A Comparative Study on the Finite Element Models for Projectiles Perforation into Reinforced Concrete Slabs
-
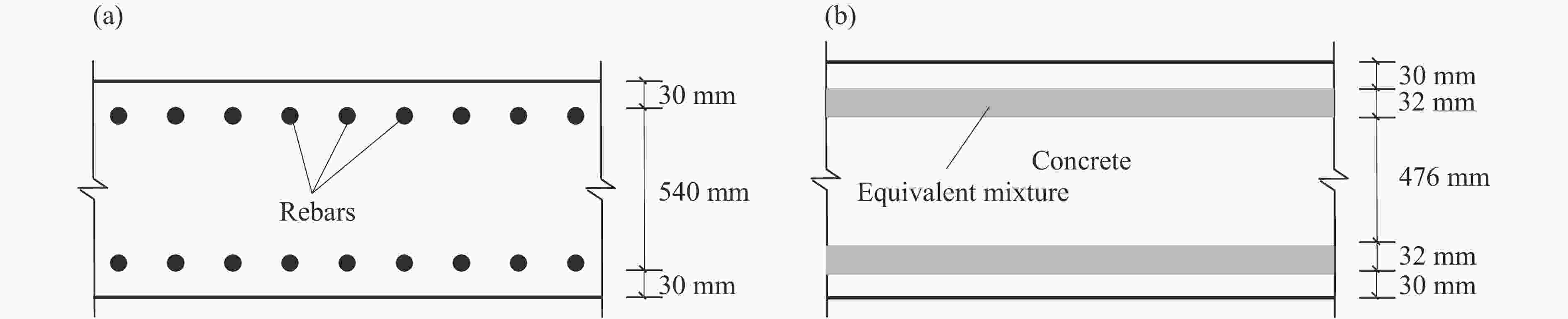
摘要: 为研究钢筋对混凝土靶侵彻作用的影响,基于混合物理论,建立了钢筋混凝土的等效混合物模型,同时还建立了将钢筋等效为钢板和素混凝土板的有限元模型,并通过弹体贯穿剩余速度、靶体压力场对两种方法进行比较,分析侵彻作用过程。计算结果表明:基于混合物理论的等效钢筋混凝土混合物模型能够较好地反映侵彻时钢筋的作用,既可以满足计算精度,又能够简化建模过程,提高计算效率,是进行侵彻数值分析的有效简化方法;钢筋混凝土板自由表面附近的钢筋分布能够提高靶对弹体的阻力,但其作用效果有限。Abstract: In order to study the rebar effect on perforation into concrete targets, the equivalent mixture model of reinforced concrete is established based on the mixture theory. Meanwhile, the model of steel equivalent to steel plate and the plain concrete slab model are given. The residual velocities, the pressure fields and perforation processes for the two models are compared. The results show that the equivalent reinforced concrete mixture model based on mixture theory can better reflect the rebar effect during the penetration, which can not only meet the calculation accuracy, but also simplify the modeling process and improve the calculation efficiency. It is an effective simplified method for numerical analysis of penetration. The distribution of rebar near the free surface of reinforced concrete slab can improve the resistance of target to projectile, but its role is limited.
-
Key words:
- reinforced concrete /
- mixture theory /
- perforation /
- finite element analysis
-
表 1 钢筋、混凝土及混合物的材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of rebar, concrete and their mixture
Materials ${\,\rho }$0/(g·cm−3) c0/(km·s−1) s0 Ys/GPa G/GPa ${\gamma }$0 $ {V{_1}} $($ {V{_2}} $) Rebar 7.85 4.57 1.49 0.32 790.0 2 0.2 Concrete 2.20 2.33 1.51 0.08 1.7 2 0.8 Mixture 3.33 2.58 1.50 0.13 2.1 2 表 2 钢筋混凝土贯穿实验与数值计算结果
Table 2. Experimental and numerical simulation results for perforation into reinforced concrete slabs
Target No. Models Impact velocity/(m·s–1) Perforation velocity/(m·s–1) Deviation/% Exp. Sim. 1 Mixture equivalent slab 300 93 106 13 2 Steel layers equivalent slab 300 93 100 8 3 Plain concrete slab 300 116 129 12 -
[1] RIERA J D. Penetration, scabbing and perforation of concrete structures hit by solid missiles [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1989, 115(1): 121–131. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(89)90265-3 [2] BARR P. Guidelines for the design and assessment of concrete structures subjected to impact [R]. London: UK Atomic Energy Authority, Safety and Reliability Directorate, 1990. [3] DANCYGIER A N. Effect of reinforcement ratio on the resistance of reinforced concrete to hard projectile impact [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1997, 172(1/2): 233–245. doi: 10.1016/S0029-5493(97)00055-1 [4] REID S R, WEN H M. Predicting penetration, cone cracking, scabbing and perforation of reinforced concrete targets struck by flat-faced projectiles [R]. UK: University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology, 2001. [5] 欧阳春, 赵国志, 杜中华, 等. 弹丸垂直侵彻钢筋混凝土介质的工程解析模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2004, 24(3): 273–277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2004.03.013OUYANG C, ZHAO G Z, DU Z H, et al. An engineering analytical model for projectiles to penetrate normally into semi-infinite reinforced concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2004, 24(3): 273–277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2004.03.013 [6] 任辉启, 何翔, 刘瑞朝, 等. 弹体侵彻混凝土过载特性研究 [J]. 土木工程学报, 2005, 38(1): 110–116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2005.01.015REN H Q, HE X, LIU R C, et al. A study on the overload characteristics of projectile penetrating concrete [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2005, 38(1): 110–116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2005.01.015 [7] 陈小伟. 穿甲/侵彻问题的若干工程研究进展 [J]. 力学进展, 2009, 39(3): 316–351. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2009.03.006CHEN X W. Advances in the penetration/perforation of rigid projectiles [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2009, 39(3): 316–351. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2009.03.006 [8] 邓勇军, 宋文杰, 陈小伟, 等. 钢筋混凝土靶侵彻的可压缩弹-塑性动态空腔膨胀阻力模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(5): 1023–1030. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0043DENG Y J, SONG W J, CHEN X W, et al. A dynamic cavity-expansion penetration model of compressible elastic-plastic response for reinforced concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(5): 1023–1030. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0043 [9] 邓勇军, 陈小伟, 姚勇. 钢筋混凝土靶侵彻过程中空腔膨胀响应分区研究 [J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50(2): 024606. doi: 10.1360/SSPMA-2019-0184DENG Y J, CHEN X W, YAO Y. Study on the cavity expansion response of the concrete target under penetration [J]. Scientia Sinica: Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2020, 50(2): 024606. doi: 10.1360/SSPMA-2019-0184 [10] BELOV N N, KOPANITSA D G, KUMPYAK O K. Calculation of reinforced concrete structures under explosive and impact loading [M]. Russian: STT, 2004: 241−245. [11] MALVAR L J, CRAWFORD J E, WESEVICH J W, et al. A plasticity concrete material model for DYNA3D [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(9/10): 847–873. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)00023-7 [12] LUCCIONI B M, ARÁOZ G F, LABANDA N A. Defining erosion limit for concrete [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2013, 4(3): 315–340. doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.4.3.315 [13] 王明洋, 邓宏见, 钱七虎. 岩石中侵彻与爆炸作用的近区问题研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(6): 2859–2863. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.008WANG M Y, DENG H J, QIAN Q H. Study on problems of near cavity of penetration and explosion in rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(6): 2859–2863. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.008 -






 下载:
下载:






