Dynamic Response Characteristics of Double-Row Suspended Steel Sheet Piles on Nearshore Slope under the Impact of Pile Hammer
-
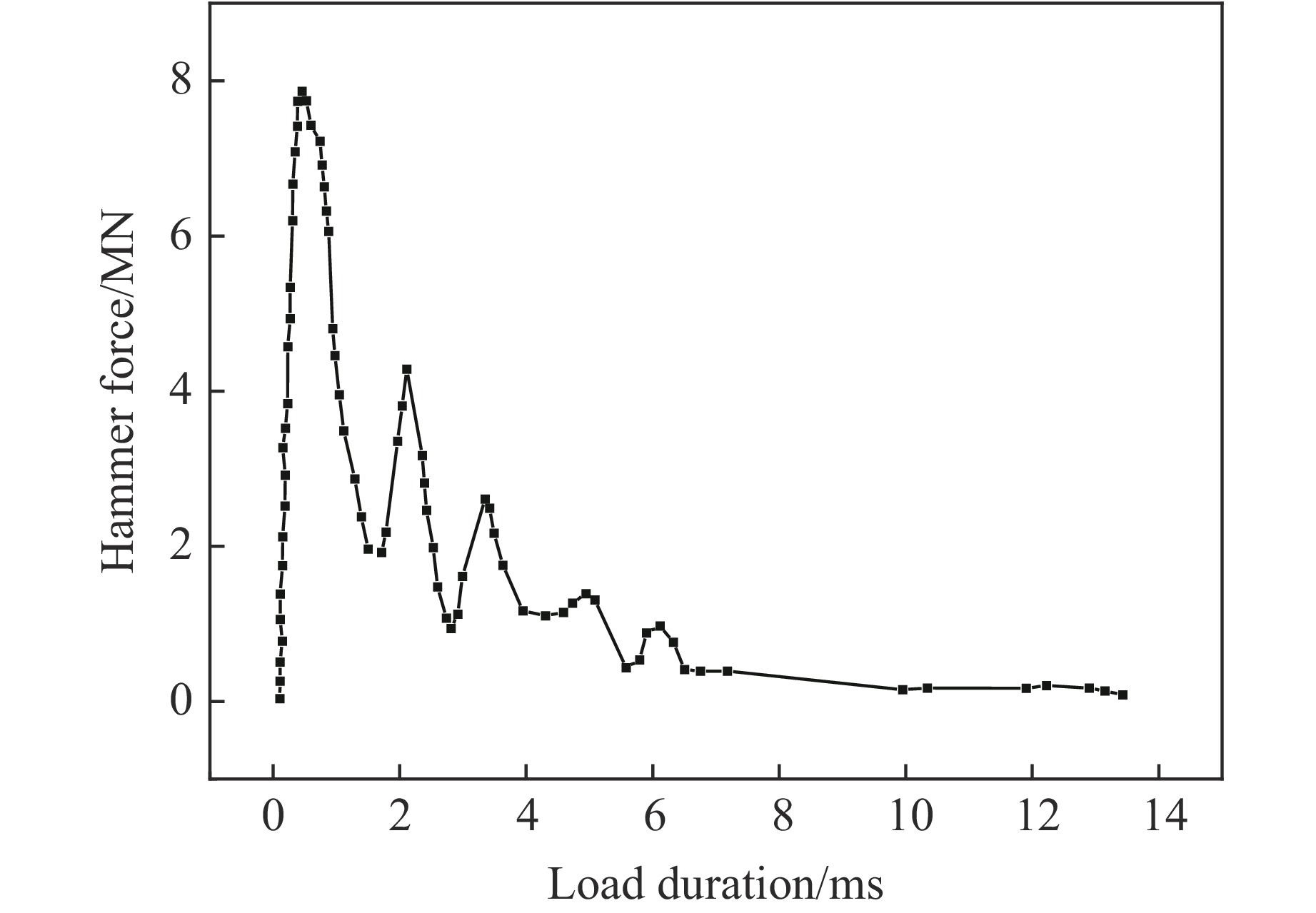
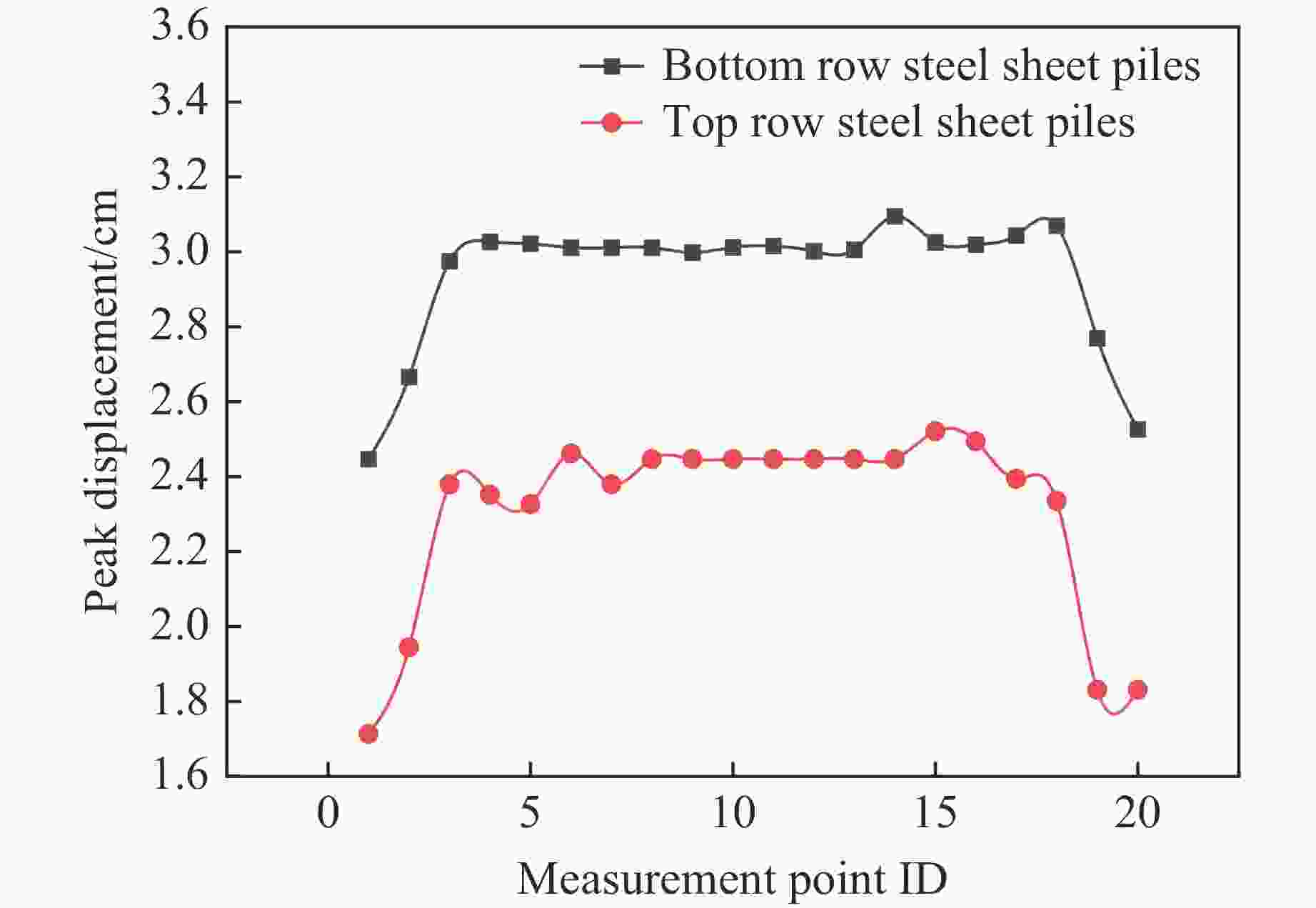
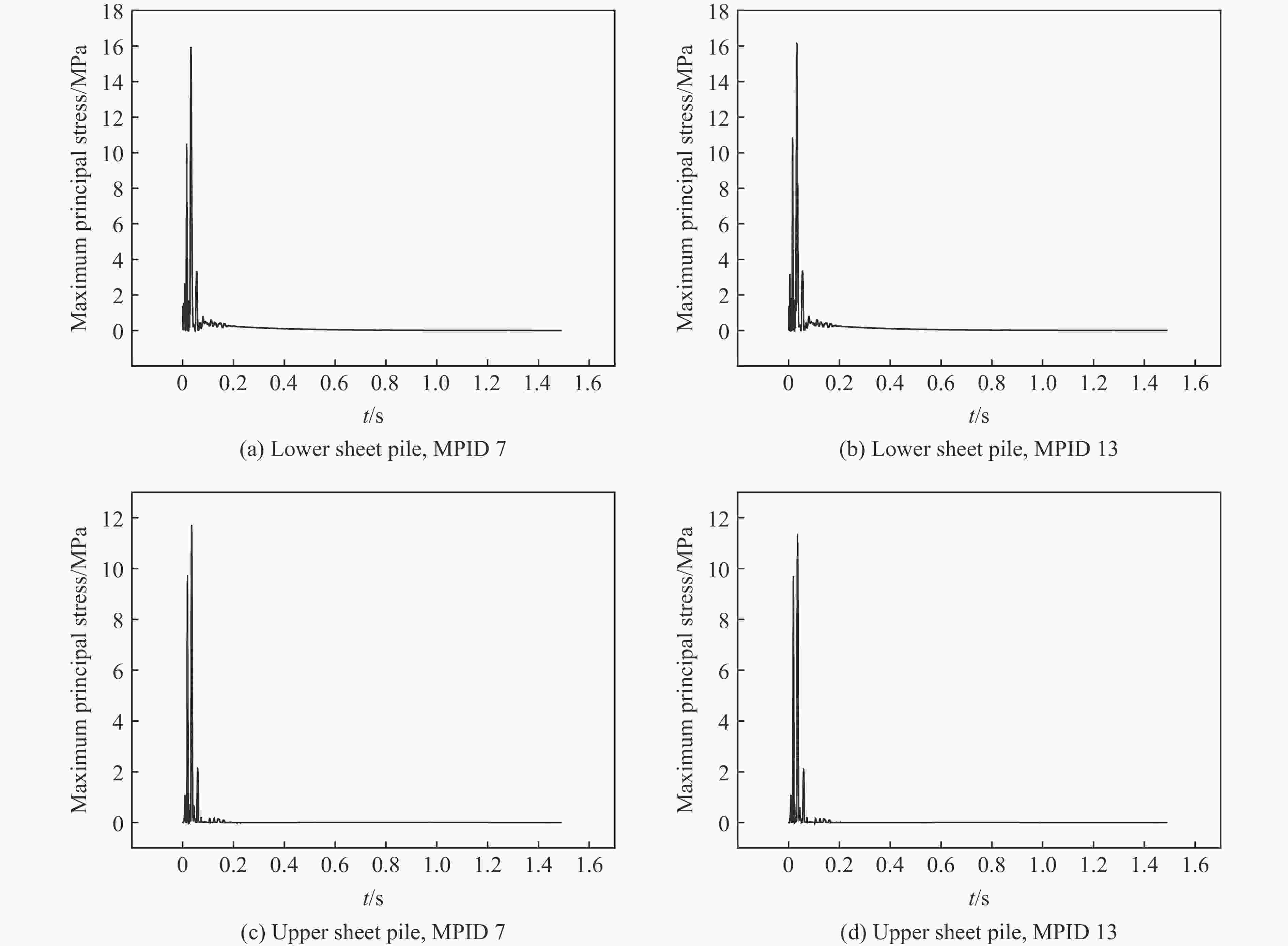
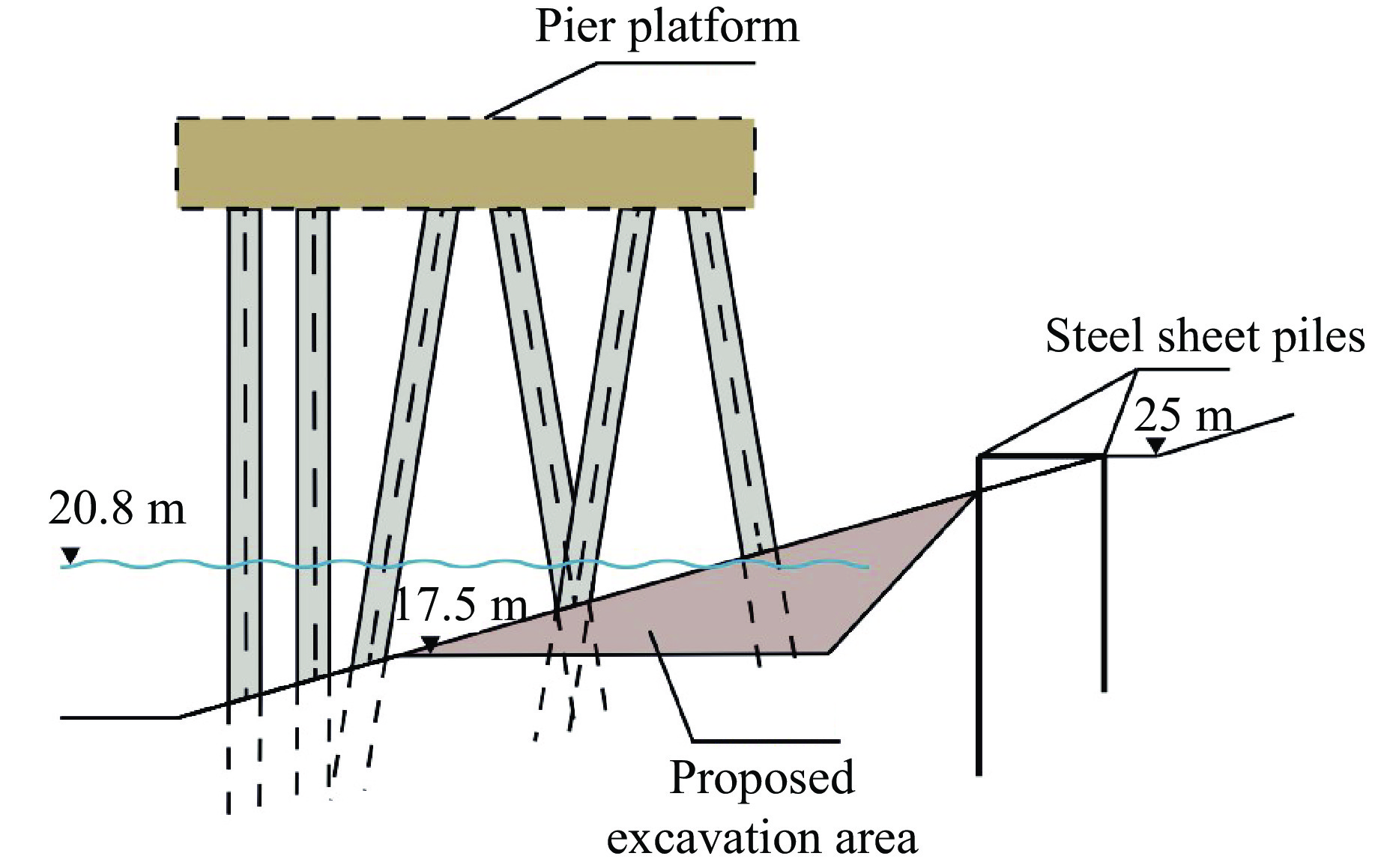
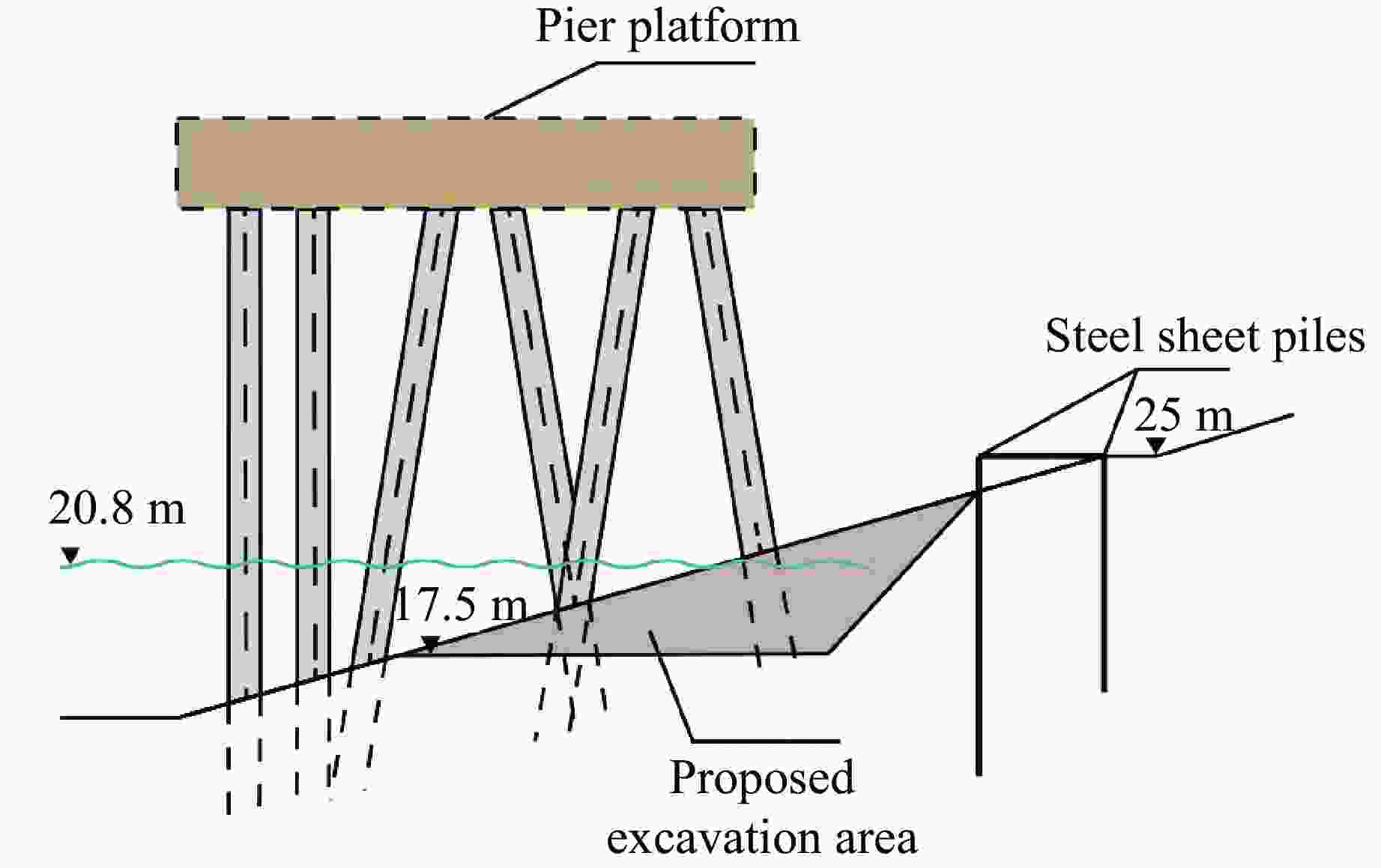
摘要: 岸坡锤击管桩施工过程中,为保证岸坡的安全稳定性,准确评估桩锤的动力荷载作用对岸坡支护钢板桩结构的影响非常重要。针对华容煤炭某码头一期工程,采用动力有限元数值模拟方法建立双排悬挂钢板桩结构计算模型;结合现场振动测试验证,分析桩锤振动作用下双排钢板桩的动力响应特性,实现桩锤振动影响下双排钢板桩的安全性评价。结果表明:钢板桩的位移变形与锤击位点相对位置的关系不大,上、下排钢板桩的最大位移分别为2.51和3.14 cm;最大主应力与锤击位点相对位置的关系不大,上、下排钢板桩的最大主应力均小于20 MPa;Mises应力最大值出现在钢板桩与锤击点垂直连线处,上、下排钢板桩的最大Mises应力分别为20.85和25.40 MPa。双排钢板桩的位移变形与应力处于安全控制范围内。Abstract: During the construction process of pile driving on nearshore slope, it is crucial to accurately assess the impact of dynamic loading from the pile hammer on the stability and safety of the slope’s supporting steel sheet pile structure. In the case of the first phase of the dock project at Huarong, a dynamic finite element numerical simulation method was employed to establish a computational model for the double-row suspended steel sheet pile structure. Through field vibration testing verification, the dynamic response characteristics of the double-row steel sheet piles under the influence of pile hammer impact were analyzed, enabling the evaluation of the safety of the double-row steel sheet piles. The research findings revealed that the displacement deformation of the steel sheet piles had little correlation with the impact location of the hammer. The maximum displacement of the lower row of steel sheet piles was 3.14 cm, while the maximum displacement of the upper row was 2.51 cm. The maximum principal stress had no significant relationship with the impact location, and the maximum principal stress of both the upper and lower rows of steel sheet piles was less than 20 MPa. The maximum von Mises stress occurred at the intersection between the steel sheet pile and the vertical line passing through the impact point of the hammer. The maximum von Mises stress for the upper row of steel sheet piles was 20.85 MPa, while for the lower row it was 25.40 MPa. The displacement deformation and stress of the double-row steel sheet piles remained within the safe control range.
-
Key words:
- pile hammer vibration /
- double-row steel sheet piles /
- dynamic response /
- safety control
-
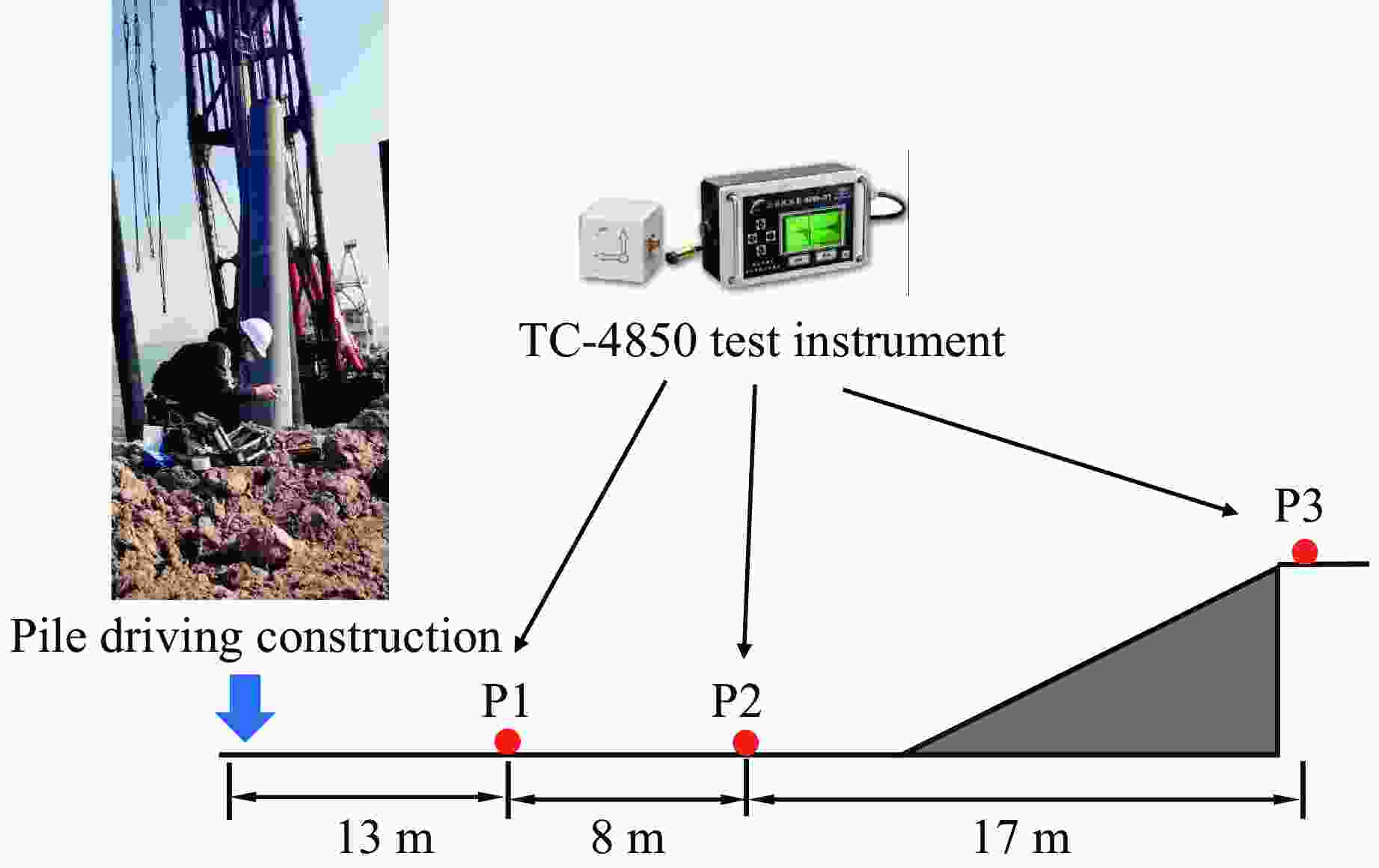
表 1 现场振动测试数据
Table 1. Field vibration test data
No. Test No. PPV/(cm·s−1) N Distance/m Ⅰ 1 2.000 7 13 2 0.632 3 21 3 0.158 6 38 Ⅱ 1 2.045 7 13 2 0.644 2 21 3 0.160 6 38 Ⅲ 1 2.025 7 13 2 0.639 3 21 3 0.160 3 38 表 2 数值模拟参数
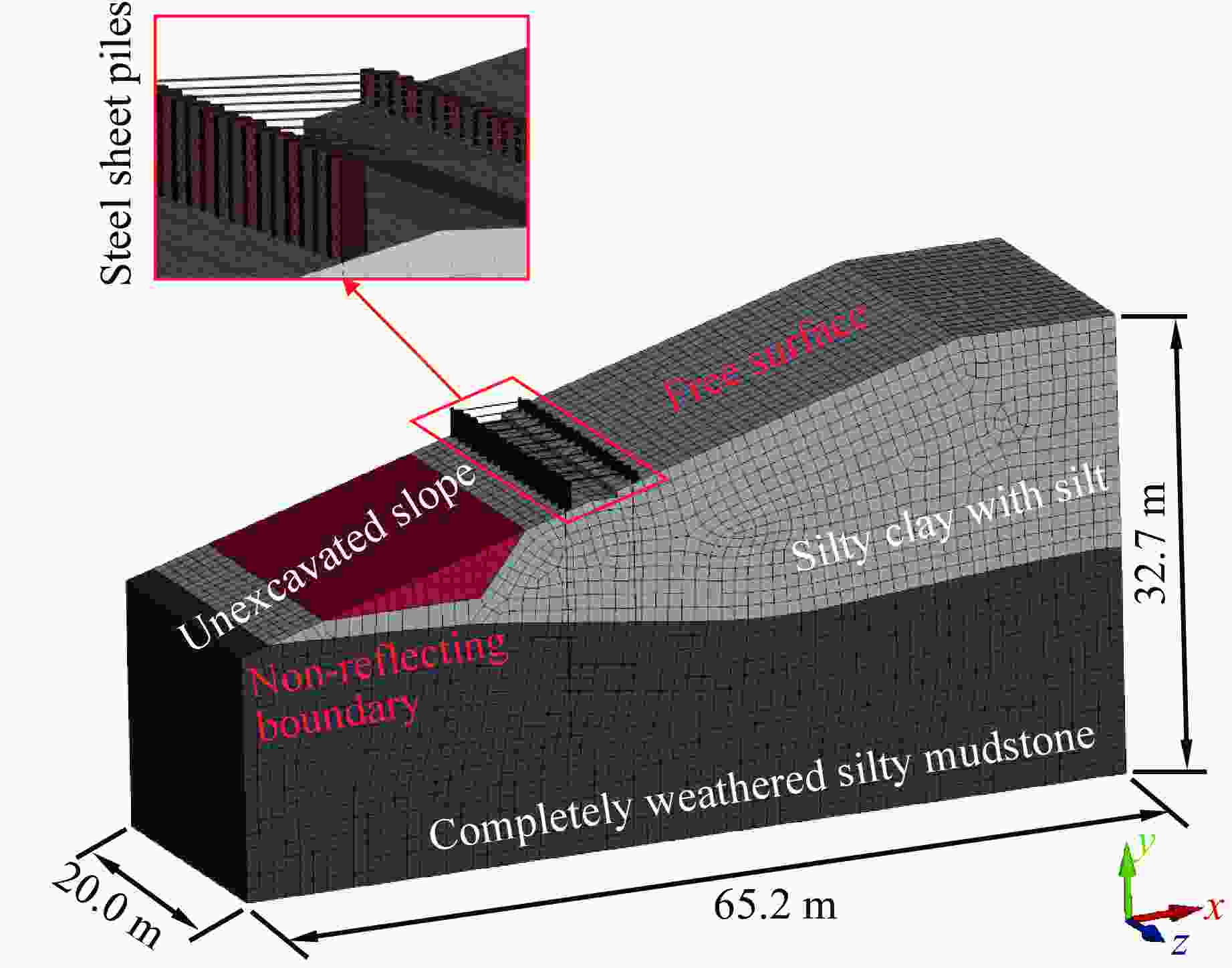
Table 2. Numerical simulation parameters
Material ρ/(kg·m−3) E0/GPa μ A/MPa B/MPa n C σ0/GPa Steel 7830 205 0.30 792 510 0.26 0.014 Clay 1900 11 0.20 0.19, 0.15 Mudstone 2230 15 0.22 0.30 表 3 质点峰值振动速度对比
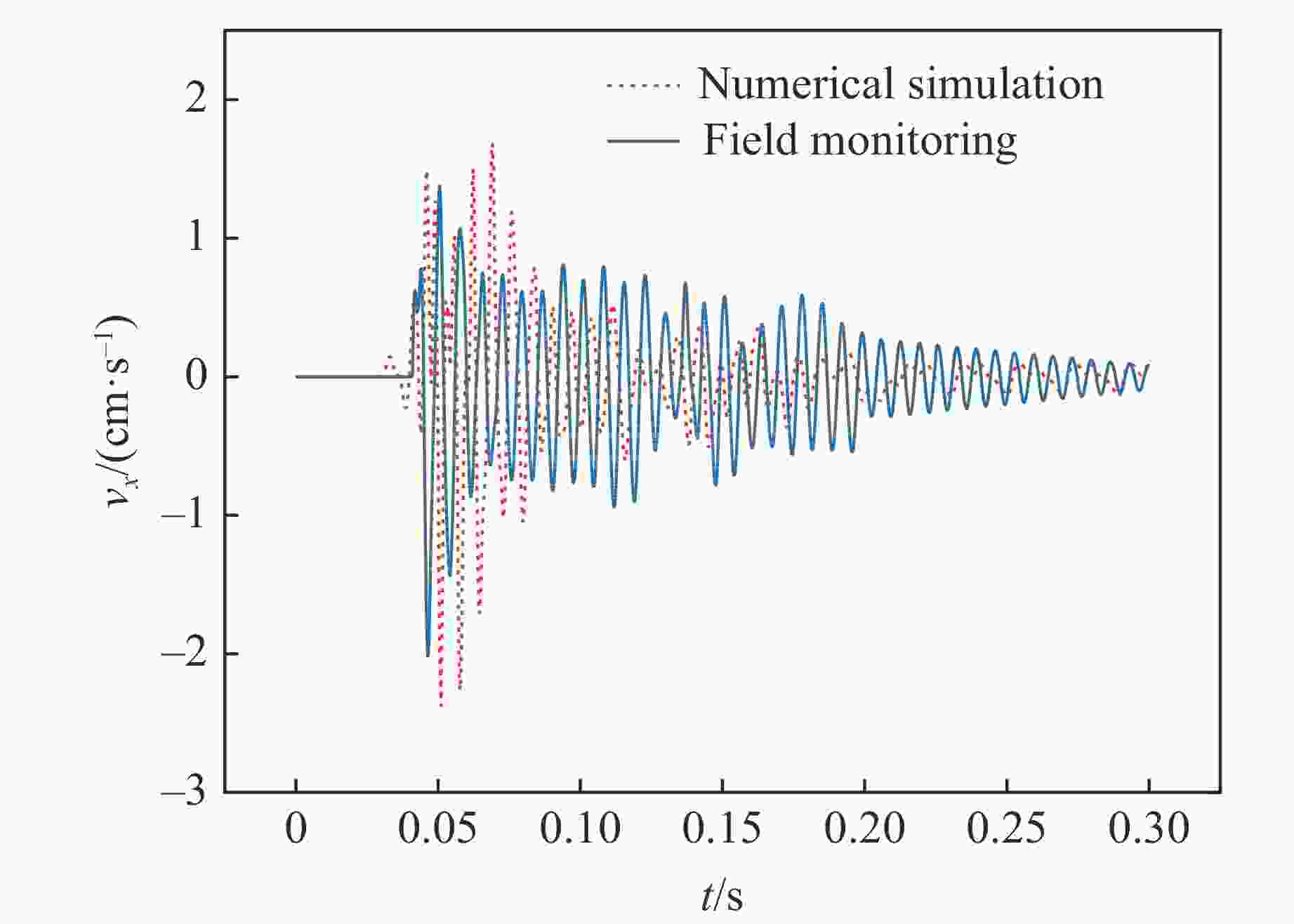
Table 3. Comparison of PPVs
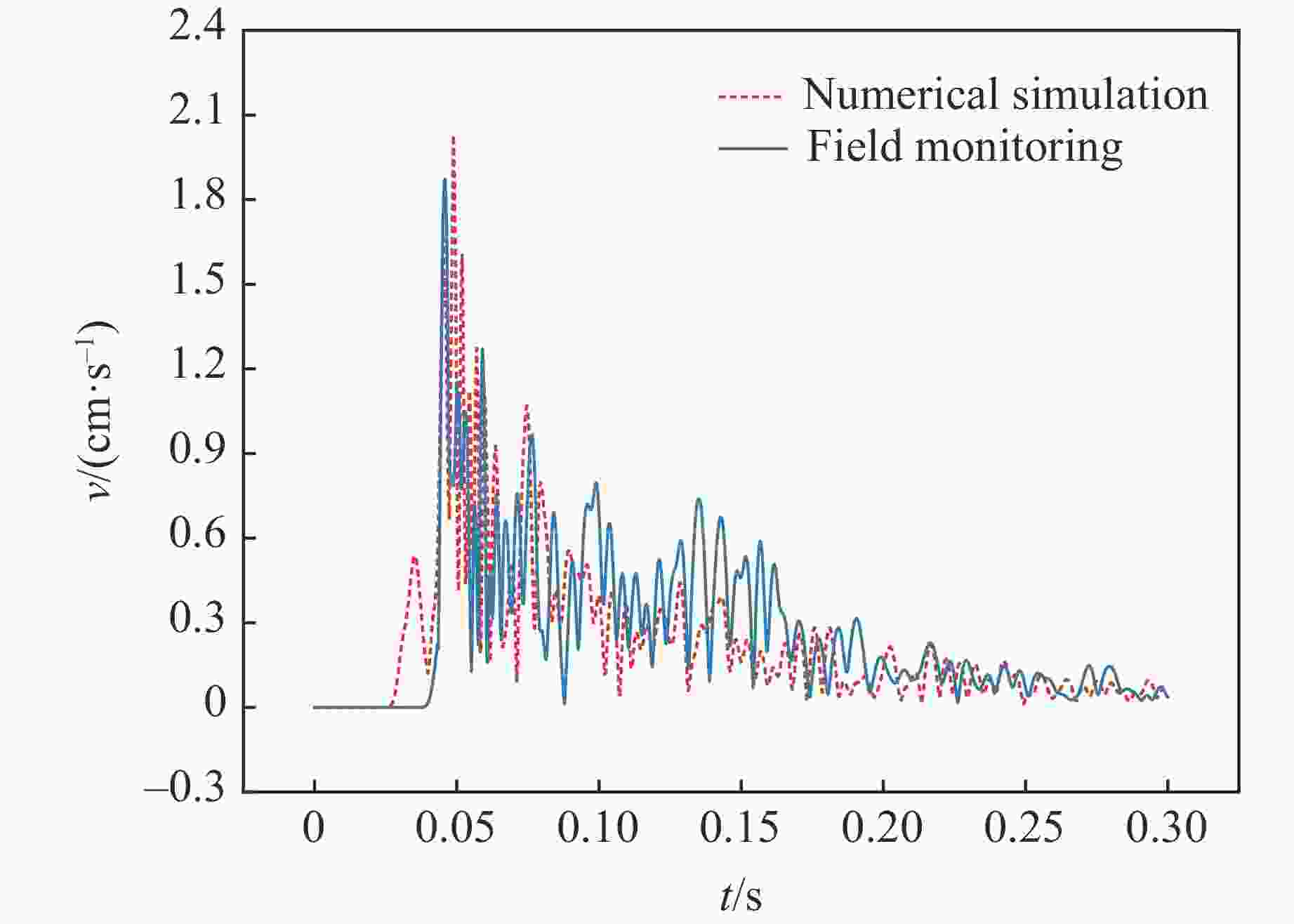
No. Burst distance/m Test PPV/(cm·s−1) Simulated PPV/(cm·s−1) Relative error/% 1 13 2.023 1.867 7.7 2 21 0.638 0.576 9.7 3 38 0.159 0.205 28.9 -
[1] 吕鹏, 董胜, 焉振, 等. U型钢板桩横向承载性能模型试验研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2023, 45(1): 1−9.LYU P, DONG S, YAN Z, et al. Experimental study on lateral bearing performance model of U-shaped steel sheet piles [J]. Marine and Lake Sciences Bulletin, 2023, 45(1): 1–9. [2] 焉振, 王元战. 考虑软基不排水强度循环弱化的格型钢板桩防波堤动力有限元分析 [J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(5): 1454–1462.YAN Z, WANG Y Z. Dynamic finite element analysis of geogrid steel sheet pile breakwater considering undrained strength degradation of soft foundation [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(5): 1454–1462. [3] 郑国兵, 黄朝煊, 袁文喜, 等. 深厚淤泥中双排钢板桩结构安全稳定性研究 [J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2020, 40(4): 71–76.ZHENG G B, HUANG C X, YUAN W X, et al. Research on the safety and stability of double-row steel sheet pile structure in deep and thick silt [J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2020, 40(4): 71–76. [4] 杨熠. 双排钢板桩围堰结构受力变形及稳定性分析 [D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020.YANG Y. Analysis of stress, deformation, and stability of double-row steel sheet pile caisson structure [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2020. [5] 曹胜敏. 高桩码头桩竖向荷载下静动力学行为研究 [D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2008.CAO S M. Study on the static and dynamic behavior of high pile wharf piles under vertical loads [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008. [6] 王娜娜. 打桩下沉过程中的动力响应研究 [D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2012.WANG N N. Study on the dynamic response during pile driving process [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2012. [7] XIA Y, JIANG N, ZHOU C, et al. Dynamic behaviors of buried reinforced concrete pipelines with gasketed bell-and-spigot joints subjected to tunnel blasting vibration [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 118: 104172. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104172 [8] JIANG N, ZHU B, ZHOU C, et al. Blasting vibration effect on the buried pipeline: a brief overview [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 129: 105709. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105709 [9] HALLQUIST J O. LS-DYNA theory manual [M]. Livermore, USA: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2006. [10] HALLQUIST J O. LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual version 971 [M]. Livermore, USA: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2007. [11] ZHOU Y, ZHANG S. Rupture and perforation responses of pressurized tubular members subjected to medium-velocity transverse impact loading [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 127: 105387. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105387 [12] YAO S, ZHANG D, LU Z, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the dynamic response of steel chamber under internal blast [J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 168: 877–888. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.03.067 [13] 邓灵敏. 基于LS-DYNA的动力沉桩全过程分析 [D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2013.DENG L M. Dynamic analysis of the entire process of pile driving based on LS-DYNA [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2013. [14] JIANG N, ZHU B, HE X, et al. Safety assessment of buried pressurized gas pipelines subject to blasting vibrations induced by metro foundation pit excavation [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 102: 103448. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103448 [15] 杜闯, 丁红岩, 张浦阳, 等. 钢板桩围堰有限元分析 [J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(Suppl 2): 159–164.DU C, DING H Y, ZHANG P Y, et al. Finite element analysis of steel sheet pile caisson [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(Suppl 2): 159–164. -






 下载:
下载: