Study on Mechanical Properties of Paper Honeycomb Structure at Medium Strain Rates
-
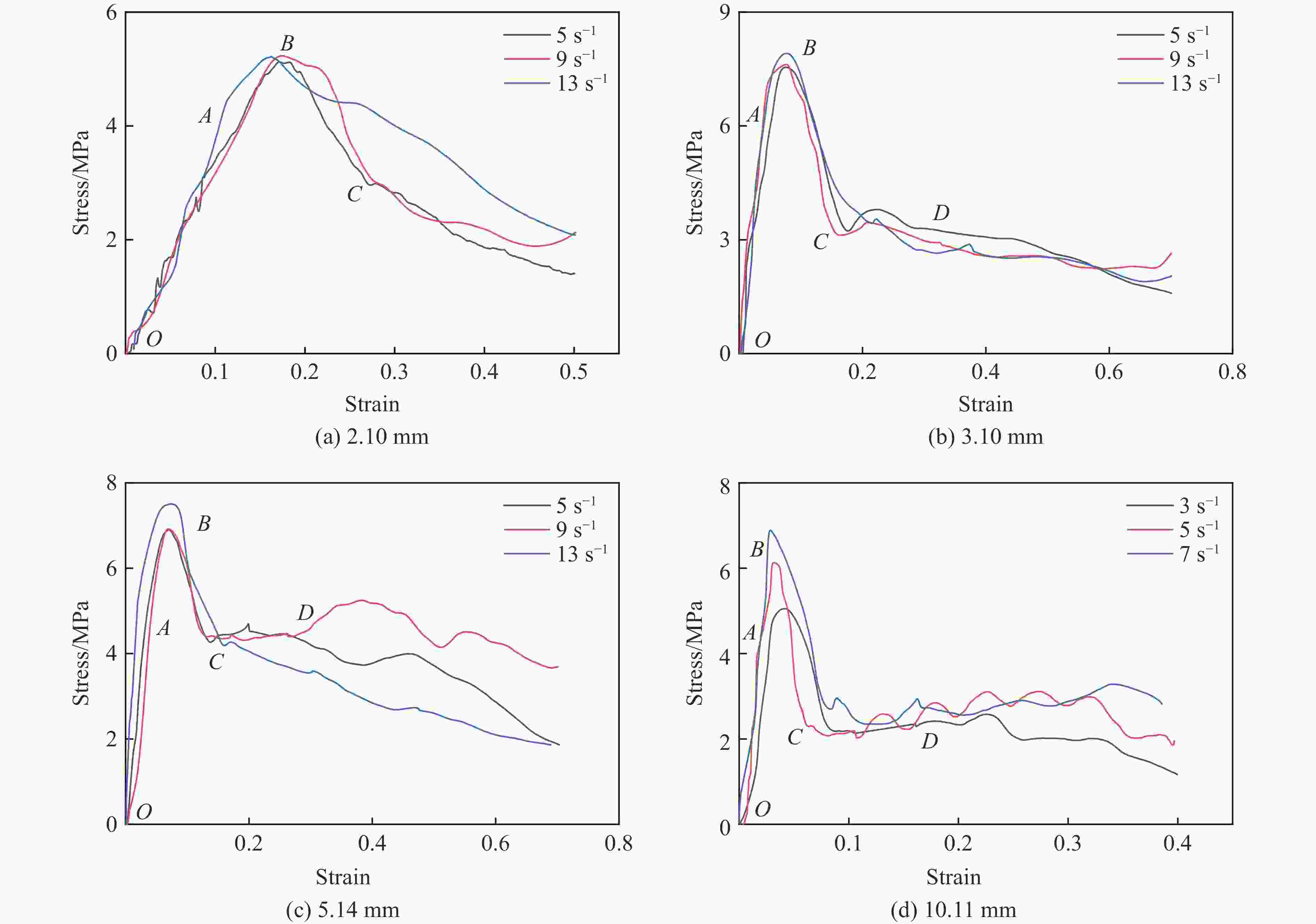
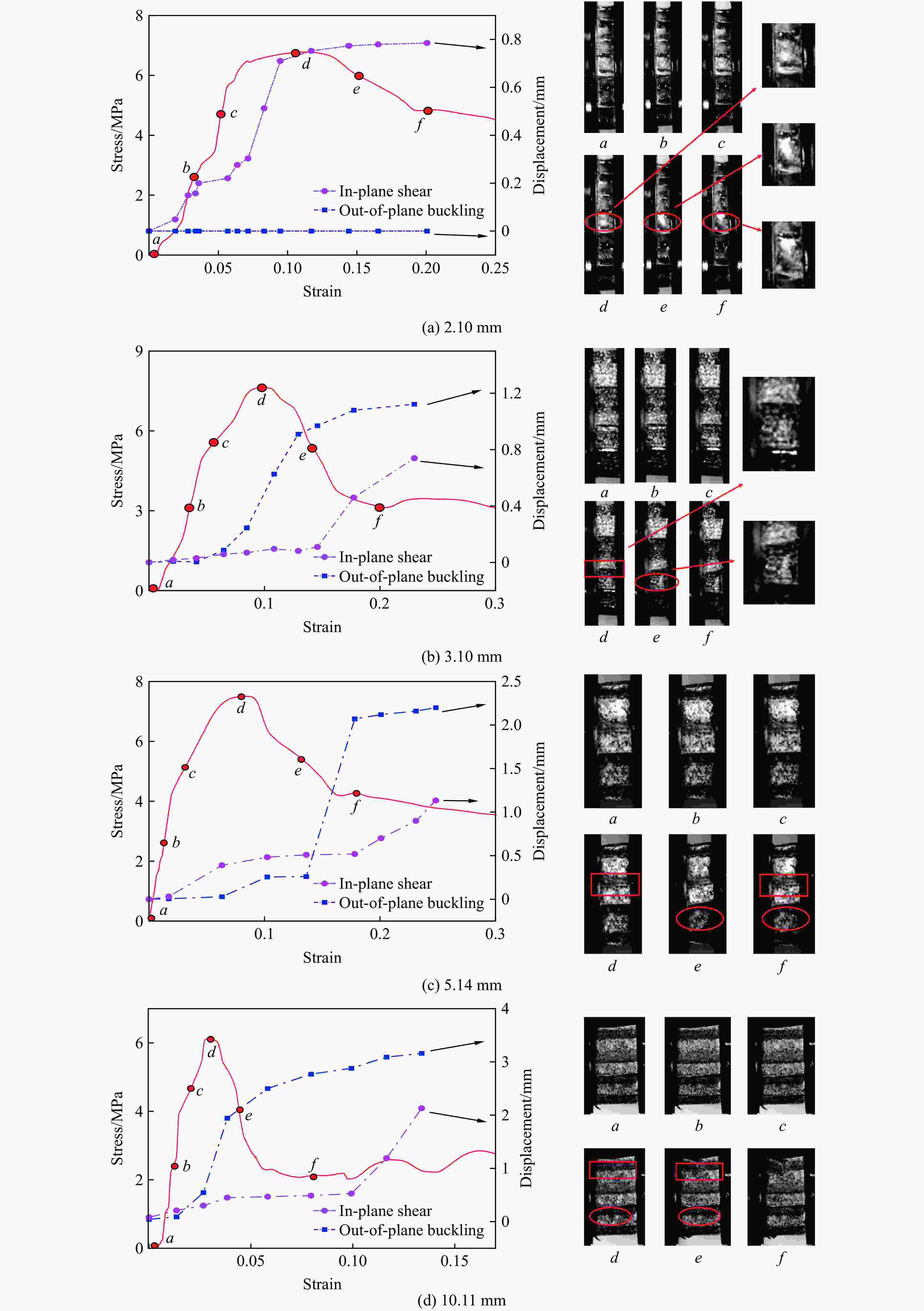
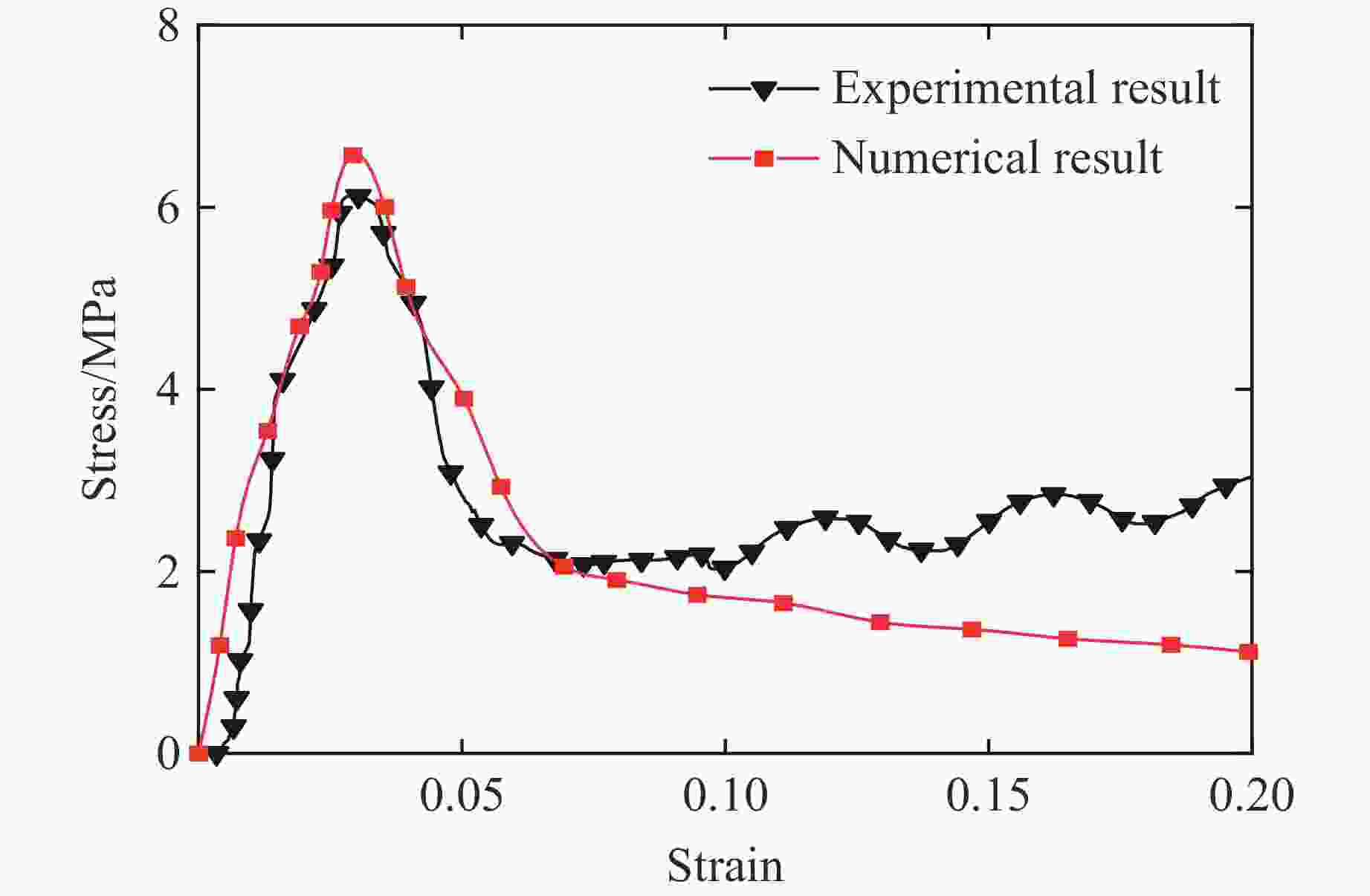
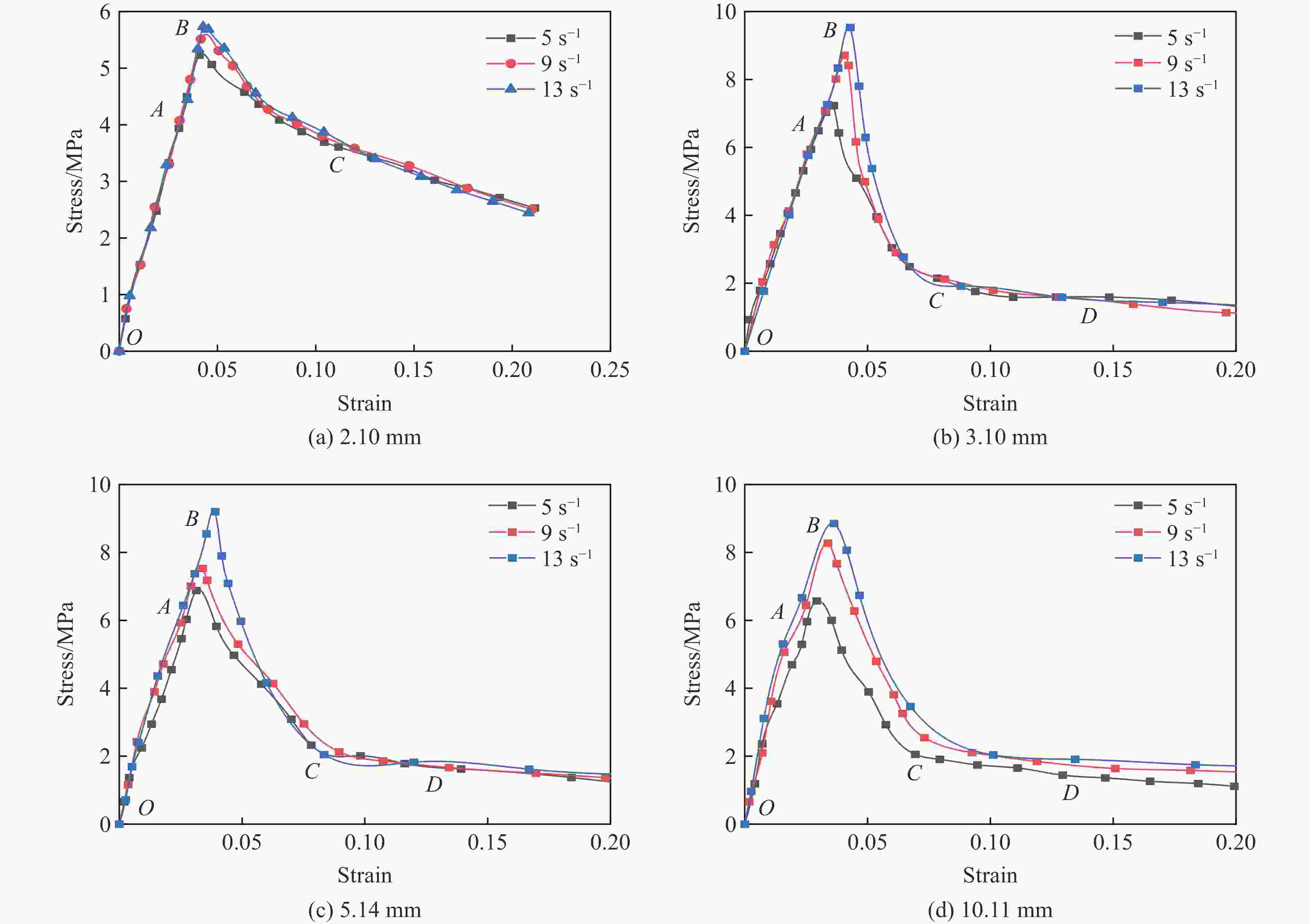
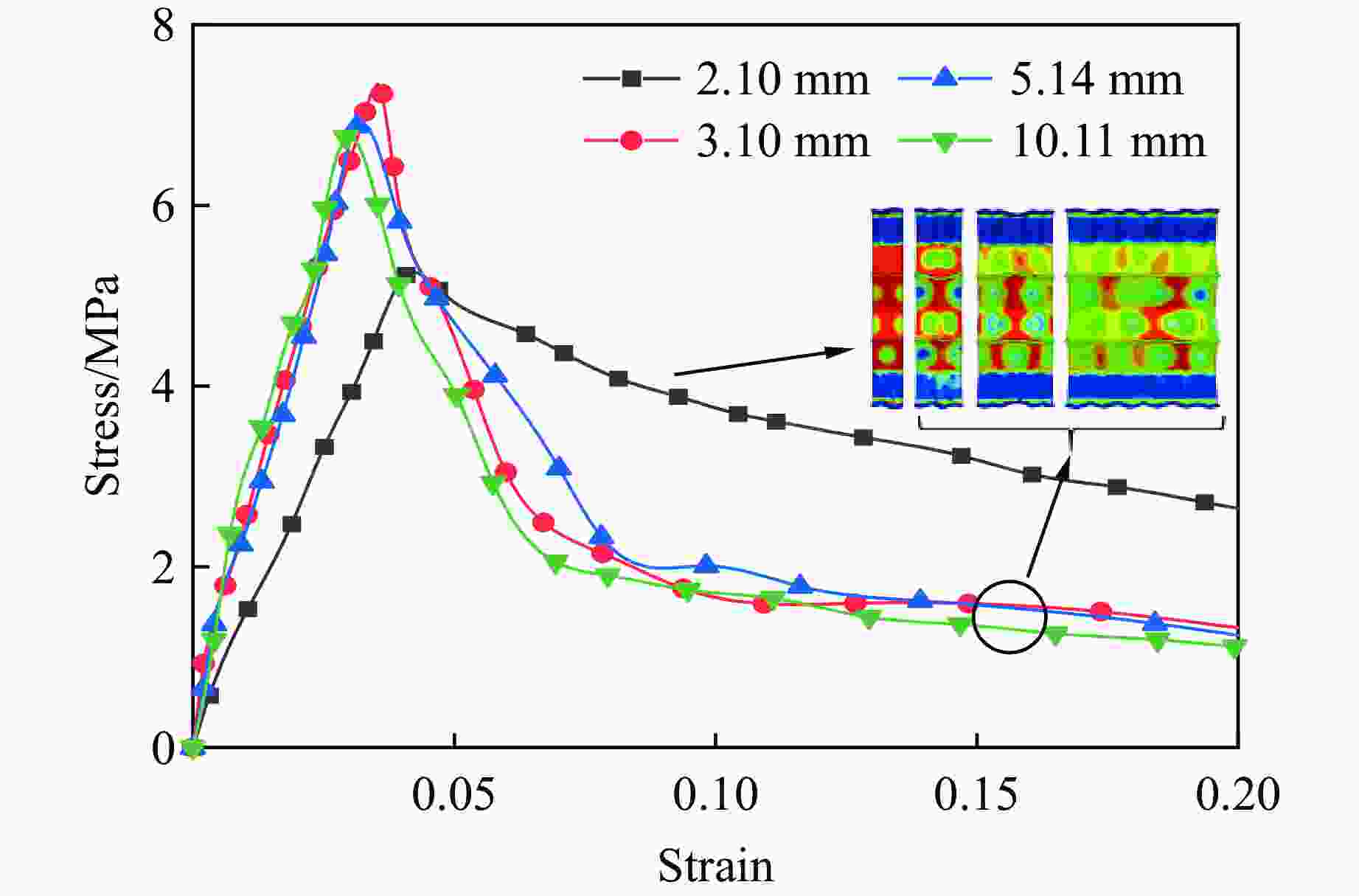
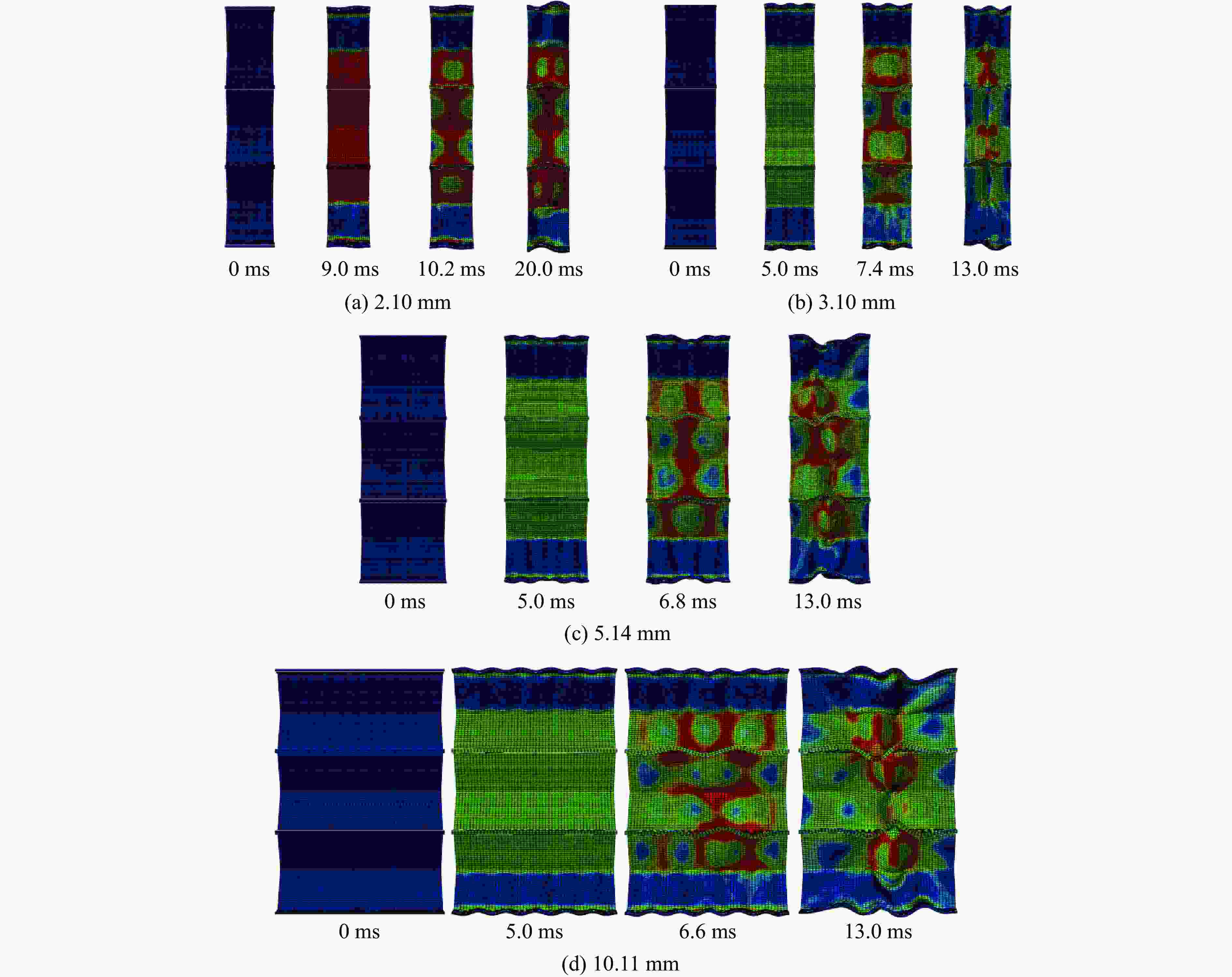
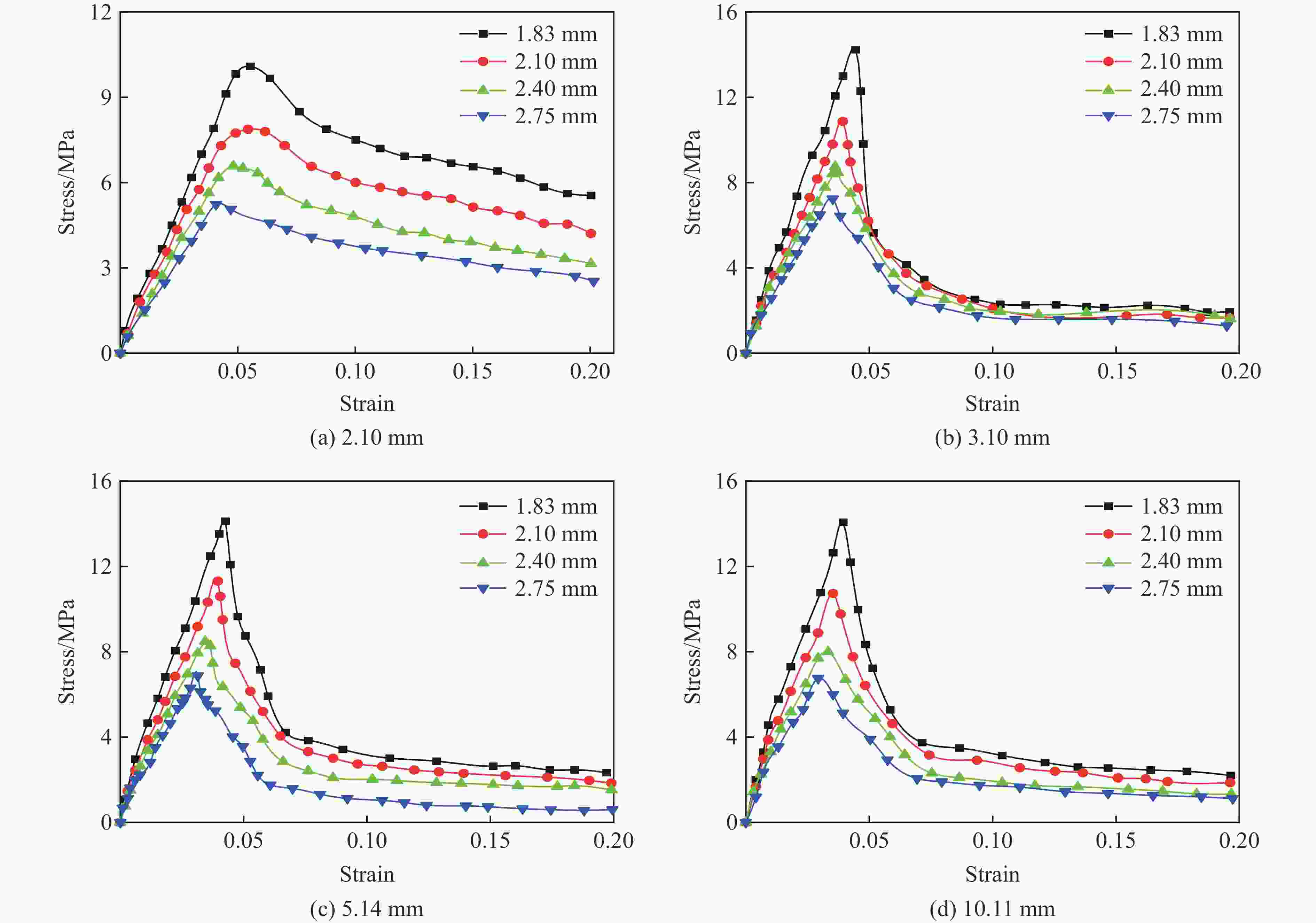
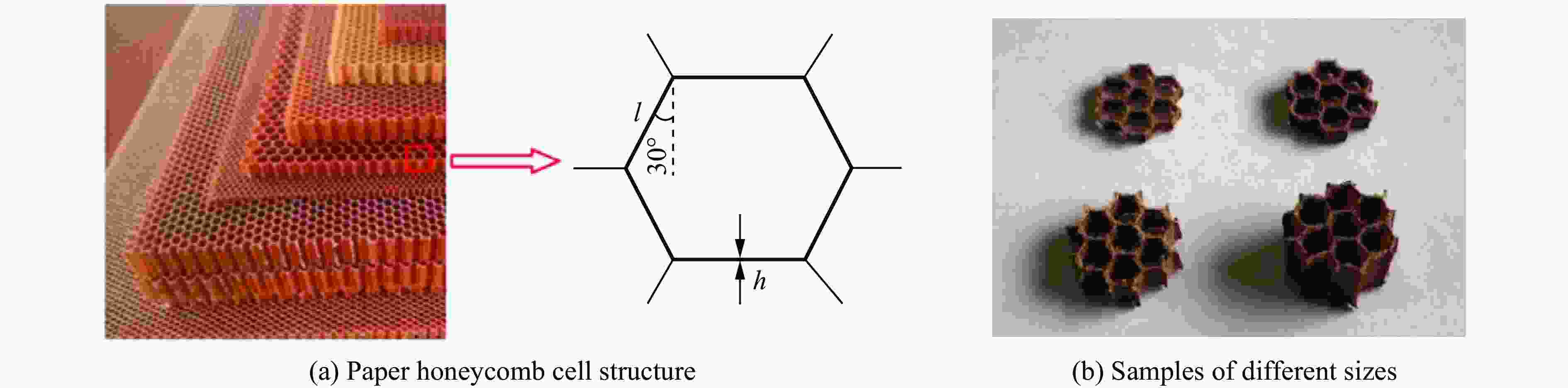
摘要: 应用新研制的中应变率实验装置结合激光干涉测速系统完成了纸蜂窝结构的动态加载实验,研究纸蜂窝结构在中应变率下的力学性能;结合高速摄影和数字图像相关方法,得到纸蜂窝结构的变形过程和动态失效机制,并采用数值方法进一步探究其动态失效机制。结果表明:纸蜂窝结构表现出明显的应变率效应;厚度为2.10 mm的纸蜂窝屈服强度明显低于其他3种尺寸,表现出异常尺寸效应,应力-应变曲线下降段也有较大差异。产生异常尺寸效应的主要原因是,随着试样尺寸的增大,纸蜂窝结构的破坏模式发生了变化。中应变率加载过程中,纸蜂窝结构的失效机制为破坏模式的转变—由面外壁屈曲破坏转变为面内剪切破坏。本研究还利用数值模型分析了胞元宽度的变化对结构力学性能的影响,该研究结果对于薄壁结构的优化设计具有很好的参考意义。Abstract: Combining the laser interferometry system, using the newly developed experimental device at medium strain rates to conduct the dynamic loading experiment of paper honeycomb structure. The purpose is to study the mechanical properties of paper honeycomb structure at medium strain rates. The deformation process and dynamic failure mechanism of paper honeycomb structure were obtained by high-speed photography and digital image correlation method. Numerical methods were used to further explore the dynamic failure mechanism. The results show that the paper honeycomb structure exhibits obvious strain rate effect. The yield strength of 2.10 mm thick paper honeycomb is obviously lower than the other three sizes, showing abnormal size effect. The descending section of stress-strain curve of 2.10 mm thick paper honeycomb is also different. The main reason for it is that the failure mode of paper honeycomb structure changes with the increase of sample size. The failure mechanism of paper honeycomb structure during the loading process at medium strain rates is the change of two failure modes, namely from out-of-plane buckling to in-plane shear. The effect of cell width on mechanical properties of the structure was analyzed by numerical model. This study is a good reference significance for the optimal design of thin-walled structures.
-
Key words:
- medium strain rate /
- paper honeycomb /
- failure mechanism /
- out-of-plane buckling /
- dynamic response
-
表 1 纸蜂窝结构的实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results of paper honeycomb structure
Sample size/mm Strain rate/s−1 The peak state Stress-drop/MPa Stress/MPa Strain 2.10 5 5.11 0.174 9 5.21 0.173 13 5.22 0.162 3.10 5 7.54 0.077 4.30 9 7.60 0.076 4.48 13 7.92 0.076 4.49 5.14 5 6.90 0.070 2.53 9 6.92 0.069 2.54 13 7.49 0.069 3.29 10.11 3 5.04 0.040 2.84 5 6.13 0.039 3.83 7 6.88 0.028 4.18 表 2 纸蜂窝基体的材料参数
Table 2. Paper honeycomb matrix’s material parameters
Poisson’s ratio Elastic modulus/GPa Compression strength/MPa Density/(kg·m–3) 0.2 4 180 1100 -
[1] MIAO C H, XU S L, SONG Y P, et al. Influence of stress state on dynamic breakage of quartz glass spheres subjected to lower velocity impacting [J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 397: 117081. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.117081 [2] CHEN M D, XU S L, YUAN L Z, et al. Influence of stress state on dynamic behaviors of concrete under true triaxial confinements [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2023, 253: 108399. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108399 [3] 卜乐虎, 王鹏飞, 武杨帆, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的两相复合结构动态力学性能研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(3): 034201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230601BU L H, WANG P F, WU Y F, et al. Research on dynamic mechanical properties of two-phase composites based on convolutional neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(3): 034201. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230601 [4] 薛晓, 乔禹, 王鹏飞, 等. 碳纳米管纤维的动态拉伸力学性能研究 [J]. 实验力学, 2020, 35(5): 811–819. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-19-213XUE X, QIAO Y, WANG P F, et al. Dynamic tensile mechanical properties of carbon nanotube fiber [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2020, 35(5): 811–819. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-19-213 [5] HUANG J, XU S, YI H, et al. Size effect on the compression breakage strengths of glass particles [J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 268: 86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.037 [6] SUN J B, FANG H. The analysis of crashworthiness and dissipation mechanism of novel floating composite honeycomb structure against ship-OWT collision [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 287: 115819. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115819 [7] HOU W B, SHEN Y X, JIANG K, et al. Study on mechanical properties of carbon fiber honeycomb curved sandwich structure and its application in engine hood [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 286: 115302. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115302 [8] WANG J F, SHI C Y, YANG N, et al. Strength, stiffness, and panel peeling strength of carbon fiber-reinforced composite sandwich structures with aluminum honeycomb cores for vehicle body [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 184: 1189–1196. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.10.038 [9] CLARKE D J, IMEDIEGWU C, MOAT R, et al. A systematic numerical and experimental study into the mechanical properties of five honeycombs [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2023, 264: 110895. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110895 [10] XU M C, ZHAO Z A, WANG P D, et al. Mechanical performance of bio-inspired hierarchical honeycomb metamaterials [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 254/255: 111866. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2022.111866 [11] WANG Z G, LI Z D, XIONG W. Numerical study on three-point bending behavior of honeycomb sandwich with ceramic tile [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 167: 63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.11.108 [12] ZHOU H, XU P, XIE S C, et al. Mechanical performance and energy absorption properties of structures combining two Nomex honeycombs [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 185: 524–536. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.11.059 [13] HEIMBS S, SCHMEER S, MIDDENDORF P, et al. Strain rate effects in phenolic composites and phenolic-impregnated honeycomb structures [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2007, 67(13): 2827–2837. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.01.027 [14] KAMAN M O, SOLMAZ M Y, TURAN K. Experimental and numerical analysis of critical buckling load of honeycomb sandwich panels [J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2010, 44(24): 2819–2831. doi: 10.1177/0021998310371541 [15] WANG D M. Impact behavior and energy absorption of paper honeycomb sandwich panels [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(1): 110–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.03.002 [16] LIU L Q, WANG H, GUAN Z W. Experimental and numerical study on the mechanical response of Nomex honeycomb core under transverse loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 121: 304–314. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.11.034 [17] YANG W C, ZHANG X F, YANG K J, et al. Shear property characterization of aramid paper and its application to the prediction of honeycomb behaviors [J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 254: 112800. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112800 [18] JANG W Y, KYRIAKIDES S. On the buckling and crushing of expanded honeycomb [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2015, 91: 81–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.02.008 [19] SHAN J F, XU S L, ZHOU L J, et al. Dynamic fracture of aramid paper honeycomb subjected to impact loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 223: 110962. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.110962 [20] PETRAS A, SUTCLIFFE M P F. Failure mode maps for honeycomb sandwich panels [J]. Composite Structures, 1999, 44(4): 237–252. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(98)00123-8 [21] CASTANIÉ B, BOUVET C, AMINANDA Y, et al. Modelling of low-energy/low-velocity impact on Nomex honeycomb sandwich structures with metallic skins [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(7): 620–634. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.02.008 [22] WU X R, YU H J, GUO L C, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of static and fatigue behaviors of composites honeycomb sandwich structure [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 213: 165–172. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.01.081 [23] 苗春贺, 徐松林, 马昊, 等. 递进式凸轮加载的中等应变率实验技术 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(3): 034101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0344MIAO C H, XU S L, MA H, et al. An experimental technique for medium strain-rate loading by a progressive cam [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(3): 034101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0344 [24] KESHAVANARAYANA S, THOTAKURI M V. Off-axis compression behaviour of honeycomb core in WT-plane [J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2009, 14(2): 173–181. doi: 10.1080/13588260802614373 [25] 徐小村. GFRP/纸蜂窝复合材料的制备及力学性能研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2020.XU X C. Preparation and mechanical properties of GFRP/paper honeycomb composites [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020. [26] KADIR N A, AMINANDA Y, DAWOOD M S I S, et al. Numerical analysis of kraft paper honeycomb subjected to uniform compression loading [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2017, 914: 012004. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/914/1/012004 [27] KILCHERT S V. Nonlinear finite element modelling of degradation and failure in folded core composite sandwich structures [D]. Stuttgart: University of Stuttgart, 2013. [28] ZHANG J, ASHBY M F. The out-of-plane properties of honeycombs [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1992, 34(6): 475–489. doi: 10.1016/0020-7403(92)90013-7 -






 下载:
下载: