Evolution Mechanism of Shale Gas Reservoirs Permeability under Thermal-Fluid-Solid Coupling
-
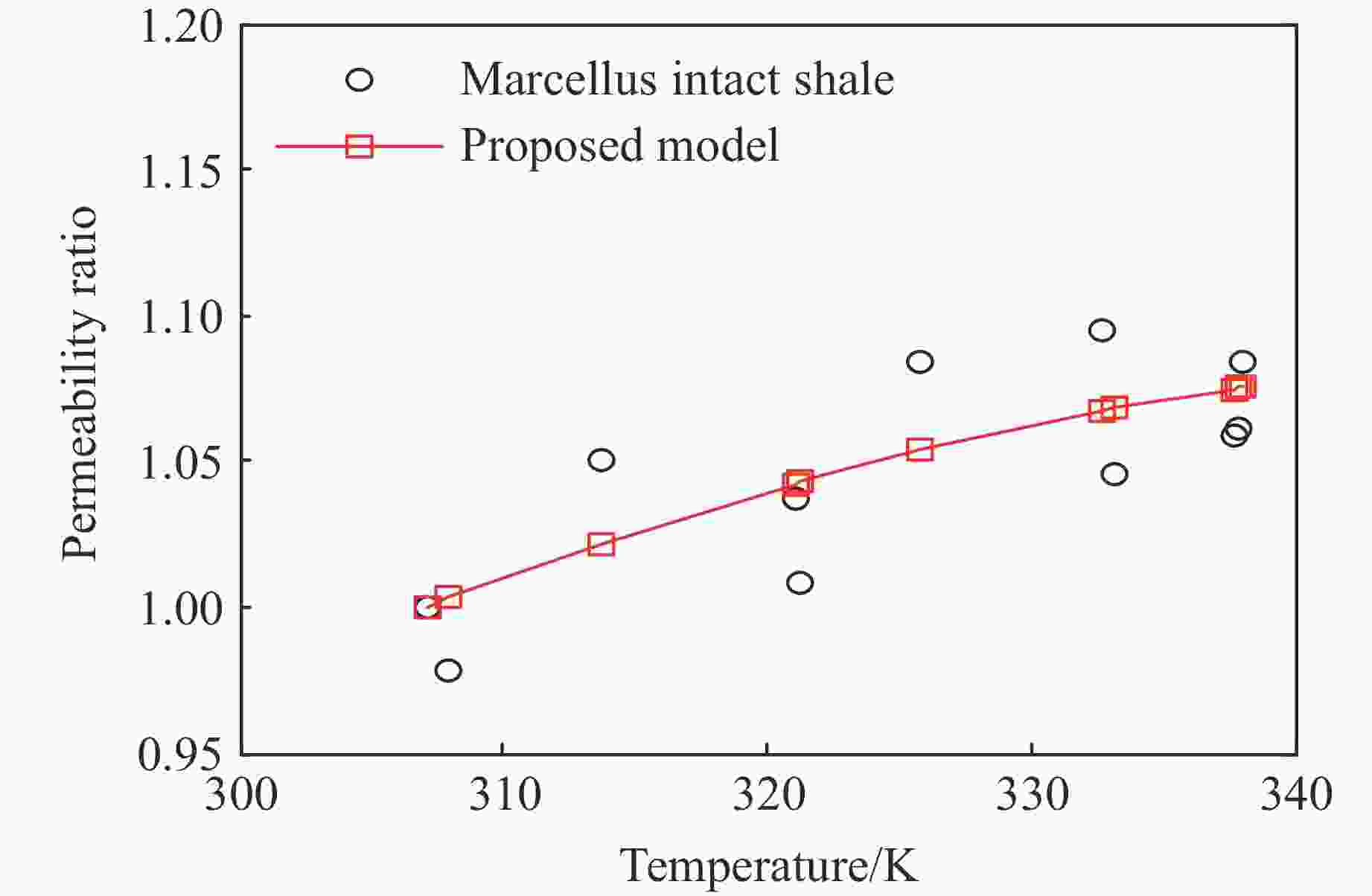
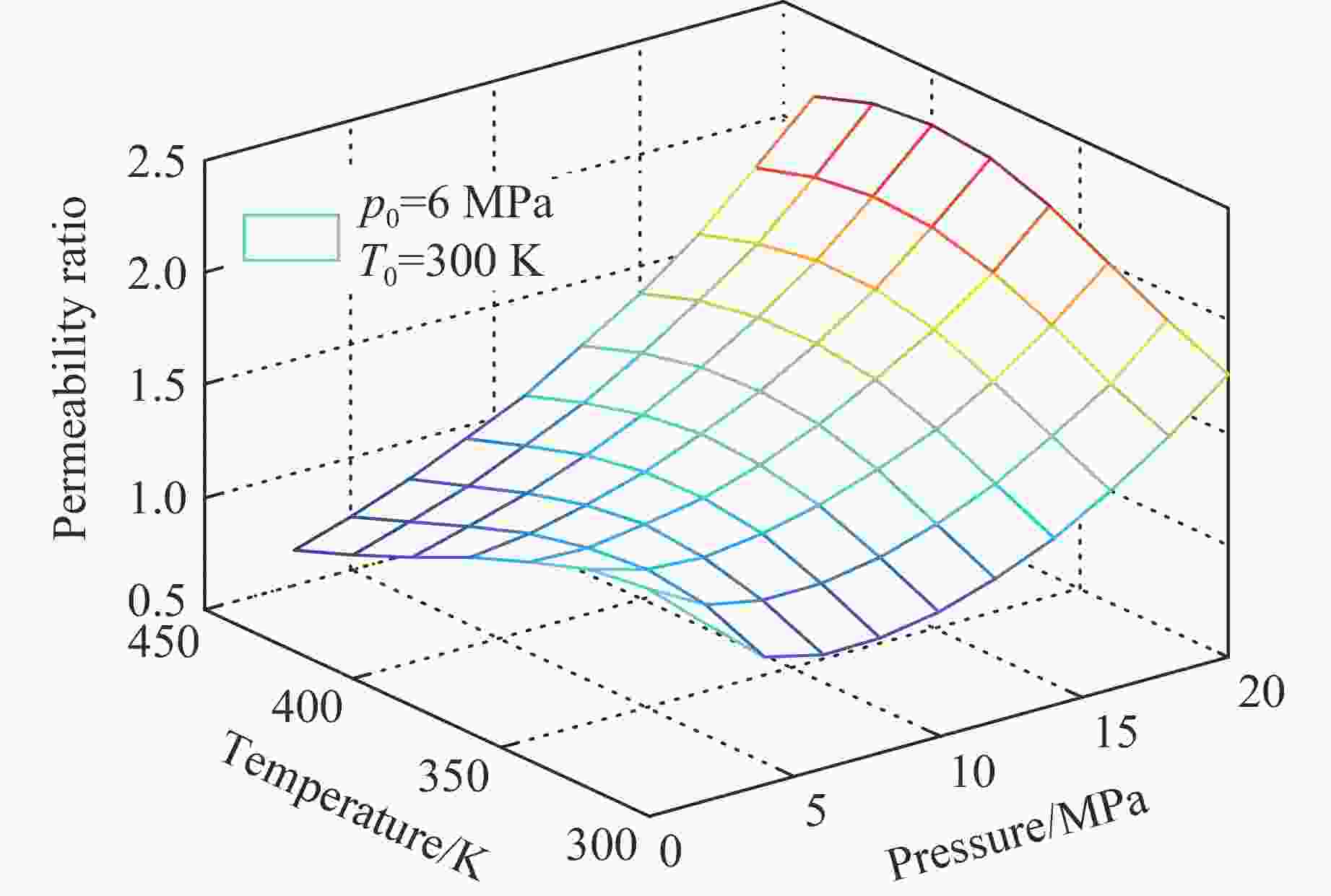
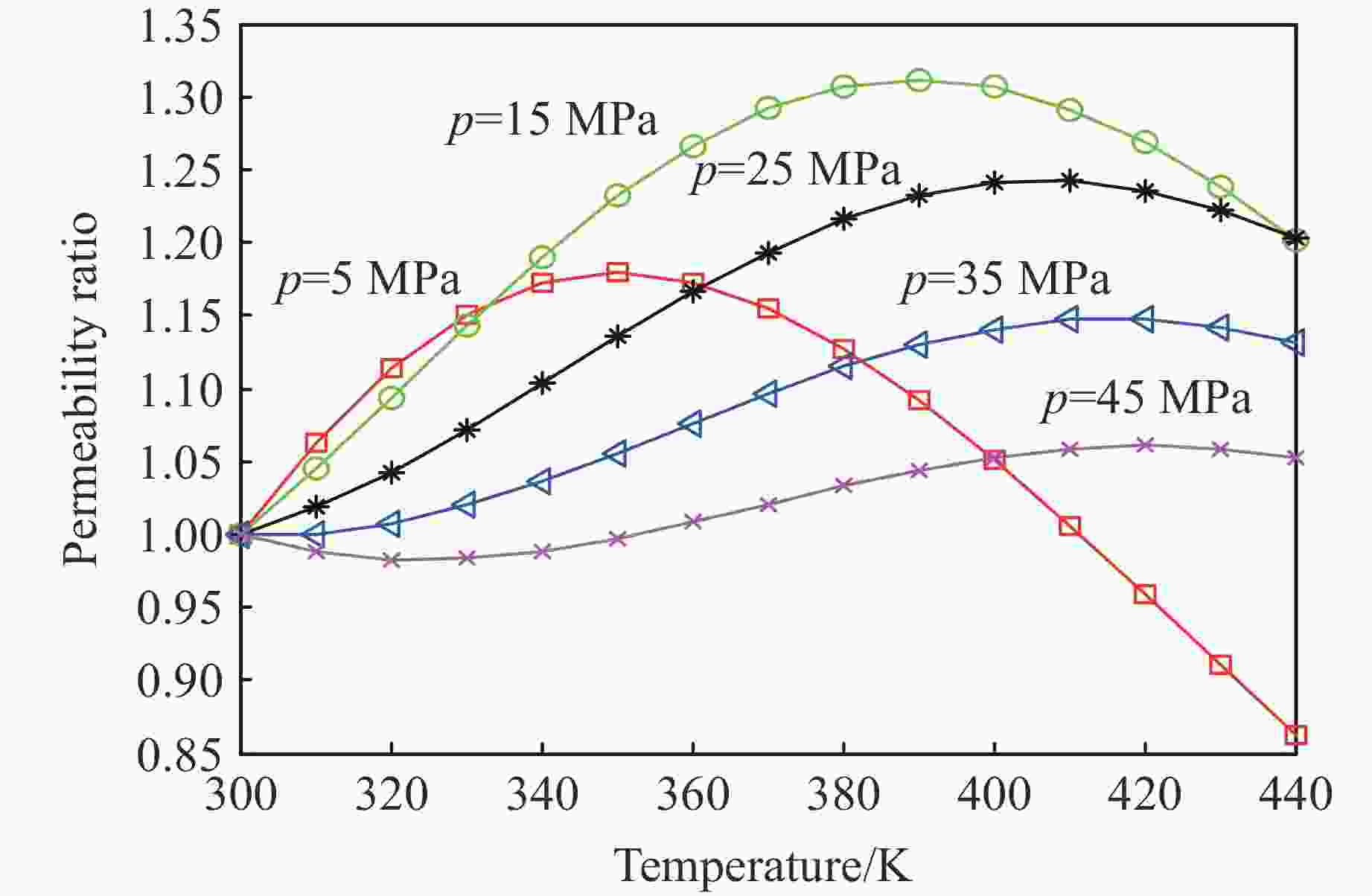
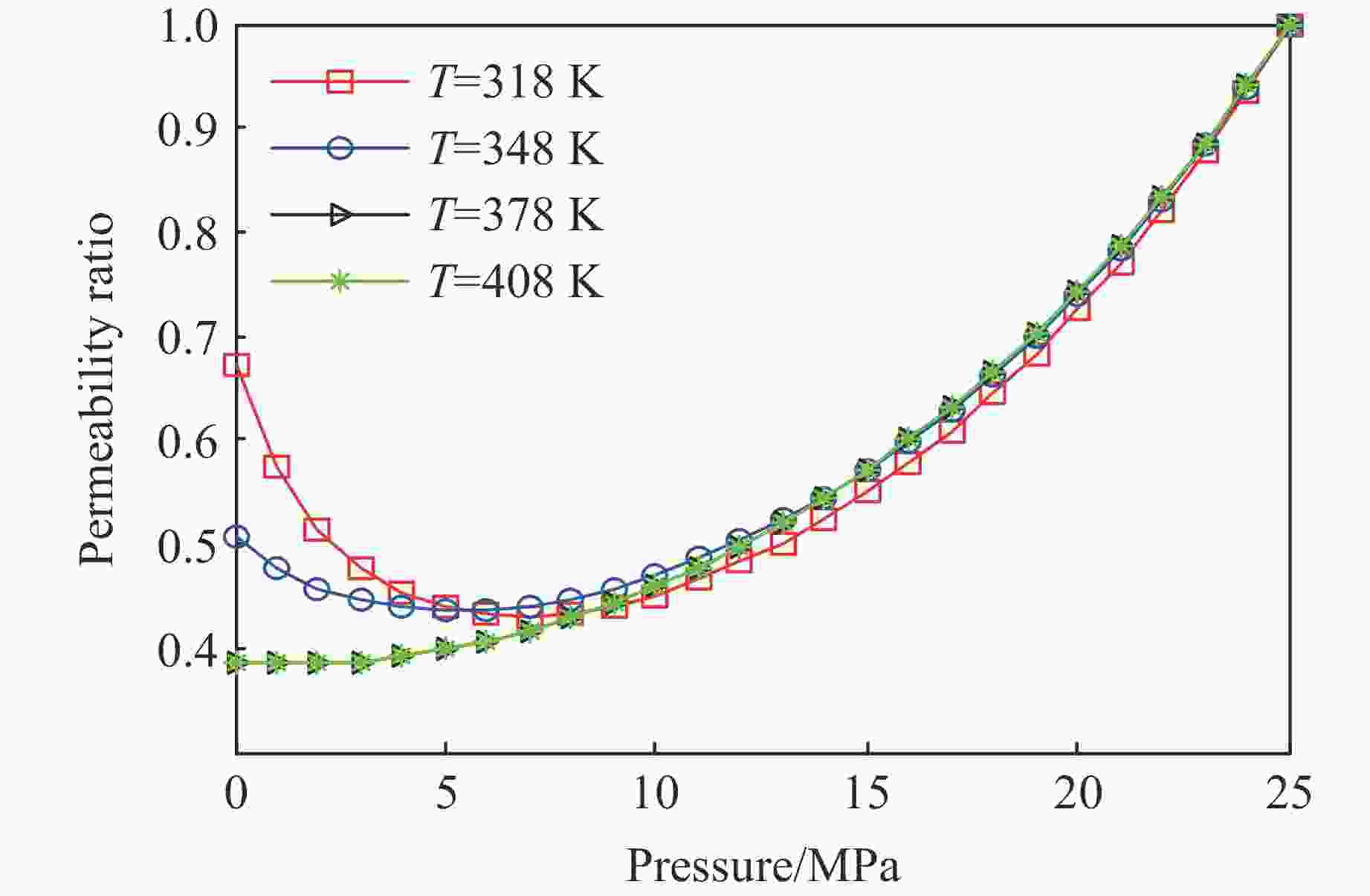
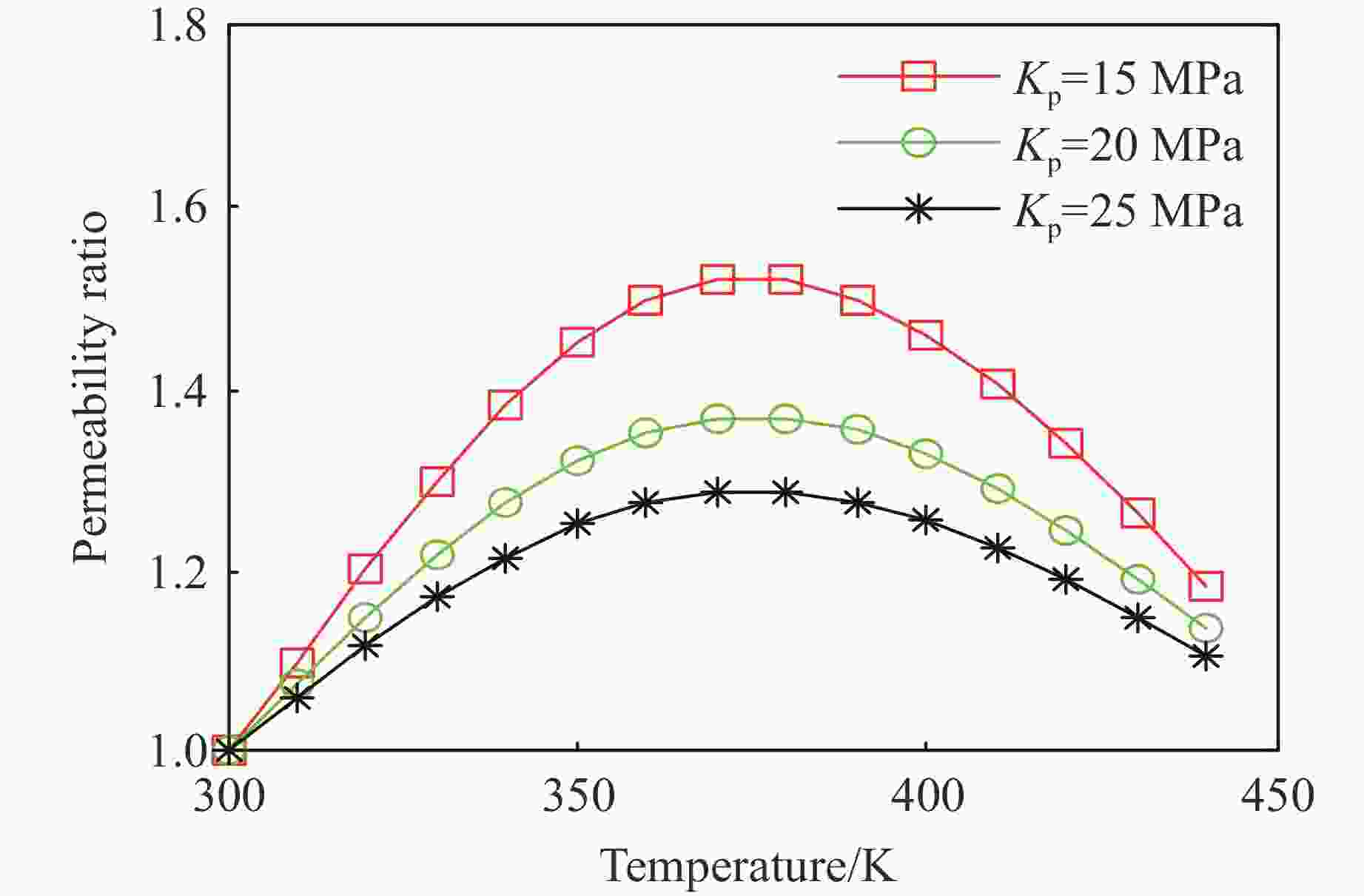
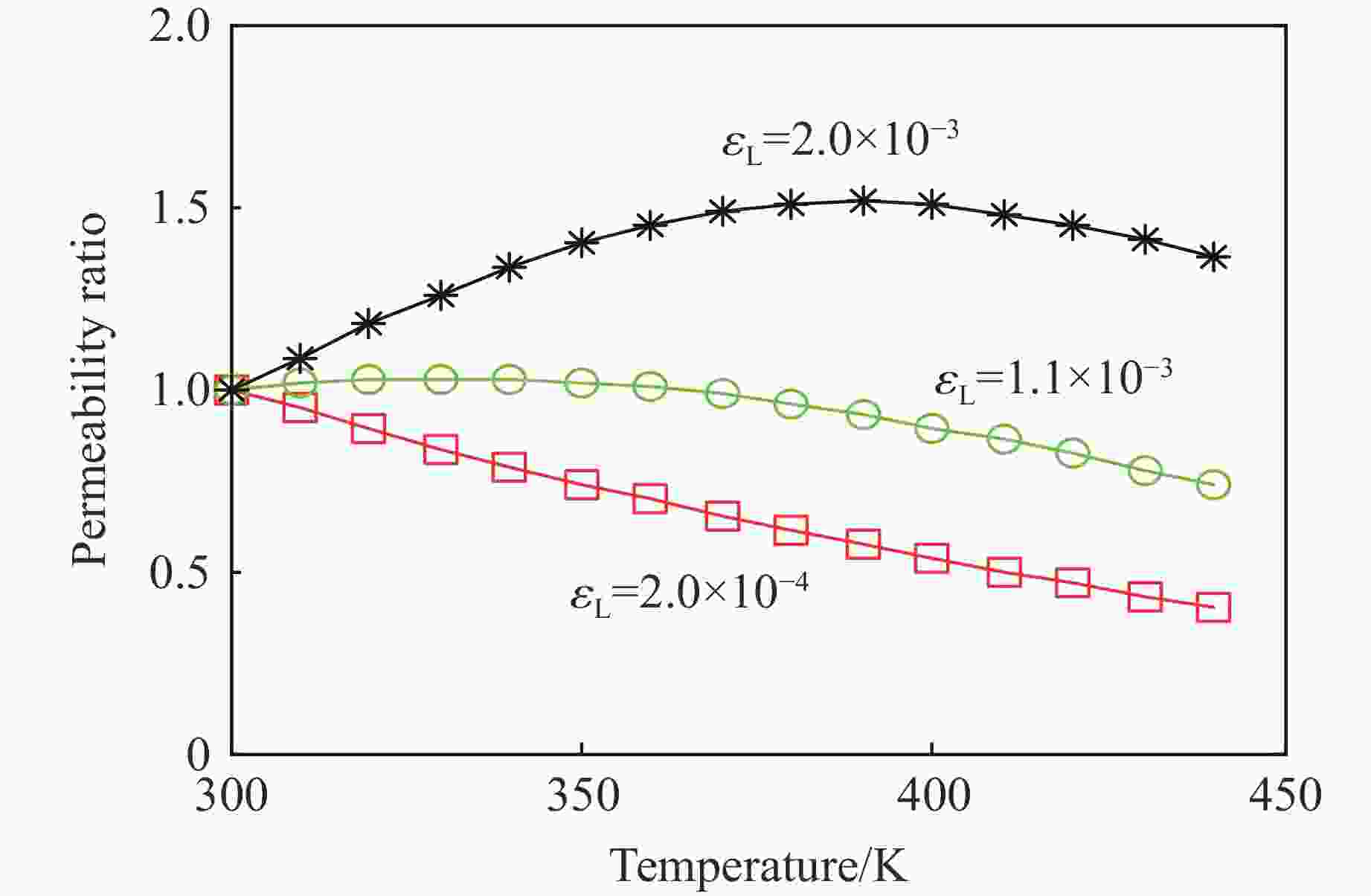
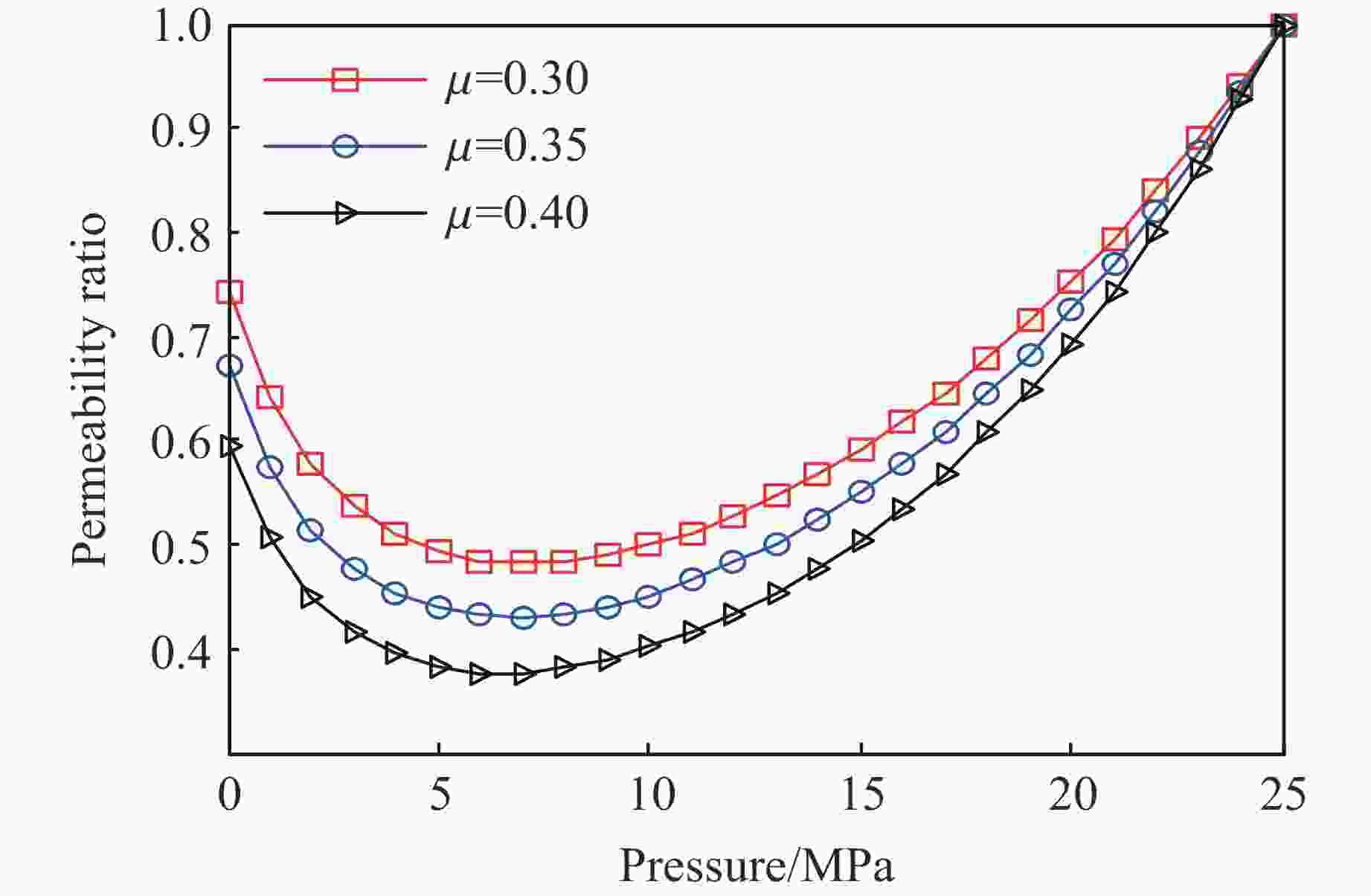
摘要: 为了研究热-流-固耦合作用下页岩渗透率的演化机制,考虑热解吸、有效应力和热膨胀对页岩渗透率的影响,提出了页岩的有效应力-渗透率模型,该模型能够分析吸附应变和热膨胀应变对页岩渗透率的影响机制。基于该模型和多孔介质弹性理论,建立了单轴应变条件下页岩气储层的热解吸渗透率模型,该模型能够探讨页岩渗透率随温度和孔隙压力的演化规律。利用室内实验观测的页岩岩样渗透率实验数据,验证了该模型的有效性和准确性。结果表明:(1)热解吸渗透率模型能较好地拟合恒压变温条件下的Marcellus页岩渗透率。(2) 探讨了恒温条件下页岩渗透率随孔压的演化机制,发现恒温条件下渗透率的演化规律呈“U形”,温度越高,渗透率随孔压下降的反弹现象越不明显。(3) 分析了恒压条件下页岩渗透率随温度的演化机制,发现恒压条件下渗透率随温度的演化规律呈“倒U形”,孔隙压力越大,温度对渗透率的影响越小。(4) 分别在恒温和恒压条件下对热解吸渗透率模型进行敏感性分析,发现泊松比越大,渗透率比值梯度越大,孔隙体积模量越大,渗透率比值梯度越小。恒压条件下,当线胀系数大于临界值或朗缪尔体应变小于临界值,渗透率的演化规律不呈现“倒U形”。恒温条件下,当朗缪尔体应变小于临界值时,渗透率的演化规律不呈现“U形”。Abstract: In order to study the evolution mechanism of shale permeability under thermal-fluid-solid coupling, the effective stress-permeability model of shale is developed considering the impact of thermal desorption and effective stress and thermal expansion on shale permeability. The proposed model is capable of revealing the influence mechanism of sorption strain and thermal expansion strain on shale permeability. Based on the model and the elastic theory of porous media, the thermal induced desorption permeability model of shale gas reservoirs under uniaxial strain condition was established. The model can discuss the evolution mechanism of shale permeability with temperature and pore pressure. The validity and accuracy of the model was verified against the laboratory measurements of shale core permeability. The following results were obtained: (1) The thermal induced desorption permeability model can fit the permeability of Marcellus shale under constant pressure and variable temperature. (2) The evolution mechanism of shale permeability with pore pressure under constant temperature is explored. The evolution law of permeability under constant temperature is U-shaped. The rebound of permeability with pore pressure decrease is less obvious with the increase of temperature. (3) The evolution mechanism of shale permeability with temperature under constant pressure condition is analyzed. The evolution law of permeability with temperature under constant pressure condition presents an inverted “U” shape. The influence of temperature on permeability is less with the increase of pore pressure. (4) The sensitivity analysis of thermal desorption permeability model under constant temperature and pressure was carried out. The larger the Poisson’s ratio is, the larger the permeability ratio gradient is. The larger the pore volume modulus, the smaller the permeability ratio gradient. At constant pore pressure, when the linear expansion coefficient is larger than the critical value or the Langmuir bulk strain is smaller than the critical value, the permeability evolution does not show an inverted “U” shape. At constant temperature, when Langmuir strain is less than critical value, permeability evolution does not show “U” shape.
-
表 1 裂隙页岩的渗透率比
Table 1. Permeability ratio of fractured shale
Temperature/K k/k0 of fractured shale 295 1.000 303 1.044 313 1.113 323 1.211 表 2 完整页岩的渗透率比
Table 2. Permeability ratio of intact shale
Temperature/K k/k0 of intact shale Temperature/K k/k0 of intact shale 307.1 1.000 332.7 1.095 308.0 0.978 333.3 1.045 313.8 1.051 337.7 1.058 321.1 1.037 337.9 1.061 321.2 1.008 338.0 1.084 325.9 1.085 -
[1] 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等. 页岩气资源评价方法与技术: 概率体积法 [J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(2): 184–191.ZHANG J C, LIN L M, LI Y X, et al. The method of shale gas assessment: probability volume method [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(2): 184–191. [2] 李敏, 庞雄奇, 罗冰, 等. 生烃潜力法在深层页岩气资源评价中的应用——以四川盆地五峰——龙马溪组优质烃源岩为例 [J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2021, 50(6): 1096–1107. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.001301LI M, PANG X Q, LUO B, et al. Application of hydrocarbon generation potential method to deep shale gas resource evaluation: a case study of high-quality source rocks of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(6): 1096–1107. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.001301 [3] GENSTERBLUM Y, MERKEL A, BUSCH A, et al. Gas saturation and CO2 enhancement potential of coalbed methane reservoirs as a function of depth [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(2): 395–420. doi: 10.1306/07021312128 [4] GENG Y D, LIANG W G, LIU J, et al. Evolution of pore and fracture structure of oil shale under high temperature and high pressure [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(10): 10404–10413. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01071 [5] 赵瑜, 王超林, 曹汉, 等. 页岩渗流模型及孔压与温度影响机理研究 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(6): 1754–1760. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.1404ZHAO Y, WANG C L, CAO H, et al. Influencing mechanism and modelling study of pore pressure and temperature on shale permeability [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(6): 1754–1760. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.1404 [6] WANG K, DU F, WANG G D, et al. Investigation of gas pressure and temperature effects on the permeability and steady-state time of Chinese anthracite coal: an experimental study [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 40: 179–188. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.02.014 [7] 吴迪, 王挺, 刘雪莹, 等. 页岩渗透特性受热力条件影响的实验研究 [J]. 实验力学, 2020, 35(3): 539–546. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-18-230WU D, WANG T, LIU X Y, et al. Experimental study on the influence of thermal conditions on shale permeability characteristics [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2020, 35(3): 539–546. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-18-230 [8] 张道川, 周军平, 鲜学福, 等. 多场耦合作用下页岩渗透特性实验研究 [J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2018, 14(3): 613–621.ZHANG D C, ZHOU J P, XIAN X F, et al. Experiment study on the coupling multi-field effect on the dynamic variation of permeability in shale [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2018, 14(3): 613–621. [9] 李波波, 高政, 杨康, 等. 考虑温度、孔隙压力影响的煤岩渗透性演化机制分析 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(2): 626–632. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0146LI B B, GAO Z, YANG K, et al. Analysis of coal permeability evolution mechanism considering the effect of temperature and pore pressure [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(2): 626–632. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0146 [10] WANG G Y, YANG D, ZHAO Y S, et al. Experimental investigation on anisotropic permeability and its relationship with anisotropic thermal cracking of oil shale under high temperature and triaxial stress [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 146: 718–725. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.10.005 [11] SCHWARTZ B, ELSWORTH D. Inverted U-shaped permeability enhancement due to thermally induced desorption determined from strain-based analysis of experiments on shale at constant pore pressure [J]. Fuel, 2021, 302: 121178. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121178 [12] TENG T, WANG J G, GAO F, et al. A thermally sensitive permeability model for coal-gas interactions including thermal fracturing and volatilization [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 32: 319–333. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.04.034 [13] JU Y, WANG J G, WANG H J, et al. CO2 permeability of fractured coal subject to confining pressures and elevated temperature: experiments and modeling [J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2016, 59(12): 1931–1942. doi: 10.1007/s11431-016-0478-5 [14] SINHA S, BRAUN E M, DETERMAN M D, et al. Steady-state permeability measurements on intact shale samples at reservoir conditions-effect of stress, temperature, pressure, and type of gas [C]//SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference. Manama, Bahrain: SPE, 2016. [15] 张宏学, 刘卫群. 非平衡解吸状态下页岩气储层渗透率演化机制 [J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(10): 2696–2704. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.1875ZHANG H X, LIU W Q. Permeability evolution mechanism of shale gas reservoir in non-equilibrium desorption state [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(10): 2696–2704. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.1875 [16] MCKEE C R, BUMB A C, KOENIG R A. Stress-dependent permeability and porosity of coal and other geologic formations [J]. SPE Formation Evaluation, 1988, 3(1): 81–91. doi: 10.2118/12858-PA [17] SEIDLE J P, JEANSONNE M W, ERICKSON D J. Application of matchstick geometry to stress dependent permeability in coals [C]//SPE Rocky Mountain Regional Meeting. Casper, Wyoming: SPE, 1992. [18] CUI X J, BUSTIN R M. Volumetric strain associated with methane desorption and its impact on coalbed gas production from deep coal seams [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(9): 1181–1202. doi: 10.1306/05110504114 [19] 张宏学. 页岩储层渗流-应力耦合模型及应用 [D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2015.ZHANG H X. Seepage and stress coupling model for shale reservoir and its application [D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2015. [20] 张宏学, 刘卫群. 海陆过渡相煤系页岩的渗流特征 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(5): 055901. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180556ZHANG H X, LIU W Q. Seepage of marine-terrigenous facies coal measures shale [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(5): 055901. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180556 [21] LI X, ELSWORTH D. Geomechanics of CO2 enhanced shale gas recovery [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 26: 1607–1619. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2014.08.010 [22] 郭为, 熊伟, 高树生, 等. 温度对页岩等温吸附/解吸特征影响 [J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(4): 481–485. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.04.14GUO W, XIONG W, GAO S S, et al. Impact of temperature on the isothermal adsorption/desorption characteristics of shale gas [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(4): 481–485. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.04.14 -







 下载:
下载: