Strain Rate Dependent Constitutive Model of Rubber
-
摘要: 为研究橡胶在不同应变率下的响应特性,建立应变率相关的橡胶黏超弹性本构模型,分别采用超弹性本构模型和黏弹性本构模型表征其非线性弹性行为和应变率相关的弹性行为。首先,对于超弹性模型,基于最小二乘法,对比了Mooney-Rivlin模型、修正的Mooney-Rivlin模型、Yeoh模型、修正的Yeoh模型、Ogden模型和Arruda-Boyce模型等超弹性本构模型的拟合能力。结果表明,经修正的Mooney-Rivlin模型和Yeoh模型的拟合优度与Ogden模型和Arruda-Boyce模型接近。在此基础上,基于一种参数较少且拟合效果良好的修正Mooney-Rivlin模型和应变率相关的Maxwell模型,建立了橡胶黏超弹性本构模型,考察了该黏超弹性本构模型在单轴拉伸和单轴压缩情况下中高应变率时的拟合能力。结果表明,对于这两种受力情况下的应变率相关的实验数据,该黏超弹性本构模型的拟合优度均在0.95以上。研究结果为大应变率范围内单轴拉伸和单轴压缩下橡胶的本构模型选择提供了参考。Abstract: In order to study the mechanical response characteristics of rubber under large loading strain rates, a strain-rate-dependent visco-hyperelastic constitutive model is established. The nonlinear and the strain-rate-dependent elastic behavior are characterized by the hyperelastic constitutive model and the viscoelastic constitutive model, respectively. Firstly, based on least square method, the fitting abilities of several hyperelastic constitutive models, i.e., Mooney-Rivlin model, the modified Mooney-Rivlin model, Yeoh model, the modified Yeoh model, Ogden model and Arruda-Boyce model, are compared. The results show that the modified Mooney-Rivlin model and the modified Yeoh model have similar fitting goodness as Ogden model and Arruda-Boyce model. Furthermore, the visco-hyperelastic constitutive model based on a modified Mooney-Rivlin model with a few parameters leading to good fitting results and the Maxwell model reflecting the strain-rate-dependent property of rubber is described. The fitting ability of the proposed model under uni-axial tension and uni-axial compression loading conditions at medium and high strain rates is assessed. It is concluded that the fitting goodness of the model is above 0.95 under both loading conditions. This study can provide a reference for the selection of constitutive models to characterize the mechanical behavior of rubber under uni-axial tension and uni-axial compression tests at different strain rates.
-
Key words:
- constitutive model /
- strain rate /
- rubber /
- least square method
-
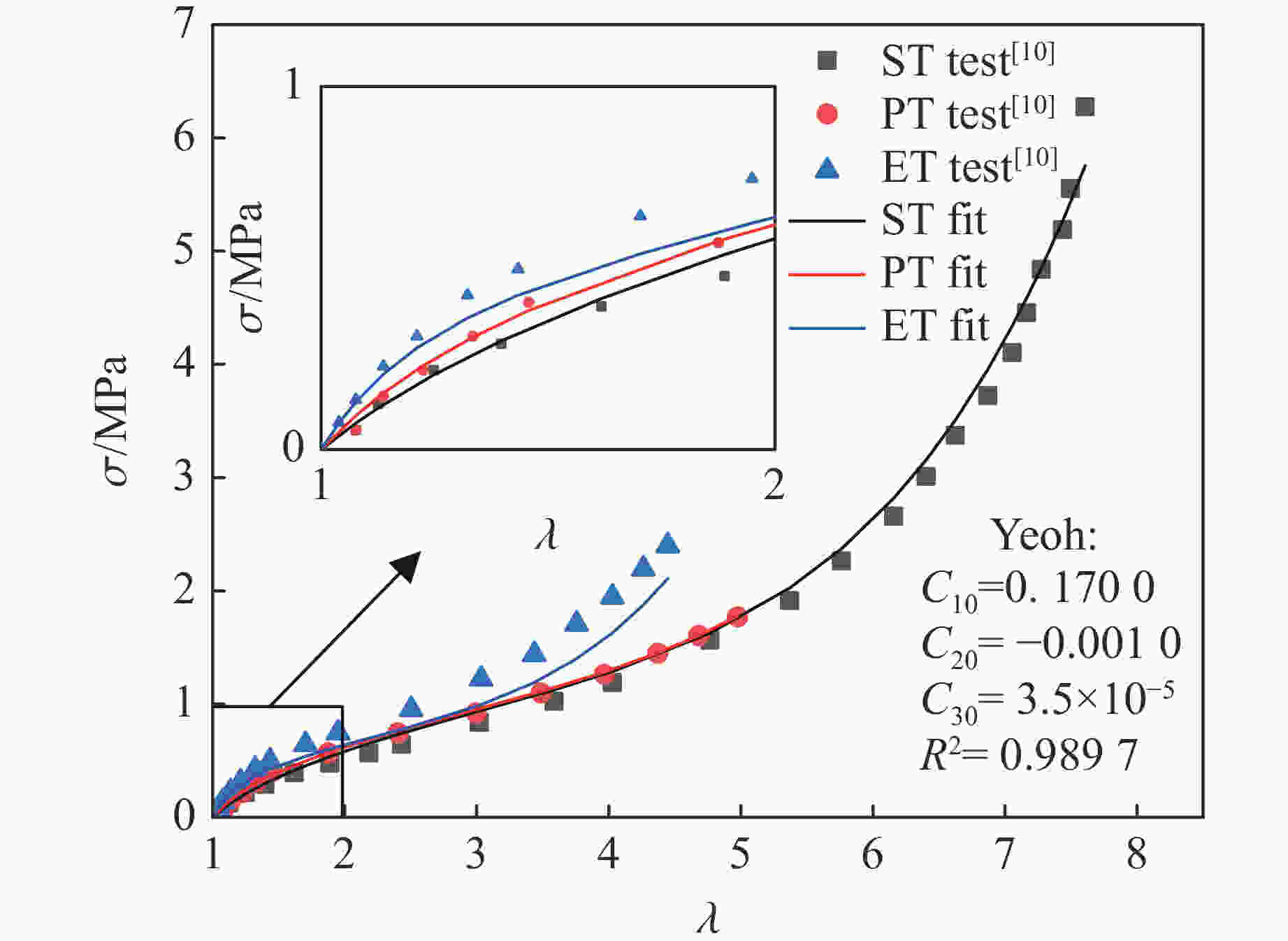
表 1 不同超弹性模型对 ST、PT 和 ET 实验数据的拟合效果比较
Table 1. Comparison of fitting results of different hyperelastic models on ST, PT and ET experimental data
Model Equation Parameters R2 M-R model Eq.(2) C10, C01 0.8043 Modified M-R model Eq.(15) C10, C01, C20 0.9704 Yeoh model Eq.(6) C10, C20, C30 0.9897 Modified Yeoh model Eq.(21) C10, C20, C30, C01 0.9961 Ogden model (N=2) Eq.(8) $ {\,\mu } $1, $ {\alpha } $1, $ {\,\mu } $2, $ {\alpha } $2 0.9769 Ogden model (N=3) Eq.(8) ${\,\mu }$1, $ {\alpha } $1, $ {\,\mu } $2, $ {\alpha } $2, ${\,\mu }$3, $ {\alpha } $3 0.9924 A-B model Eq.(10) $\,\mu$, $ {\lambda } $m 0.9891 表 2 单轴拉伸和单轴压缩实验的拟合参数值
Table 2. Fitting parameter values of the uni-axial tensile and the uni-axial compression experiment
-
[1] 胡小玲, 刘秀, 李明, 等. 炭黑填充橡胶超弹性本构模型的选取策略 [J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(5): 34–42, 48.HU X L, LIU X, LI M, et al. Selection strategies of hyperelastic constitutive models for carbon black filled rubber [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(5): 34–42, 48. [2] 龚科家, 危银涛, 叶进雄. 填充橡胶超弹性本构参数试验与应用 [J]. 工程力学, 2009, 26(6): 193–198.GONG K J, WEI Y T, YE J X. Constitutive parametric experiment of tire rubber hyperelastic laws with application [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(6): 193–198. [3] ELIAS H G. Macromolecules, volume 1: structure and properties [M]. Boston, MA: Springer, 2012. [4] MOONEY M. A theory of large elastic deformation [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1940, 11(9): 582–592. doi: 10.1063/1.1712836 [5] RIVLIN R S, SAUNDERS D W. Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials. Ⅶ. Experiments on the deformation of rubber [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1951, 243(865): 251–288. [6] YEOH O H. Some forms of the strain energy function for rubber [J]. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 1993, 66(5): 754–771. doi: 10.5254/1.3538343 [7] OGDEN R W. Non-linear elastic deformations [M]. New York: Dover Publications, 1997. [8] OGDEN R W. Large deformation isotropic elasticity: on the correlation of theory and experiment for incompressible rubberlike solids [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1972, 326(1567): 565–584. [9] ARRUDA E M, BOYCE M C. A three-dimensional constitutive model for the large stretch behavior of rubber elastic materials [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1993, 41(2): 389–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(93)90013-6 [10] TRELOAR L R G. Stress-strain data for vulcanized rubber under various types of deformation [J]. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 1944, 17(4): 813–825. doi: 10.5254/1.3546701 [11] BOYCE M C, ARRUDA E M. Constitutive models of rubber elasticity: a review [J]. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 2000, 73(3): 504–523. doi: 10.5254/1.3547602 [12] STEINMANN P, HOSSAIN M, POSSART G. Hyperelastic models for rubber-like materials: consistent tangent operators and suitability for Treloar’s data [J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2012, 82(9): 1183–1217. doi: 10.1007/s00419-012-0610-z [13] MARCKMANN G, VERRON E. Comparison of hyperelastic models for rubber-like materials [J]. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 2006, 79(5): 835–858. doi: 10.5254/1.3547969 [14] 肖锐, 向玉海, 钟旦明, 等. 考虑缠结效应的超弹性本构模型 [J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(4): 1028–1037. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-008XIAO R, XIANG Y H, ZHONG D M, et al. Hyperelastic model with entanglement effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(4): 1028–1037. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-008 [15] 施成, 周恒为, 丁明明, 等. 一种基于分子链统计理论的橡胶超弹性混合本构模型 [J]. 应用化学, 2021, 38(2): 228–235.SHI C, ZHOU H W, DING M M, et al. A hyperelastic mixed constitutive model for rubber based on molecular chain statistical theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2021, 38(2): 228–235. [16] 付宾, 杨晓翔, 李庆. 炭黑填充橡胶材料改进Mooney模型 [J]. 固体力学学报, 2017, 38(5): 408–415.FU B, YANG X X, LI Q. A revised Mooney model of carbon black filled-rubber materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2017, 38(5): 408–415. [17] 李雪冰, 危银涛. 一种改进的Yeoh超弹性材料本构模型 [J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(12): 38–43. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.05.0388LI X B, WEI Y T. An improved Yeoh constitutive model for hyperelastic material [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(12): 38–43. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.05.0388 [18] 魏志刚, 陈海波. 一种新的橡胶材料弹性本构模型 [J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(2): 473–483. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-303WEI Z G, CHEN H B. A new elastic model for rubber-like materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(2): 473–483. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-303 [19] 段宇星, 杨强, 赵苗苗, 等. 弹性体材料应变率相关力学行为模型 [J]. 橡胶工业, 2020, 67(12): 899–903.DUAN Y X, YANG Q, ZHAO M M, et al. Strain rate-related mechanical behavior model of elastomer material [J]. China Rubber Industry, 2020, 67(12): 899–903. [20] CANDAU N, OGUZ O, PEUVREL-DISDIER E, et al. Effect of the strain rate on damage in filled EPDM during single and cyclic loadings [J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(12): 3021. doi: 10.3390/polym12123021 [21] WANG Y L, LI Z, LI X, et al. Effect of the temperature and strain rate on the tension response of uncured rubber: experiments and modeling [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2020, 148: 103480. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2020.103480 [22] 周相荣, 王强, 涂耿伟. 弯曲型橡胶缓冲器冲击试验与数值仿真 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2007, 26(4): 97–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2007.04.023ZHOU X R, WANG Q, TU G W. Impact test and simulation for rubber shock absorbers of bending structures [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2007, 26(4): 97–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2007.04.023 [23] 林玉亮, 卢芳云, 卢力. 高应变率下硅橡胶的本构行为研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2007, 21(3): 289–294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2007.03.012LIN Y L, LU F Y, LU L. Constitutive behaviors of a silicone rubber at high strain rates [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2007, 21(3): 289–294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2007.03.012 [24] 杨建兴, 张江涛, 乔炎亮, 等. 硅橡胶动态压缩性能SHPB测试方法及其本构模型研究 [J]. 高分子通报, 2021(4): 27–34.YANG J X, ZHANG J T, QIAO Y L, et al. SHPB test method for the dynamic compressive properties and dynamic constitutive model of silicon rubber [J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2021(4): 27–34. [25] TSCHOEGL N W. Constitutive equations for elastomers [J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A-1: Polymer Chemistry, 1971, 9(7): 1959–1970. doi: 10.1002/pol.1971.150090714 [26] 卢强, 王占江, 王礼立, 等. 基于ZWT方程的线黏弹性球面波分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2013, 33(5): 463–470. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2013)05-0463-08LU Q, WANG Z J, WANG L L, et al. Analysis of linear visco-elastic spherical waves based on ZWT constitutive equation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2013, 33(5): 463–470. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2013)05-0463-08 [27] 曹侃. 聚碳酸酯动态拉伸力学行为的测试与表征 [D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2012.CAO K. Experimental investigation and modeling of dynamic tension behavior of polycarbonate [D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2012. [28] 吴长河, 冯晓伟, 叶培, 等. 应变率对硫化橡胶压缩力学性能的影响 [J]. 功能材料, 2013, 44(8): 1098–1101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2013.08.009WU C H, FENG X W, YE P, et al. Effect of strain rate on mechanical properties of vulcanized rubber [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2013, 44(8): 1098–1101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2013.08.009 [29] 郭玲梅, 汪洋, 徐伟芳. 硅橡胶拉伸行为的应变率相关性测试和表征 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33(5): 054101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180664GUO L M, WANG Y, XU W F. Experimental investigation and modeling of strain-rate dependence on tensile behavior of silicone rubbers [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33(5): 054101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180664 -







 下载:
下载: