High-Pressure Synthesis of Copper-Based Rare-Earth Perovskite La1–xNdxCuO3 (0≤x≤1)
-
摘要: 在高温高压条件下,利用自主设计加工的Walker型高压组件合成新型铜基稀土过渡金属钙钛矿La1–xNdxCuO3(0≤x≤1)。结构精修结果表明:La1–xNdxCuO3(0≤x≤0.4)具有菱方结构,空间群为
$R\overline 3 c $ ;当0.5≤x≤0.7时,该体系表现出$R\overline 3 c $ 菱方结构与Pnma正交结构共存的混合相;进一步增加Nd的掺杂比例,当0.8≤x≤1时样品具有单一的Pnma正交结构。获得了La1–xNdxCuO3(0≤x≤1)的完整结构相图,为深入研究稀土-3d过渡金属氧化物的磁性、金属-绝缘体相变等物性演化规律提供了新的材料选项。-
关键词:
- 高压合成 /
- 铜基稀土-3d过渡金属氧化物 /
- 金属绝缘体相变
Abstract: The copper-based rare-earth perovskites La1–xNdxCuO3(0≤x≤1) have been synthesized in the two-stage Walker-type high-pressure apparatus. The refined crystal structure results revealed that La1–xNdxCuO3 (0≤x≤0.4) adopts a rhombohedral structure with the space group$R\overline 3 c $ . When 0.5≤x≤0.7, a mixed phase with both$R\overline 3 c $ rhombohedral and Pnma orthorhombic structures was observed in the system. With a further increase in Nd3+ doping, the system exhibits a single Pnma orthorhombic phase when x=0.8, 0.9 and 1. A comprehensive structural phase diagram of La1–xNdxCuO3 (0≤x≤1) was established in this study, providing a new material platform for investigating the magnetic properties, metal-insulator transitions, and other physical property evolutions in rare-earth 3d transition metal oxides. -
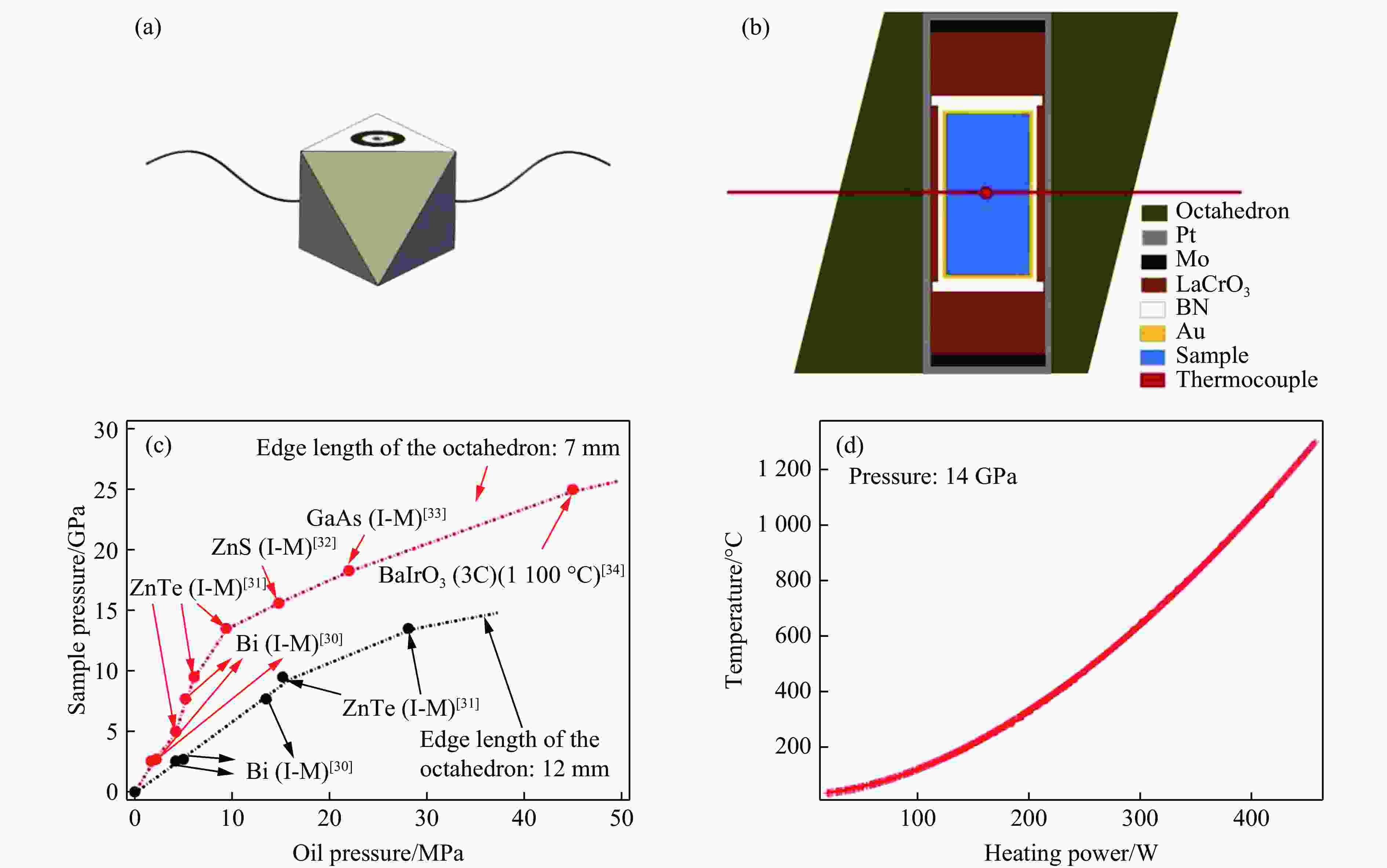
表 1 La1–xNdxCuO3 (0≤x≤1)样品合成的压力和温度优化条件
Table 1. Pressure and temperature conditions of synthesizing La1–xNdxCuO3 (0≤x≤1)
Sample Pressure/GPa Temperature/℃ Time/min LaCuO3 6 1000 30 La0.9Nd0.1CuO3 6 1000 30 La0.8Nd0.2CuO3 6 1000 30 La0.7Nd0.3CuO3 10 1000 30 La0.6Nd0.4CuO3 10 1000 30 La0.5Nd0.5CuO3 10 1000 30 La0.4Nd0.6CuO3 10 1000 30 La0.3Nd0.7CuO3 14 1000 30 La0.2Nd0.8CuO3 14 1000 30 La0.1Nd0.9CuO3 14 1000 30 NdCuO3 14 1000 30 表 2 La1–xNdxCuO3(0≤x≤1)的晶格参数
Table 2. Structural parameters of La1–xNdxCuO3 (0≤x≤1)
Sample Space group Lattice parameters/Å RP/% RWP/% Chi2 LaCuO3 $R\overline 3 c $ a=b=5.4976(6), c=13.2062(9) 3.05 5.59 7.01 La0.9Nd0.1CuO3 $R\overline 3 c $ a=b=5.4976(9), c=13.1917(5) 1.45 1.92 1.10 La0.8Nd0.2CuO3 $R\overline 3 c $ a=b=5.4988(9), c=13.1732(7) 1.25 1.68 0.79 La0.7Nd0.3CuO3 $R\overline 3 c $ a=b=5.4961(1), c=13.1625(7) 1.91 2.73 2.48 La0.6Nd0.4CuO3 $R\overline 3 c $ a=5.4933(9), c=13.1326(6) 2.41 4.14 7.09 La0.5Nd0.5CuO3 Phase 1: $R\overline 3 c $ (36.43%) a=b=5.4627(1), c=13.2988(9) 4.23 5.85 2.42 Phase 2: Pnma (63.57%) a=6.1821(1), b=7.3597(8), c=5.4318(7) 4.23 5.85 2.42 La0.4Nd0.6CuO3 Phase 1: $R\overline 3 c $ (43.49%) a=b=5.4571(7), c=13.2982(1) 1.25 1.68 0.79 Phase 2: Pnma (56.51%) a=6.5015(2), b=7.6552(6), c=5.3354(4) 1.25 1.68 0.79 La0.3Nd0.7CuO3 Phase 1: $R\overline 3 c $ (44.42%) a=b=5.4542(6), c=13.3191(9) 3.76 4.81 1.43 Phase 2: Pnma (55.58%) a=6.3189(6), b=7.2736(7), c=5.3706(8) 3.76 4.81 1.43 La0.2Nd0.8CuO3 Pnma a=6.3197(8), b=7.2408(1), c=5.3561(1) 7.75 9.92 2.20 La0.1Nd0.9CuO3 Pnma a=6.3045(3), b=7.2421(7), c=5.3462(9) 1.54 2.24 1.66 NdCuO3 Pnma a=6.3039(2), b=7.2176(2), c=5.3334(5) 1.72 2.48 1.42 -
[1] FIEBIG M, LOTTERMOSER T, FRÖHLICH D, et al. Observation of coupled magnetic and electric domains [J]. Nature, 2002, 419(6909): 818–820. doi: 10.1038/nature01077 [2] WU J G, WANG J. Multiferroic behavior of BiFeO3–RTiO3 (Mg, Sr, Ca, Ba, and Pb) thin films [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(2): 026101. doi: 10.1063/1.3452324 [3] DONG S, YU R, YUNOKI S, et al. Double-exchange model study of multiferroic RMnO3 perovskites [J]. The European Physical Journal B, 2009, 71(3): 339–344. doi: 10.1140/epjb/e2009-00225-1 [4] KHARE N. Handbook of high-temperature superconductor electronics [M]. New York: Marcel Dekker, 2003. [5] VON HELMOLT R, WECKER J, HOLZAPFEL B, et al. Giant negative magnetoresistance in perovskitelike La2/3Ba1/3MnO x ferromagnetic films [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 71(14): 2331–2333. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.2331 [6] GOODENOUGH J B, ZHOU J S. Orbital ordering in orthorhombic perovskites [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2007, 17(23): 2394–2405. doi: 10.1039/b701805c [7] MARTÍNEZ-LOPE M J, ALONSO J A, RETUERTO M, et al. Evolution of the crystal structure of RVO3 (R=La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Tb, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Y) perovskites from neutron powder diffraction data [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 47(7): 2634–2640. doi: 10.1021/ic701969q [8] KUMARI S, PAUL S, RAJ S. Electronic structure of RVO3 (R=La and Y): effect of electron ( U) and exchange ( J) correlations [J]. Solid State Communications, 2017, 268: 20–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2017.09.017 [9] SAGE M H. Orbital, charge and magnetic order of RVO3 perovskites [D]. Groningen: University of Groningen, 2006. [10] SINGH K D, PANDIT R, KUMAR R. Effect of rare earth ions on structural and optical properties of specific perovskite orthochromates; RCrO3 (R=La, Nd, Eu, Gd, Dy, and Y) [J]. Solid State Sciences, 2018, 85: 70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2018.10.001 [11] ZVEZDIN A K, GAREEVA Z V, CHEN X M. Multiferroic order parameters in rhombic antiferromagnets RCrO3 [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2021, 33(38): 385801. doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ac0dd6 [12] SIBANDA E T. Structural, magnetic and electronic properties of rare-earth based chromium oxides [D]. Johannesburg: University of Johannesburg, 2023. [13] ALONSO J A, MARTÍNEZ-LOPE M J, CASAIS M T, et al. Evolution of the Jahn-Teller distortion of MnO6 octahedra in RMnO3 perovskites (R=Pr, Nd, Dy, Tb, Ho, Er, Y): a neutron diffraction study [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2000, 39(5): 917–923. doi: 10.1021/ic990921e [14] KAJIMOTO R, MOCHIZUKI H, YOSHIZAWA H, et al. R-dependence of spin exchange interactions in RMnO3 (R=rare-earth ions) [J]. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 2005, 74(9): 2430–2433. doi: 10.1143/JPSJ.74.2430 [15] WARSHI M K, MISHRA V, SAGDEO A, et al. Structural, optical and electronic properties of RFeO3 [J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(7): 8344–8349. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.023 [16] NAKHAEI M, KHOSHNOUD D S. Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of RFeO3 (R=Dy, Ho, Yb & Lu) compounds [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32(11): 14286–14300. doi: 10.1007/s10854-021-05992-6 [17] SINGH N, RHEE J Y, AULUCK S. Electronic and magneto-optical properties of rare-earth orthoferrites RFeO3 (R= Y, Sm, Eu, Gd and Lu) [J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2008, 53(2): 806–811. doi: 10.3938/jkps.53.806 [18] ALONSO J A, MARTíNEZ-LOPE M J, DE LA CALLE C, et al. Preparation and structural study from neutron diffraction data of RCoO3 (R=Pr, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) perovskites [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2006, 16(16): 1555–1560. doi: 10.1039/B515607F [19] ITOH M, HASHIMOTO J, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Spin state and metal-insulator transition in LaCoO3 and RCoO3 (R=Nd, Sm and Eu) [J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2000, 281/282: 510–511. doi: 10.1016/S0921-4526(99)01044-3 [20] WANG W R, XU D P, SU W H, et al. Raman active phonons in RCoO3 (R=La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, and Dy) perovskites [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2005, 22(9): 2400. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/22/9/072 [21] ZHOU J S, GOODENOUGH J B, DABROWSKI B. Exchange interaction in the insulating phase of RNiO3 [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 95(12): 127204. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.127204 [22] FERNÁNDEZ-DÍAZ M, ALONSO J A, MARTÍNEZ-LOPE M, et al. Charge disproportionation in RNiO3 perovskites [J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2000, 276/278: 218–221. doi: 10.1016/S0921-4526(99)01416-7 [23] FREELAND J W, VAN VEENENDAAL M, CHAKHALIAN J. Evolution of electronic structure across the rare-earth RNiO3 series [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 2016, 208: 56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.elspec.2015.07.006 [24] KARPPINEN M, YAMAUCHI H, ITO T, et al. High-pressure synthesis and thermal decomposition of LaCuO3 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 1996, 41(1): 59–62. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5107(96)01624-8 [25] ZHOU J S, ARCHIBALD W, GOODENOUGH J B. Approach to Curie-Weiss paramagnetism in the metallic perovskites La1– x Nd x CuO3 [J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 61(5): 3196–3199. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.61.3196 [26] CHEN B H, WALKER D, SUARD E, et al. High pressure synthesis of NdCuO3– δ perovskites (0≤ δ≤0.5) [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1995, 34(8): 2077–2083. doi: 10.1021/ic00112a020 [27] YU J B, LI Z H, SU W K. Synthesis of quinolines by N-Deformylation and aromatization via solvent-free, high-speed ball milling [J]. Synthetic Communications, 2013, 43(3): 361–374. doi: 10.1080/00397911.2011.599103 [28] XU W H, LI C Y. Efficient synthesis of cucurbiturils and their derivatives using mechanochemical high-speed ball milling (HSBM) [J]. High Performance Polymers, 2021, 33(5): 509–518. doi: 10.1177/0954008320967057 [29] HOSSEINI S G, POURMORTAZAVI S M, HAJIMIRSADEGHI S S. Thermal decomposition of pyrotechnic mixtures containing sucrose with either potassium chlorate or potassium perchlorate [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2005, 141(3): 322–326. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.01.002 [30] HUSBAND R J, O’BANNON E F, LIERMANN H P, et al. Compression-rate dependence of pressure-induced phase transitions in Bi [J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 14859. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94260-y [31] SOYKAN C, ÖZDEMIR KART S. Structural, mechanical and electronic properties of ZnTe polymorphs under pressure [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 529: 148–157. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.170 [32] CHEN X R, LI X F, CAI L C, et al. Pressure induced phase transition in ZnS [J]. Solid State Communications, 2006, 139(5): 246–249. doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2006.05.043 [33] SUZUKI T, YAGI T, AKIMOTO S. Precise determination of transition pressure of GaAs [C]//22nd High Pressure Conference. 1981. [34] CHENG J G, ISHII T, KOJITANI H, et al. High-pressure synthesis of the BaIrO3 perovskite: a Pauli paramagnetic metal with a Fermi liquid ground state [J]. Physical Review B, 2013, 88(20): 205114. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.88.205114 [35] YOUNG R A. The Rietveld method [M]. Oxford: International Union of Crystallography, 1993. [36] BRINGLEY J F, SCOTT B A, LA PLACA S J, et al. Structure and properties of the LaCuO3– δ perovskites [J]. Physical Review B, 1993, 47(22): 15269. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.15269 [37] ZHOU J S, GOODENOUGH J B, DABROWSKI B. Transition from Curie-Weiss to enhanced Pauli paramagnetism in RNiO3 (R=La, Pr, … Gd) [J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 67(2): 020404. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.67.020404 -








 下载:
下载: