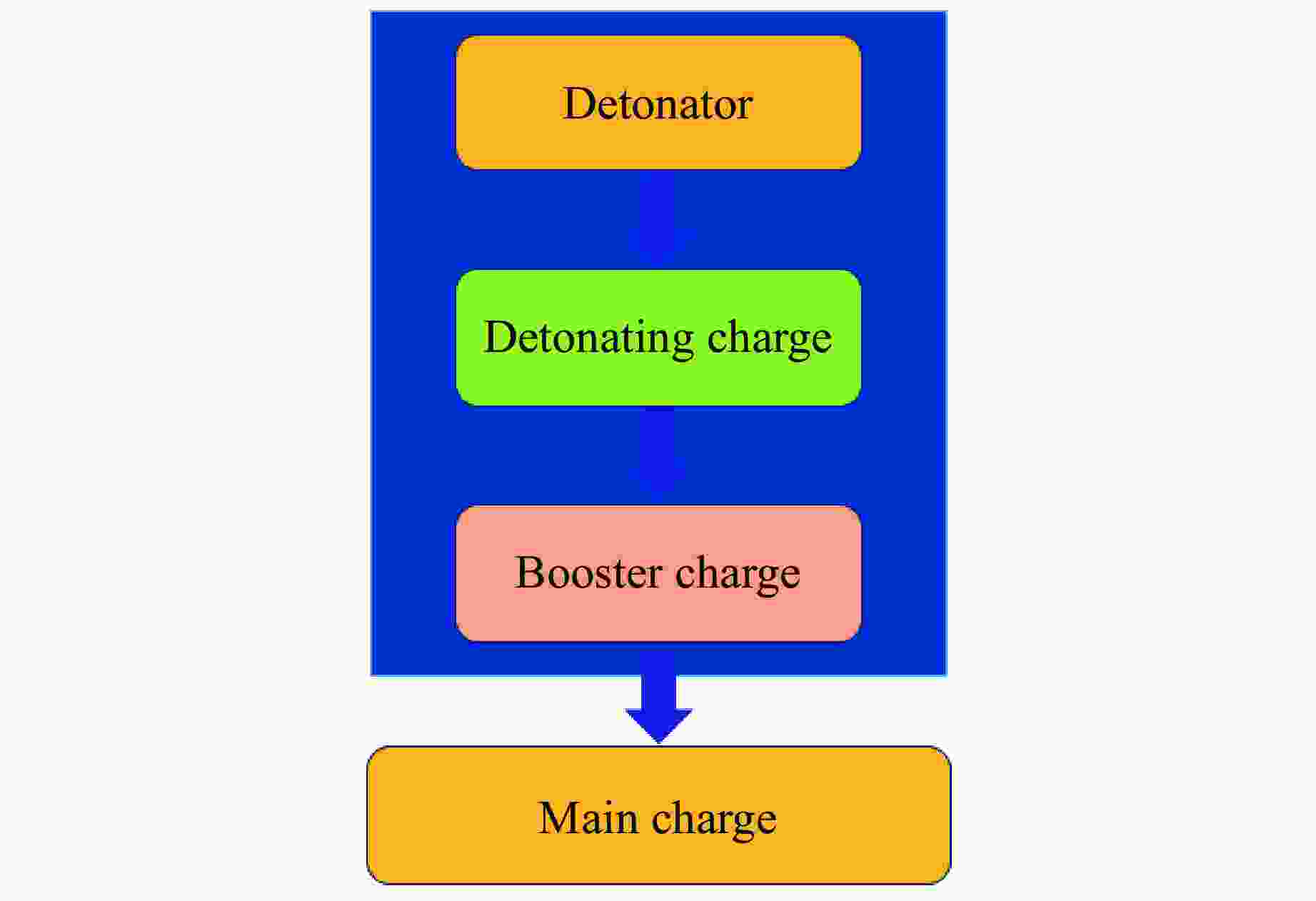
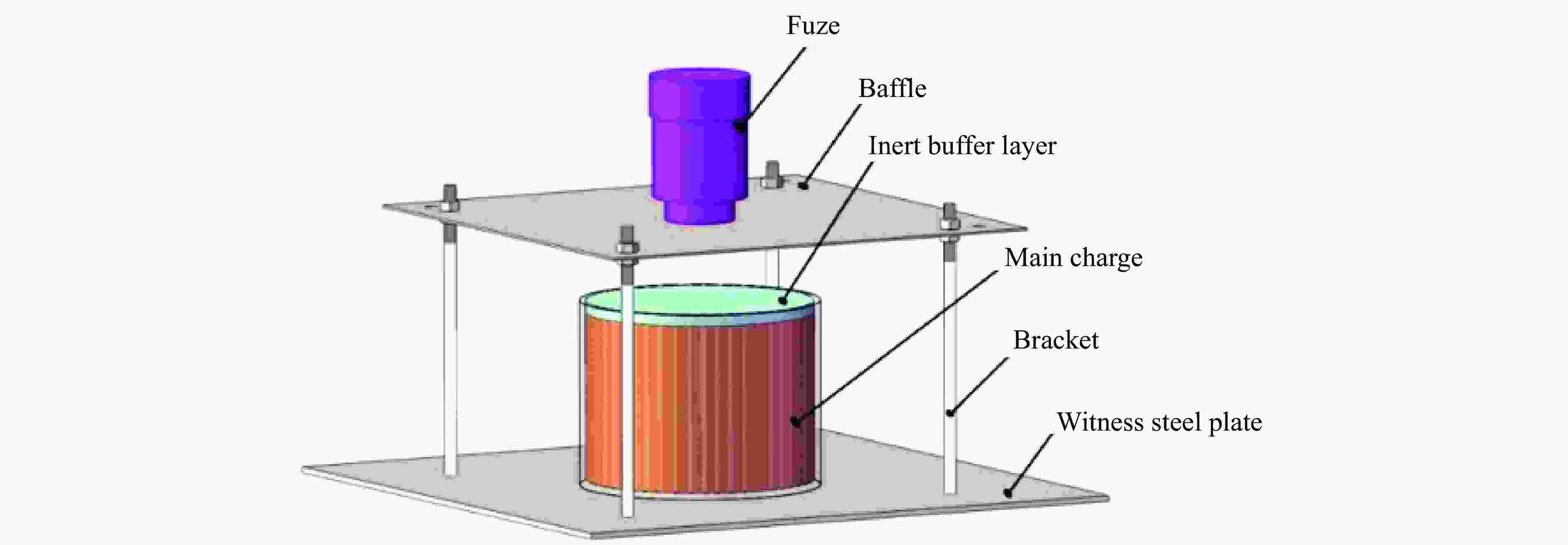
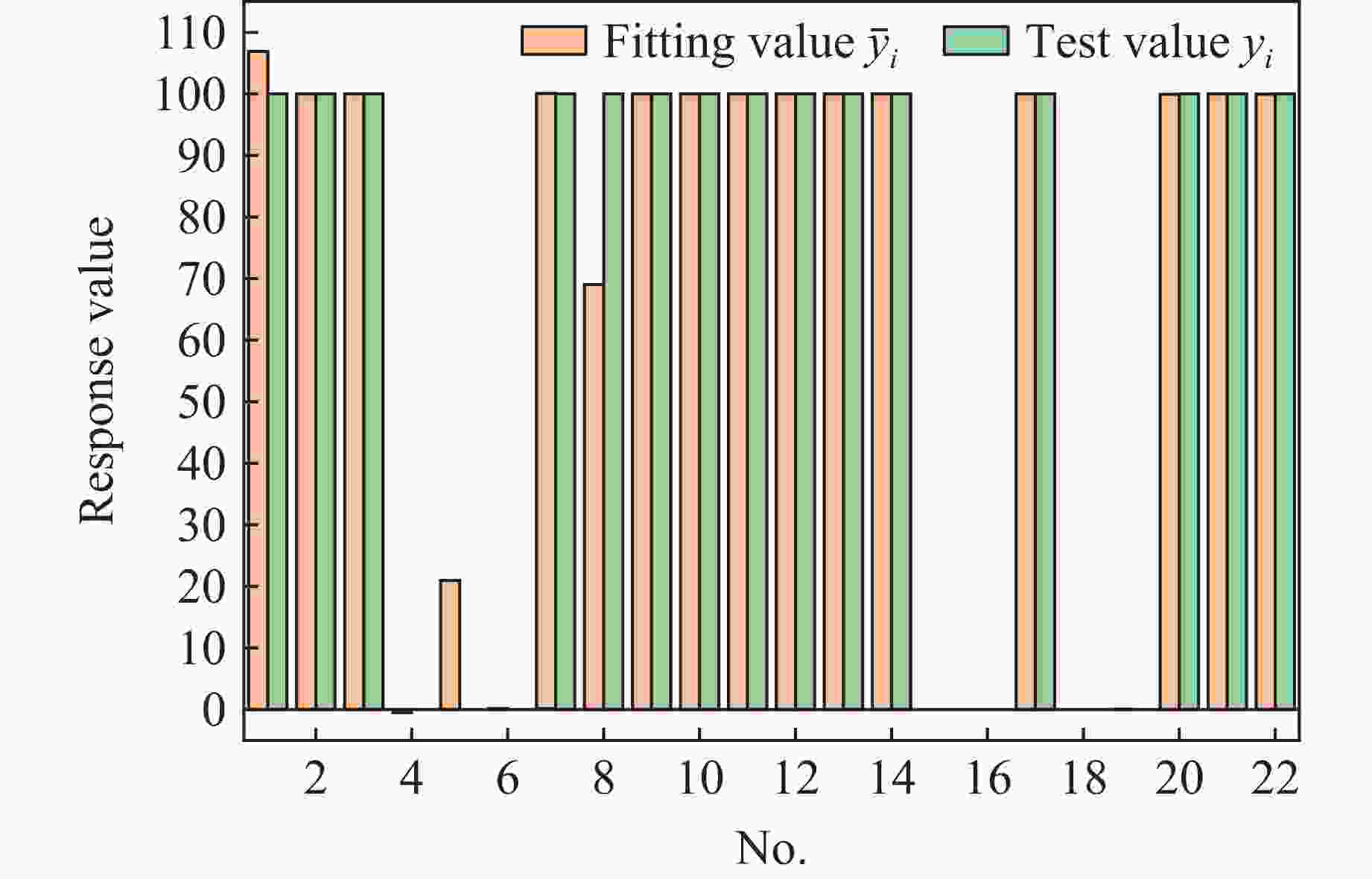
Tests and Sensitive Factors Analysis on Detonation Reliability of Charge for Kinetic Energy Penetrator Warhead
-
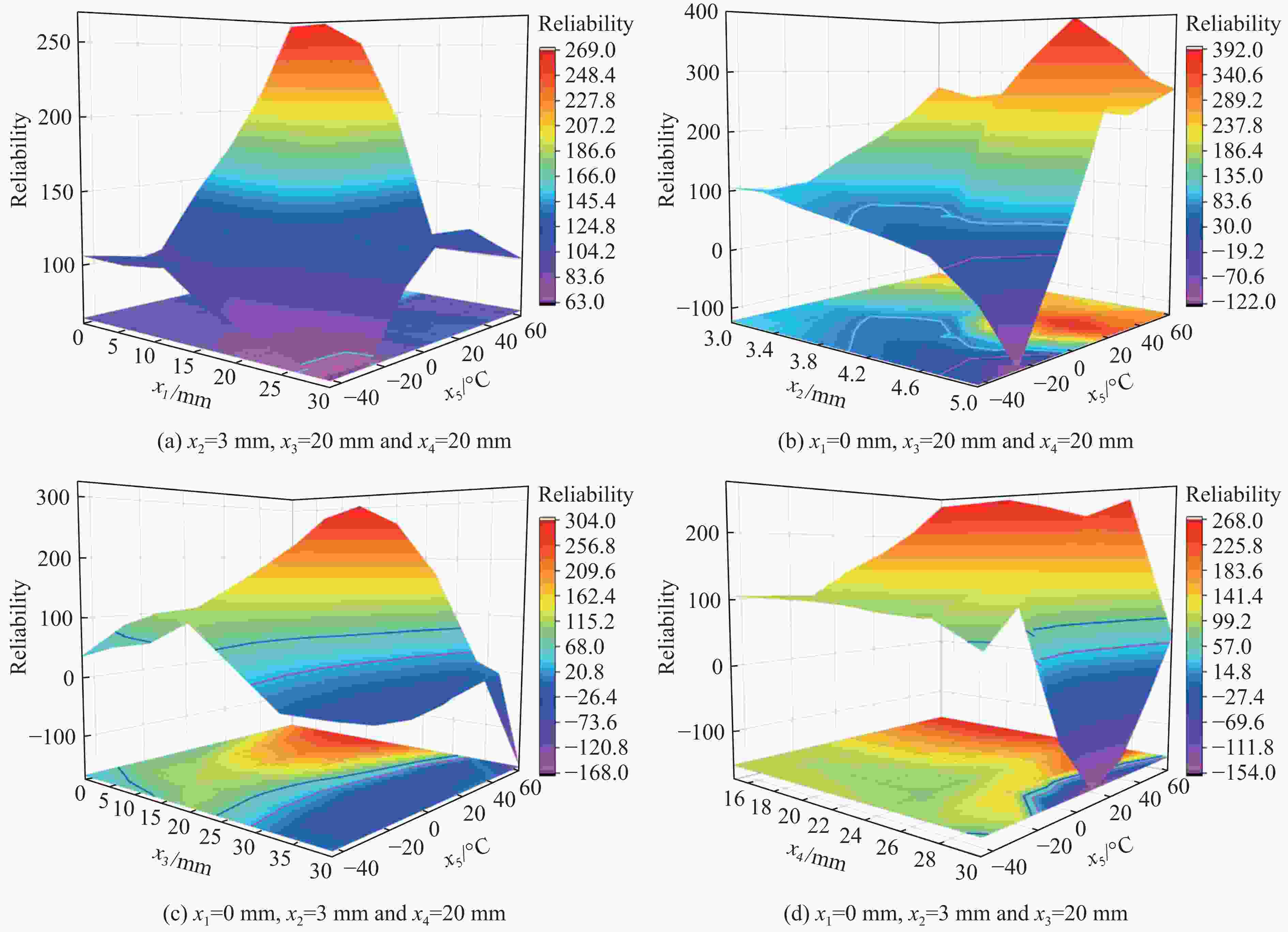
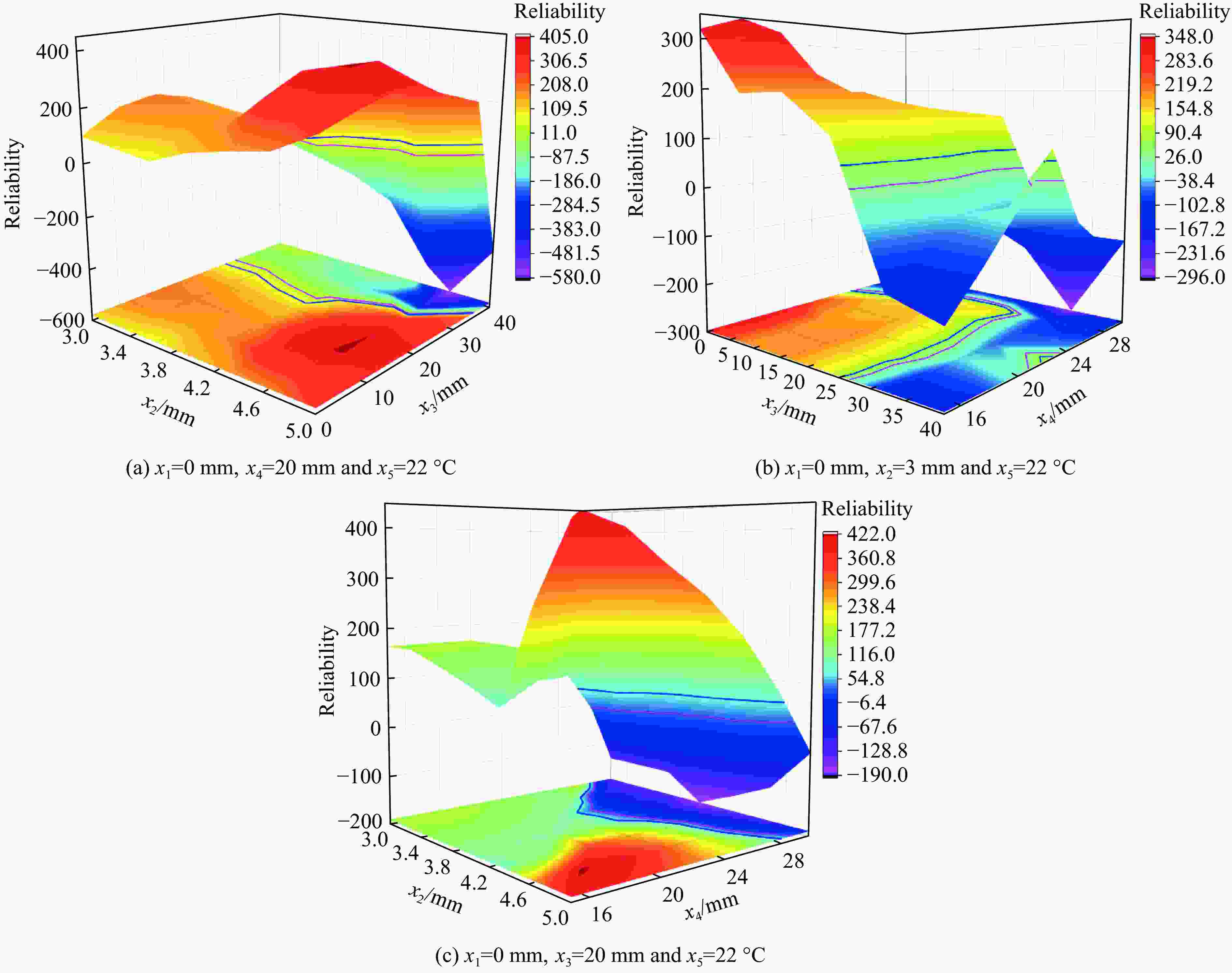
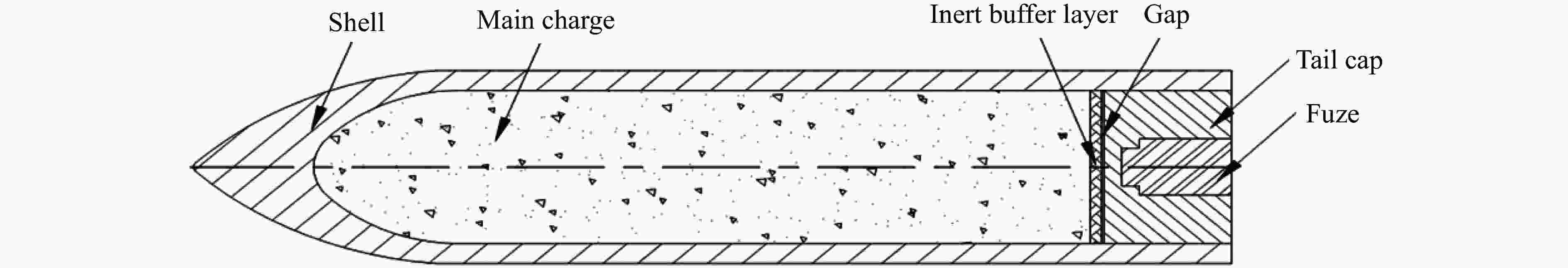
摘要: 为研究弹体结构设计对弹体装药起爆可靠性的影响,设计了一种低成本、便捷式引战静态匹配试验装置,开展了不同条件下引信与装药的传爆裕度试验。基于移动最小二乘法,构建了可表征起爆可靠性的多变量响应函数,定量分析了各敏感因素及其耦合作用对起爆可靠性的影响规律。结果表明:传爆间隙和缓冲层厚度对弹体装药起爆影响较大,而隔板厚度在预设3~5 mm范围内的影响较小;为保证动能侵彻弹在使用环境温度范围内可靠作用,引信相对偏离位置、隔板厚度、传爆间隙以及缓冲层厚度分别不应超过25、3.5、25以及22 mm。该试验装置、分析方法及研究成果可为动能侵彻弹结构设计及可靠性验证提供借鉴和指导。Abstract: In order to investigate the influence of projectile structure design on the detonation reliability, a low-cost and portable static test device for fuze-warhead coordination is designed in this paper to carry out the tests of detonation transfer margin under different conditions. Based on the moving least square method, the multivariable response function is constructed to evaluate the detonation reliability and quantitatively analyze influence of the sensitive factors and coupled effects. The results indicate that the gap distance and the thickness of inert buffer layer have more significant impact on the detonation of the warhead charge while the influence of the interlayer thickness is relatively small within the preset range of 3–5 mm. To ensure the reliability of kinetic energy penetrators under ambient temperature, the relative position of fuze, the interlayer thickness, the gap distance and the thickness of inert buffer layer should not exceed 25, 3.5, 25, and 22 mm, respectively. The test device, analysis method and research results will provide a good reference and guideline for structural design and reliability verification of kinetic energy penetrators.
-
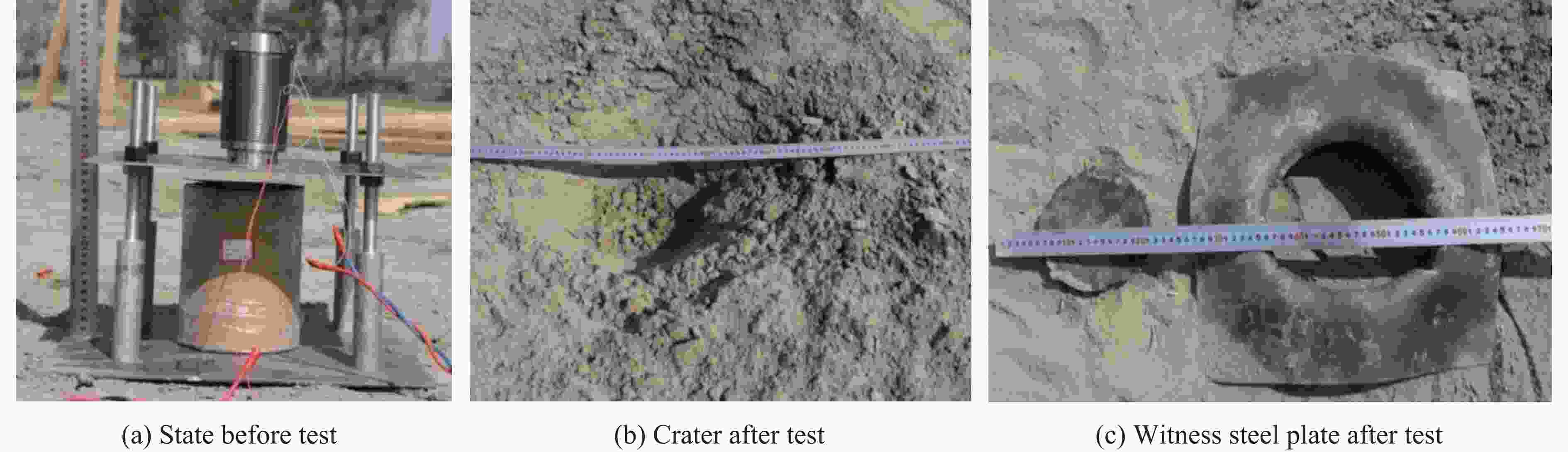
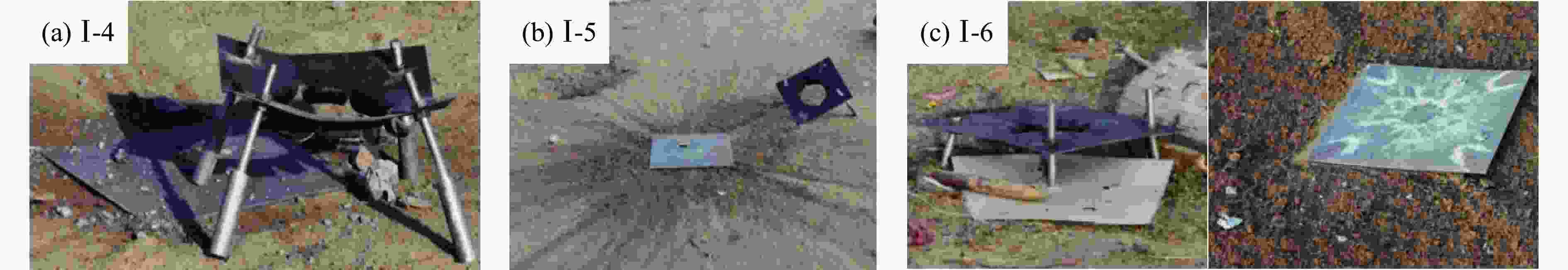
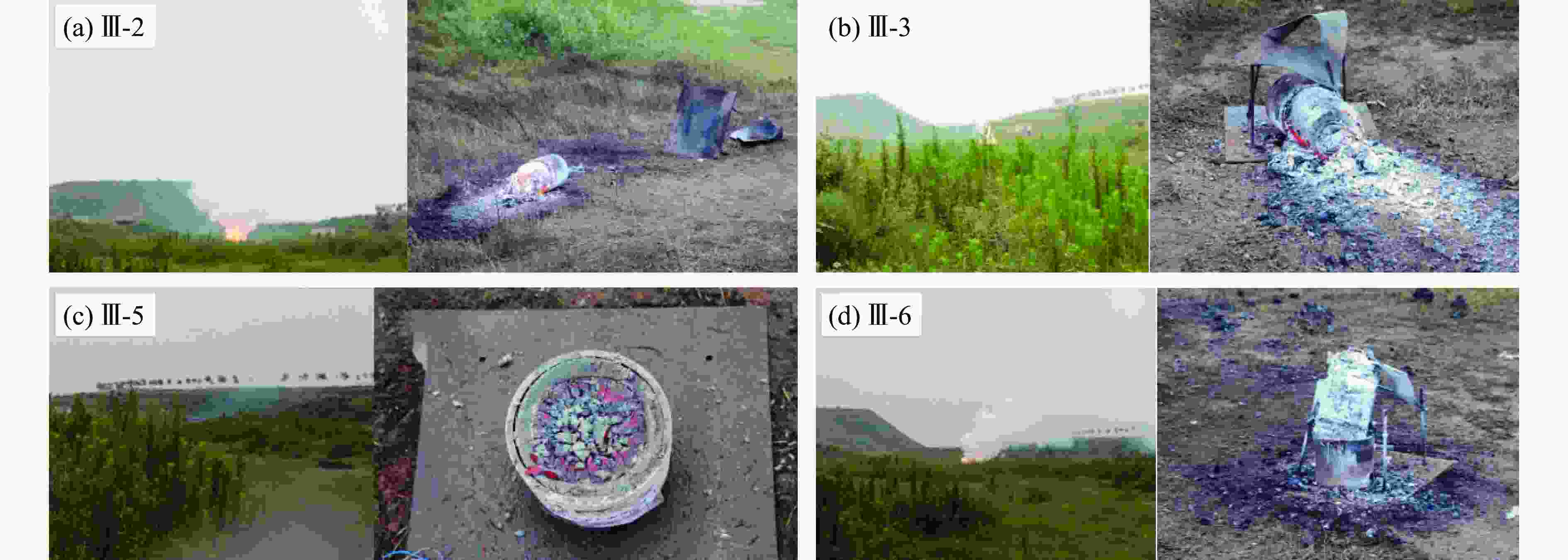
表 1 不同条件下传爆裕度试验的测试结果
Table 1. Test results of the detonation transfer margin under different conditions
Case Relative position
of fuze/mmThickness of interlayer/mm Distance of gap/mm Thickness of inert buffer layer/mm Temperature/℃ Result Ⅰ -1 0 3 20 20 –45 Detonation Ⅰ -2 0 3 20 20 22 Detonation Ⅰ -3 0 3 30 20 60 Detonation Ⅰ -4 0 3 40 20 –45 Unexploded Ⅰ -5 0 3 30 20 –45 Unexploded Ⅰ -6 0 3 30 20 22 Unexploded Ⅰ -7 0 3 25 20 22 Detonation Ⅰ -8 0 3 25 20 –45 Detonation Ⅱ -1 30 3 30 15 22 Detonation Ⅱ -2 30 3 40 15 22 Detonation Ⅱ -3 30 3 30 15 –45 Detonation Ⅱ -4 30 3 40 15 –45 Detonation Ⅱ -5 30 3 30 15 60 Detonation Ⅲ -1 30 5 20 20 60 Detonation Ⅲ -2 30 5 20 25 60 Unexploded Ⅲ -3 0 5 5 30 60 Unexploded Ⅲ -4 30 5 30 15 60 Detonation Ⅲ -5 0 5 0 30 –45 Unexploded Ⅲ -6 30 5 20 20 –45 Unexploded Ⅲ -7 30 5 20 15 –45 Detonation Ⅳ -1 30 5 20 15 22 Detonation Ⅳ -2 30 5 20 20 22 Detonation -
[1] 高伟亮, 孙桂娟, 杨建超, 等. 国外钻地武器侵彻试验用弹等效模拟技术研究 [J]. 防护工程, 2022, 44(5): 21–25.GAO W L, SUN G J, YANG J C, et al. Research on equivalent simulation technology of a foreign Earth-penetrating weapon trial projectile [J]. Protective Engineering, 2022, 44(5): 21–25. [2] 党爱国, 李晓军. 国外钻地武器发展回顾及展望 [J]. 飞航导弹, 2014(6): 35–39.DANG A G, LI X J. Review and prospect of the development of foreign Earth-penetrating weapons [J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2014(6): 35–39. [3] 黄亨建, 路中华, 刘晓波, 等. 欧美钝感弹药技术发展现状与趋势 [J]. 含能材料, 2017, 25(8): 618–621. doi: 10.11943/j.issn.1006-9941.2017.08.00XHUANG H J, LU Z H, LIU X B, et al. Present situation and development trend of insensitive munition technologies from Europe and America [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2017, 25(8): 618–621. doi: 10.11943/j.issn.1006-9941.2017.08.00X [4] 杨舒棋, 张旭, 彭文杨, 等. 钝感炸药冲击起爆反应过程的PDV技术 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(2): 023402. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190856YANG S Q, ZHANG X, PENG W Y, et al. PDV technology of shock initiation reaction process of insensitive explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(2): 023402. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190856 [5] 文雯, 王淑娟, 代晓淦, 等. TATB基PBX及其与HNS复合装药的高速破片撞击安全性 [J]. 含能材料, 2021, 29(5): 399–405. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020163WEN W, WANG S J, DAI X G, et al. High-speed impact safety properties the TATB-based plastic-bonded explosive and its HNS compound charge influence [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2021, 29(5): 399–405. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020163 [6] 黄瑨. CL-20、TATB基复合装药结构的3D打印成型及安全性研究 [D]. 绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2019.HUANG J. A kind of CL-20 and TATB-based composite charge structure by 3D printing technology and its safety study [D]. Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2019. [7] 张百磊, 常双君, 欧亚鹏. 浇注钝感PBX的研究进展及发展趋势 [J]. 化学推进剂与高分子材料, 2015, 13(1): 42–45, 64.ZHANG B L, CHANG S J, OU Y P. Research progress and development trend of casting desensitized PBX [J]. Chemical Propellants & Polymeric Materials, 2015, 13(1): 42–45, 64. [8] 李媛媛, 高立龙, 李巍, 等. 抗过载炸药装药侵彻安全性试验研究 [J]. 含能材料, 2010, 18(6): 702–705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2010.06.021LI Y Y, GAO L L, LI W, et al. Experiment research on security of insensitive explosive charge during penetration [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2010, 18(6): 702–705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2010.06.021 [9] 马田, 李鹏飞, 周涛, 等. 钻地弹动能侵彻战斗部技术研究综述 [J]. 飞航导弹, 2018(4): 83–86, 92.MA T, LI P F, ZHOU T, et al. A review on technology of Earth penetrator warhead [J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2018(4): 83–86, 92. [10] 常龙. 某弹的多功能引信传火及传爆序列结构优化设计 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳理工大学, 2020.CHANG L. Optimization design of multifunctional fuze fire transmission and explosive transmission sequence structure of a projectile [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Ligong University, 2020. [11] 尚雅玲, 彭艳垒, 梁捷. 引信抗大过载技术研究及方案设计 [J]. 舰船电子工程, 2012, 32(6): 121–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2012.06.044SHANG Y L, PENG Y L, LIANG J. Research of fuze resisting high g-load technology and scheme design [J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2012, 32(6): 121–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2012.06.044 [12] 李晓峰, 王亚斌, 吴碧. 侵彻弹药引信技术 [M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2016: 31–37.LI X F, WANG Y B, WU B. Fuze of penetration ammunition [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2016: 31–37. [13] 张波. 空面导弹系统设计 [M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2013: 435–436.ZHANG B. Air-to-surface missile system design [M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2013: 435–436. [14] 陈鹏, 屈可朋, 李亮亮, 等. PBX炸药剪切流动点火性能的实验研究 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2020, 43(1): 69–73, 80.CHEN P, QU K P, LI L L, et al. Experimental study on shear-flow ignition performance of PBX explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives and Propellants, 2020, 43(1): 69–73, 80. [15] 崔银锋, 周伟江, 康乐. 引信传爆序列能量匹配性设计与试验 [J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(3): 337–344. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.03.015CUI Y F, ZHOU W J, KANG L. Design and test of energy matching for detonation train of fuze [J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(3): 337–344. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.03.015 [16] 肖向东, 肖有才, 蒋海燕, 等. 冲击波作用下引信传爆序列殉爆的数值模拟 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(5): 054202. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210706XIAO X D, XIAO Y C, JIANG H Y, et al. Numerical simulation and analysis of fuze explosive trains under shock waves [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(5): 054202. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210706 [17] 姚奎光, 王淑娟, 樊星, 等. 不同机械约束下压装PBX炸药反应演化行为 [J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(8): 1772–1778. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0445YAO K G, WANG S J, FAN X, et al. Reaction evolution behaviors of pressed plastic-bonded explosive (PBX) under different mechanical confinement conditions [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(8): 1772–1778. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0445 [18] 白志玲, 段卓平, 李治, 等. 热刺激约束DNAN基不敏感熔铸炸药装药点火后反应演化调控模型 [J]. 含能材料, 2023, 31(10): 1004–1012. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2023160BAI Z L, DUAN Z P, LI Z, et al. Regulation model for reaction evolution of confined DNAN-based cast explosives after ignition under thermal stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2023, 31(10): 1004–1012. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2023160 [19] 楼建锋, 张树道. 不同点火方式下HMX基PBX炸药反应演化过程的特征分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(2): 022301. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0300LOU J F, ZHANG S D. Characteristic analysis of reaction evolution process of HMX-based PBX explosive under different ignition modes [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(2): 022301. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0300 [20] 张世林, 黎殿来, 黄德雨. 某型深弹引信传爆序列设计与仿真 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2015, 35(3): 58–62.ZHANG S L, LI D L, HUANG D Y. Design and simulation on explosive trains in fuze of a certain type of depth charge bombs [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2015, 35(3): 58–62. [21] 梁争峰, 石震, 徐茜萍, 等. 限制性模块化传爆装置可靠性试验 [J]. 火工品, 2012(1): 7–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2012.01.005LIANG Z F, SHI Z, XU Q P, et al. Reliability test of confined modular detonation transmission device [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2012(1): 7–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2012.01.005 [22] 高金霞, 赵卫刚, 郑腾. 侵彻战斗部装药抗过载技术研究 [J]. 火工品, 2008(4): 4–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2008.04.002GAO J X, ZHAO W G, ZHENG T. Study on the anti-overloading technique for penetrating warhead charge [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2008(4): 4–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2008.04.002 [23] 黄辉, 黄亨建, 王杰, 等. 安全弹药的发展思路与技术途径 [J]. 含能材料, 2023, 31(10): 1079–1087. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2023165HUANG H, HUANG H J, WANG J, et al. Development ideas and technical approaches for safety ammunition [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2023, 31(10): 1079–1087. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2023165 [24] 彭文杨, 钟斌, 谷岩, 等. 金属隔层和空气间隙对钝感炸药冲击起爆的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(3): 033402. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190816PENG W Y, ZHONG B, GU Y, et al. Effects of metal interlayer and air gap on the shock initiation of insensitive explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(3): 033402. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190816 [25] 徐恒威, 梁斌, 刘俊新, 等. 起爆偏心对聚能装药射流成型过程及威力参量的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(1): 015102.XU H W, LIANG B, LIU J X, et al. Effect of initiation eccentricity on shaped charge jet forming process and power parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(1): 015102. [26] 董理赢. 引信传爆序列殉爆反应特性研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020.DONG L Y. Study on the characteristics of the sympathetic detonation reaction in fuze explosive trains [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2020. [27] 田秀琦. 不同环境温度下JO-9C传爆药冲击起爆特性研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020.TIAN X Q. Study on shock initiation characteristics of JO-9C booster at different ambient temperatures [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2020. [28] 金丽, 杨振英, 张玉若, 等. 一种直列式传爆序列的装药传爆性能试验研究 [J]. 含能材料, 2012, 20(1): 105–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2012.01.025JIN L, YANG Z Y, ZHANG Y R, et al. Performance of an in-line explosive trains [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2012, 20(1): 105–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2012.01.025 [29] 梁斌, 石啸海, 余春祥, 等. 装药驱动飞片引爆炸药性能影响参数分析 [J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(8): 893–909.LIANG B, SHI X H, YU C X, et al. Analysis of effects on shock initiation performances for booster charge structure parameters [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(8): 893–909. [30] 欧阳昌明, 段卓平, 孙宝平, 等. 冲击波和破片复合作用下装药起爆实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2013, 33(Suppl 1): 63–66.OUYANG C M, DUAN Z P, SUN B P, et al. Experimental study on initiation of charge under combined shock wave and fragment impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2013, 33(Suppl 1): 63–66. [31] COCHRAN K R, FAN L, DEVOE D L. Moving reflector type micro optical switch for high-power transfer in a MEMS-based safety and arming system [J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2004, 14(1): 138–146. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/14/1/019 [32] 刘卫, 褚恩义, 刘兰, 等. 基于飞片冲击起爆原理的微起爆序列技术研究进展 [J]. 含能材料, 2023, 31(6): 606–634. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2023043LIU W, CHU E Y, LIU L, et al. Review on micro fire-train based on flyer impact initiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2023, 31(6): 606–634. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2023043 [33] LANCASTER P, SALKAUSKAS K. Surfaces generated by moving least squares methods [J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1981, 37(155): 141–158. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1981-0616367-1 [34] QI W C, QIU Z P. A collocation interval analysis method for interval structural parameters and stochastic excitation [J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2012, 55(1): 66–77. doi: 10.1007/s11433-011-4570-z -






 下载:
下载: