Numerical Investigation on Effect of Interface Modelling of Rock-Rubble Shielding Overlays on the Anti-Penetration Capability
-
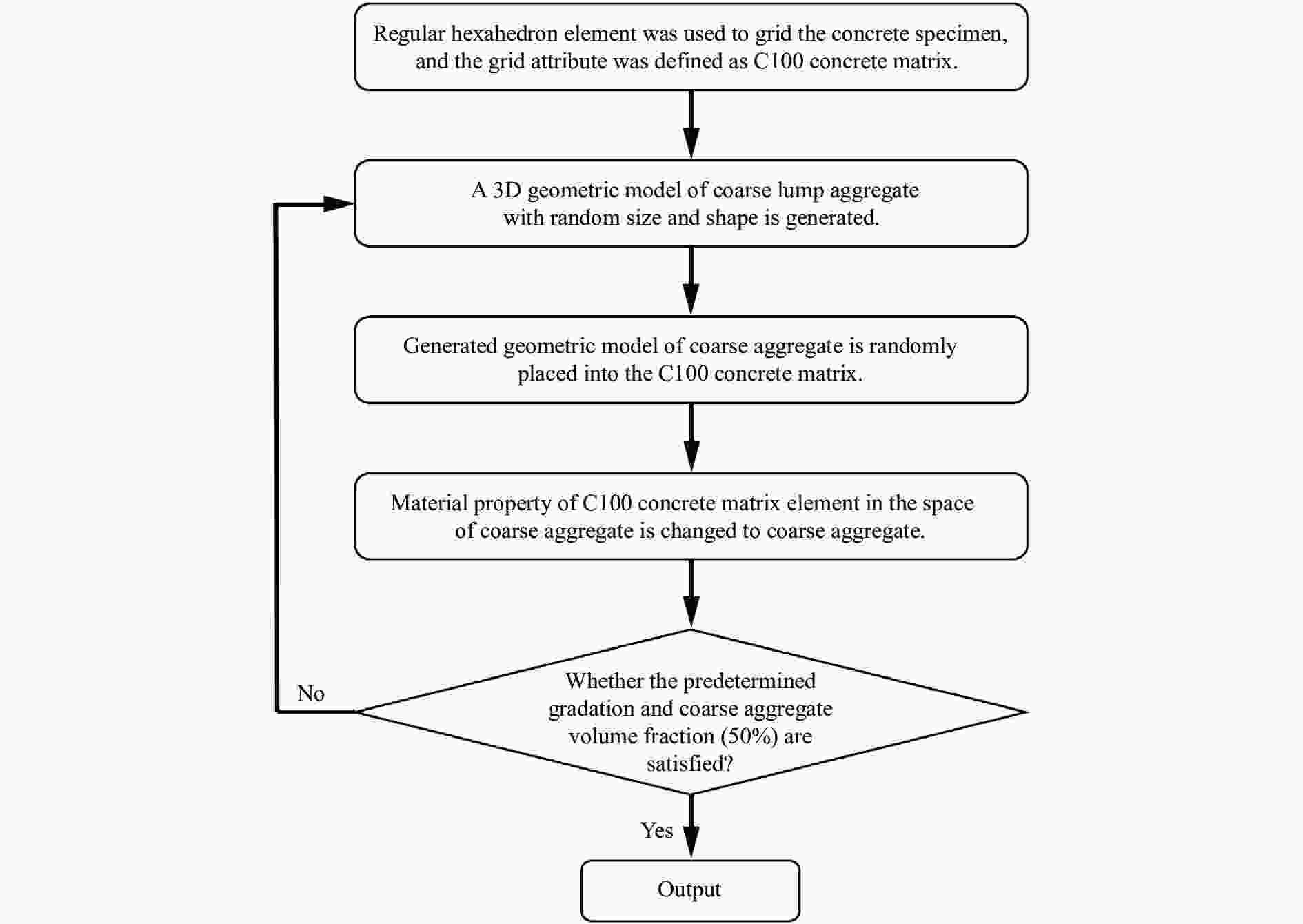
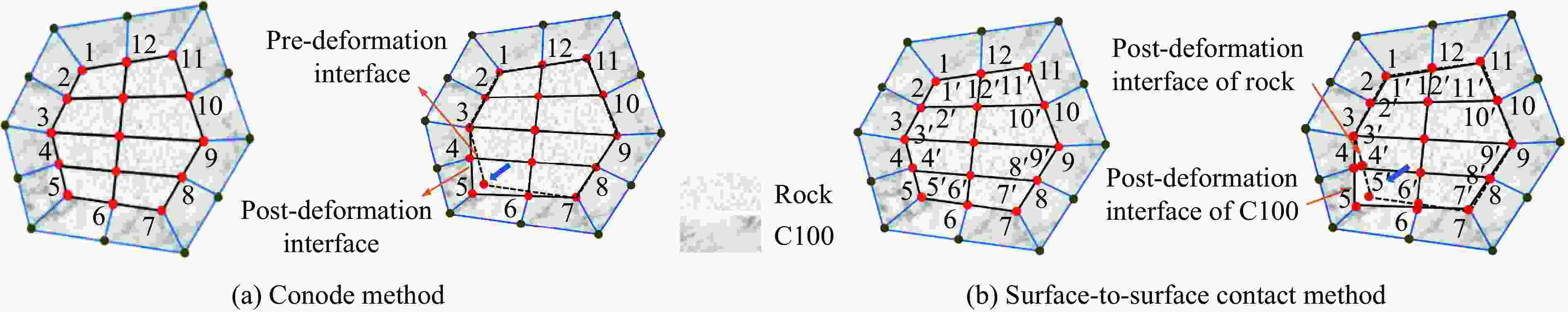
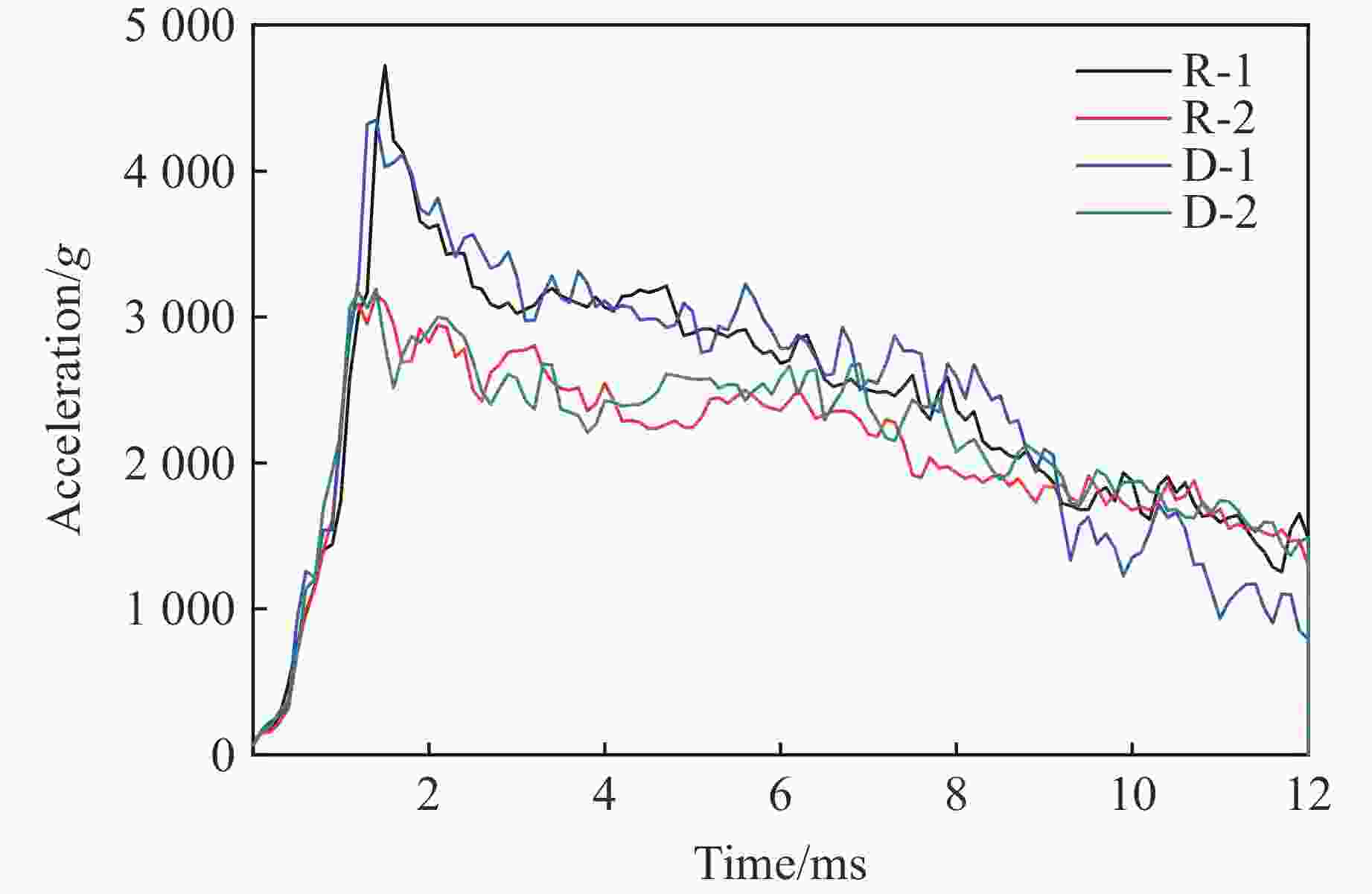
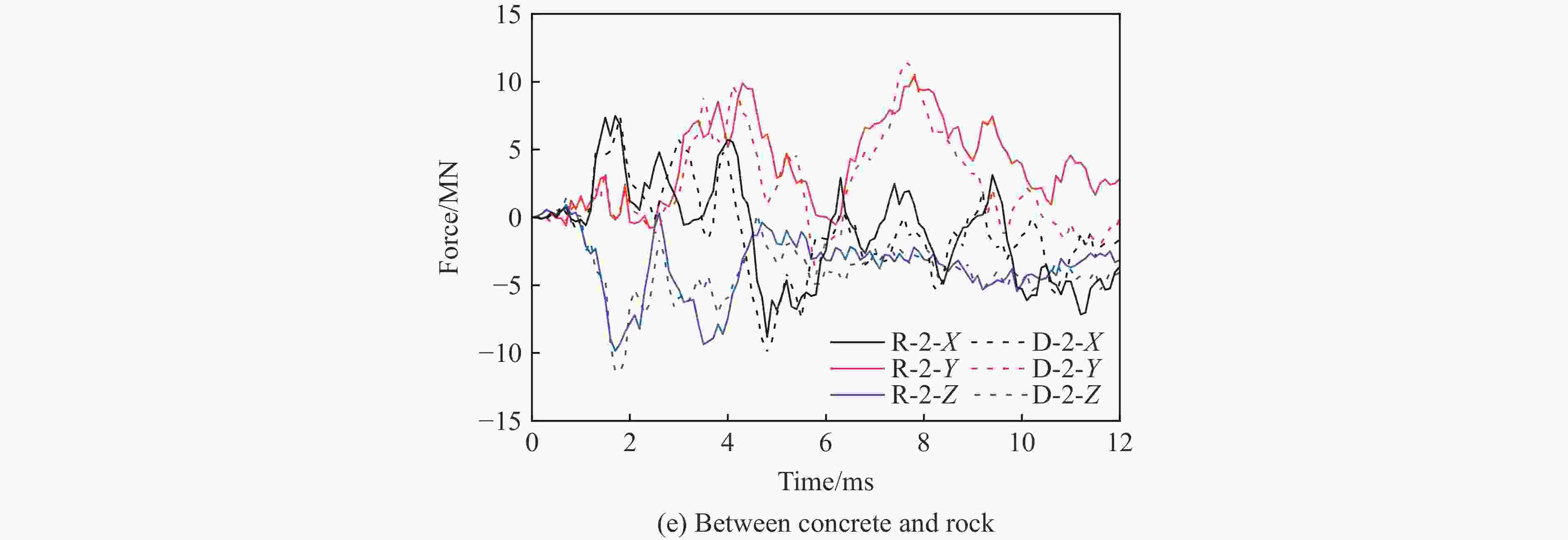
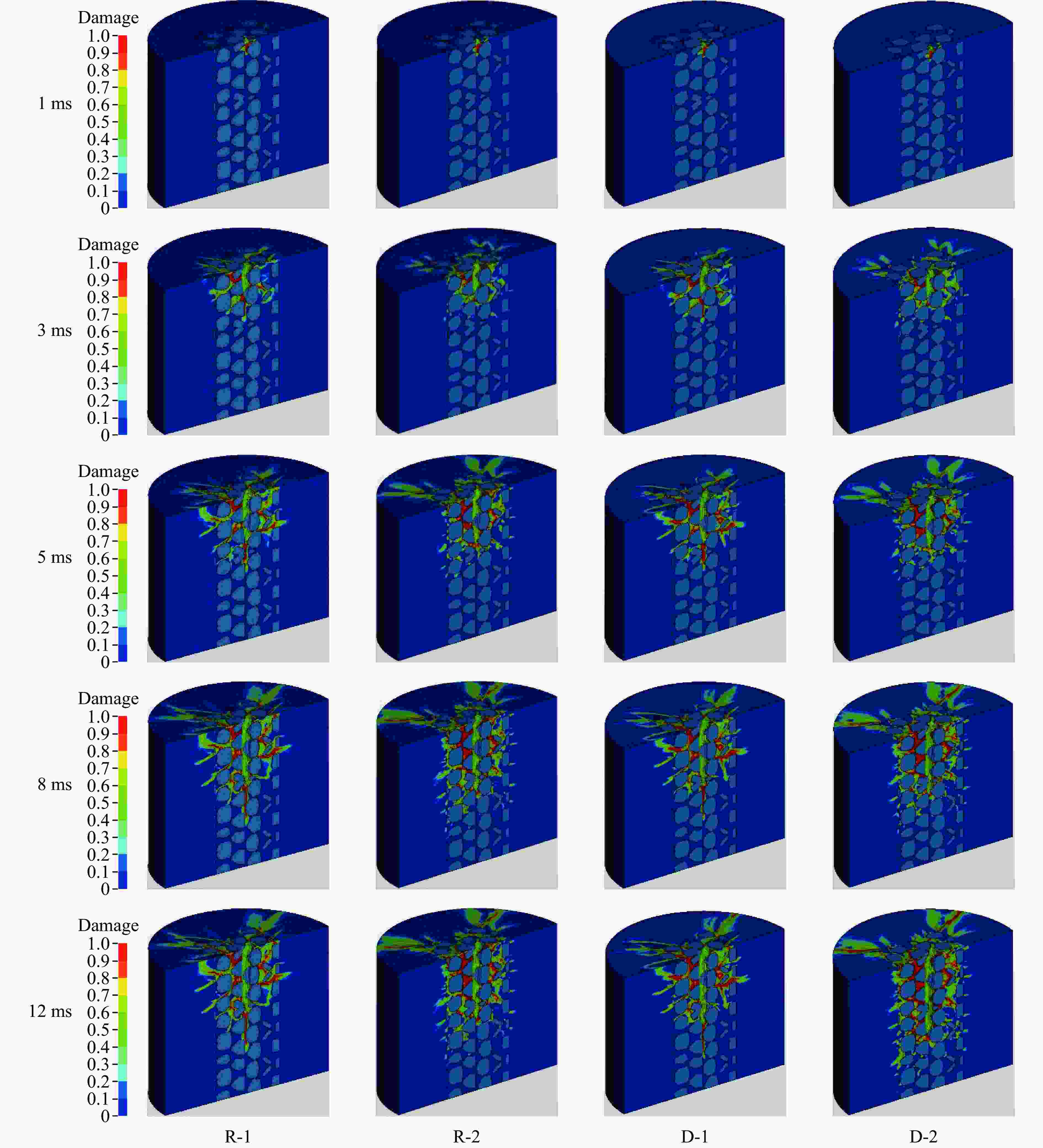
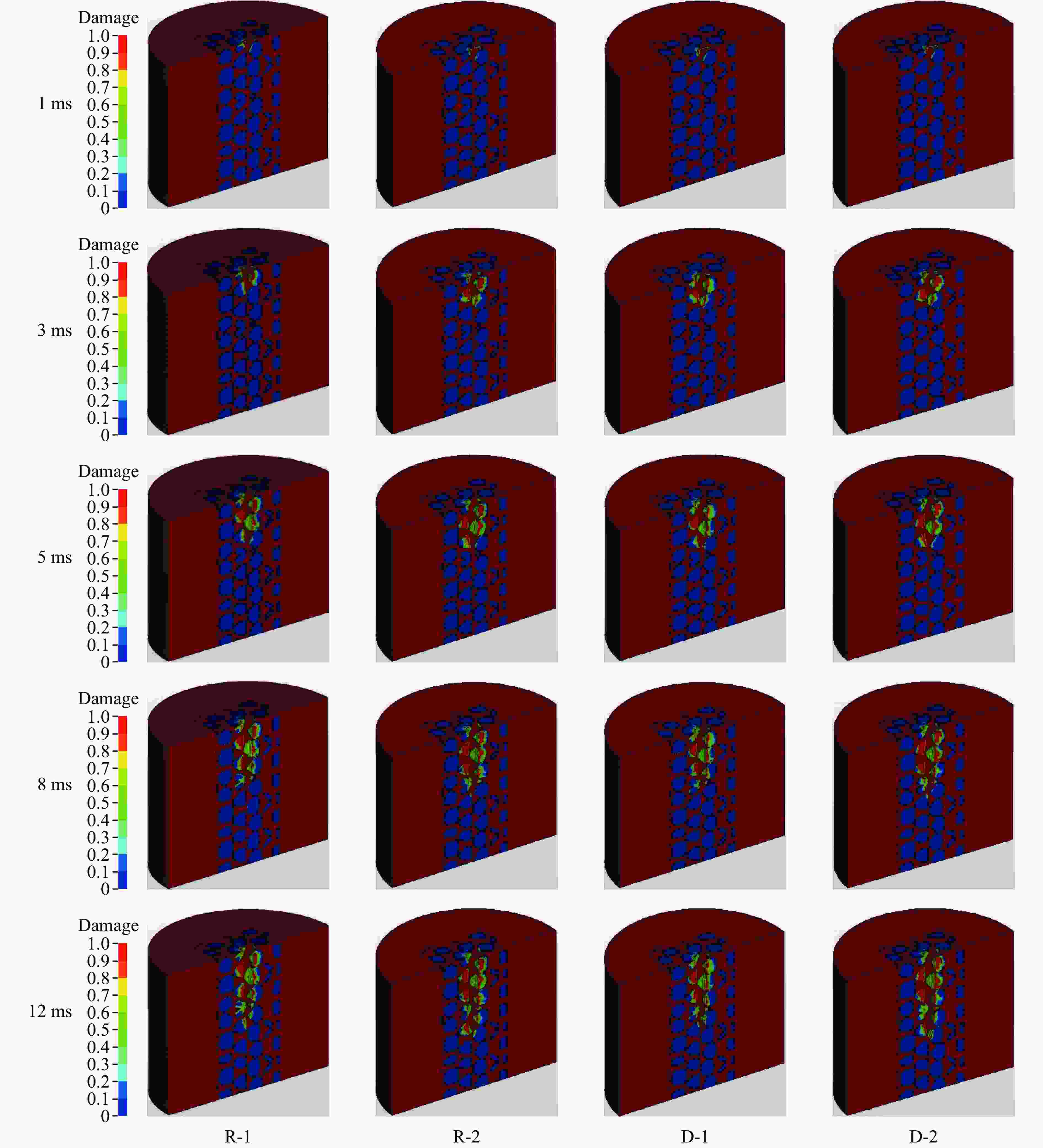
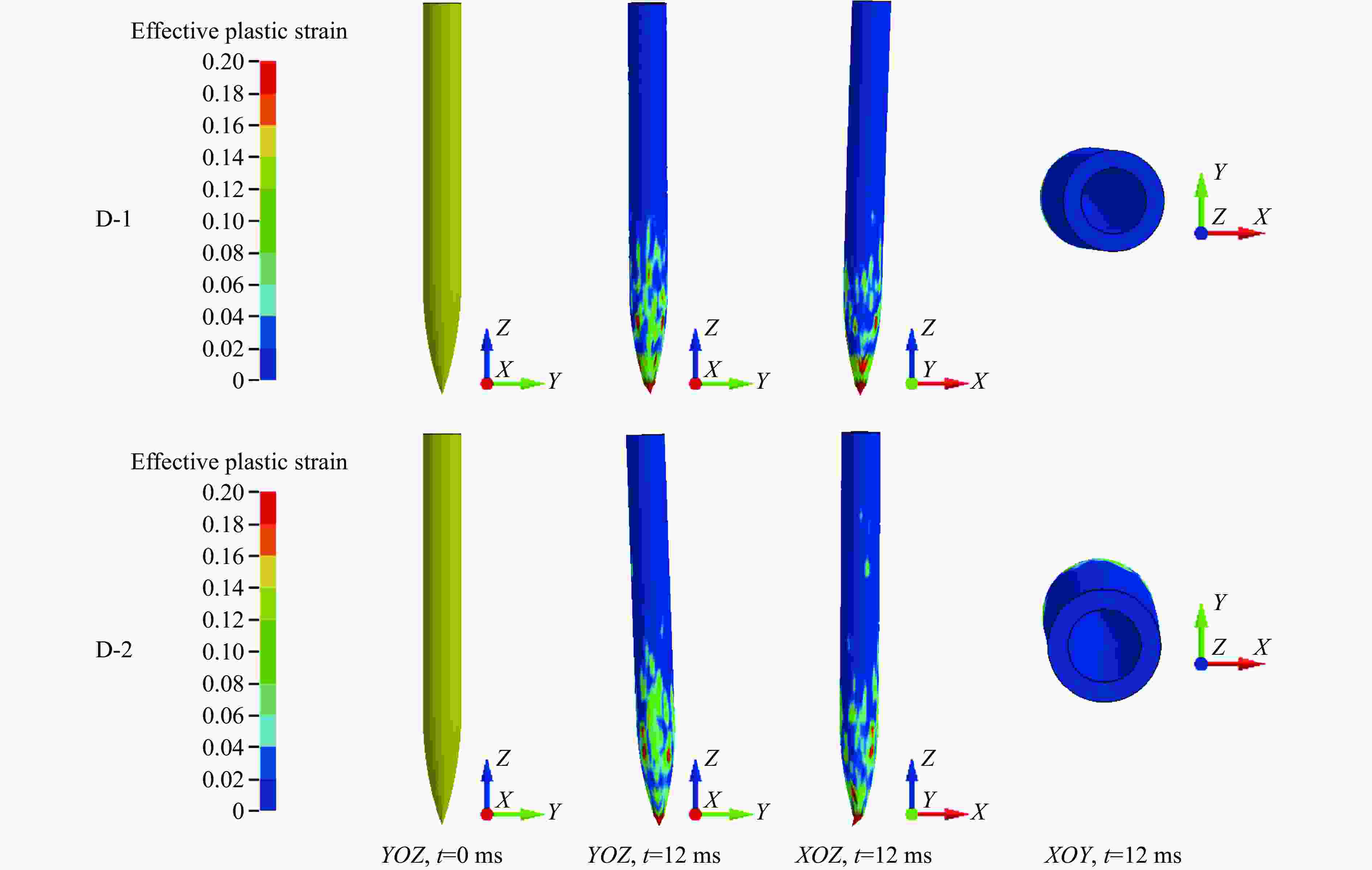
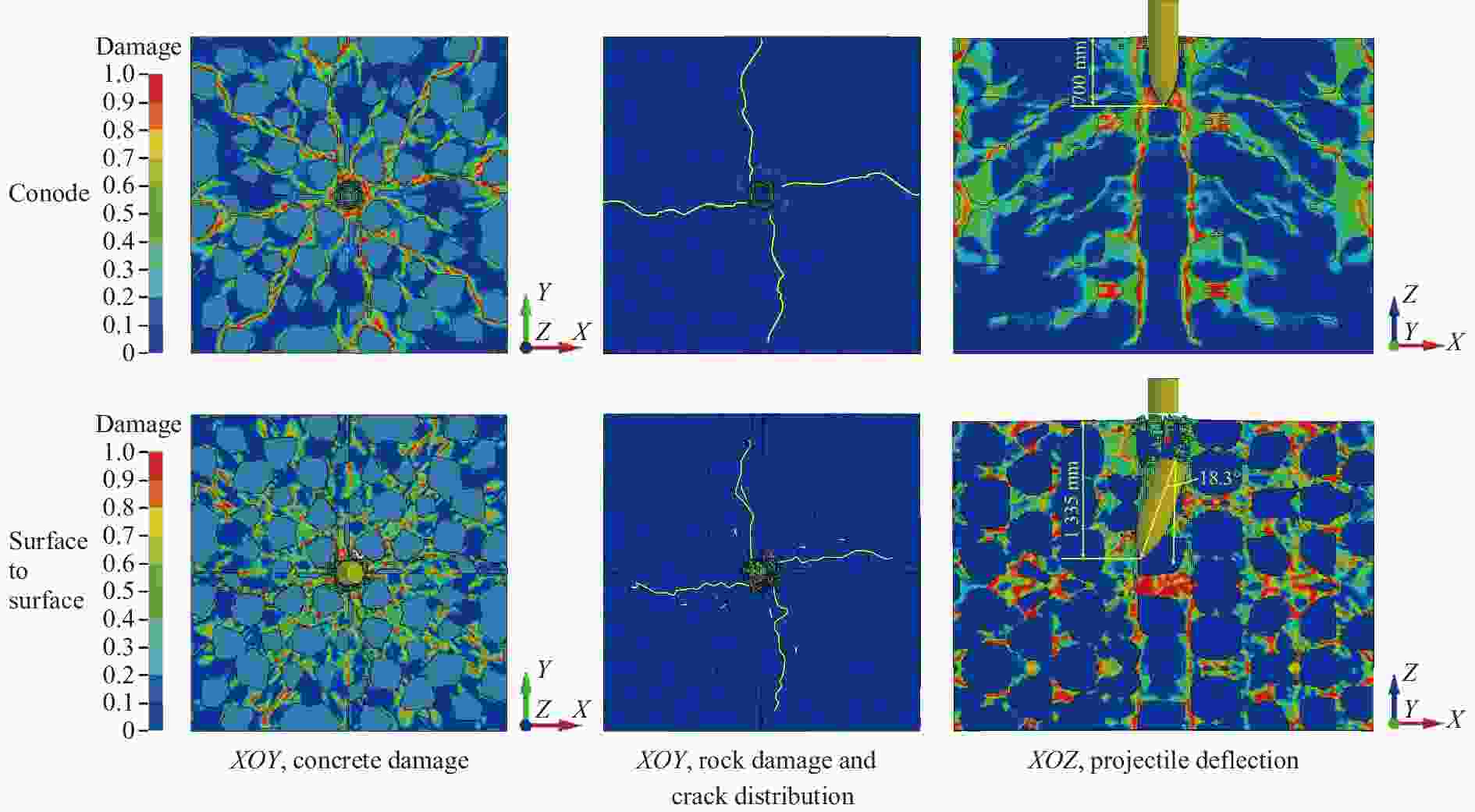
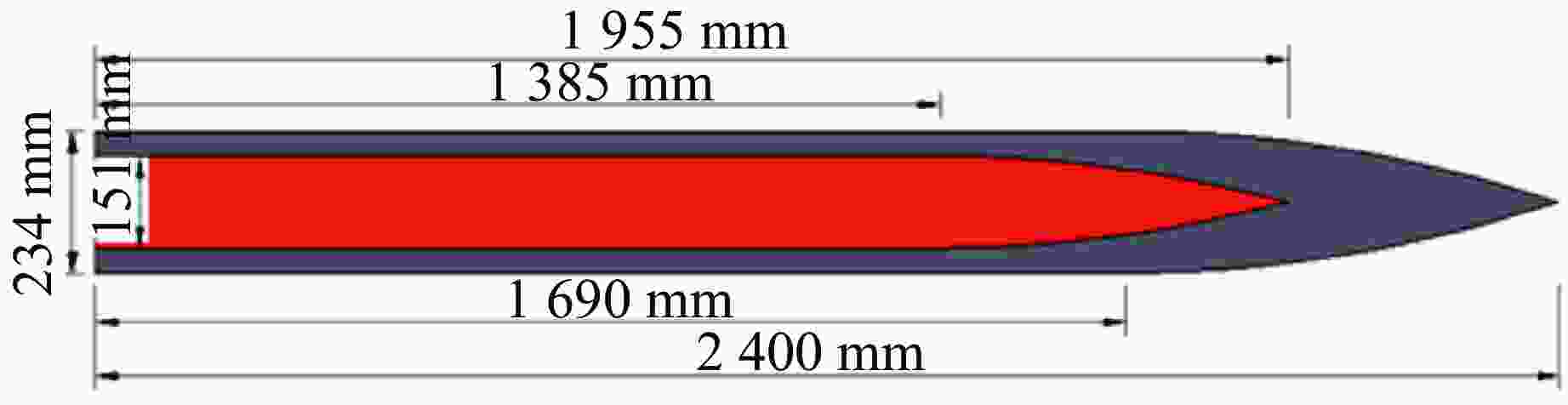
摘要: 基于三维细观建模方法和Kong-Fang混凝土材料模型,开展了某弹体侵彻块石混凝土遮弹层的数值模拟研究。采用块石与基体混凝土共节点建模和面面接触建模两种方式,探讨了界面对弹体过载、侵彻深度以及混凝土与块石损伤破坏的影响。数值模拟结果表明:块石与混凝土共节点建模方式强化了块石与混凝土间的界面效应,高估了靶体的整体性,而面面接触建模方式弱化了界面效应,故采用共节点建模方式时,弹体过载(加速度)偏大,侵彻深度偏小;采用共节点建模方式时,损伤区域沿C100混凝土和块石交界面发展,损伤区域连续,而采用面面接触建模方式时,损伤区域在弹道近区连续,近区与远区损伤不连续。基于数值模拟结果,进一步对块石混凝土遮弹层的工程设计计算提出了实用性建议。Abstract: Based on the Kong-Fang concrete material model proposed recently and the three-dimensional mesoscopic model, the penetration of a typical warhead into rock-rubble overlays was numerically simulated. The influence of interface modelling of rock-rubble overlays on the projectile overload (or acceleration), penetration depth and failure in concrete and rock was discussed by considering two well-known methods, i.e., the conode method and surface-to-surface contact method. Numerical results demonstrated that the interface between concrete and rock is overestimated when using the conode method, leading to a larger projectile acceleration and a smaller penetration depth. While the surface-to-surface contact method underestimates the interface effect, resulting in a smaller projectile acceleration and a larger penetration depth. Furthermore, the damage evolutions are different: it is continuous and develops along the interface of concrete and rock using the conode method, while it is only continuous in the area near the projectile and becomes discontinuous beyond this area. Finally, based on the numerical simulations, the practical suggestions for engineering design of rock-rubble overlays are given.
-
Key words:
- 3D mesoscale model /
- rock-rubble overlays /
- penetration /
- interface effect
-
表 1 C100混凝土模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of C100 concrete
a1 a2 εfrac d1 d2 d3 α 0.587 6 0.025/fc 0.01 0.04 1.5 0.000 1 1.0 表 2 HJC材料模型参数
Table 2. HJC material model parameters
Basic mechanical parameters Damage parameters Strain-rate parameter ρ/(kg·m−3) fc/MPa G/GPa T/MPa D1 D2 εmin C 2 600 120 28.7 8 0.04 1 0.01 0.007 Strength surface parameters Pressure parameters A B N Smax pcrush/MPa μcrush K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa 0.3 2.5 0.007 7 40 0.002 16 12 25 42 表 3 计算工况
Table 3. Calculation cases
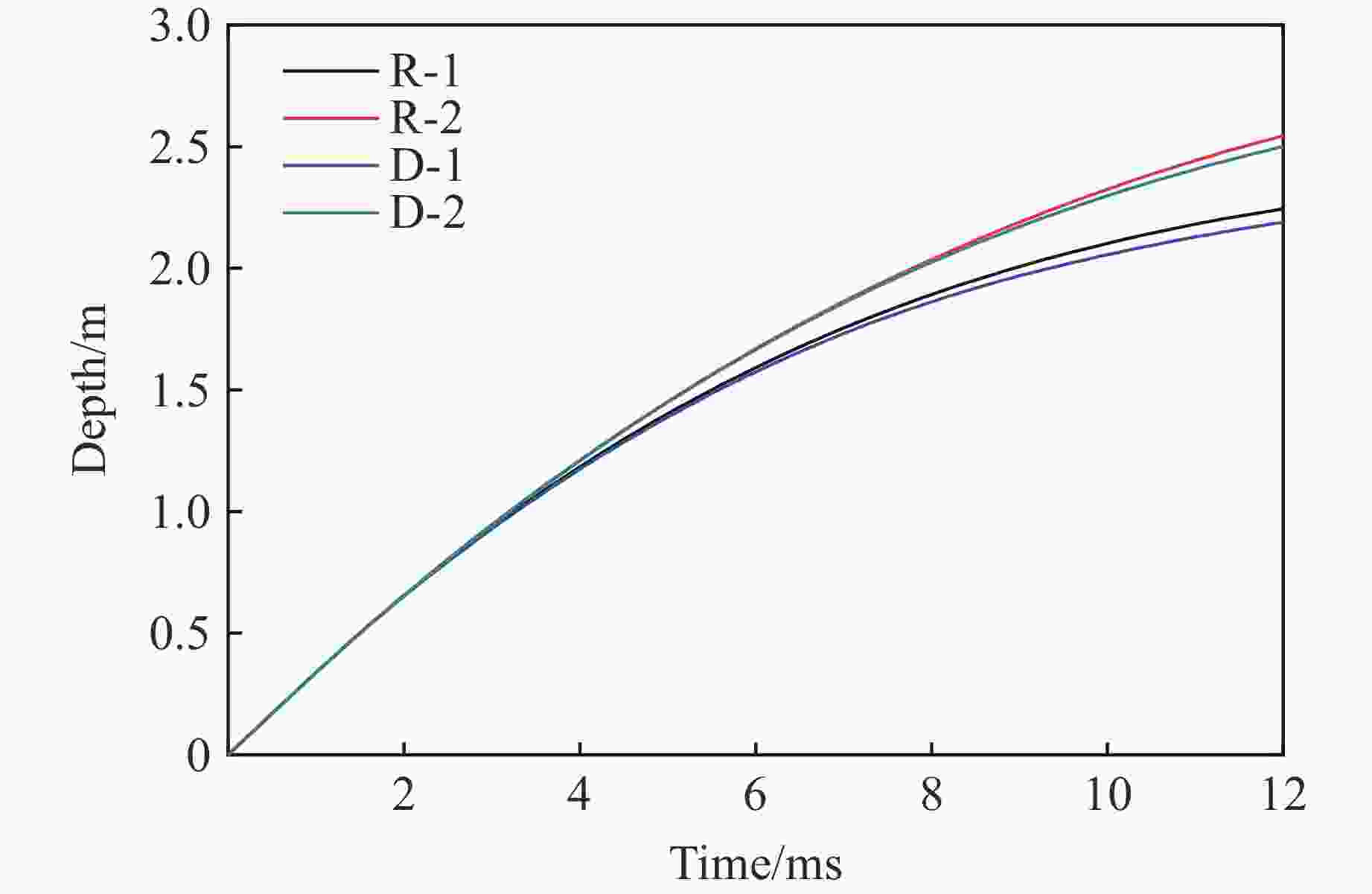
Cases Projectile property Contact mode Number 1 Rigid Conede R-1 2 Surface-to-surface R-2 3 Deformation Conede D-1 4 Surface-to-surface D-2 -
[1] 闫焕敏, 张志刚, 葛涛, 等. 防护工程中遮弹层的研究进展 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2016, 39(1): 127–132. doi: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20160105.001YAN H M, ZHANG Z G, GE T, et al. Research progress of bursting layer in protection engineer [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2016, 39(1): 127–132. doi: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20160105.001 [2] AUSTIM C F, HALSEY C C, CLODT R L. Protection systems development: ESL-TR-83-39 [R]. Florida, USA: Engineering and Services Laboratory, Air Force Engineering and Services Center, Tyndall Air Force Base, 1982. [3] GELMAN M D, RICHARD B N, ITO Y M. Impact of armor-piercing projectile into array of large caliber boulders [R]. Waterways Experiment Station, 1987. [4] ROHANI B. Penetration of kinetic energy projectiles into rock-rubbles/boulder overlays [R]. Vicksburg, Mississippi, USA: U. S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, 1987. [5] LANGHEIM H, PAHL H, SCHMOLINSKE E, et al. Subscale penetration tests with bombs and advanced penetration against hardened structures [C]//The Sixth International Symposium Interaction of Non-Nuclear Munitions with Structures. Panama, Florida, USA: Wright Laboratory Air Base Systems Branch, 1993: 12–17. [6] 姚焕忠, 韩国建, 程国亮. 块石高强固结体抗侵彻性能试验研究 [J]. 防护工程, 2013, 35(3): 17–21.YAO H Z, HAN G J, CHENG G L. Experimental research and analysis on anti-penetration performance of nubby stone concretion [J]. Protective Engineering, 2013, 35(3): 17–21. [7] 穆朝民, 施鹏, 辛凯. 射弹侵彻块石遮弹层的数值模拟 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2012, 35(5): 4–8.MU C M, SHI P, XIN K. Numerical simulation on rock anti-penetration layer against penetrating [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2012, 35(5): 4–8. [8] 逄高伟, 方秦, 孔祥振, 等. WDU-34/B战斗部侵彻块石遮弹层的数值模拟研究 [J]. 防护工程, 2020, 42(4): 15–22.PANG G W, FANG Q, KONG X Z. Numerical simulation of WDU-34/B warhead penetrating into rubble burster layer [J]. Protective Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 15–22. [9] FANG Q, ZHANG J H. 3D numerical modeling of projectile penetration into rock-rubble overlays accounting for random distribution of rock-rubble [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 63: 118–128. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.08.010 [10] 方秦, 张锦华, 还毅, 等. 全级配混凝土三维细观模型的建模方法研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2013, 30(1): 14–21.FANG Q, ZHANG J H, HUAN Y, et al. The investigation into three-dimensional mesoscale modelling of fully-graded concrete [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(1): 14–21. [11] 方秦, 罗曼, 张锦华, 等. 弹体侵彻刚玉块石混凝土复合靶体的数值分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(4): 489–495. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)04-0489-07FANG Q, LUO M, ZHANG J H, et al. Numerical analysis of the projectile penetration into the target of corundum-rubble concrete composite overlay [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(4): 489–495. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)04-0489-07 [12] 宫俊, 吴昊, 方秦, 等. 刚玉骨料超高性能水泥基材料抗侵彻试验和细观数值模拟 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(1): 55–63.GONG J, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Test and mesoscale numerical simulation for corundum-aggregate ultra-high performance cementitious composites against projectile penetration [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(1): 55–63. [13] 方秦, 杜涛, 彭永, 等. 对遮弹层抗弹体侵彻性能的讨论 [J]. 防护工程, 2014, 36(5): 31–36.FANG Q, DU T, PENG Y, et al. Discussion on the performance of the overlays against the penetration of projectiles [J]. Protective Engineering, 2014, 36(5): 31–36. [14] KONG X Z, FANG Q, CHEN L, et al. A new material for concrete subjected to intense dynamic loadings [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 120: 60–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.05.006 [15] ZHANG S B, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Numerical prediction of dynamic failure in concrete targets subjected to projectile impact by a modified Kong-Fang material model [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 144: 103633. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103633 [16] WANG Y, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Modelling damage mechanisms of concrete under high confinement pressure [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 150: 103815. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103815 [17] KONG X Z, FANG Q, LI Q M, et al. Modified K&C model for cratering and scabbing of concrete slabs under projectile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 217–228. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.02.016 [18] WU H, FANG Q, CHEN X W, et al. Projectile penetration of ultra-high performance cement based composites at 510–1 320 m/s [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 74: 188–200. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.10.041 [19] HUANG X P, KONG X Z, CHEN Z Y, et al. A computational constitutive model for rock in hydrocode [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 145: 103687. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103687 [20] YANG S B, KONG X Z, WU H, et al. Constitutive modelling of UHPCC material under impact and blast loadings [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 153: 103860. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103860 [21] HUANG X P, KONG X Z, HU J, et al. The influence of free water content on ballistic performances of concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 139: 103530. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103530 [22] LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual version 971 [M]. Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), 2007. [23] MALVAR L J, CRAWFORD J E, WESEVICH J W, et al. A plasticity concrete material model for DYNA3D [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(9): 847–873. [24] 方秦, 孔祥振, 吴昊, 等. 岩石Holmquist-Johnson-Cook模型参数的确定方法 [J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(3): 197–204.FANG Q, KONG X Z, WU H, et al. Determination of Holmquist-Johnson-Cook constitutive model parameters of rock [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(3): 197–204. [25] USACE. Structures to resist the effects of accidental explosions: UFC 3−340−02 [R] Washington, DC: USACE, 2014. [26] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HICKERSON J P, et al. Penetration of concrete targets with deceleration-time measurements [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28: 479–497. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00108-2 -






 下载:
下载: