Influence of Penetration Deflection by the Shape of Tail Oblique Cone of Projectile
-
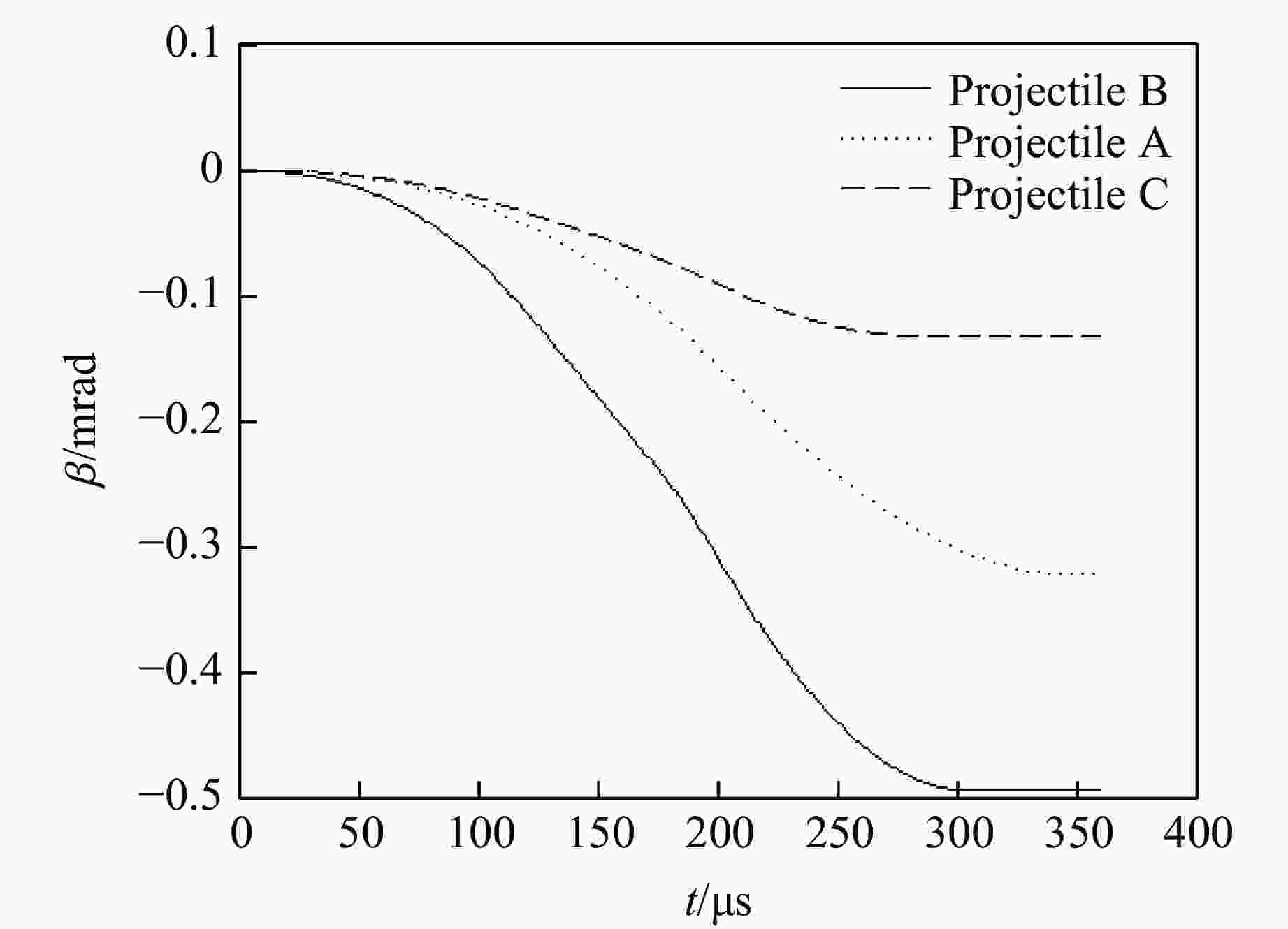
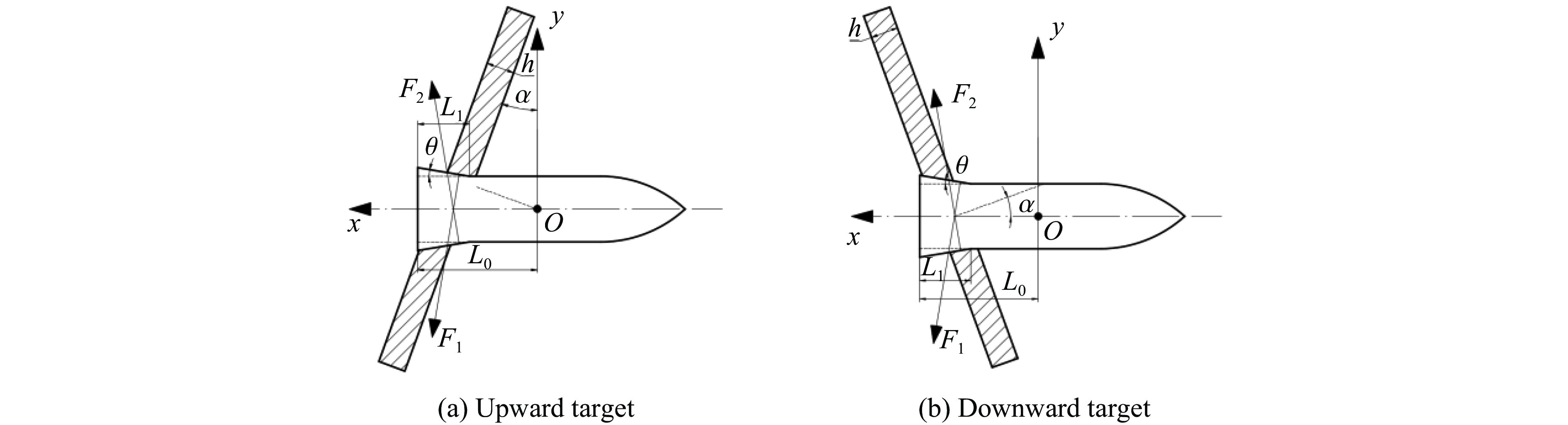
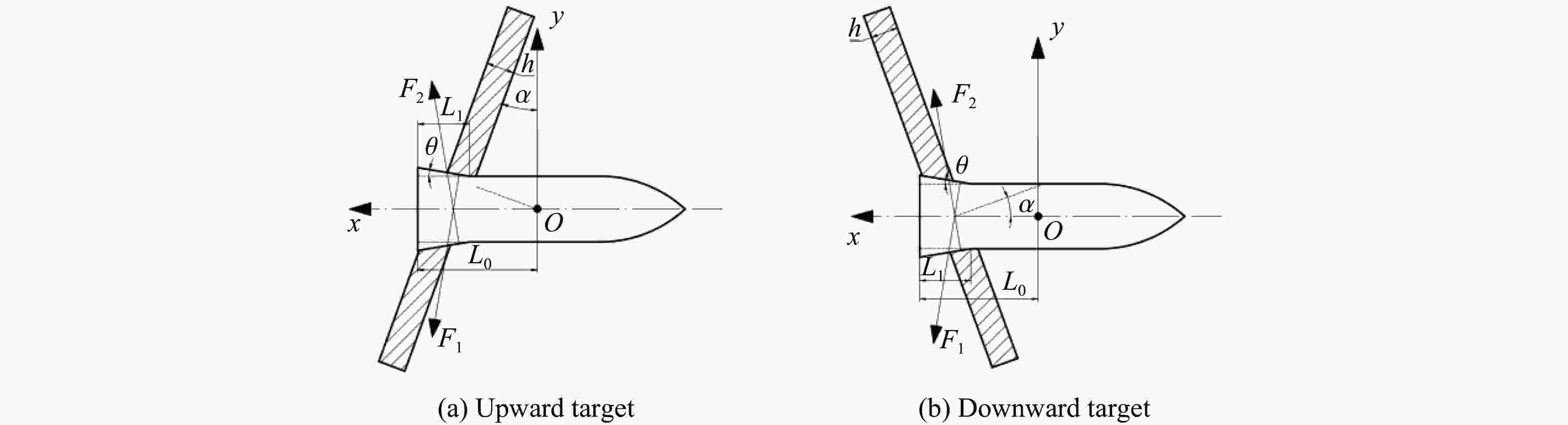
摘要: 针对弹体斜侵彻多层靶时弹道发生的偏转问题,建立了弹体尾部为斜锥面结构的弹体侵彻偏转理论计算模型,获得了当速度为0.2~1.2 km/s、着角为−30°~20°、弹体半径为30~60 mm、尾飘斜面与弹轴的夹角为0°~4°时偏转随尾部结构的变化规律,通过与试验结果进行对比,验证了模型的准确性。结果表明:弹体侵彻仰靶时,弹尾形成负的偏转力矩,弹体产生“低头”效果;弹体侵彻俯靶时,弹尾形成正的偏转力矩,弹体产生“抬头”效果;弹体尾部斜锥面产生的垂直弹轴的偏转力矩约为平行弹轴的偏转力矩的100倍;增大尾飘斜面与弹轴的夹角、尾飘长度、弹体半径均可增大偏转力矩;与增大尾飘长度相比,增大尾飘斜面与弹轴的夹角对增大偏转力矩更有效。Abstract: Aiming at the problem of deflection when the projectile obliquely penetrates a multi-layer target, a theoretical calculation model of the projectile deflection caused by the oblique cone structure of the projectile tail is established, and the change rule of the deflection with the tail structure is obtained at the working conditions of the velocity of 0.2−1.2 km/s, the angle of attraction of −30°−20°, the radius of the projectile body of 30–60 mm, and the angle between bevel plane of tail and the projectile shaft of 0°−4°. Moreover, the accuracy of the model is verified by comparing with the test results. The results showed that the tail of the projectile forms a negative deflection moment and the projectile produces a “head down” effect when the tail of the projectile penetrated upward target, and the tail of the projectile forms a positive deflection moment and the projectile produces a “head up” effect when the tail of the projectile penetrated downward target; the deflection moment of vertical axis is about 100 times greater than that of parallel axis. The deflecting moment can be increased by increasing the angle between bevel plane of tail and the projectile shaft, the length of the tail, and the radius of the projectile. Increasing the angle between bevel plane of tail and the projectile shaft is more effective in increasing the deflection moment than increasing the tail length.
-
Key words:
- multi-layer target /
- penetration /
- deflection moment /
- tail shape /
- oblique cone structure
-
表 1 计算工况
Table 1. Calculation conditions
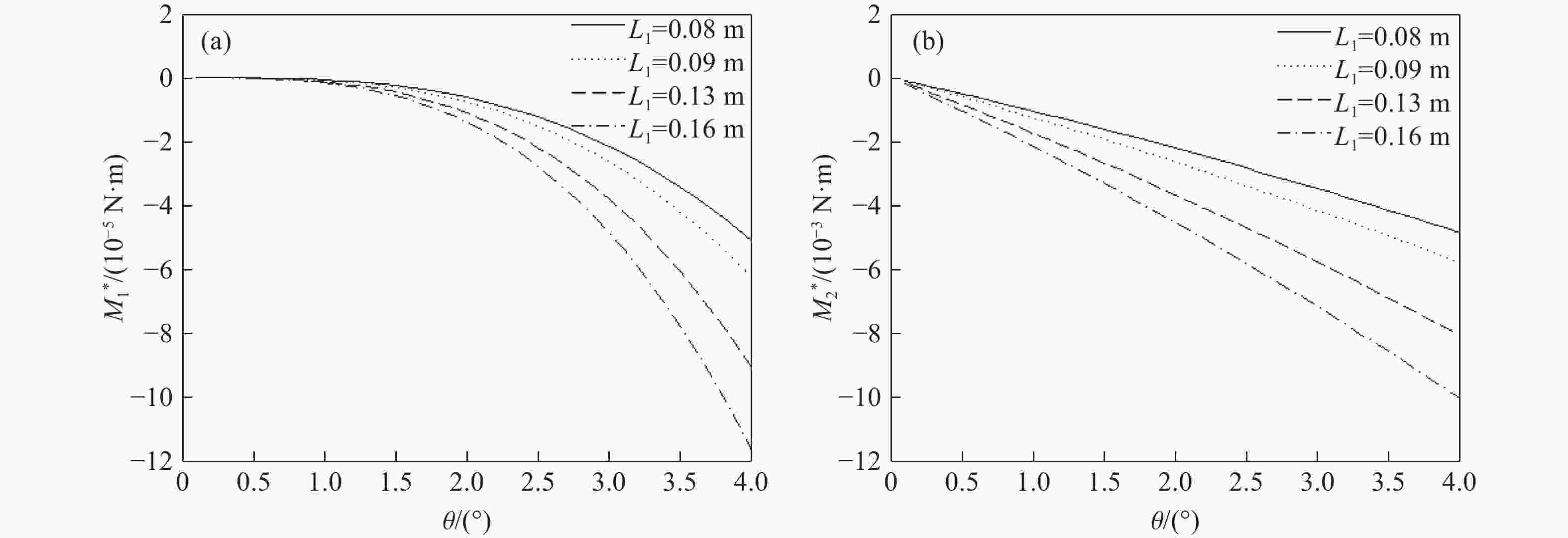
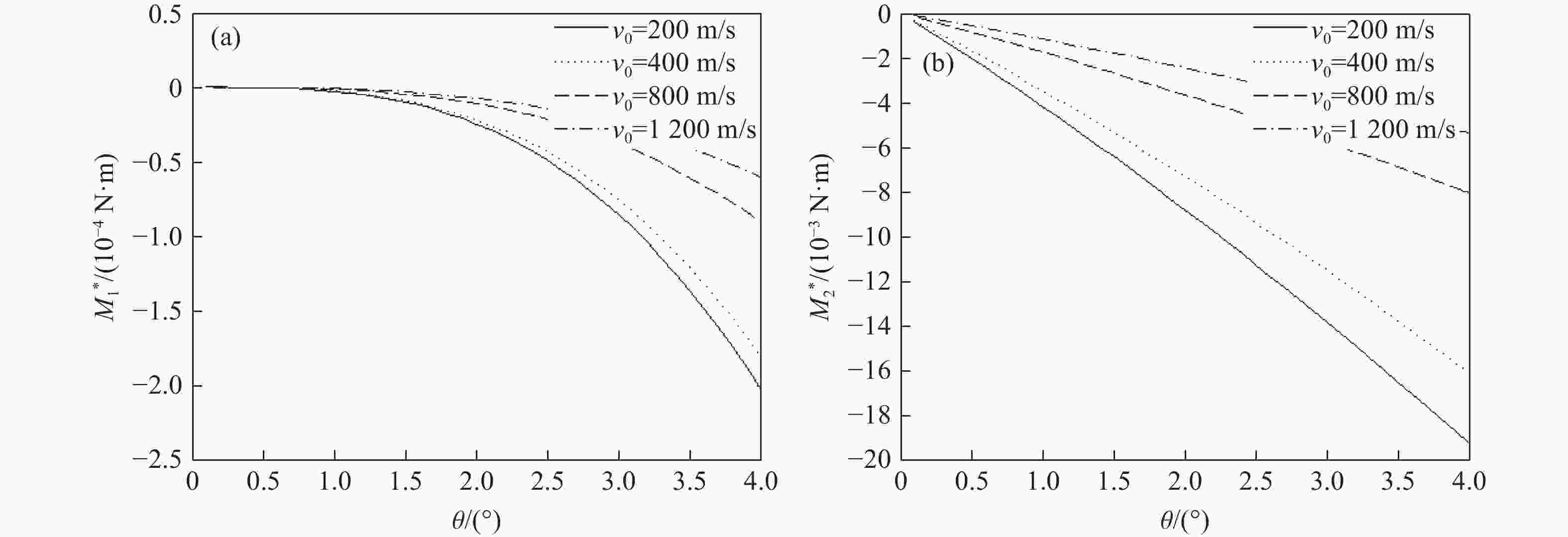
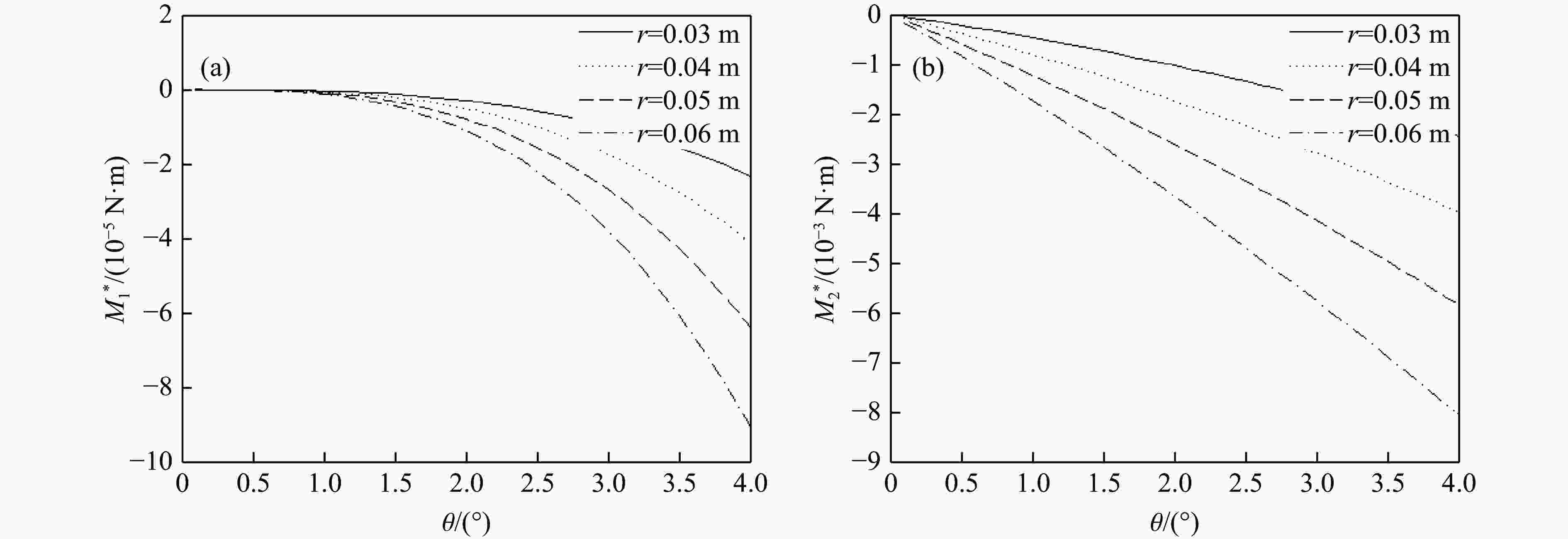
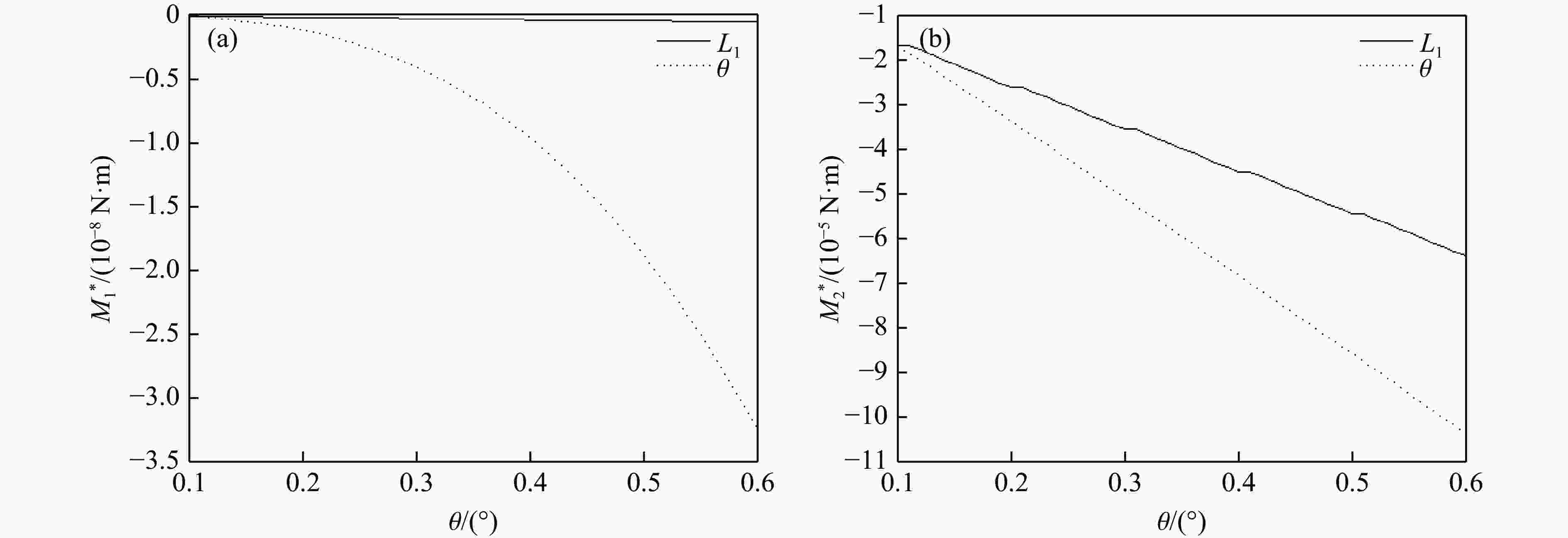
No. v0/(m·s−1) α/(°) r/m L1/m Variable 1 800 10 0.06 0.08, 0.09, 0.13, 0.16 θ 2 200, 400, 800, 1200 10 0.06 0.13 θ 3 800 10, 20, −15, −30 0.06 0.13 θ 4 800 10 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06 0.13 θ 5 400 10 0.06 θ, L1 表 2 弹体结构参数
Table 2. Structural parameters of projectiles
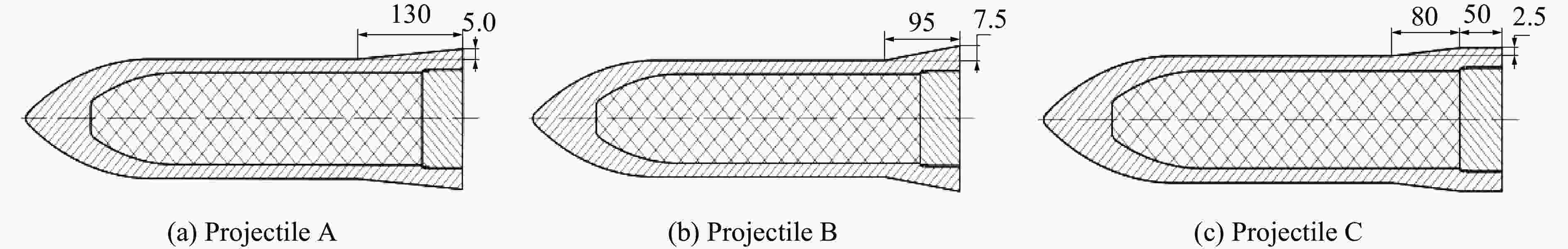
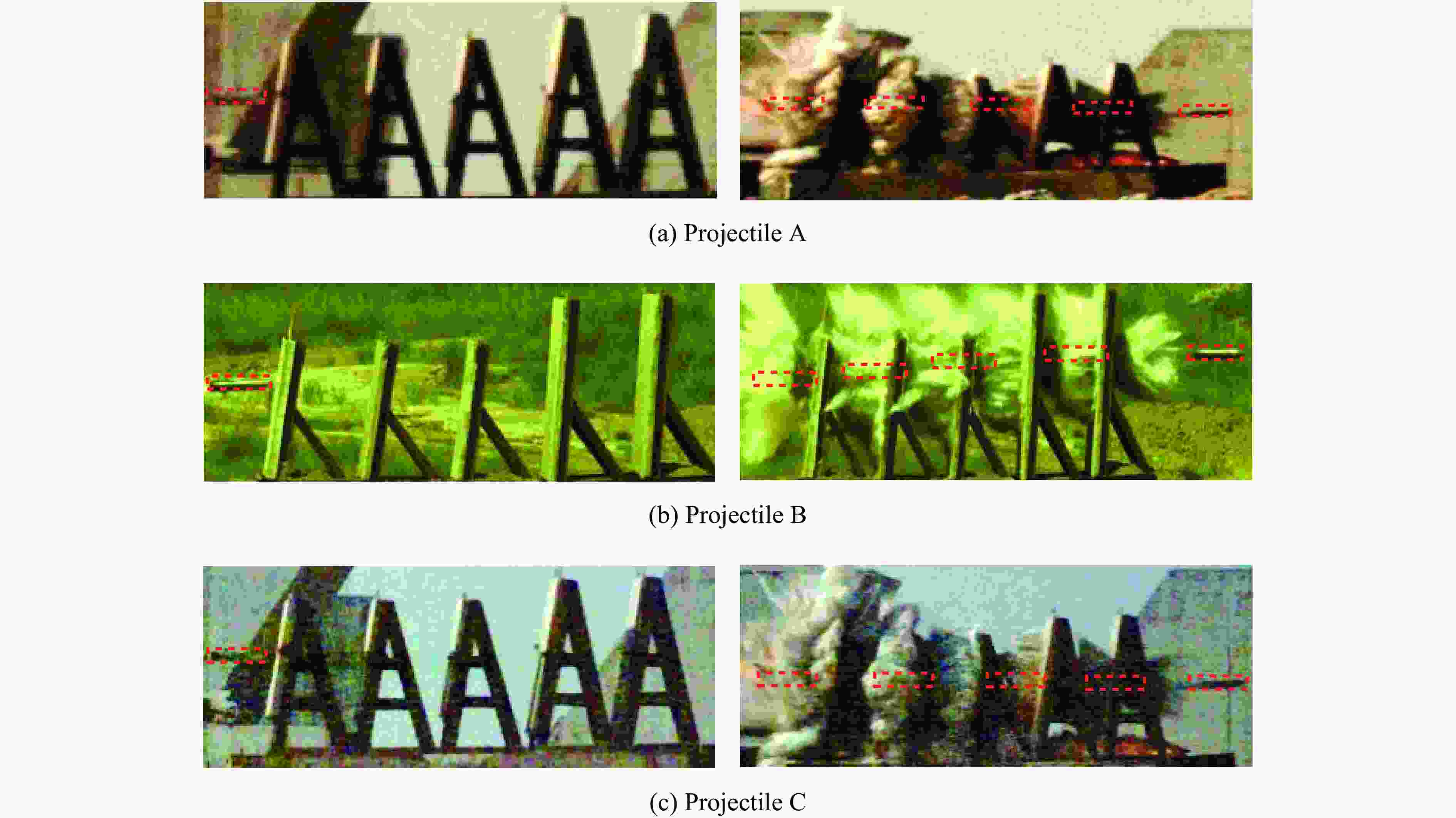
Projectile r/mm L0/mm L1/mm θ/(°) I/(kg·m2) A 60 230 130 2.2 0.5035 B 60 230 95 4.5 0.5098 C 60 230 130 1.8 0.5029 表 3 侵彻试验结果
Table 3. Penetration test results
Projectile v0/(m·s−1) β0/(°) β5/(°) (β5–β0)/(°) ${ \bar \beta} $/(°) A 795 0.3 0.1 −0.2 −0.20 A 802 0 −0.2 −0.2 B 791 0.5 0 −0.5 −0.45 B 796 0.2 −0.2 −0.4 C 806 0 −0.1 −0.1 –0.10 C 801 0.1 0 −0.1 表 4 弹体尾部结构引起的偏转角度的计算结果
Table 4. Calculated results of deflection angle by change of tail projectile
Projectile β1/(°) β2/(°) β3/(°) β4/(°) β5/(°) δ/% A −0.018 −0.041 −0.077 −0.140 −0.250 25 B −0.029 −0.079 −0.160 −0.300 −0.530 18 C −0.008 −0.016 −0.028 −0.049 −0.081 8 -
[1] 李鹏飞, 吕永柱, 周涛, 等. 弹头形状对侵彻多层靶弹道的影响 [J]. 含能材料, 2021, 29(2): 124–131. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020291LI P F, LYU Y Z, ZHOU T, et al. Influence of nose shape of projectile on the penetration trajectory of multilayer target [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2021, 29(2): 124–131. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020291 [2] 葛超, 董永香, 陆志超, 等. 弹丸头部对斜侵彻弹道偏转影响研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(2): 255–262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.02.010GE C, DONG Y X, LU Z C, et al. Ballistic deflection on oblique penetration of projectiles with different noses [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(2): 255–262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.02.010 [3] 张丁山, 谷鸿平, 徐笑, 等. 截卵形头部平台直径对初始侵彻弹道偏转的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(5): 055102. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200655ZHANG D S, GU H P, XU X, et al. Effects of truncated ovate nose diameter of the penetration warhead on the ballistic deflection [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(5): 055102. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200655 [4] 杜华池, 张先锋, 刘闯, 等. 弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶的弹道特性 [J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(6): 1204–1214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.06.010DU H C, ZHANG X F, LIU C, et al. Trajectory characteristics of projectile obliquely penetrating into steel target with multi-layer space structure [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(6): 1204–1214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.06.010 [5] 薛建锋, 沈培辉, 王晓鸣. 弹体斜侵彻混凝土过程中弹道偏转仿真分析 [J]. 系统仿真学报, 2017, 29(8): 1801–1808. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201708021XUE J F, SHEN P H, WANG X M. Simulation analysis on ballistic deflection of projectile obliquely penetrating into concrete [J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2017, 29(8): 1801–1808. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201708021 [6] 康海峰, 代廷静, 沈培辉, 等. 弹体形状对侵彻弹道的影响分析 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2012, 32(2): 73–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2012.02.020KANG H F, DAI T J, SHEN P H, et al. The analysis of the influence of projectile’s shape on penetration trajectory [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2012, 32(2): 73–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2012.02.020 [7] 段卓平, 李淑睿, 马兆芳, 等. 刚性弹体斜侵彻贯穿混凝土靶的姿态偏转理论模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(6): 063302. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0411DUAN Z P, LI S R, MA Z F, et al. Analytical model for attitude deflection of rigid projectile during oblique perforation of concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(6): 063302. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0411 [8] 高旭东, 李庆明. 带攻角斜侵彻混凝土的弹道偏转分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(Suppl 2): 33–39.GAO X D, LI Q M. Trajectory analysis of projectile obliquely penetrating into concrete target at attack angle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(Suppl 2): 33–39. [9] 吴普磊, 李鹏飞, 董平, 等. 攻角对弹体斜侵彻多层混凝土靶弹道偏转影响的数值模拟及试验验证 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2018, 41(2): 202–207. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2018.02.017WU P L, LI P F, DONG P, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental verification on the influence of angle of attack on ballistic deflection of oblique penetrating multi-layer concrete targets for projectile [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2018, 41(2): 202–207. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2018.02.017 [10] 邓勇军, 陈小伟, 姚勇, 等. 基于细观混凝土模型的刚性弹体正侵彻弹道偏转分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(3): 377–386. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0377-10DENG Y J, CHEN X W, YAO Y, et al. On ballistic trajectory of rigid projectile normal penetration based on a meso-scopic concrete model [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(3): 377–386. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0377-10 [11] 成丽蓉, 汪德武, 贺元吉, 等. 弹体斜侵彻多层间隔混凝土薄靶姿态偏转机理研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1009–1016. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.299CHENG L R, WANG D W, HE Y J, et al. Effect of projectile oblique penetrating into multi-layered thin concrete slabs on attitude deflection [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2022, 42(10): 1009–1016. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.299 [12] 马兆芳, 段卓平, 欧卓成, 等. 尾裙对弹体斜侵彻混凝土薄靶弹道的影响规律研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2015, 35(6): 576–579, 584. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.06.006MA Z F, DUAN Z P, OU Z C, et al. Investigation on the influence rules of the tapered tail projectile penetration into thin concrete target [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(6): 576–579, 584. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.06.006 [13] 柴传国, 皮爱国, 武海军, 等. 卵形弹体侵彻混凝土开坑区侵彻阻力计算 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(5): 630–634. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)05-0630-06CHAI C G, PI A G, WU H J, et al. A calculation of penetration resistance during cratering for ogive-nose projectile into concrete [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(5): 630–634. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)05-0630-06 [14] 张爽, 武海军, 黄风雷. 刚性弹正侵彻钢筋混凝土靶阻力模型 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(11): 2081–2092. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.001ZHANG S, WU H J, HUANG F L. Resistance model of rigid projectile penetrating into reinforced concrete target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(11): 2081–2092. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.001 -






 下载:
下载: