Reliability Optimization Design of Anti-Penetration Perforated Armor
-
摘要: 孔结构装甲在满足抗侵彻性能的同时需实现减重,因而轻量化设计具有工程实际意义。以孔结构装甲的轻量化为设计目标,抗侵彻性能为约束条件,考虑不确定性因素的影响,开展孔结构装甲的可靠性优化设计。样本点采用最优拉丁超立方法设计生成,孔结构装甲抗侵彻仿真的参数化建模及响应计算通过商业软件ANSYS的二次开发实现,引入Kriging代理模型和期望改变量(expected improvement, EI)加点法构建性能函数,最后采用序列优化与可靠性评估方法(sequential optimization and reliabilityassessment, SORA)进行可靠性优化设计。结果表明,可靠性优化后,孔结构装甲在满足抗侵彻性能和相关可靠度指标的前提下,可有效地实现减重11.5%。研究结果可为其他抗侵彻防护结构的可靠性优化设计提供参考。Abstract: Perforated armor can effectively reduce weight while meeting anti-penetration performance. Structural lightweight design of perforated armor has practical engineering significance. Considering the influence of uncertain factors, a reliability optimization design of a perforated armor was realized in this research. In the process of the reliability optimization design, the light weight of the perforated armor was taken as the goal of the design, and the anti-penetration performance was taken as the constraint condition. The optimal Latin hypercube design method was used to generate sample points. Based on a development of the commercial software ANSYS, the parametric modeling and the response calculation of the anti-penetration simulation of the perforated armor were realized. The Kriging surrogate model and the expected improvement maximization method were introduced to construct the performance functions. The sequential optimization and the reliability assessment method were applied in the reliability optimization design of the perforated armor. Under the premise of meeting the anti-penetration performance requirements and having a related reliability indicator of 0.9, the weight of the perforated armor after the reliability optimization can be effectively reduced by 11.5%. The research can provide references for the reliability optimization design of other anti-penetration structures.
-
Key words:
- perforated armor /
- lightweight design /
- Kriging model /
- reliability optimization
-
状态方程是描述材料压力、体积、温度之间相互关系的函数,在流体力学中,与描述能量、动量、质量守恒的偏微分方程一起,构成了预测材料动态压缩行为的完备流体力学方程组。精密的状态方程模型在材料科学、高压物理、天体物理、地球物理等基础学科领域[1-2],以及聚变点火、冲击防护等涉及材料动态冲击响应的各个应用领域都具有不可或缺的重要作用[3-5]。
材料在高温和高压下普遍会发生相变现象[6],例如:随着温度升高,大部分材料会发生固-液熔化相变;锡、铁等金属在高压加载下会发生固-固相变等。相变不仅导致材料本身的物理性质,如内能、熵、密度、电导率、体模量、剪切强度等,发生不连续变化,在冲击加载下还会导致冲击波分裂等现象。对这些突变行为的精确物理描述需要多相状态方程模型[7-8]。多相状态方程模型全面描述了在相应的压力-温度空间中材料所有可能经历的相结构,以及各相的内能、熵、体模量等宏观物性随压力、体积、温度等状态参量演化的基本物理规律,因此,它不仅是研究材料动态压缩特性的重要理论工具,也是构建材料多相强度模型、相变动力学模型等其他精密理论模型的前提。
构建多相状态方程模型时,需要校准的模型参数高达十几乃至数十个,而且各单相状态方程应满足在各自相图区域内吉布斯自由能最低等严苛的约束条件。这导致任何一个单相状态方程模型参数的校准,不仅需要考虑其在自身相图区域的压缩特性,还需要确保其与其他相的相边界和相稳定性不被改变。传统上一般采用手动方式逐步迭代校准状态方程模型参数,不但建模效率低,而且需要较高的调参经验,难以满足当前实验与理论协同研究对理论建模的快节奏和低门槛的要求。
现代化的数字化科研平台将实验仿真设计—数据分析解读—结果反馈应用等过程用数字化的模型与数据连通,形成了高效、快捷、低成本的新研究范式,涌现出了“化学机器人”等智能化数字实验室[9]。状态方程建模程序在应用于数字化科研平台时,所面对的材料类型丰富,需要对不同类型的材料构建与其本身特性相符的状态方程模型,例如:对于含铁磁相的材料,需要构建含磁贡献的状态方程模型[10]。此外,数字化科研平台还需要程序自动完成状态方程模型参数校准,构建的状态方程模型能够被其他计算程序直接调用,以便贯通模型评估和其他计算应用。
鉴于此,本课题组发展了AEOS(automated equation of state)多相状态方程建模方法及计算程序[11]。通过模块化设计,AEOS建模程序可以对不同类型的材料完成多相状态方程模型的自由组装;通过调用平衡相图、自由能、声速、比热等热力学计算模块以及ICON算法[12]等参数优化模块,AEOS可完成多相状态方程模型参数的自动化校准;最后,调用自带的冲击测温模拟等状态方程实验仿真模块,或者将AEOS嵌入流体力学计算程序中,AEOS程序可对自动校准的状态方程模型进行检验。本研究以锡的AEOS多相状态方程理论建模和计算应用为例,简要介绍AEOS建模程序的功能构成和建模流程、AEOS的数字化相图计算方法、基于ICON优化算法的状态方程模型参数自动校准方法、冲击测温实验模拟方法等理论方法,介绍AEOS构建的金属锡的固-液两相和多相状态方程模型以及这些模型的简单应用,最后进行简要的总结和展望。
1. AEOS建模方法流程
AEOS多相状态方程建模程序是基于Fortran 90程序语言编写的,既可以作为主程序独立完成材料的多相状态方程建模与计算应用,也可以作为程序模块嵌入其他流体力学计算软件提供多相状态方程计算功能。下面将简要介绍AEOS的主要工作流程和相关计算方法。
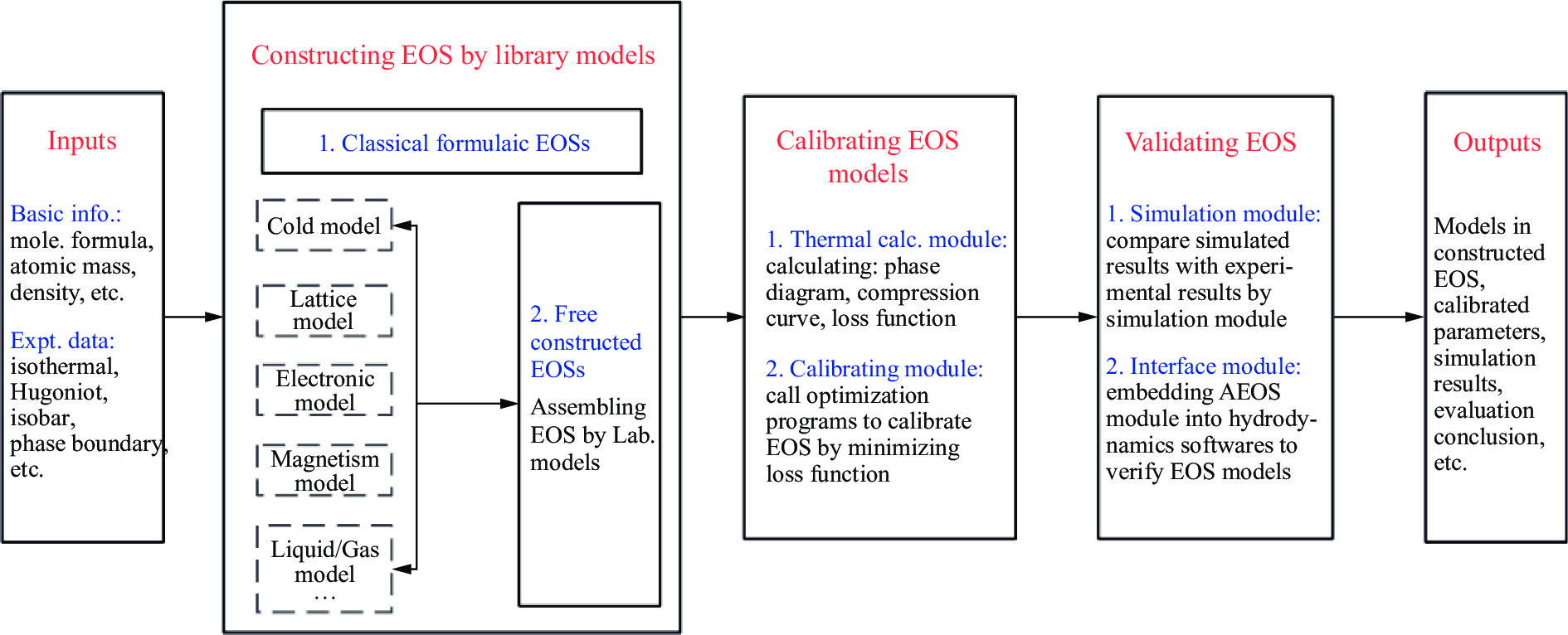
如图1所示,AEOS的主体功能由状态方程模型库和模型构造模块、状态方程校准模块、用于模型校验和计算应用的状态方程实验仿真模块、输入模块、输出模块5部分组成。
AEOS以材料的状态方程实验数据和基础物性参数为输入信息,通过从物理模型库中选取合适的子系统模型构造材料的多相状态方程模型,再调用热力学计算模块和计算机优化算法,自动校准状态方程模型参数,实现材料状态方程的快速理论建模。对于完成校准的状态方程模型,可以通过调用自带的状态方程实验仿真模块开展模型评估和实验数据分析解读;也可以将AEOS模块内嵌在流体力学计算软件中,使构建完成的状态方程模型可以用于更多情形的实验结果仿真与分析解读,再通过理论与实验结果的交叉比对,评估状态方程模型。通过输出模块,AEOS输出构建的多相状态方程模型形式、校准参数、相关实验的理论计算仿真结果、建模精度的评估等结果,用于模型校验与计算应用。
AEOS 建模方法具有模型自由组装、平衡相态感知计算等功能。AEOS的状态方程构造模块可以根据用户输入信息从冷能、晶格热、电子热、液体模型等模型库中抽取相应的子系统模型,组合出材料各单相的状态方程模型,再将各单相状态方程按一定的方式组合构成多相状态方程模型;也可以指定程序,依据一定规则自动组合或穷举产生多相状态方程模型。AEOS的热力学计算模块对于热力学平衡过程具有相态自动感知的计算功能,计算时无需额外提供材料的相态信息。相态感知计算功能在第一次调用时会首先基于吉布斯自由能相等原则计算多相状态方程模型的平衡相边界、相图等信息(或直接从“Pb.info”文件中读取),并将其存入计算机内存;之后,所有的计算均先根据平衡相图确定应该调用哪些单相状态方程模型,再根据材料所处的相态计算其相应的热力学性质。
构建完成的状态方程模型的模型组装方式和校准参数等信息保存在材料数据库中,命名为“MEOS.para”。AEOS通过读写数据库中的MEOS.para文件,实现状态方程模型与参数在不同应用程序和平台中的数据交换和存储。
2. AEOS建模方法
2.1 相图的数字化表示与计算
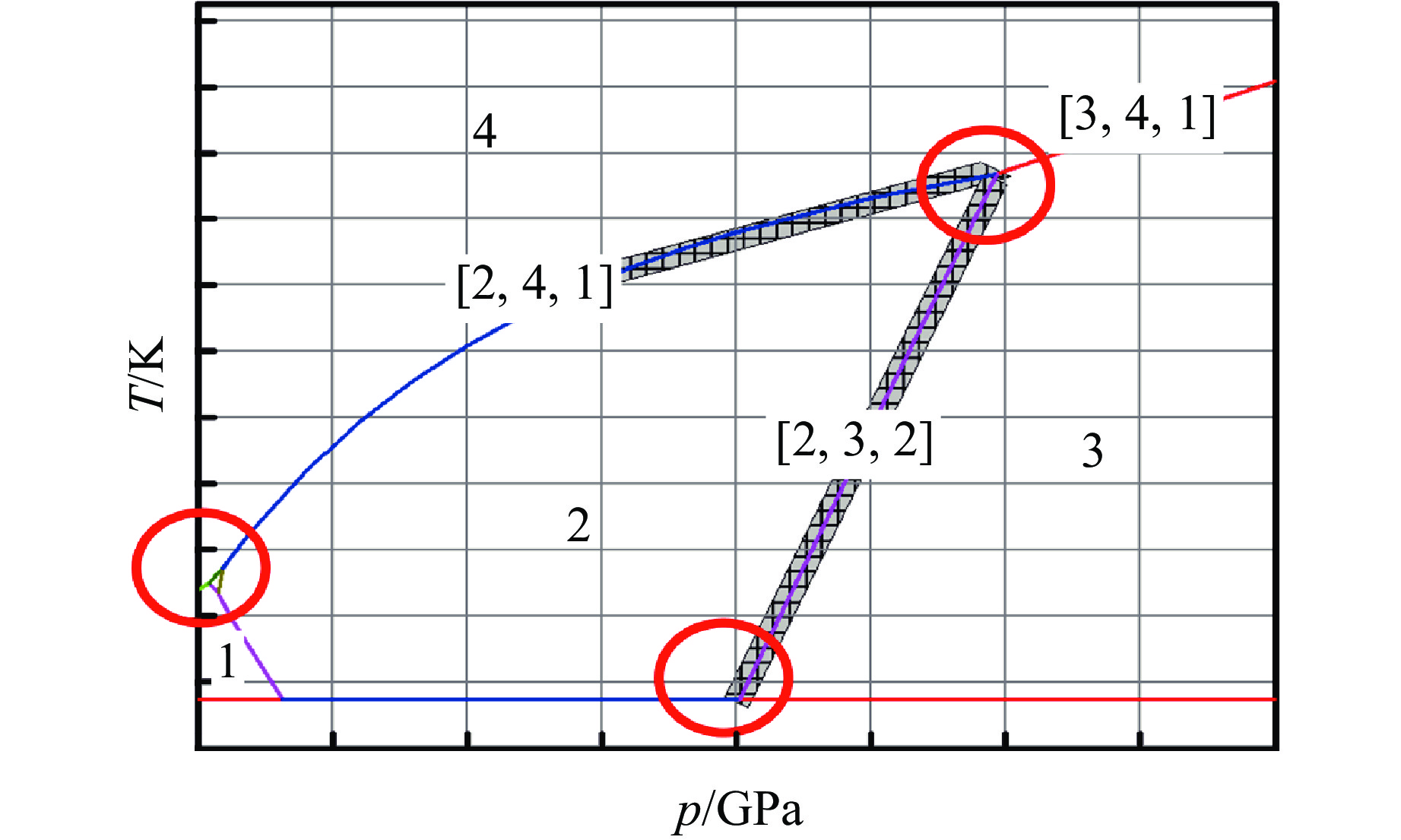
为了便于在建模程序中计算与多相状态方程模型对应的热力学平衡相图,并依据相图开展单相或多相共存状态的热力学性质计算,发展了相图的数字化表示与计算功能。如图2所示,发展了相图的单相区、相边界、三相点的指标化方法,并将感兴趣的压力-温度(p-T)空间按一定的压力间隔划分为网格,在网格点上计算所有可能稳定存在的相边界以及位于网格点之间的三相点。在此基础上实现相图及相边界拓扑关系在计算程序中的数字化表示、计算、存储,以及平衡相态识别等功能。
假设某种材料具有bcc(body-centered cubic)、fcc(face-centered cubic)、hcp(hexagonal close-packed)、液相共4个相结构。不妨用数字1代表bcc结构,数字2代表fcc结构,数字3代表hcp结构,数字4代表液相。在图2的示例中,数字1、2、3、4分别标记了bcc、fcc、hcp、液相这4个相的纯相区。对其中每两个相[i, j]的相边界,用一个三元数[i, j, Nij] 表示,其中:i 、j分别表示该相边界两侧的纯相区,且i < j;Nij = 1, 2,表示等压升温时相变的方向,若Nij = 1,则表示在p-T相图上相i处于相边界[i, j, Nij]的下方,若Nij = 2,则表示在p-T相图上相i处于相边界[i, j, Nij]的上方。三相点是3条相边界[i, j, Nij]、[i, k, Nik]、[j, k, Njk]的交点,用六元数[i, j, k, Nij, Nik, Njk]表示,其中i < j < k。于是,p-T相图中每一个纯相区i由所有含相i指标的相边界包围而成;i、j的两相共存区域由相边界[i, j, Nij]以及两端的三相点包围而成。
借助上述指标化方法,AEOS将平衡相图分解为纯相区、两相共存区和三相共存区,用于相图的计算机识别和存储;通过将相边界信息在网格点之间插值,再根据热力学平衡状态的(p, T)、(V, E)(其中V为比容,E为能量)等输入信息,可以计算得到相应的相结构和相组分。
AEOS采用自由能形式的多相状态方程模型,各单相i的状态方程的自由能函数Fi可由冷能Fic、热电子项Fie和离子振动项Fiion等相关子系统构成,其表达为
Fi=Fci+Fei+Fioni+Felsei (1) 式中:
Felsei 为其他修正项。AEOS利用热力学平衡时各相的压力、温度以及吉布斯自由能相等的特性,计算获得多相状态方程的相边界和平衡相图,表达式为
pi=pj (2) Ti=Tj (3) Fi+piVi=Fj+pjVj (4) 为了增强计算方法的鲁棒性,计算相边界时,在每个压力网格点上,先搜索得到相变温度的大致范围,再根据式(4)采用牛顿法或折半查找法获得精确的相变压力和温度,以及相边界两侧两个相的密度、内能、熵等热力学量。将相边界指标相同的相变压力-温度离散点连接起来,即可得到一条p-T相边界。依次完成所有相边界离散点的连接,绘出与多相状态方程模型对应的p-T相图。类似地,将相边界指标相同的密度-能量离散点连接起来,可以得到密度-能量(ρ-U)相图。
计算平衡两相或三相共存的相比例时,一般需要在ρ-U相图上进行。在ρ-U相图上,两相的相边界扩展为具有上、下两个边界的“二维带”,当输入的密度-能量坐标(ρx, Ux)处于“二维带”内部时,体系处于两相共存状态;对于三相点,3条相边界的“二维带”相交,重叠部分构成的“三角形区域”为ρ-U相图上的三相点,当输入的(ρx, Ux)处于“三角形”内部时,体系处于三相共存状态。关于两相或三相共存时相比例计算的详细方法可以参考文献[13]。
2.2 状态方程模型参数的自动较准
多相状态方程需要校准的参数数量较多,对其中任何一个单相状态方程模型参数进行校准时,不仅要保证该单相模型在自身相区的精确性,还要确保在整个相区中其他相的相边界和相稳定性不被改变。采用手动方式很难兼顾这两点。为此,将具有全局优化能力的计算机智能优化算法用于校准模型参数,相比手动方式,在建模效率和精度上均具有明显的优势。Cox等[14-15]利用粒子群优化算法构建了Al、Ti、Sn等材料含十多个校准参数的多相状态方程模型,均取得了很好的应用效果。Velizhanin等[16]采用粒子群算法结合拟牛顿算法,构建了碳含20余个校准参数的多相状态方程模型,通过理论模型计算的碳的三相点、固-固/固-液相边界、比热容等与实验结果一致。
AEOS采用自编的高维参数智能全局优化程序(ICON)实现了对多相状态方程模型参数的自动校准[12]。ICON是基于遗传算法和插值下降方法编写的用于高维参数方程全局参数优化的计算程序,既有很好的全局极小搜索能力,又有高精度的局部极小求解能力。
状态方程模型参数校准:通过使状态方程模型的理论值与相对参考值(一般是实验值)的均方根偏差(δ)达到全局最小的方法来确定最优化的模型参数。其中,δ在参数校准计算中起到目标函数的作用,其表达式为
δ=[1NN∑i=1(ψEOSi−ψEXPiψEXPi)2]1/2 (5) 式中:
ψEOSi 、ψEXPi 分别为第i组数据的理论计算值和实验值,N为参与评估的实验数据的个数。AEOS在校准模型参数时使用的每一组实验数据都与材料的一个真实相态k对应。对处于非冲击雨贡纽状态的每一组实验数据,用其处在相态k的热力学状态量(pik, Tik)为自变量,通过调用单相k的状态方程模型,求出该组实验数据其他热力学量的理论估计值。所有k相的实验数据对总目标函数的贡献为
δk,1={1NkNk∑i=1[ψEOSi(pik,Tik)−ψEXPi(pik,Tik)ψEXPi(pik,Tik)]2}1/2 (6) 式中:Nk为相k中用于评估的实验值的个数。
对于处于冲击雨贡纽状态的每一组实验数据,只采用其处在相态k的热力学状态pik为自变量,通过调用单相k的状态方程模型求解pik状态的雨贡纽方程,可求得该组实验数据所对应冲击雨贡纽状态的其他热力学量的理论估计值。此时,所有k相的实验数据对总目标函数的贡献为
δk,1={1NkNk∑i=1[ψEOSi(pik)−ψEXPi(pik)ψEXPi(pik)]2}1/2 (7) 对于实验测量的相边界数据,若相k与L个相组成的每一组相边界的实验数据为(pikL, TikL),则所有k相的相边界实验数据的理论估计值对总目标函数的贡献表示为
δk,2={1NkNk∑i=1∑L=1,21L+1[Gk(pikL,TikL)−GkL(pikL,TikL)Gk(pikL,TikL)]2}1/2 (8) 式中:L=1对应两相的相边界情形,L=2对应三相点情形;Gk(pikL, TikL)为调用的单相k的状态方程模型在热力学状态点(pikL, TikL)处求得的吉布斯自由能;GkL(pikL, TikL)为调用的相界处与单相k相邻的第L相的状态方程模型在热力学状态点(pikL, TikL)处求得的吉布斯自由能。
在校准单相状态方程模型参数时,要确保每个单相的状态方程的相稳定性与真实材料的相稳定性一致。对材料真实相态k的每一组实验数据所对应的热力学状态(pik, Tik),调用单相k的状态方程模型,可以求出其吉布斯自由能Gk(pik, Tik);同时,通过AEOS的相态感知计算,可以求得当前多相状态方程模型在热力学状态(pik, Tik)下自由能最低的那个相态k0及其吉布斯自由能Gk0(pik, Tik)。由此,定义惩罚函数Pf,其表达式为
Pf=M∑k=1Nk∑i=1max (9) 式中:M为多相状态方程模型中总的相态数。当相k0与真实相态k为同一个相时,惩罚函数对总目标函数的贡献等于零;当k0与k不是同一个相时,惩罚函数对总目标函数的贡献大于零。
利用式(6)~式(9),总目标函数可表示为
\delta=\sum_{k=1}^{M}\left(\delta_{k, 1}+\delta_{k, 2}\right)+P_{\rm f} (10) AEOS在校准模型参数时,先调用热力学计算模块计算得到所有实验值的理论估计值,再由式(10)计算得到模型的总目标函数值。随后,调用ICON程序优化模型参数,使总目标函数值达到全局最小。式(10)定义的目标函数δ具有均方根偏差的意义,可以用δ的大小评估校准后状态方程模型的优劣。最终,对于校准完成的状态方程模型,要求其惩罚函数对总目标函数的贡献为零。此外,AEOS也提供了冲击测温实验模拟等状态方程实验仿真模块,用于评估校准后的状态方程模型性能。
2.3 冲击测温实验模拟
AEOS提供了声速实验、多次冲击加载过程、等熵加/卸载过程、冲击测温实验等状态方程实验的仿真模块,用于评估校准后的状态方程模型性能,或用于相关实验的数据分析解读。其中,对于声速、等熵加/卸等过程的计算方法,很多教材和文献中都有介绍,这里不再累述,只简要介绍AEOS基于文献[17]中的多层介质模型发展的冲击测温实验模拟方法。
在金属材料状态方程的实验研究中,常用辐射法测量冲击波温度,特别是冲击卸载线上的固-液熔化温度。谭华等[17]改进了冲击测温实验的多层介质模型,通过实验测量金属样品经过冲击加载、样品-窗口界面卸载以及样品-窗口界面传热之后的界面温度TI,再利用多层介质模型由界面温度TI反演计算冲击温度TH。在谭华等[17]的多层介质模型基础上,开发了可以处理固-液相变的冲击测温实验模拟方法,计算过程如下。
对于金属样品的冲击加载过程,冲击压力为pH的末态温度TH可由状态方程模型结合冲击雨贡纽方程直接计算得到。
对于金属样品的等熵加/卸载过程,若中间未发生相变,由等熵关系,利用状态方程模型逐步积分式(11)和式(12),得到以冲击末态为起始点的等熵加/卸载状态[18]
\left(\frac{{\rm d} T}{{\rm d} V}\right)_{S}=-\frac{T}{c_{V}}\left(\frac{\partial p}{\partial T}\right)_{V} (11) T_{\rm R}=T_{\rm H}+\int \nolimits_{V_{\rm H}}^{V_{\rm R}} \frac{T}{c_{V}}\left(\frac{\partial p}{\partial T}\right)_{V} {\rm d} V (12) 式中:TR、VR分别为等熵加/卸载末态的温度和体积,TH、VH分别为冲击末态的温度和体积,cV为比定容热容。
若等熵过程中发生了固-液相变,则固-液熔化线处的熵发生突变。AEOS采用过热熔化模型计算相变时熵的变化。先假设金属保持原本的相态等熵加/卸载到虚拟的过热状态
T'_{\rm{R}} ,再利用状态方程计算从过热状态T'_{\rm{R}} 回到平衡态TR需要释放或吸收热量ΔE。若ΔE小于此时的熔化潜热ΔQ,则样品处于固-液混合态,末态温度TR等于该压力下的熔化温度Tm;若ΔE大于ΔQ,则样品释放/吸收热量ΔQ后在某熔化温度Tx处转变为纯的固态或液态,再以此Tx状态为新的等熵加/卸载起始点,继续加/卸载到与窗口匹配的压力pR;对此过程应用式(11)和式(12),可以得到样品最终的等熵加/卸载温度TR。计算界面温度TI:根据多层介质模型,若样品的最终状态为固-液混合态,则样品-窗口界面温度TI近似等于当前压力下样品的熔化温度,即TI = Tm;若样品末态为纯固态或液态,则样品-窗口界面温度TI可由TR和窗口的末态温度Tw表示为[17]
T_{\rm I}=T_{\rm R}-\frac{T_{\rm R}-T_{\rm W}}{1+\alpha_{14}}, \;\;\;\;\;\;\alpha_{14}=\sqrt{\frac{\left(\rho c_{V} K\right)_{\rm {sample }}}{\left(\rho c_{V} K\right)_{\rm {window}}}} (13) 式中:(ρcVK)sample为等熵加/卸载末态时样品的密度、比定容热容与热导率的乘积,(ρcVK)window为等熵加/卸载末态时窗口的密度、比定容热容与热导率的乘积。
AEOS的实验仿真模块主要用于状态方程类实验的实验设计与数据分析解读,并具有一定的状态方程模型校验与性能评估能力。通过将AEOS程序模块嵌入其他流体力学计算程序,AEOS可以为更多类型的实验提供数据分析解读服务,也可以更加全面地评估和校验所构建的状态方程模型。
3. 锡的计算结果与讨论
以金属锡的多相状态方程建模与应用为例,介绍AEOS建模程序在理论建模和计算应用方面的良好表现。
采用AEOS构建了3套锡的状态方程模型,其中:模型1是参考Gray状态方程形式[19]的固-液两相状态方程模型,模型2和模型3是锡的含β、bct(body centered tetragonal)固相和一个液相的多相状态方程模型。在优化模型参数时,将不同种类数据的δ按等同权重的方式计入目标函数。参数初值取文献参考值[19-24],然后以初始值为中值,上下浮动约50%,通过控制参数取值区间的上下限,避免无物理意义的多极值解。
模型1是为了测试AEOS对形式固定的经典状态方程模型的模型校准和计算应用功能而构建的。对于模型1的固相,其能量和压力表达式为
E(V, T)=E_{\rm c}(V)+\frac{3 R T}{ A_{\rm z}}+\frac{1}{2} g\left(N_{\rm e}, V\right) T^{2} (14) p(V, T)=p_{\rm c}(V)+\frac{\gamma(V)}{V} \frac{3 R T}{A_{\rm z}}+\frac{\gamma_{\rm e}}{2 V} g\left(N_{\rm e}, V\right) T^{2} (15) E_{\rm c}(V)=\frac{C^{2} x^{2}}{2(1-S x)}\left(1+\frac{1}{3} S x\right) (16) p_{\rm c}(V)=\frac{C^{2} x}{V_{0}(1-x)(1-S x)^{2}} (17) \gamma(V)=\gamma_{0}-a x (18) x=1-\frac{V}{V_{0}} (19) g(N_{\rm e}, V)=165.72 {\text{π}}^{2} R N_{\rm e}^{\tfrac{1}{3}}\left(V A_{\rm z}\right)^{\tfrac{2}{3}} (20) 式中:Ec、pc分别为零温下的冷能和冷压,V0为零温零压下的比容,C、S分别为冲击波速度-粒子速度关系中的常数项和一次项系数,x为压缩度,γ0为零温零压下的Grüneisen系数,a为Grüneisen系数随压缩度变化的比例系数,Ne为锡的价电子数,Az为原子量(g/mol),R为理想气体常数(8.314 J/(mol·K)),γe=2/3。
对于模型1的液相,其能量以固相为参考,表达式为
E(V, T)=E_{\rm c}(V)+\frac{3 R T} { A_{\rm z}}+\frac{1}{2} g\left(N_{\rm e}, V\right) T^{2}+\Delta S T_{\rm m}(V) (21) 式中:ΔS为固-液熔化熵,单位取理想气体常数R;Tm(V)为固-液熔化温度,由Lindemann定律给出
\frac{{\rm d} \ln T_{\rm m}}{{\rm d} \ln V}=-2\left[\gamma_{0 {\rm m}}-a_{\rm m}\left(1-\frac{V}{V_{0}}\right)\right]+\frac{2}{3} (22) 式中:γ0m为零压下固液熔化态的Grüneisen系数,am为固液熔化态的Grüneisen系数随压缩度变化的比例系数。
利用金属锡的冲击雨贡纽线、等温压缩线、熔化线、冲击声速等实验数据,应用AEOS程序构建了锡的固-液两相状态方程模型,校准后的模型参数如表1所示,其中:Tm0为常压下的熔化温度。
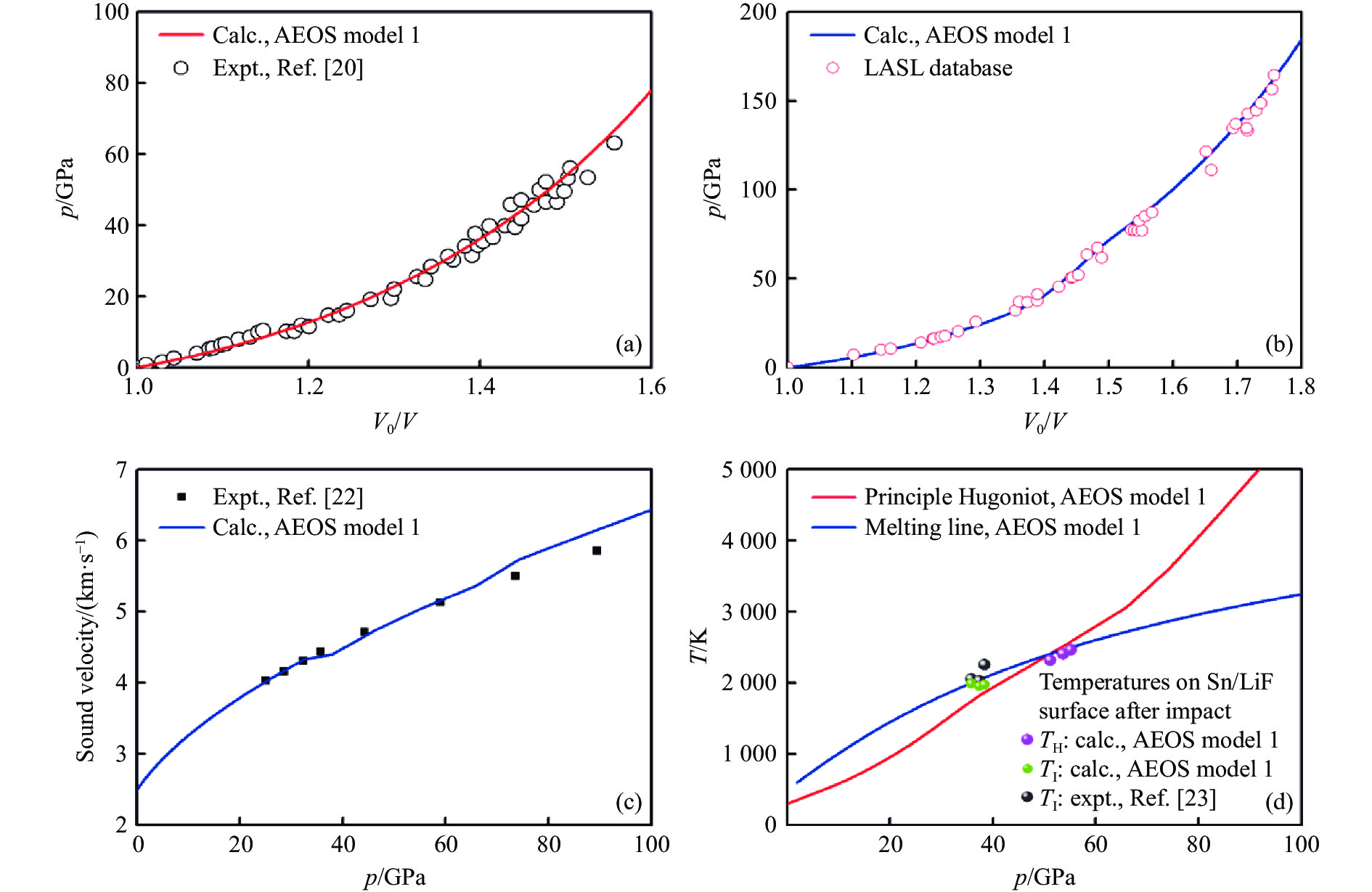
表 1 锡的固-液两相状态方程模型1的校准参数Table 1. Calibrated parameters of the solid-liquid two-phase EOS model 1 for tinV0/(cm3·g−1) C/(km·s−1) S γ a Ne 0.1341 2.612 1.482 1.47 0 4.0 ΔS Tm0/K γ0m am 1.16R 836.9 2.20 0.035 用AEOS程序构建了锡的固-液两相状态方程模型1,并将模型1计算的冲击声速、冲击卸载温度与文献[20-23]中的结果进行比较,如图3所示。对于冲击雨贡纽p- V0/V关系和声速,模型1计算的理论结果与实验结果的δ在3 %左右;对于固-液熔化线和等温压缩线,由于真实锡材料的β-bct相变造成熔化线和等温压缩线的拐折,超出了模型1固-液两相状态方程的描述能力,导致其δ在5%左右;对于界面温度,模型1计算的总体δ约为4 %。可见,模型1的计算结果与实验结果具有良好的一致性,验证了AEOS程序中的经典状态方程计算模块、优化算法以及实验仿真等模块的有效性和良好性能。
为了测试AEOS程序的多相状态方程自由组装功能以及状态方程模型的校准和计算应用功能,构建了两套锡的含β、bct两个固相以及一个液相的多相状态方程模型,即模型2和模型3。在冷能模型库中构建了一个Birch-Murnagahan方程形式的冷能模型[24],在晶格自由能模型库和电子自由能模块库中各构建了一个晶格[19]和热电子[24]的子状态方程模型,并利用AEOS的模型组装功能,形成了如下形式的锡的多相状态方程模型。
模型2和模型3的自由能为
F(V, T)=E_{0}+E_{\rm c}(V)+F_{\rm I}(V, T)+F_{\rm e}(V, T) (23) 式中:E0为待定的能量常数。
Ec(V)采用Birch-Murnagahan方程形式[24]
E_{\rm c}(V)=\int\nolimits_{V_{0}}^{V} p_{\rm c}(V) {\rm d}V (24) p_{\rm c}(V)=\frac{3}{2} B_{0}\left(\frac{V_{0}}{V}\right)^{\tfrac{5}{3}}\left[\left(\frac{V_{0}}{V}\right)^{\tfrac{2}{3}}-1\right]\left\{1+\frac{a_{1}}{2}\left[\left(\frac{V_{0}}{V}\right)^{\tfrac{2}{3}}-1\right]\right\} (25) 式中: B0为零温零压下的体模量,a1为无量纲常数。
模型2中晶格部分的自由能形式是在Cox[24]所建模型的基础上对其γ(V)作了部分修改,将晶格比定容热容固定为3R得到的,表达式为
F_{\rm I}(V, T)=\frac{3 R T}{A_{\rm z}}\left\{1+\frac{V_{0}-V}{V}\left[\gamma_{0}-a\left(1-\frac{V}{V_{0}}\right)\right]+\ln \left(\frac{T_{\rm {ref }}}{T}\right)\right\}-\Delta S(T-T_{\rm {ref}}) (26) 式中:Tref为参考态的温度,固相的Tref取室温300 K,液相的Tref取锡的常压熔化温度505 K。
为了考察晶格自由能模型变化对多相状态方程模型精度的影响,在模型3中,将模型2中晶格自由能方程即式(26)的晶格比定容热容由常数3R修改为可调参数cV0。
模型2和模型3中电子部分的自由能表达式均采用与模型1相同的形式
F_{\rm e}(V, T)=-\frac{1}{2} g\left(N_{\rm e}, V_{0}\right)\left(\frac{V}{V_{0}}\right)^{\gamma_{\rm e}} T^{2} (27) 式中:Ne为锡的价电子数,本研究中取为4.0;γe=2/3。
采用模型2和模型3,用AEOS分别较准了锡的两套多相状态方程模型参数。在模型2和模型3的参数校准过程中,除了各相态的等温压缩数据、冲击雨贡纽数据、声速等实验或理论参考数据之外,其余所有相的固-固、固-液相边界数据以及三相点数据等都参与了参数校准过程。通过调用ICON优化程序,使状态方程模型的理论值与实验值的相对偏差达到全局最小,得到了模型2和模型3的校准参数,如表2和表3所示。其中,β相作为参考相,校准参数时其能量E0和熵ΔS保持为常数零。
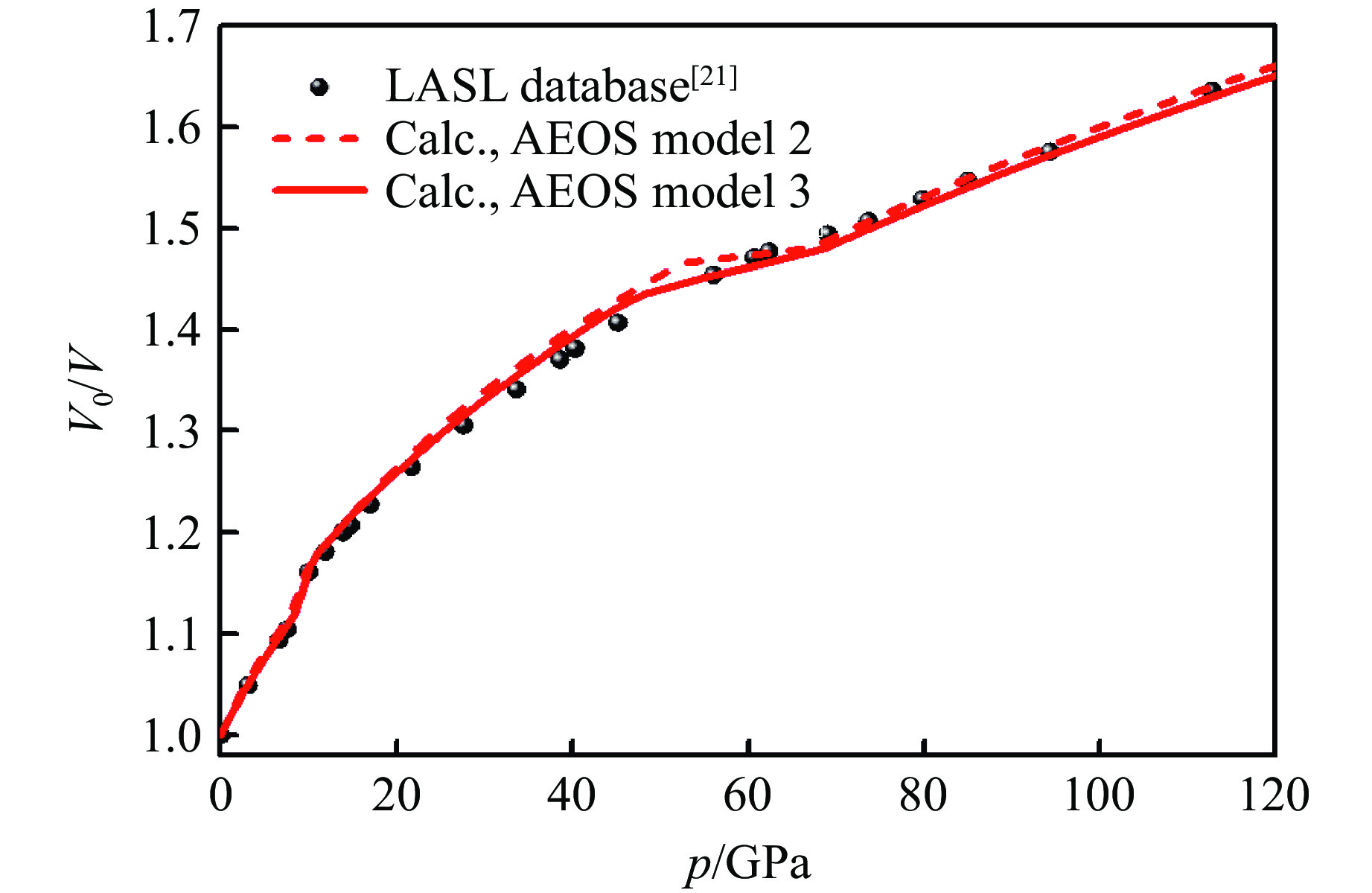
表 2 锡的多相状态方程模型2的校准参数Table 2. Calibrated parameters of the multiphase EOS model 2 for tinPhase E0/(J·g−1) V0/(cm3·g−1) B0/GPa a1 γ a ΔS β 0 0.1369 56.75 1.39 1.85 0.78 0 bct 36.3 0.1329 59.78 0.70 2.66 3.57 1.23R Liquid −16.6 0.1425 45.06 1.89 1.56 1.75 3.22R 表 3 锡的多相状态方程模型3的校准参数Table 3. Calibrated parameters of the multiphase EOS model 3 for tinPhase E0/(J·g−1) V0/(cm3·g−1) B0/GPa a1 γ a cV0/(J·g−1·K−1) ΔS β 0 0.1369 56.7 0.75 1.54 1.64 0.233 0 bct 32.5 0.1338 54.8 1.14 2.42 3.48 0.254 1.18R Liquid −14.7 0.1413 48.0 1.75 1.53 1.74 0.302 3.43R 模型2和模型3计算的锡的室温等温p-V0/V线、冲击雨贡纽p-V0/V线以及冲击声速与实验结果均高度一致。如图4所示,模型2和模型3计算的冲击雨贡纽p-V0/V线在β-bct固-固相变处与实验结果完全一致。在β-液相相变处,模型2计算的冲击熔化开始压力为40 GPa,导致计算的p-V线在40 GPa发生偏转,与实验结果[21]存在较大偏差;而模型3计算的冲击熔化开始压力为50 GPa,与实验结果的偏差很小。图4的计算结果表明,锡的冲击熔化开始压力略高于50 GPa。
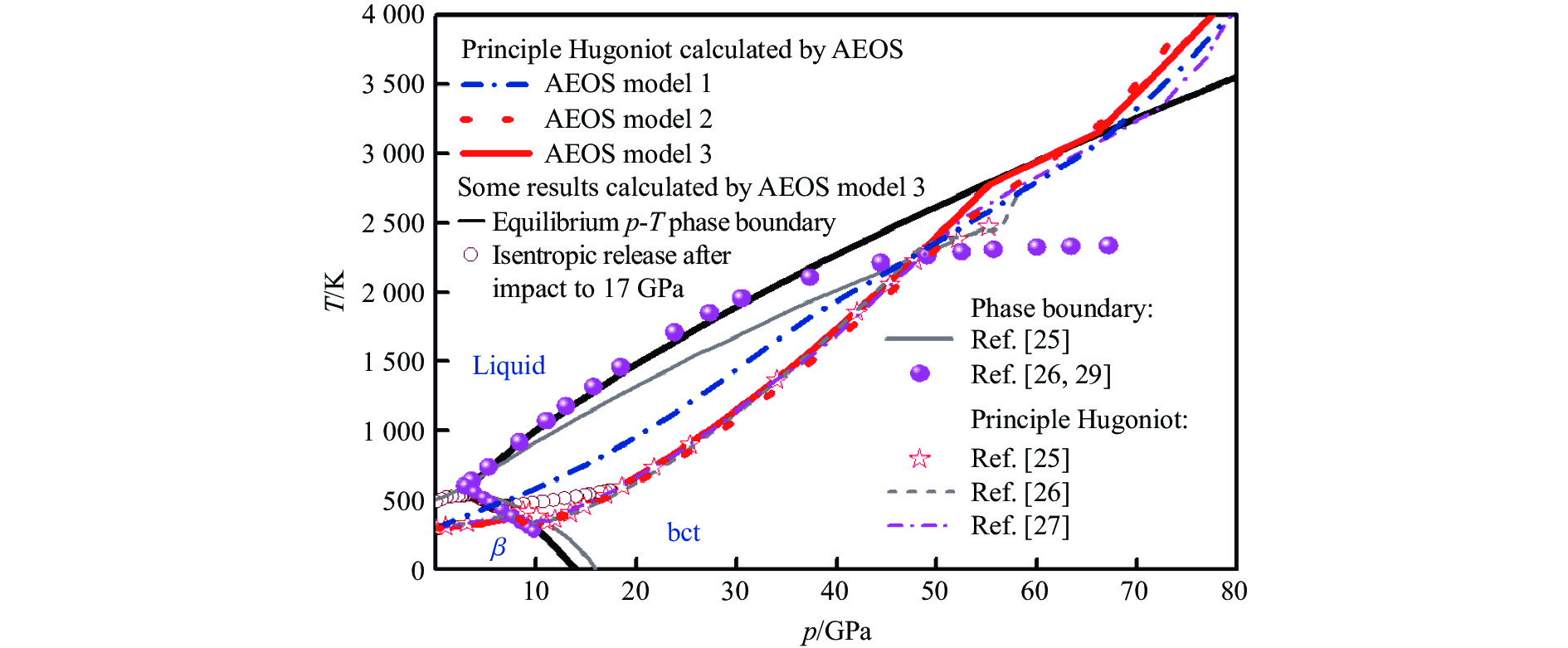
相比p-V0/V线,p-T线对状态方程模型参数变化更敏感。如图5所示,将AEOS构建的锡的3个模型的冲击雨贡纽p-T线理论计算结果作对比,可以看出:模型1在固相区计算的冲击温度均高于其他文献结果[25-27],但在液相区计算的冲击温度与其他文献结果[25-27]吻合良好。这解释了图3(d)中模型1模拟的冲击测温实验的界面温度理论结果与实验结果基本一致的原因。模型2中所有相的比定容热容均取为3R,导致从20 GPa冲击压力开始,所计算的冲击温度逐渐偏离其他文献结果[25-27]。模型3对所有相的比定容热容进行了参数校准,其计算的冲击温度在固相区得到了很好的改善,在液相区则与模型1以及Rehn等[27]的结果基本一致。对比模型2和模型3的计算结果表明,对固相区晶格比热容随压力和温度变化关系的准确建模是下一步改进锡多相状态方程模型精度的方向。
图5给出了模型3计算的所有相的固-固和固-液相边界。模型3计算的锡在常温常压下的熔化温度为501 K,与实验结果505 K[28]非常接近。计算的β-bct-液相三相点为(3.2 GPa, 571 K),与Xu等[29]测量的(3.02 GPa, 562 K)以及Kingon等[28]测量的(2.9 GPa, 582 K)都符合得很好。此外,模型3计算的β-bct固体相界以及40 GPa以下的固-液熔化相界与实验结果[26, 29]吻合良好,40 GPa压力以上的固-液熔化相界与Rehn等[27]的结果基本一致。
为了测试AEOS用于流体力学计算模拟的性能,将AEOS嵌入开源一维流体力学模拟程序,用AEOS模型3计算了锡冲击到17 GPa再等熵卸载到常压的p-T路径,其中一维流体力学模拟计入了塑性功引起的温升,给出的冲击温度略高于直接用雨贡纽方程计算的冲击温度。如图5所示,计算结果表明,沿着卸载路径,锡先经过β-bct固-固相界,然后沿着β-bct固-固相界到达β-bct-液相三相点,最后沿β相与液相的相边界卸载到常温的固-液熔化状态。该计算结果表明,卸载时沿β-bct固-固相界,锡的卸载温度升高可使其进入固-液混合态。这可以很好地解释了杨靖[30]在低压15.4 GPa的冲击压力下发现的Sn的微喷颗粒呈现固-液混合态的实验现象。
4. 结 论
通过多相状态方程模型的自动组装,采用计算机智能优化算法自动校准状态方程模型参数,发展了自动化多相状态方程建模程序方法AEOS。利用AEOS自带的状态方程实验仿真模块,或者将AEOS嵌入流体力学计算软件,可以将构建好的状态方程模型快速用于状态方程模型验证评估、相关的实验设计及实验结果分析解读。
利用AEOS构建了锡的3套状态方程模型,理论模型的计算结果与相关实验结果基本一致,充分验证了AEOS的可靠性和适用性。通过3套状态方程模型的对比研究,模型3给出了与实验结果的相对偏差最小的多相状态方程模型,且计算结果表明,锡的冲击熔化开始压力略高于50 GPa。通过改进模型3的晶格自由能模型,锡的多相状态方程建模精度有望得到进一步提升。
通过将状态方程模型3应用于开源一维流体力学模型程序,计算发现,锡冲击到17 GPa再等熵卸载至常压的p-T路径会经过β-bct-液相三相点,很好地解释了15.4 GPa的冲击压力下锡的微喷颗粒呈现固-液混合态的实验现象。
未来通过丰富AEOS的物理模型库,并与大型数据库相结合,AEOS可以自动高速地完成大量材料的多相状态方程建模工作,在大型数字化科研平台和高通量材料物性计算中将具有广阔的应用前景。
-
Component ρ/(kg·m−3) E/GPa G/GPa v A/MPa B/MPa n C \dot{\varepsilon} 0/s−1 cp/(J·kg−1·K−1) T0/K Tm/K m Target material 7 850 206 80 0.30 1200 1 580 0.175 0.004 0.000 1 450 300 1 800 1.00 Bullet core 7 850 206 80 0.30 1900 1 100 0.065 0.050 0.001 0 477 300 1 800 1.00 Brass jacket 8 960 124 46 0.34 90 292 0.310 0.025 1.000 0 386 300 1 356 1.09 表 2 孔结构装甲可靠性优化设计相关变量的约束范围
Table 2. Ranges of the relevant variables in reliability optimization design of perforated structure armor
R/mm d/mm v/(m∙s−1) \theta /(°) 4.5−6.2 7.8−12.4 834−874 85−95 表 3 最优拉丁超立方法抽取的采样点和响应
Table 3. Sampling points and responses obtained by the optimal Latin hypercube method
R/mm d/mm v/(m·s−1) \theta /(°) v′/(m·s−1) m′/g 6.052 10.200 870.522 94.130 811.129 4.662 5.978 8.600 867.043 86.304 808.016 4.889 5.387 8.400 844.435 93.261 760.791 4.854 4.796 12.200 842.696 86.739 675.821 4.112 4.722 8.800 837.478 85.435 603.861 3.958 4.943 11.800 874.000 87.174 710.546 4.245 5.017 11.600 856.609 90.652 667.470 4.005 5.239 10.800 872.261 92.826 780.641 4.506 5.683 11.200 853.130 88.478 754.275 4.529 5.461 9.200 849.652 85.870 747.881 4.622 4.870 9.800 846.174 91.957 691.675 4.366 5.830 11.000 847.913 93.696 762.888 4.720 5.535 12.000 868.783 89.783 761.734 4.493 4.500 12.400 851.391 91.522 568.453 3.551 6.126 10.400 839.217 89.348 782.666 4.794 5.609 7.800 840.957 88.043 788.874 4.941 5.313 10.600 835.739 92.391 719.739 4.375 5.757 9.000 834.000 91.087 759.182 4.708 6.200 8.200 858.348 95.000 814.127 5.034 4.648 11.400 860.087 85.000 701.905 4.282 5.091 9.400 865.304 88.914 725.571 4.170 5.904 10.000 863.565 90.217 800.931 4.745 5.165 8.000 861.826 94.565 767.436 4.786 4.574 9.600 854.870 87.609 648.105 4.038 表 4 剩余速度响应代理模型构建的新增样本和响应
Table 4. Added samples and responses built by residual velocity response surrogate model
R/mm d/mm v/(m·s−1) \theta /(°) v′/(m·s−1) 4.668 12.400 835.174 91.508 562.223 6.200 12.400 837.169 92.044 779.260 4.500 9.031 843.095 86.100 604.955 4.501 12.399 857.090 88.573 529.787 4.503 9.796 853.839 86.088 619.838 6.200 12.400 837.029 85.000 757.080 表 5 剩余质量响应代理模型构建的新增样本和响应
Table 5. Added samples and responses built by residual mass response surrogate model
R/mm d/mm v/(m·s−1) \theta /(°) m′/g 6.200 12.395 835.626 85.000 4.713 4.500 7.800 873.789 85.000 3.846 4.500 7.800 856.411 88.096 4.159 4.500 12.400 834.180 92.023 3.463 6.200 7.800 834.000 85.000 5.209 4.500 12.400 834.000 94.902 3.448 表 6 校核样本点和结果
Table 6. Check samples and results
R/mm d/mm v/(m·s−1) \theta /(°) v′/(m·s−1) Residual velocity
accuracy checkingm′/g Residual mass
accuracy checkingSur. Sim. AAE/% MAE/(m·s−1) Sur. Sim. AAE/% MAE/g 5.860 11.480 874 91 805.051 805.150 0.58 8.394 4.700 4.650 1.58 0.105 4.500 12.400 850 90 555.406 552.960 3.636 3.531 6.200 8.720 842 87 820.845 814.010 5.116 5.048 4.840 9.640 866 85 698.654 690.260 4.159 4.229 5.180 10.560 834 93 697.718 701.010 4.288 4.329 5.520 7.800 858 95 788.991 793.070 4.933 4.929 Note: Sur. means surrogate model. 表 7 随机变量参数的概率分布信息
Table 7. Probability distribution information of random variables and parameters
Symbol Distribution pattern Mean Variance Variable upper limit Variable lower limit R Normal distribution {\,\mu _R} 0.02{\,\mu _R} 4.5 mm 6.2 mm d Normal distribution {\,\mu _d} 0.02{\,\mu _d} 7.8 mm 12.4 mm v Normal distribution 854 m/s 17.08 m/s \theta Normal distribution 90° 1.8° 表 8 孔结构装甲优化参数结果
Table 8. Parameter results of the optimization of perforated structure armor
Variable R/mm d/mm n1 n2 Initial design 6.00 10.00 10 11 Reliability optimization 5.06 7.83 13 15 Note: {n_1} is the maximum hole quantity in each row; {n_2} is the maximum hole quantity in each column. 表 9 输出响应和孔结构装甲质量属性
Table 9. Output responses and the quality attributes of perforated structure armor
Responses v'/({\text{m}\cdot\text{s}^{ {-1} } } ) m'/{\text{g} } M/{\text{g} } \sigma /({\text{g}\cdot\text{cm}^{{-2} } } ) L_{ \rm{wd} }/% Initial design 794.460 4.739 331.168 3.31 0 Reliability optimization 739.480 4.557 292.940 2.93 11.50 Note: M is the mass of the perforated armor; \sigma is the surface density of the perforated armor; L_{\rm{wd}} is the lightweight degree
of the perforated armor. -
[1] CHOCRON S, ANDERSON C E JR, GROSCH D J, et al. Impact of the 7.62 mm APM2 projectile against the edge of a metallic target [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(5): 423–437. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00063-4 [2] BEN-MOSHE D, TARSI Y, ROSENBERG G. An armor assembly for armored vehicles: EP 0209221 [P]. 1986. [3] KILIÇ N, BEDIR S, ERDIK A, et al. Ballistic behavior of high hardness perforated armor plates against 7.62 mm armor piercing projectile [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 63: 427–438. [4] MISHRA B, RAMAKRISHNA B, JENA P K, et al. Experimental studies on the effect of size and shape of holes on damage and microstructure of high hardness armour steel plates under ballistic impact [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 43: 17–24. [5] RADISAVLJEVIC I, BALOS S, NIKACEVIC M, et al. Optimization of geometrical characteristics of perforated plates [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 49: 81–89. [6] 王郑. 间隙对穿孔装甲抗弹性能影响的数值分析 [J]. 科技创新与生产力, 2016(2): 87–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2016.02.087WANG Z. Numerical analysis about the influence of intervals on the ballistic performance of perforated armor [J]. Sci-Tech Innovation and Productivity, 2016(2): 87–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2016.02.087 [7] 王建波, 闫慧敏, 范秉源, 等. 弹着点对多孔钢板抗弹性能影响的数值模拟 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33(6): 73–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.06.022WANG J B, YAN H M, FAN B Y, et al. Numerical simulation analysis about the influence of the hitting position on the ballistic performance of the multi-hole steel plate [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33(6): 73–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.06.022 [8] 胡丽萍, 王智慧, 满红, 等. 孔结构间隙复合装甲位置效应研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33(1): 89–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.01.025HU L P, WANG Z H, MAN H, et al. Study on the spot effect of spaced composite armor with multi-holes [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33(1): 89–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.01.025 [9] 秦庆华, 崔天宁, 施前, 等. 孔结构金属装甲抗弹能力的数值模拟 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(5): 055105.QIN Q H, CUI T N, SHI Q, et al. Numerical study on ballistic resistance of metal perforated armor to projectile impact [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(5): 055105. [10] 肖红亮, 李晓源, 时捷, 等. 倾角效应对高强度钢板抗弹性能的影响 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2011, 34(6): 36–40.XIAO H L, LI X Y, SHI J, et al. Influence of obliquity effect on the ballistic performance of high strength steel plate [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2011, 34(6): 36–40. [11] 李换芝. 倾角穿孔装甲对14.5 mm穿燃弹防护性能的影响 [J]. 科技创新与生产力, 2016(2): 90–91, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2016.02.090LI H Z. Influence of oblique perforated armor on the protective performance of the 14.5 mm armor-piercing incendiary [J]. Sci-Tech Innovation and Productivity, 2016(2): 90–91, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2016.02.090 [12] 彭吉祥, 崔天宁, 金永喜, 等. 斜孔结构装甲设计及抗弹性能研究 [J]. 应用力学学报, 2021, 38(3): 893–901.PENG J X, CUI T N, JIN Y X, et al. Research on design and ballistic resistance of perforated armor with oblique holes [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 38(3): 893–901. [13] BURIAN W, ŻOCHOWSKI P, GMITRZUK M, et al. Protection effectiveness of perforated plates made of high strength steel [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 126: 27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.12.006 [14] CUI T N, QIN Q H, YAN W M, et al. Ballistic resistance of novel amorphous-alloy-reinforced perforated armor [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2021, 34(1): 12–26. doi: 10.1007/s10338-020-00180-1 [15] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates, and high temperatures [C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics. The Hague, 1983: 541−547. [16] 张冬冬, 郭勤涛. Kriging响应面代理模型在有限元模型确认中的应用 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(9): 187–191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.09.036ZHANG D D, GUO Q T. Application of Kriging response surface in finite element model validation [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(9): 187–191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.09.036 [17] 周宁. ANSYS-APDL高级工程应用实例分析与二次开发 [M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2007. [18] JONES D R, SCHONLAU M, WELCH W J. Efficient global optimization of expensive black-box functions [J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1998, 13(4): 455–492. doi: 10.1023/A:1008306431147 [19] SIMPSON T W, POPLINSKI J D, KOCH P N, et al. Metamodels for computer-based engineering design: survey and recommendations [J]. Engineering with Computers, 2001, 17(2): 129–150. doi: 10.1007/PL00007198 [20] KRIGE D G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand [J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1951, 52(6): 119–139. [21] 郭领. 孔结构金属装甲抗小口径穿甲弹的厚度效应 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2012.GUO L. The thickness effect of metal armor with poerstructure penetrating by Small caliber projectile [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2012. [22] STANAG N. Protection levels for occupants of logistic and light armoured vehicles [S]. 2004. [23] DU X P, CHEN W. Sequential optimization and reliability assessment method for efficient probabilistic design [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2004, 126(2): 225–233. doi: 10.1115/1.1649968 [24] AOUES Y, CHATEAUNEUF A. Benchmark study of numerical methods for reliability-based design optimization [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2010, 41(2): 277–294. doi: 10.1007/s00158-009-0412-2 [25] HUANG Z L, JIANG C, ZHOU Y S, et al. An incremental shifting vector approach for reliability-based design optimization [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 53(3): 523–543. doi: 10.1007/s00158-015-1352-7 [26] ZHANG Z, DENG W, JIANG C. Sequential approximate reliability-based design optimization for structures with multimodal random variables [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2020, 62(2): 511–528. doi: 10.1007/s00158-020-02507-5 -








 下载:
下载:


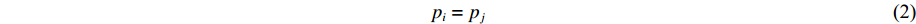
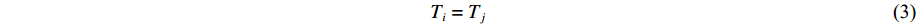
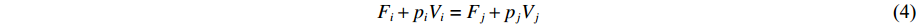
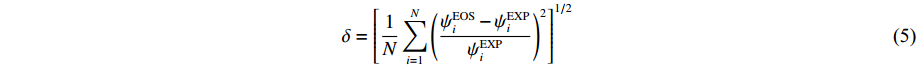
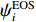
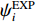
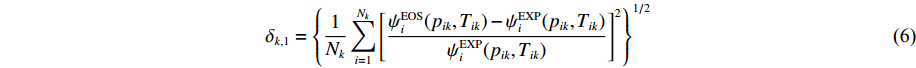
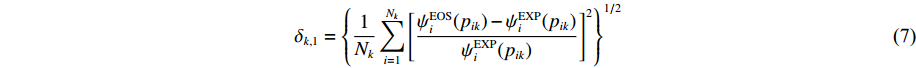
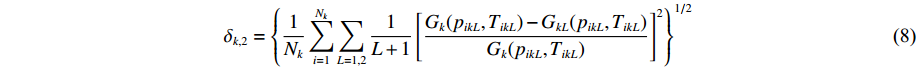
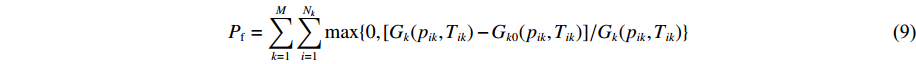
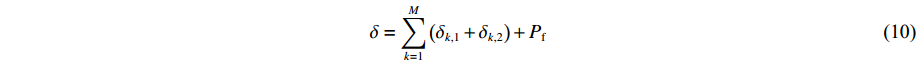
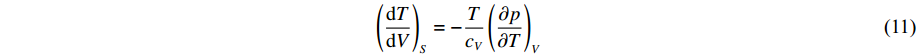
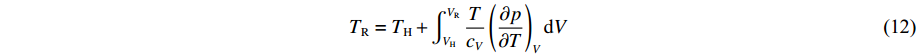
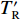
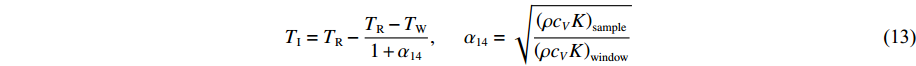
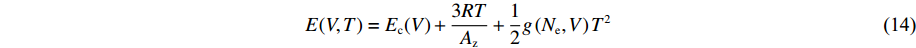
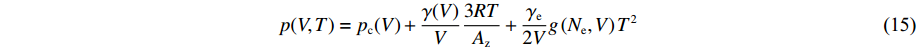
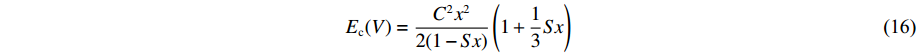
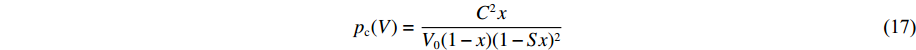
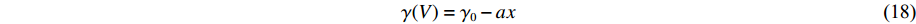
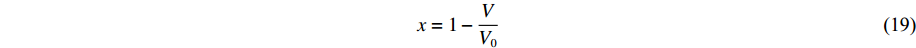
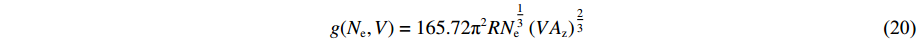
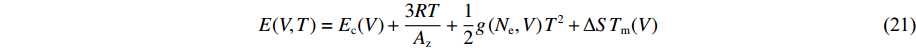
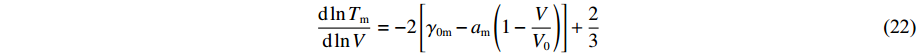

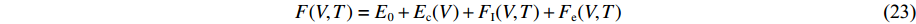
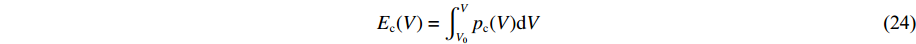
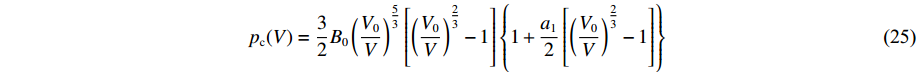
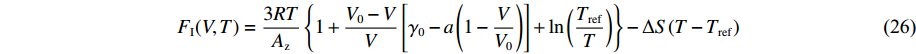
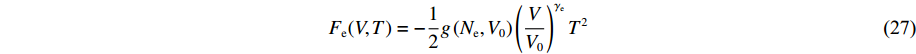



 下载:
下载: