Cooling Fields Induced Giant Magnetoresistance in High-Pressure Synthesized Double Perovskite Y2NiIrO6
-
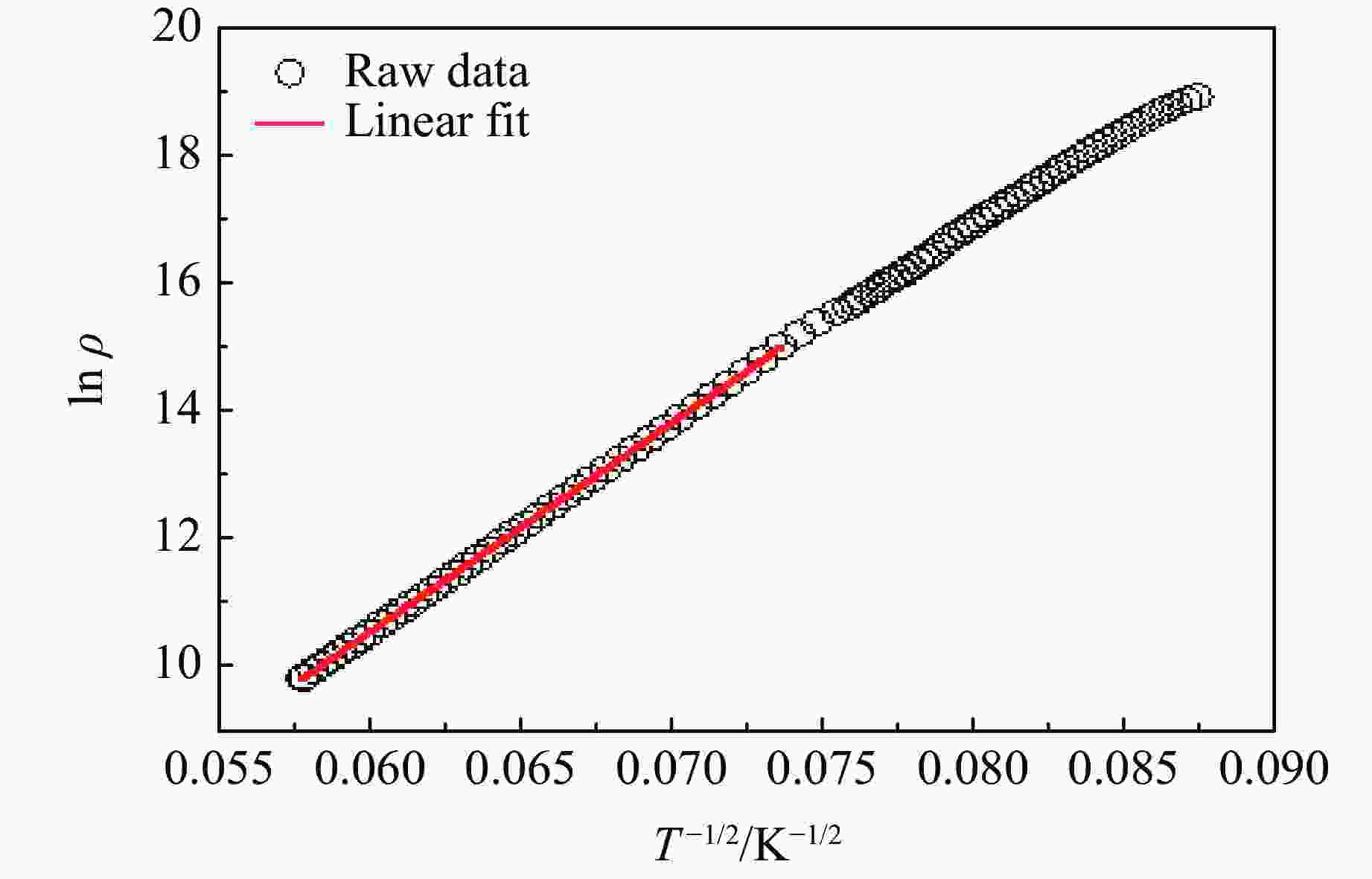
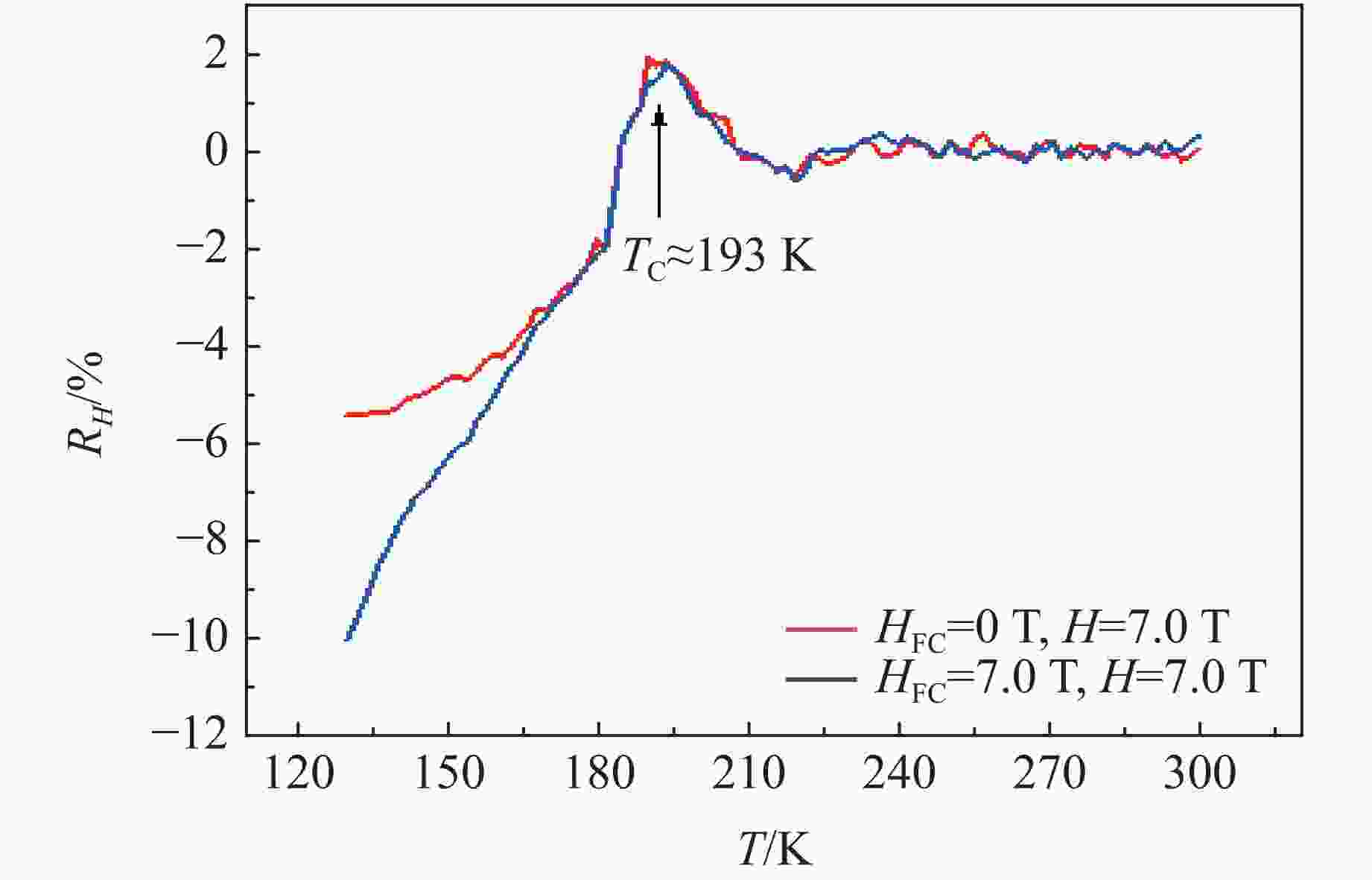
摘要: 双钙钛矿材料Y2NiIrO6的亚铁磁转变温度为192 K,因其奇异的交换偏置效应而受到广泛关注。系统研究了Y2NiIrO6的低温晶体结构、电导行为及磁电阻性能,发现该材料在130 K时保持了290 K时的晶体结构,并在130~300 K的温区内表现出半导体电导行为。在居里温度以上的顺磁状态,其导电行为可以用Efros-Shklovskii变程跃迁模型拟合,在居里温度以下,亚铁磁有序使电阻行为偏离该模型。更为有趣的是,亚铁磁序诱导了材料的负磁电阻效应,并且7.0 T的场冷诱导了–10%的巨磁电阻效应。这一新机制为探索新型巨磁电阻材料提供了全新的研究思路。Abstract: Double perovskite Y2NiIrO6 is a ferrimagnetic material with Curie temperature of 192 K. It has drawn wide attention owing to its remarkable exchange-bias effect. Here, we studied the low-temperature crystal structure, electron transport properties and magnetoresistance of Y2NiIrO6. The crystal structure under 130 K is almost identical with that of room-temperature. The material shows semiconducting behavior in the temperature range of 130 to 300 K. Above Curie temperature it can be well describe as Efros-Shklovskii variable-range hopping model. Below Curie temperature, a departure occurs due to the forming of long-range ferrimagnetic ordering. It is interesting to find that the magnetic ordering results into negative magneto-resistance. Moreover, giant magnetoresistance up to –10% is induced by cooling field of 7.0 T. This mechanism of this remarkable effect provides a new boulevard to discover new type of giant magneto-resistance materials.
-
表 1 YNIO在290和130 K下的晶格参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of YNIO at 290 and 130 K
T/K Space group a/Å b/Å c/Å β/(o) B'-B'' antisite/% 290 P21/n 5.265 2 5.684 7 7.584 6 90.14 7.5 130 P21/n 5.263 1 5.683 0 7.580 9 90.16 7.5 T/K Position Y Ni Ir O1 O2 O3 290 0.021 8, 0.077 5
0.249 01/2, 0, 1/2 1/2, 0, 0 0.184 3, –0.191 4,
0.055 30.619 5, –0.042 6,
0.254 70.323 3, 0.307 3,
0.059 8130 0.022 1, 0.078 8,
0.249 11/2, 0, 1/2 1/2, 0, 0 0.183 9, –0.189 3,
0.051 70.618 4, –0.047 1,
0.253 30.322 2, 0.308 0,
0.061 2 -
[1] WU S M, CYBART S A, YU P, et al. Reversible electric control of exchange bias in a multiferroic field-effect device [J]. Nature Materials, 2010, 9(9): 756–761. [2] PARKIN S S P, ROCHE K P, SAMANT M G, et al. Exchange-biased magnetic tunnel junctions and application to nonvolatile magnetic random access memory (invited) [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 85(8): 5828–5833. [3] LEIGHTON C, SONG M, NOGUÉS J, et al. Using magnetoresistance to probe reversal asymmetry in exchange biased bilayers [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000, 88(1): 344–347. [4] BOBO J F, GABILLET L, BIBES M. Recent advances in nanomagnetism and spin electronics [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2004, 16(5): S471–S496. [5] OHLDAG H, SCHOLL A, NOLTING F, et al. Correlation between exchange bias and pinned interfacial spins [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(1): 017203. [6] SHIRATSUCHI Y, NOUTOMI H, OIKAWA H, et al. Detection and in situ switching of unreversed interfacial antiferromagnetic spins in a perpendicular-exchange-biased system [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(7): 077202. [7] LIU Z H, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG H G, et al. Giant exchange bias in Mn2FeGa with hexagonal structure [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 109(3): 032408. [8] DING L, CHU L H, MANUEL P, et al. Giant spontaneous exchange bias in an antiperovskite structure driven by a canted triangular magnetic structure [J]. Materials Horizons, 2019, 6(2): 318–325. [9] MANIV E, MURPHY R A, HALEY S C, et al. Exchange bias due to coupling between coexisting antiferromagnetic and spin-glass orders [J]. Nature Physics, 2021, 17(4): 525–530. [10] PATRA M, MAJUMDAR S, GIRI S. Exchange bias effect and intragranular magnetoresistance in Nd0.84Sr0.16CoO3 [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2009, 21(48): 486003. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/21/48/486003 [11] GIRI S, PATRA M, MAJUMDAR S. Exchange bias effect in alloys and compounds [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2011, 23(7): 073201. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/23/7/073201 [12] JANA S, MIDDEY S, RAY S. Spin-valve-type magnetoresistance: a generic feature of ferromagnetic double perovskites [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2010, 22(34): 346004. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/22/34/346004 [13] DENG Z, WANG X, WANG M Q, et al. Giant exchange-bias-like effect at low cooling fields induced by pinned magnetic domains in Y2NiIrO6 double perovskite [J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(17): 2209759. [14] CHENG J G, ZHOU J S, GOODENOUGH J B, et al. High-pressure synthesis and physical properties of perovskite and post-perovskite Ca1− x Sr x IrO3 [J]. Physical Review B, 2011, 83(6): 064401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.83.064401 [15] PENG S Z, ZHU D Q, LI W X, et al. Exchange bias switching in an antiferromagnet/ferromagnet bilayer driven by spin-orbit torque [J]. Nature Electronics, 2020, 3(12): 757–764. [16] WEI Q Q, WANG H L, ZHAO X P, et al. Electron mobility anisotropy in (Al, Ga)Sb/InAs two-dimensional electron gases epitaxied on GaAs (001) substrates [J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(7): 072101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/7/072101 [17] DENG Z, RETUERTO M, LIU S Z, et al. Dynamic ferrimagnetic order in a highly distorted double perovskite Y2CoRuO6 [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(20): 7047–7054. [18] DENG Z, KANG C J, CROFT M, et al. A pressure-induced inverse order-disorder transition in double perovskites [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(21): 8240–8246. doi: 10.1002/anie.202001922 [19] TOBY B H. EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS [J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2001, 34(2): 210–213. doi: 10.1107/S0021889801002242 [20] BUCHNER M, HENNE B, NEY V, et al. Transition from a hysteresis-like to an exchange-bias-like response of an uncompensated antiferromagnet [J]. Physical Review B, 2019, 99(6): 064409. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.064409 [21] NAYAK A K, NICKLAS M, CHADOV S, et al. Design of compensated ferrimagnetic Heusler alloys for giant tunable exchange bias [J]. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(7): 679–684. doi: 10.1038/nmat4248 [22] NAYAK A K, NICKLAS M, CHADOV S, et al. Large zero-field cooled exchange-bias in bulk Mn2PtGa [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110(12): 127204. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.127204 [23] NAKATSUJI S, DOBROSAVLJEVIĆ V, TANASKOVIĆ D, et al. Mechanism of hopping transport in disordered mott insulators [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93(14): 146401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.146401 [24] FISHER B, GENOSSAR J, CHASHKA K B, et al. Variable range hopping in A2MnReO6 (A=Ca, Sr, Ba) [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(3): 033716. doi: 10.1063/1.2967820 [25] LIU X Y, RINEY L, GUERRA J, et al. Colossal negative magnetoresistance from hopping in insulating ferromagnetic semiconductors [J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(11): 112502. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/11/112502 -







 下载:
下载: