王雪松, 刘卫东, 刘典. 新型反四手性蜂窝结构的面内拉伸弹性 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(8): 4849–4861. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20221107.003WANG X S, LIU W D, LIU D. In-plane tensile elasticity of a novel anti-tetrachiral cellular structure [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(8): 4849–4861. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20221107.003 [12] JIAO C X, YAN G. Design and elastic mechanical response of a novel 3D-printed hexa-chiral helical structure with negative Poisson’s ratio [J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 212: 110219. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110219 [13] ZHOU H Y, JIA K C, WANG X J, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of low velocity impact response of foam concrete filled auxetic honeycombs [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 154: 106898. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106898 [14] 尤泽华, 肖俊华, 王美芬. 弧边内凹蜂窝负泊松比结构的力学性能 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7): 3570–3580. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210729.003YOU Z H, XIAO J H, WANG M F. Mechanical properties of arc concave honeycomb structure with negative Poisson’s ratio [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(7): 3570–3580. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210729.003 [15] 卢子兴, 王欢, 杨振宇, 等. 星型-箭头蜂窝结构的面内动态压溃行为 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8): 1893–1900. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180908.001LU Z X, WANG H, YANG Z Y, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing of star-arrowhead honeycomb structure [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(8): 1893–1900. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180908.001 [16] 杨泽水, 薛玉祥, 刘爱荣. 三维负泊松比星型结构冲击动力学研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2022, 39(Suppl 1): 356–363. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.05.S057YANG Z S, XUE Y X, LIU A R. Study on the impact dynamics of three-dimensional star-shaped structure with negative Poisson’s ratio [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2022, 39(Suppl 1): 356–363. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.05.S057 [17] GUO M F, YANG H, ZHOU Y M, et al. Mechanical properties of 3D hybrid double arrow-head structure with tunable Poisson’s ratio [J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 119: 107177. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.107177 [18] 田新宇, 邓庆田, 李新波, 等. 多孔工字梁的准静态压缩稳定性及能量吸收性能 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(4): 044103. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230657TIAN X Y, DENG Q T, LI X B, et al. Quasi-static compression stability and energy absorption performance of cellular I-beam [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(4): 044103. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230657 [19] 王博, 张雄, 徐胜利. 2D周期蜂窝结构面内静动态压缩力学行为研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2009, 41(2): 274–281. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2009-2-2007-400WANG B, ZHANG X, XU S L. Mechanical behavior of 2D periodic honeycombs under in-plane uniaxial compression [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2009, 41(2): 274–281. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2009-2-2007-400 [20] 龙凯, 谷先广, 韩丹. 考虑泊松效应的材料/结构一体化设计方法 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(6): 1252–1260. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20161024.001LONG K, GU X G, HAN D. A concurrent design method for microstructures of materials and macrostructures by considering the Poisson effect [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(6): 1252–1260. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20161024.001 [21] BATES S R G, FARROW I R, TRASK R S. 3D printed polyurethane honeycombs for repeated tailored energy absorption [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 112: 172–183. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.08.062 [22] ZHOU J, LIU H B, DEAR J P, et al. Comparison of different quasi-static loading conditions of additively manufactured composite hexagonal and auxetic cellular structures [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2023, 244: 108054. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.108054 [23] LI Y, CHEN Z H, XIAO D B, et al. The dynamic response of shallow sandwich arch with auxetic metallic honeycomb core under localized impulsive loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 137: 103442. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103442 [24] LUO H C, REN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanical properties of foam-filled hexagonal and re-entrant honeycombs under uniaxial compression [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 280: 114922. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114922 [25] OH J H, KIM J S, NGUYEN V H, et al. Auxetic graphene oxide-porous foam for acoustic wave and shock energy dissipation [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 186: 107817. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107817 -






 下载:
下载: