Experimental Investigation of Spall Damage in Pure Aluminum with Helium Bubbles
-
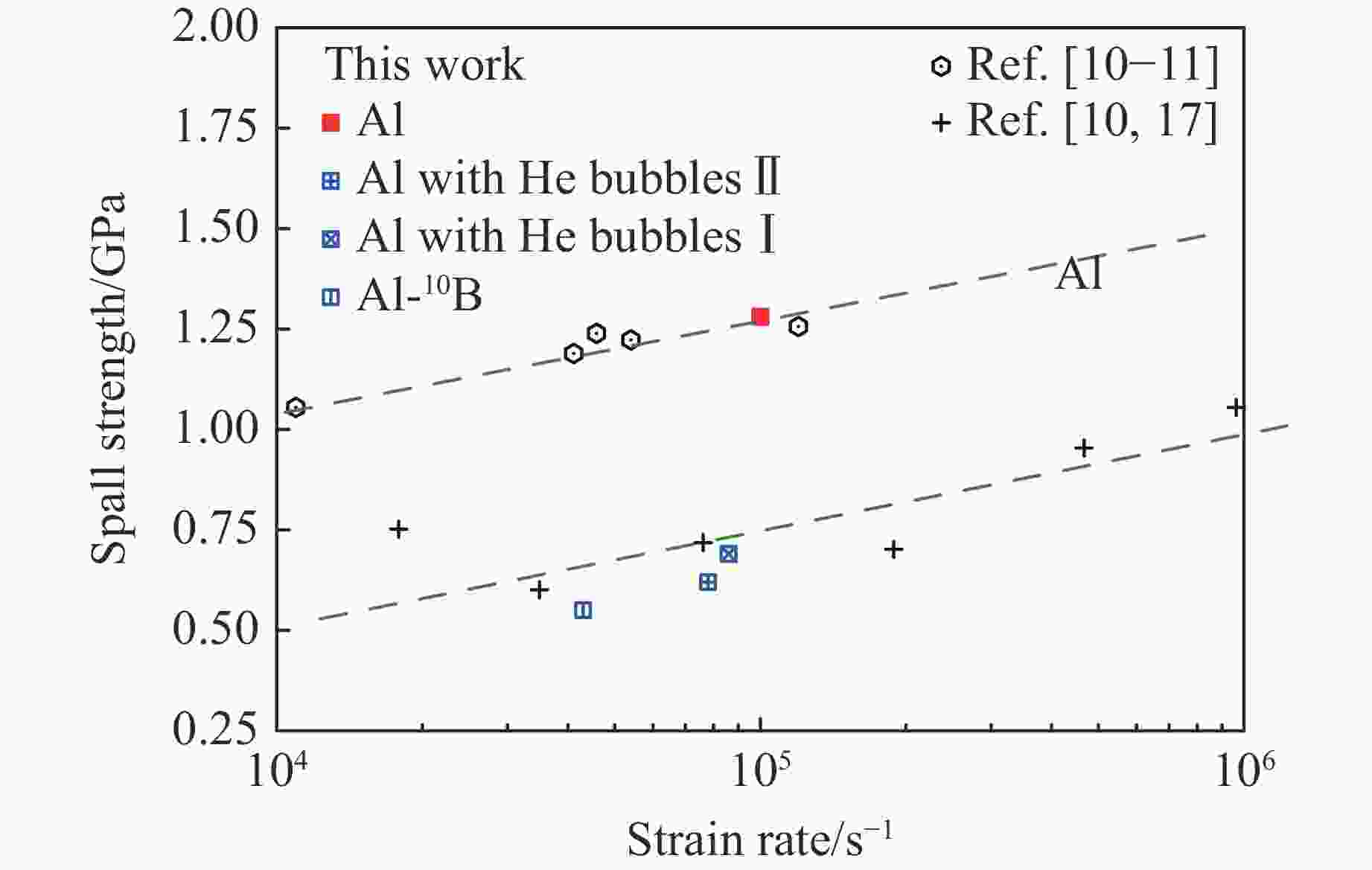
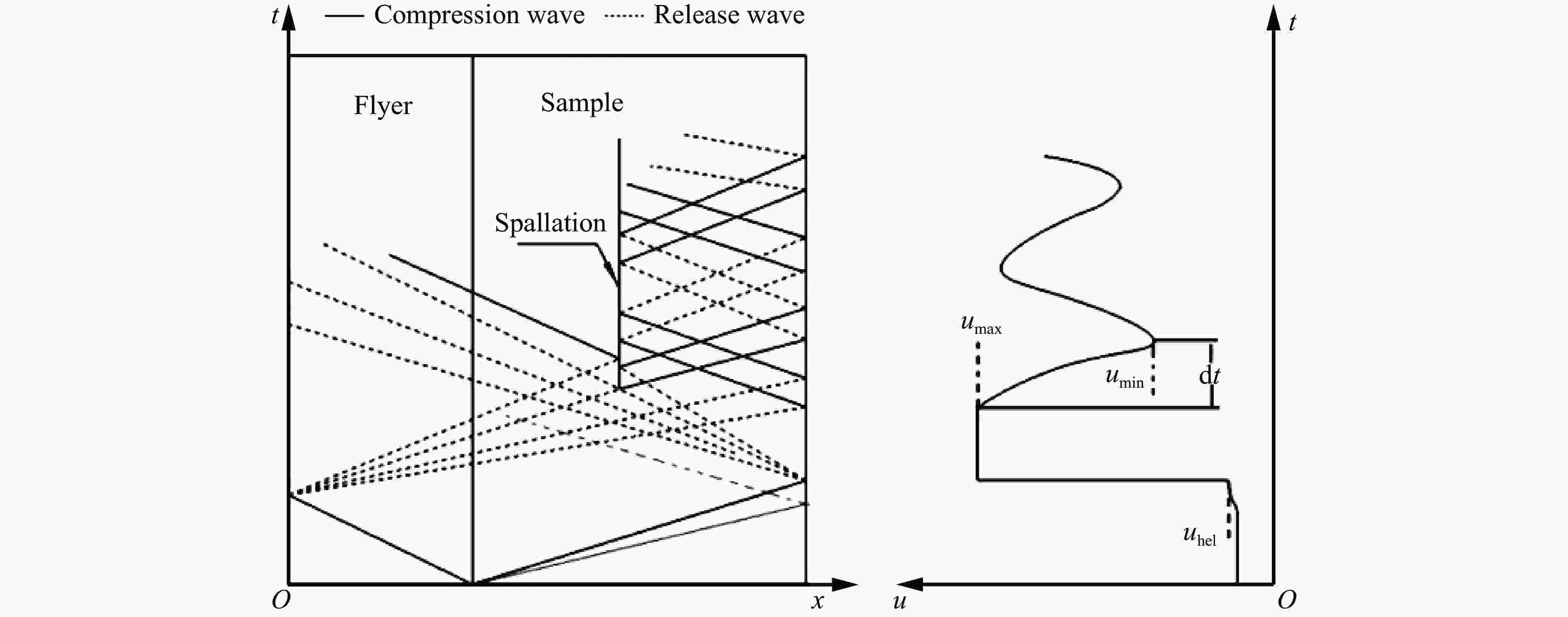
摘要: 含氦泡材料的动态断裂性能是多个研究领域关注的重点。采用平板冲击实验技术,对含有氦泡、硼等杂质的铝材料进行了层裂实验研究,由双光源混频系统分别测量了纯铝、掺硼铝以及两种氦浓度的含氦泡铝样品的自由面速度,对比分析了不同杂质影响下铝材料的层裂强度及其差异。实验显示:纯铝的层裂强度为1.28 GPa,引入硼杂质使铝的层裂强度显著降低,降低幅度接近50%;中子辐照掺硼铝引入氦泡后,对铝的层裂性能没有造成进一步影响,说明采用中子辐照掺硼铝方法制备含氦泡铝时,氦泡效应不显著,即氦泡对材料的动态断裂性能影响有限。此外,根据实验测量结果,简要讨论了硼和氦泡等对铝的Hugoniot弹性极限的影响。Abstract: The dynamic fracture behavior of material containing helium bubbles is the focus of many research fields. In this work, the spall damage of pure aluminum containing boron inclusions or helium bubbles is studied by plane impact experiments. The experiments were done for three types of targets: pure aluminum, Al-10B and neutron irradiated Al-10B to obtain helium bubbles. The targets response to the dynamic loading was obtained from the free surface velocity profiles which were measured by dual laser heterodyne velocimetry. The results show that, the spall strength and Hugoniot elastic limit of these targets were calculated. It is found that the spall strength of pure aluminum is 1.28 GPa, and the addition of 10B in pure aluminum reduces the spall strength of material by about 50%. However, Al-10B with helium bubbles is not found to have higher spall strength compared to samples without bubbles, which means that the influence of helium bubble on the dynamic fracture properties of the material is not significant. In addition, the effects of boron and helium bubbles on the Hugoniot elastic pole of aluminum are discussed.
-
Key words:
- boron /
- helium bubbles /
- pure aluminum /
- irradiation damage /
- spall strength
-
表 1 实验数据
Table 1. Experimental data
Exp. No. LY12
thickness/mmFlyer
velocity/(m·s−1)Sample
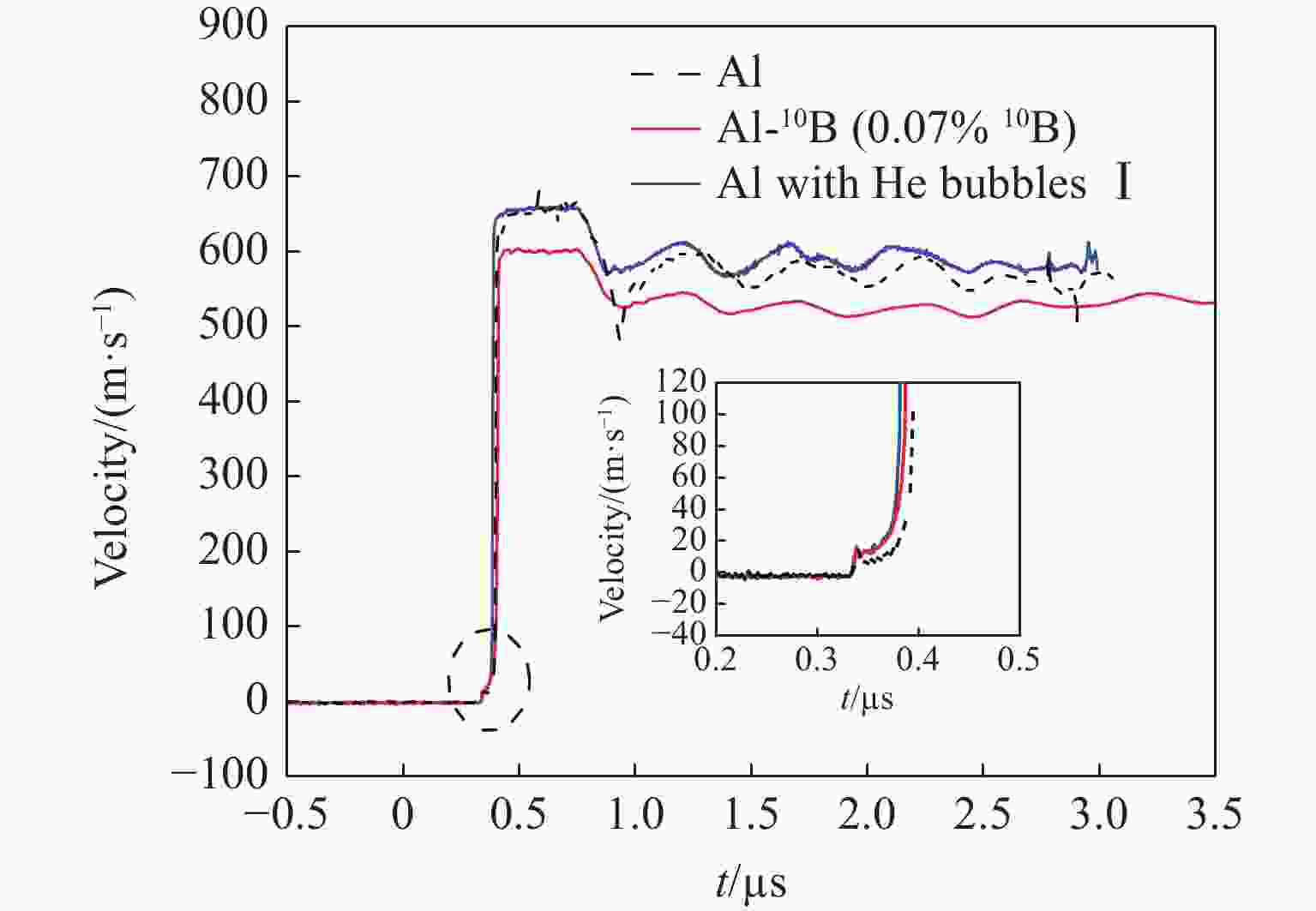
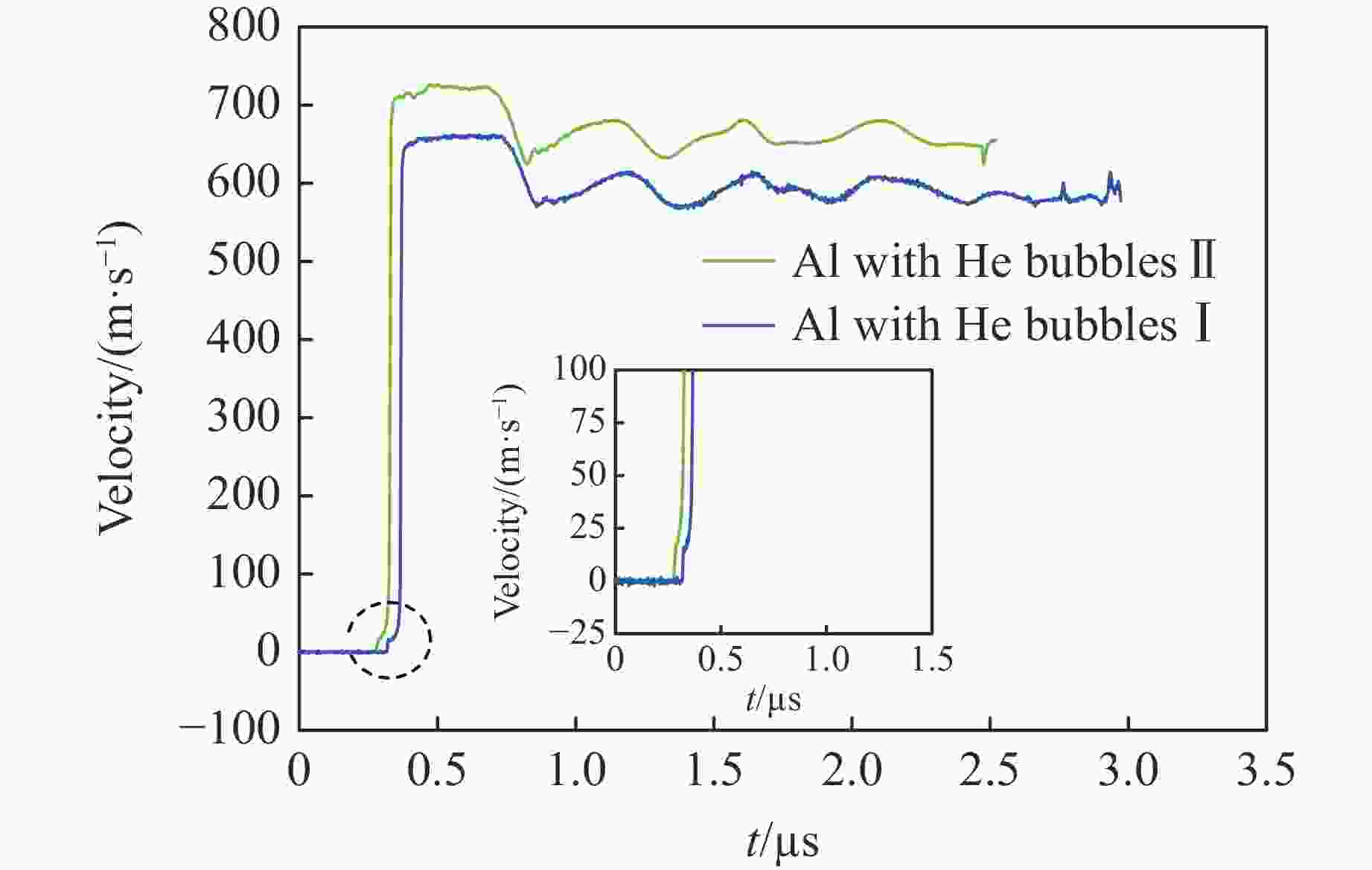
thickness/mmYhel/GPa $\sigma $spall/GPa $ \dot{\varepsilon } $/(104 s−1) Material Shot 1 1.500 654 2.925 0.062 1.28 9.1 Al 2.736 0.123 0.62 7.8 Al with He bubbles Ⅰ Shot 2 1.503 603 3.050 0.130 0.55 4.3 Al-10B (0.07% 10B) Shot 3 1.500 720 2.776 0.153 0.69 8.6 Al with He bubbles Ⅱ 表 2 密度和声速
Table 2. Density and sound velocity
Material ${\,\rho }$0/(g·cm−3) c1/(km·s−1) ct/(km·s−1) cb/(km·s−1) Al 2.699 6.561 3.130 5.476 Al with He bubbles Ⅰ 2.696 6.514 3.180 5.381 Al-10B (0.07% 10B) 2.699 6.542 3.155 5.434 Al with He bubbles Ⅱ 2.695 6.505 3.215 5.341 -
[1] 吕铮, 刘春明. 快中子反应堆核心结构材料的辐照损伤 [J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2011, 10(3): 203–208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.03.011LÜ Z, LIU C M. Irradiation damage of structural materials for fast reactor application [J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2011, 10(3): 203–208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.03.011 [2] ZINKLE S J. Fusion materials science: overview of challenges and recent progress [J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2005, 12(5): 058101. doi: 10.1063/1.1880013 [3] BLOOM E E, BUSBY J T, DUTY C E, et al. Critical questions in materials science and engineering for successful development of fusion power [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 367/370: 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.02.007 [4] 张崇宏, 杨义涛, 宋银, 等. 一种低活化铁素体/马氏体钢的高能重离子辐照效应研究 [J]. 原子核物理评论, 2009, 26(1): 48–54. doi: 10.11804/NuclPhysRev.26.01.048ZHANG C H, YANG Y T, SONG Y, et al. Analysis of effects in a low-activation ferritic/martensitic steel by high-energy heavy-ion irradiation [J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 2009, 26(1): 48–54. doi: 10.11804/NuclPhysRev.26.01.048 [5] BIRTCHER R C, DONNELLY S E, TEMPLIER C. Evolution of helium bubbles in aluminum during heavy-ion irradiation [J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 50(2): 764–769. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.764 [6] IWAKIRI H, YASUNAGA K, MORISHITA K, et al. Microstructure evolution in tungsten during low-energy helium ion irradiation [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2000, 283: 1134–1138. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3115(00)00289-0 [7] VISHNYAKOV V M, DONNELLY S E, CARTER G. The influence of impurities on the growth of helium-induced cavities in silicon [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(1): 238–244. doi: 10.1063/1.1576493 [8] 高云亮, 朱芫江, 李进平. Al辐照损伤初期的第一性原理研究 [J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(5): 057104. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.057104GAO Y L, ZHU Y J, LI J P. First-principle study of initial irradiation damage in aluminum [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(5): 057104. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.057104 [9] GLAM B, STRAUSS M, ELIEZER S, et al. Shock compression and spall formation in aluminum containing helium bubbles at room temperature and near the melting temperature: experiments and simulations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 65: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.10.010 [10] GLAM B, ELIEZER S, MORENO D, et al. Dynamic fracture and spall in aluminum with helium bubbles [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2010, 163(1): 217–224. doi: 10.1007/s10704-009-9437-1 [11] XIAO D W, HE L F, ZHOU P, et al. Spall in aluminium with helium bubbles under laser shock loading [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2017, 34(5): 056201. doi: 10.1088/0256-307x/34/5/056201 [12] ZHOU T T, HE A M, WANG P, et al. Spall damage in single crystal Al with helium bubbles under decaying shock loading via molecular dynamics study [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2019, 162: 255–267. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2019.02.019 [13] NOVIKOV S A. Spall strength of materials under shock load [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics, 1967(3): 109–120. [14] JOHNSON J N, GRAY Ⅲ G T, BOURNE N K. Effect of pulse duration and strain rate on incipient spall fracture in copper [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 86(9): 4892–4901. doi: 10.1063/1.371527 [15] DAVISON L, SHAHINPOOR M. High-pressure shock compression of solids Ⅲ [M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1998: 93–95. [16] 陶天炯, 翁继东, 王翔. 一种双光源外差测试技术 [J]. 光电工程, 2011, 38(10): 39–45.TAO T J, WENG J D, WANG X. A dual laser heterodyne velocimetry [J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2011, 38(10): 39–45. [17] 何方成, 宫兆斌. 超声波声速测量技术及其在材料评价中的应用 [J]. 材料工程, 2003(8): 33–34, 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2003.08.009HE F C, GONG Z B. Ultrasonic velocity measuring technology and its application in materials evaluation [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2003(8): 33–34, 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2003.08.009 [18] CHEN X, ASAY J R, DWIVEDI S K. Spall behavior of aluminum with varying microstructures [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 99(2): 023528. doi: 10.1063/1.2165409 -






 下载:
下载: