Numerical Simulation of Granite Penetration Based on Lagrange and SPH Algorithm
-
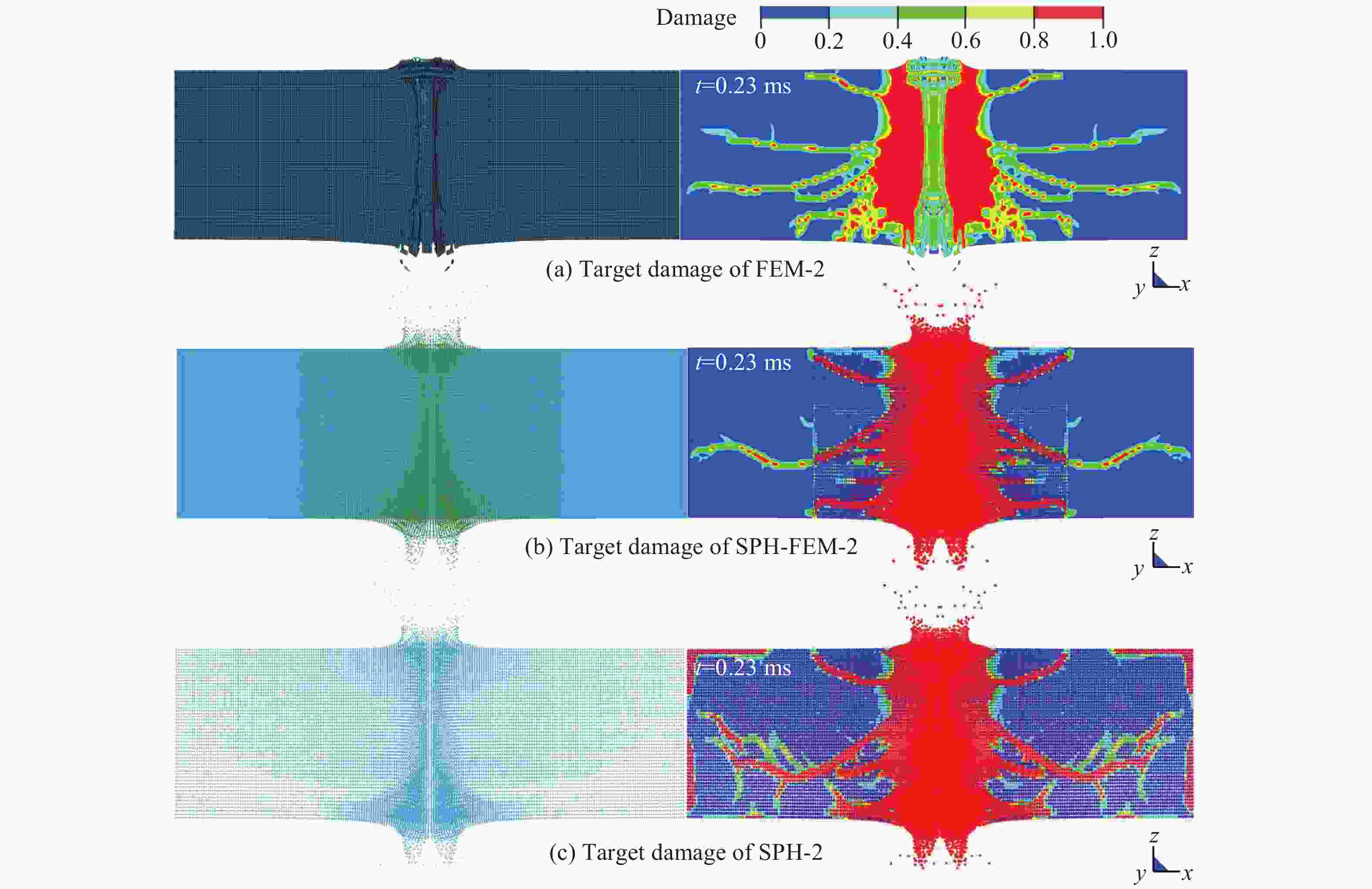
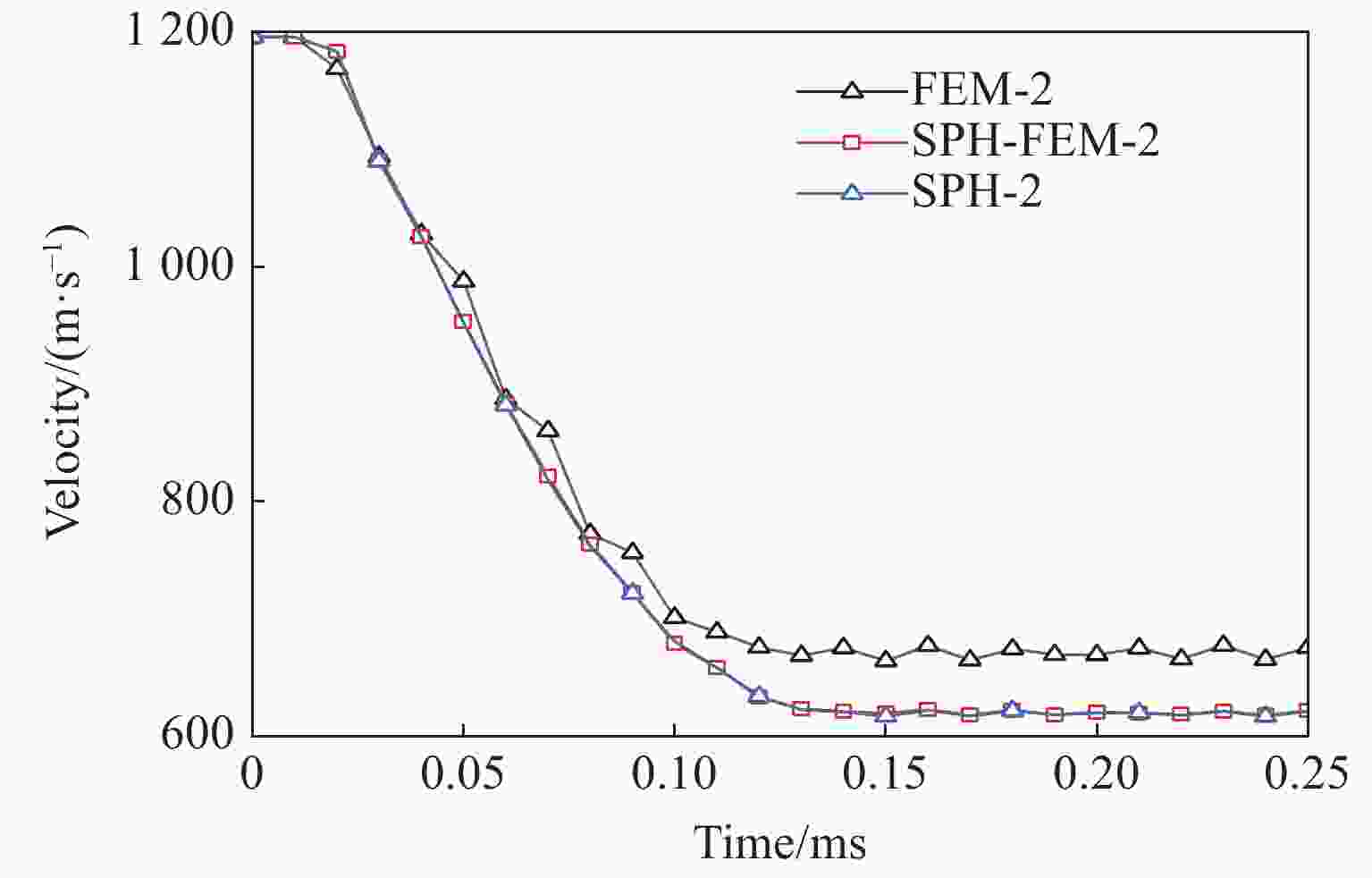
摘要: 为研究不同算法对弹体侵彻花岗岩模拟的影响,基于仿真分析软件LS-DYNA中的Lagrange算法及SPH(Smooth particle hydrodynamics)算法,采用Lagrange、SPH-Lagrange耦合及SPH算法分别对弹体侵彻、贯穿花岗岩靶体进行数值模拟,并从计算效率、侵彻深度、速度衰减、靶体损伤、Mises应力分布多方面对比模拟结果,分析3种算法用于研究岩石侵彻问题的优势和不足。研究表明:Lagrange算法的计算效率最高,计算精度高,但存在单元畸变、无撞击溅射、无后坑区等问题;SPH算法的计算效率最低,但模拟效果良好;SPH-Lagrange耦合算法兼具二者优势,但会导致应力滞后和应力波不稳定衰减。在大型模拟中应优先选用Lagrange算法和SPH-Lagrange耦合算法。
-
关键词:
- 弹体侵彻 /
- 花岗岩靶体 /
- Lagrange算法 /
- SPH-Lagrange耦合算法 /
- SPH算法
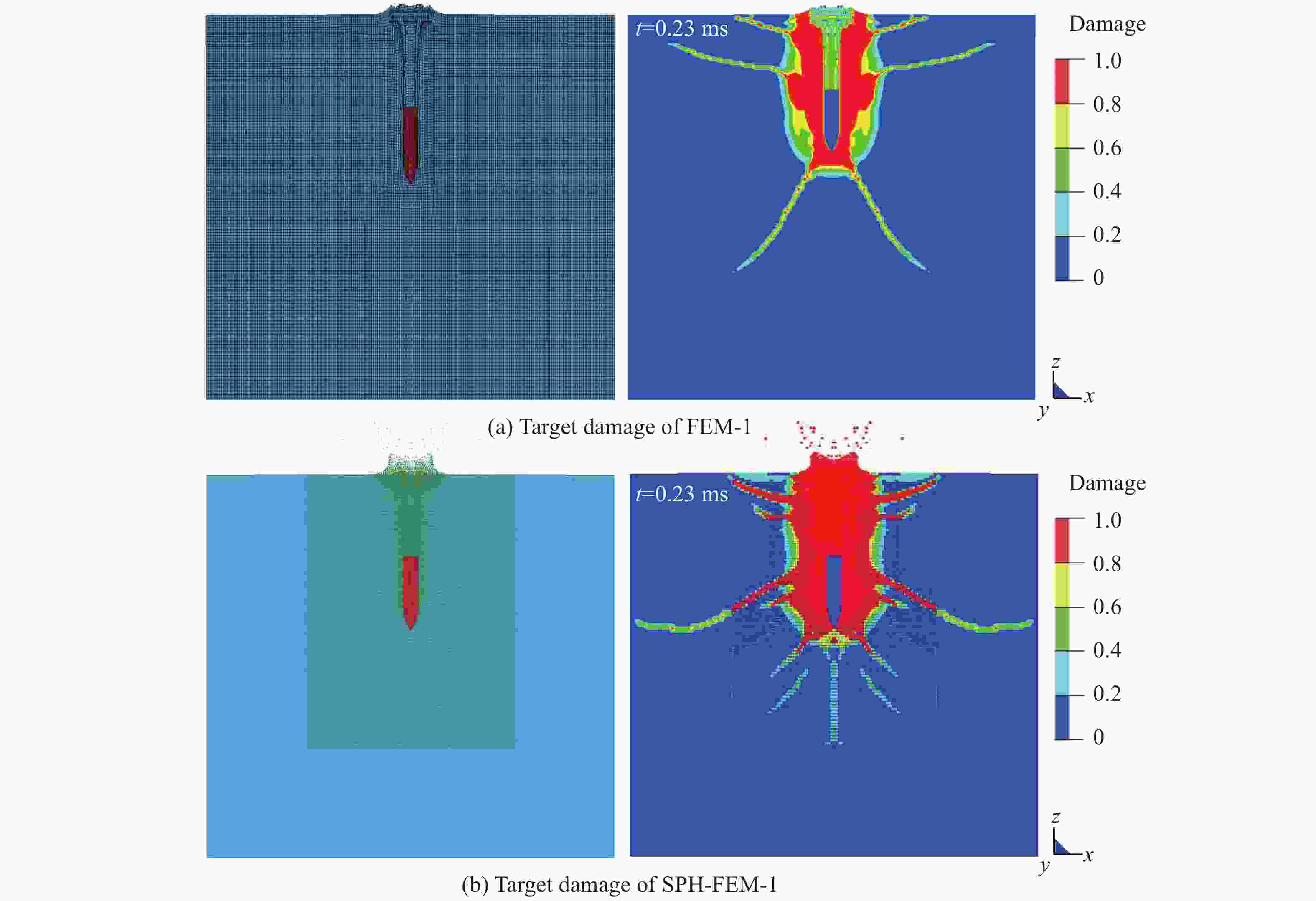
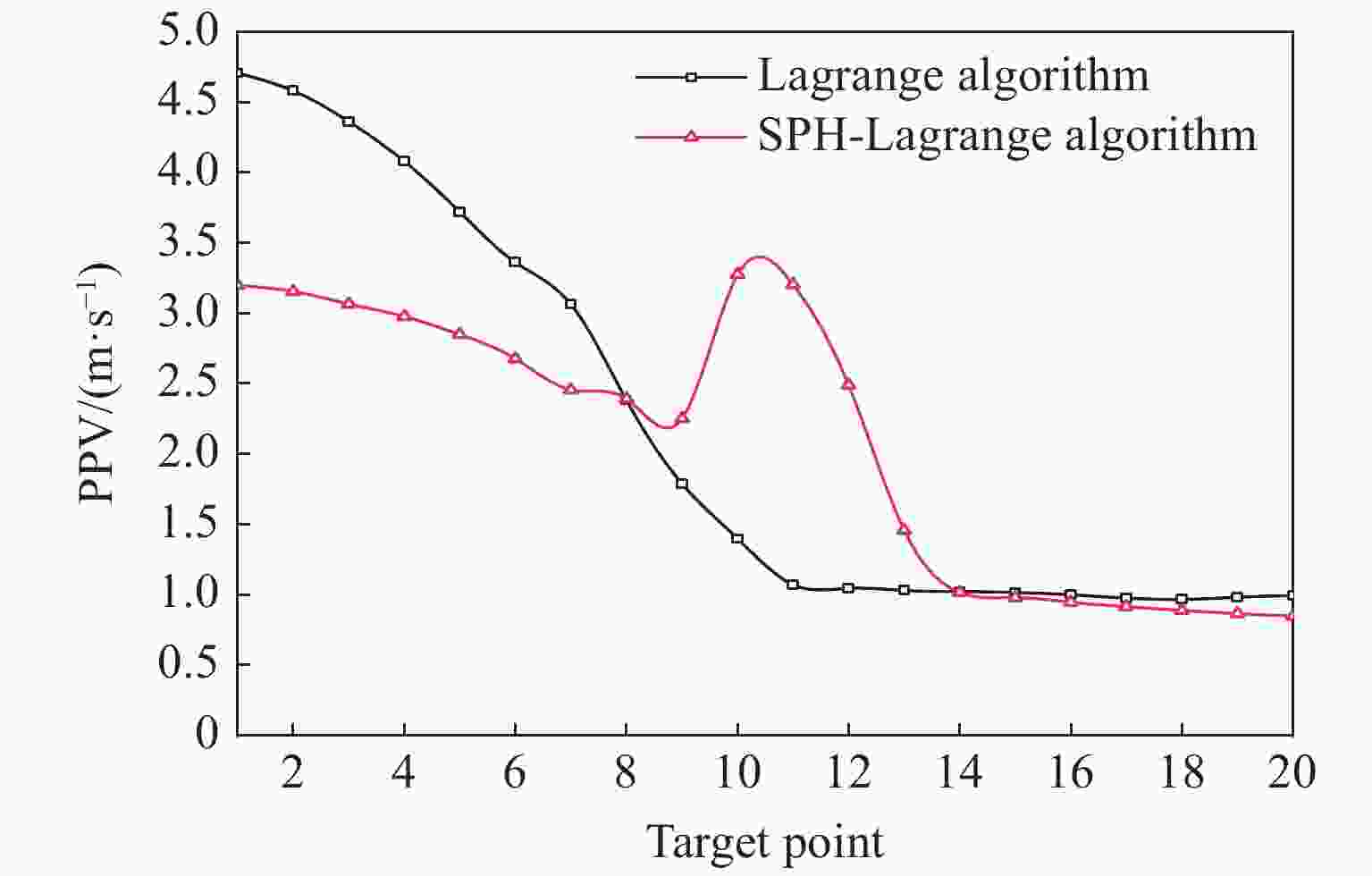
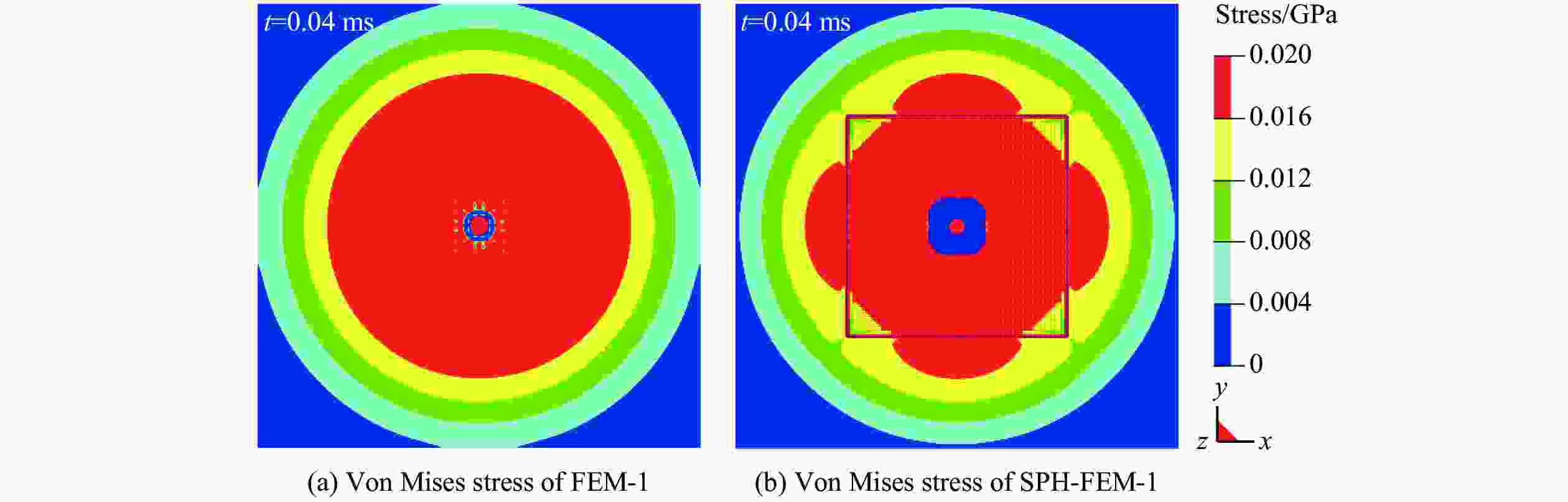
Abstract: To study the influence of different algorithms on penetration simulations of granite target subjected to projectile, Lagrange, SPH-Lagrange coupling and SPH (smooth particle hydrodynamics) algorithms are used for penetration simulations, based on Lagrange and SPH algorithms within LS-DYNA software. By comparing the numerical results through calculation efficiency, penetration depth, velocity attenuation, target damage and Mises stress distribution, the advantages and disadvantages of three algorithms are obtained. The results show that: Lagrange algorithm has the highest calculation efficiency and accuracy, but it has some problems such as element distortion, no impact sputtering, and no back-pit area. Although SPH algorithm has the lowest calculation efficiency, the calculated target damage is basically consistent with experiment. SPH-Lagrange coupling algorithm has both advantages, but it can produce stress hysteresis and unstable stress wave attenuation. Lagrange and SPH-Lagrange coupling algorithms are preferred in large-scale simulation. -
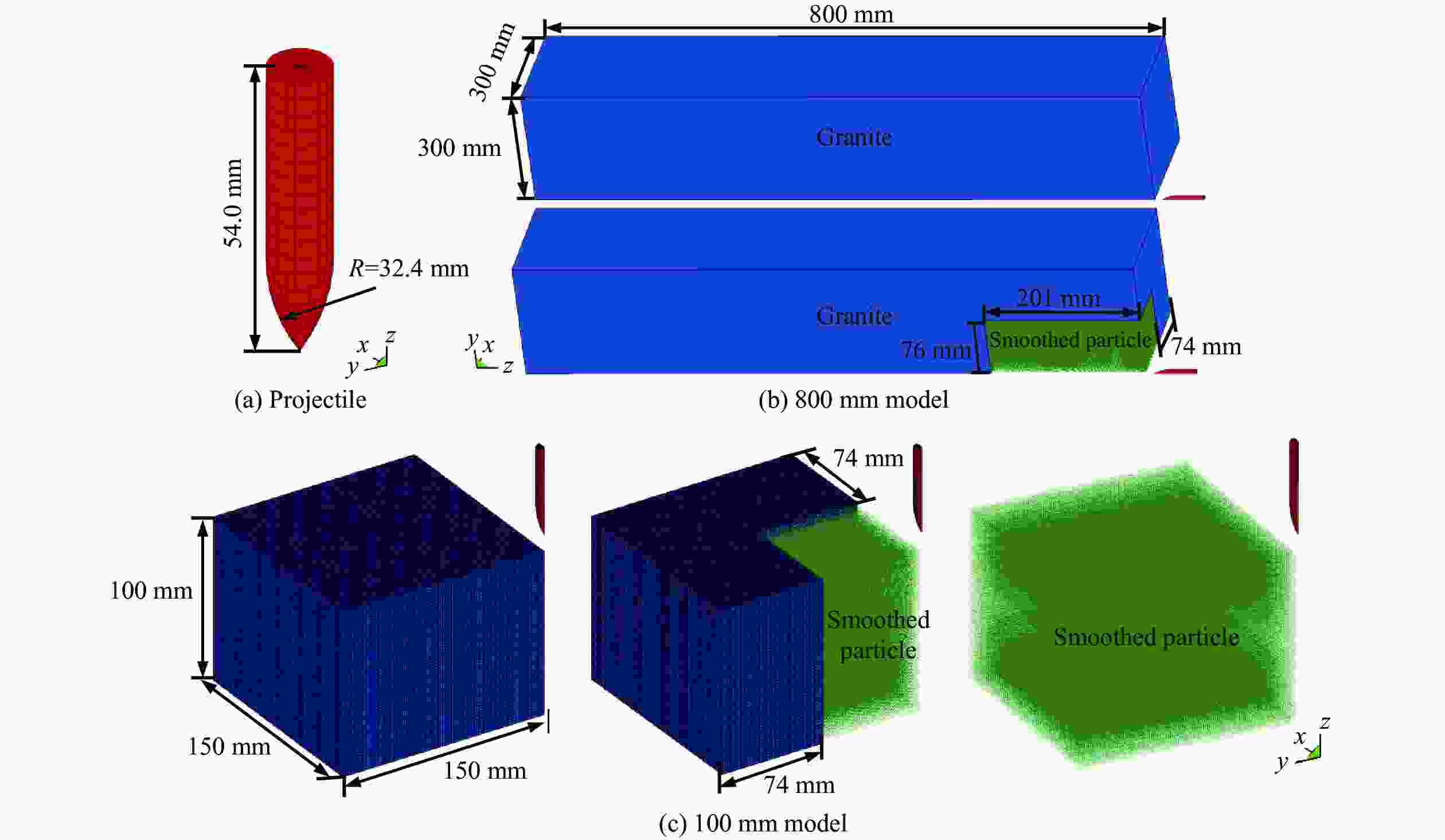
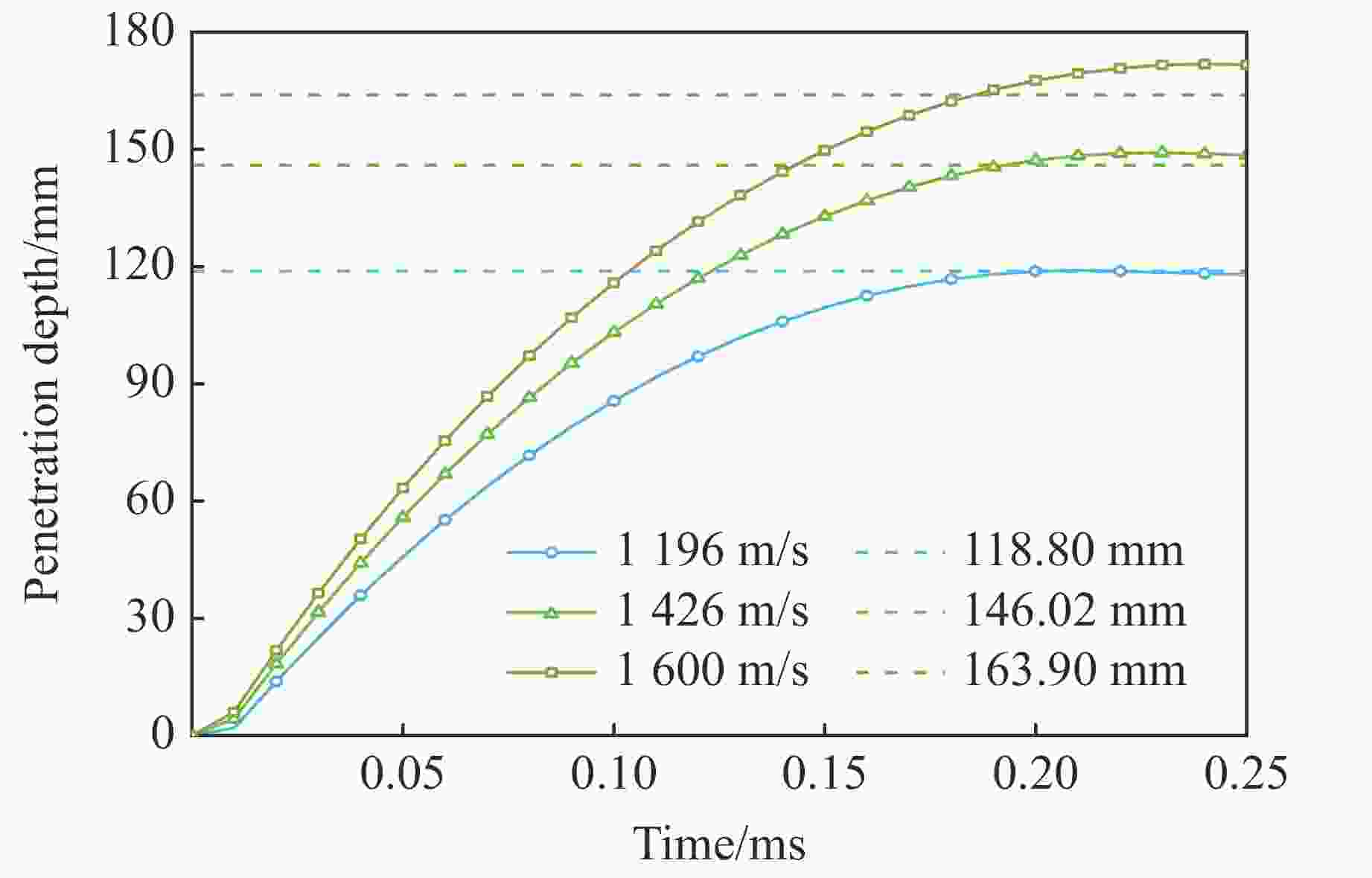
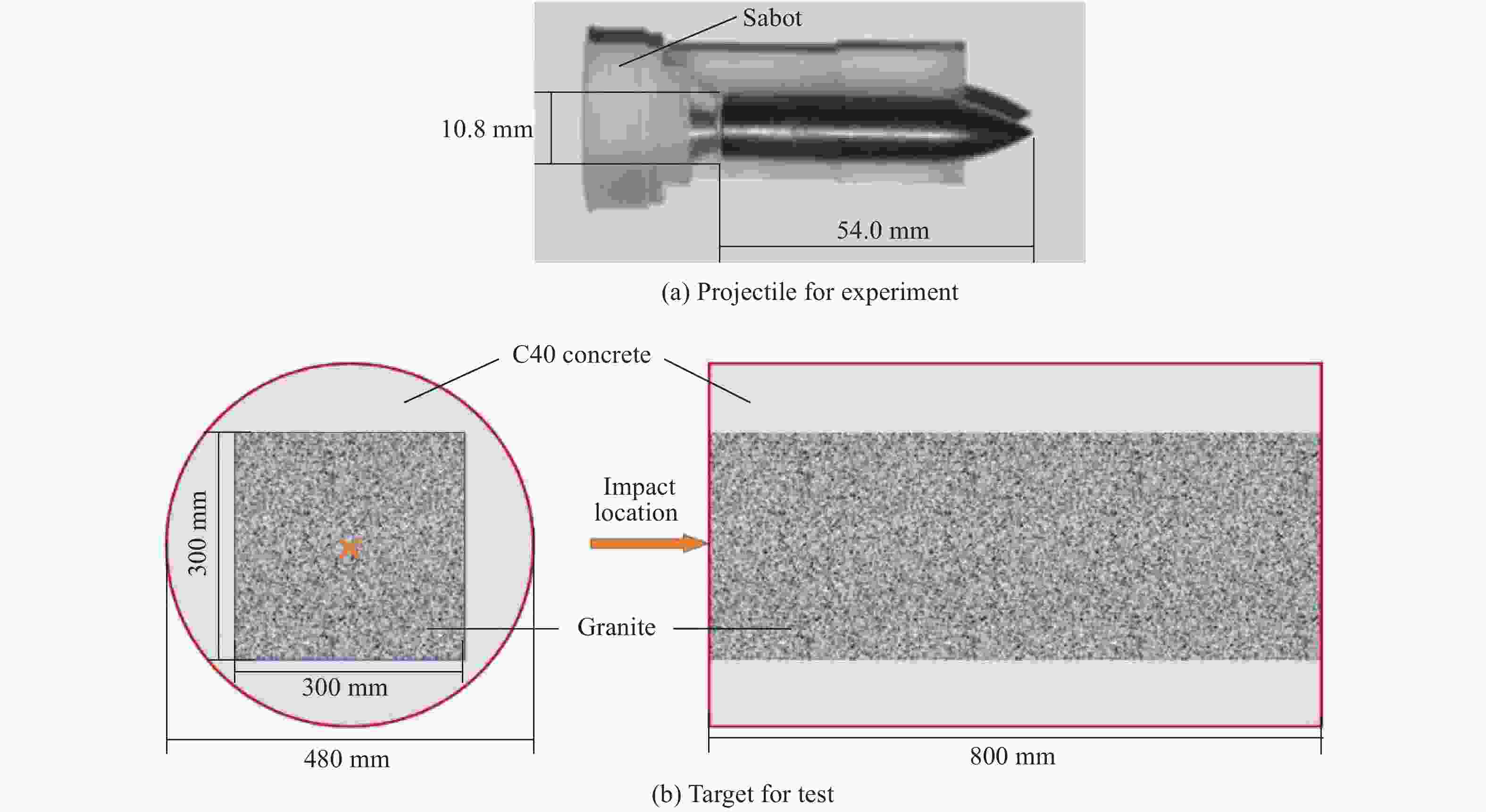
表 1 侵彻实验数据
Table 1. Test results of projectile penetration
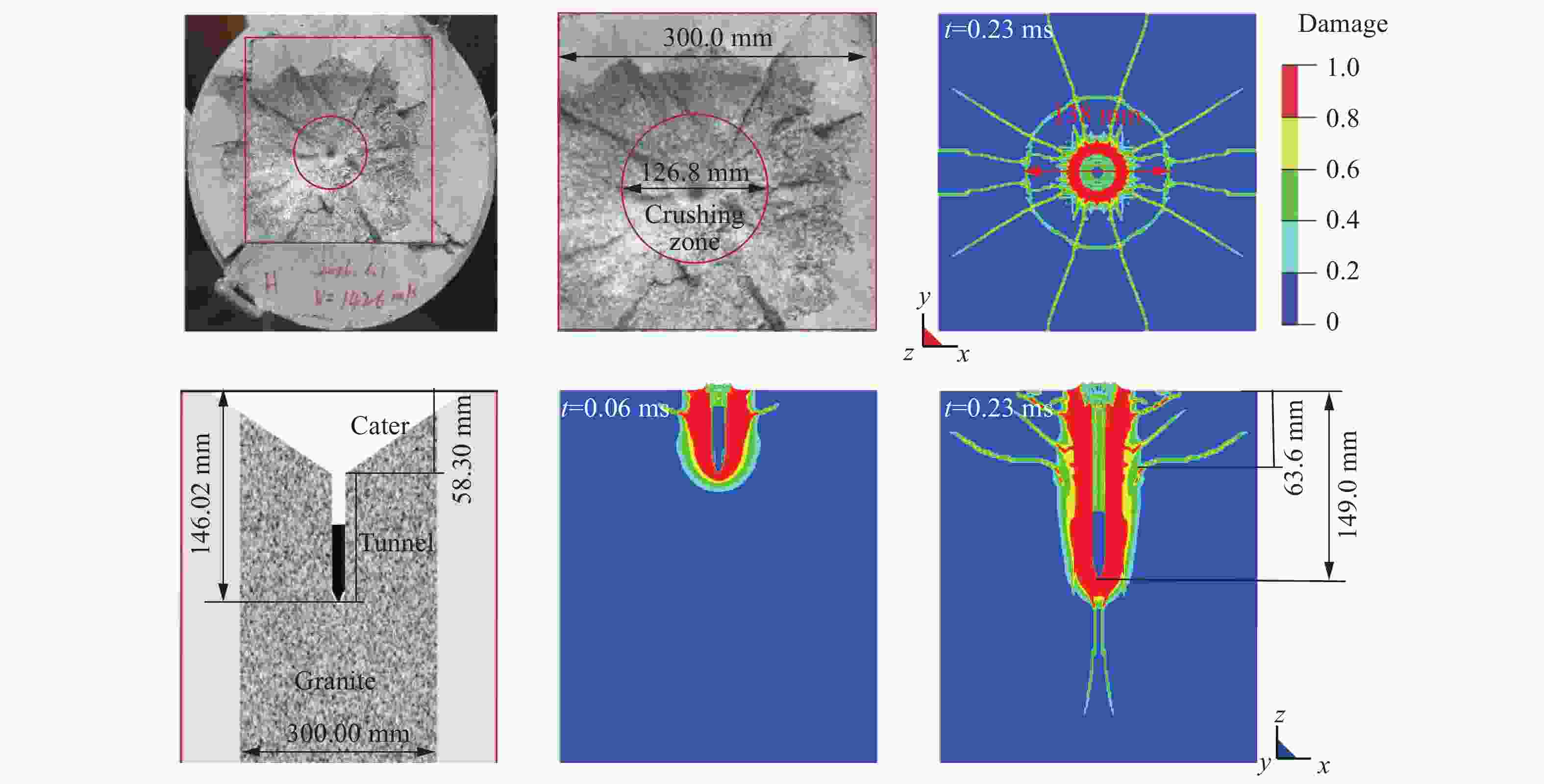
No. Launch velocity/(m·s−1) Depth of penetration/mm Mass of the residual projectile/g 1 1196 118.80 31.65 2 1426 146.02 31.42 3 1430 155.80 31.32 4 1600 163.90 30.83 表 2 子弹材料参数
Table 2. Properties of test projectile
ρp/(kg·m−3) Poisson’s ratio Et /GPa C Failure strain
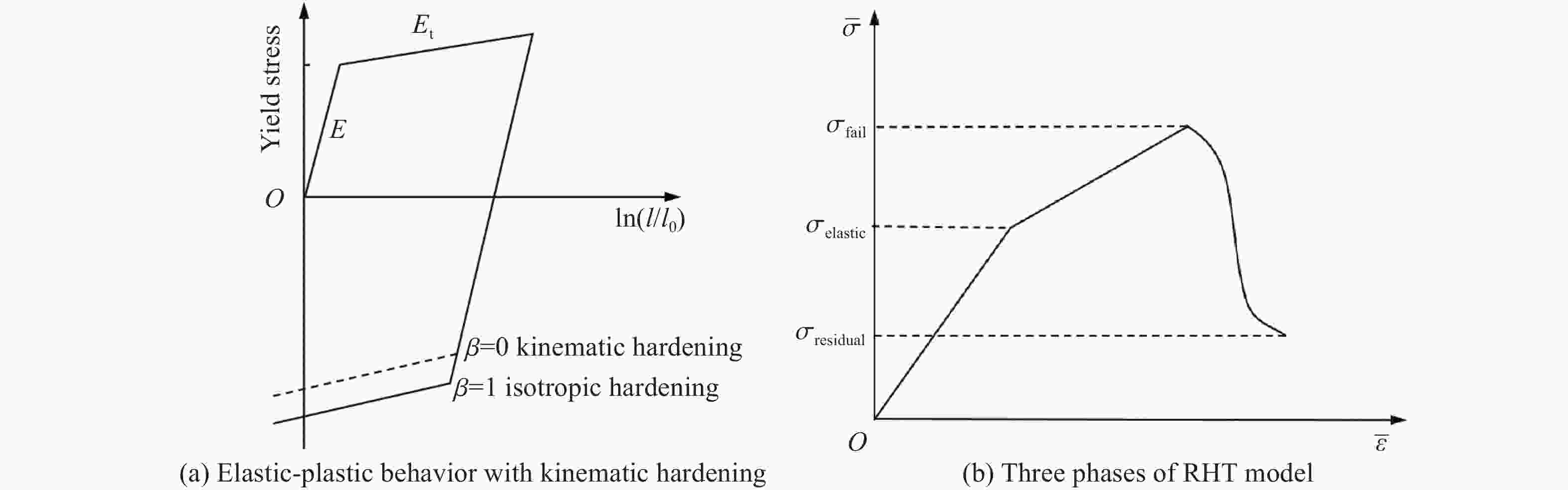
7850 0.3 6.1 0.219 1.5 E/GPa f/GPa β P VP 211 1.3 1 3.3 0 表 3 RHT模型参数
Table 3. Parameters of RHT material model
Mass density/(kg·m−3) Elastic shear modulus/GPa Eroding plastic strain Parameter for polynomial
EOS B02670.0 21.0 2.0 1.68 Parameter for polynomial
EOS B1Parameter for polynomial
EOS T1/GPaFailure surface
parameter AFailure surface
parameter N1.68 47.1 1.60 0.56 Compressive strength/MPa Relative shear strength Relative tensile strength Lode angle dependence
factor Q0150.0 0.38 0.10 0.64 Lode angle dependence
factor BParameter for polynomial
EOS T2/GPaReference compressive
strain rate/s–1Reference tensile
strain rate/s–10.05 0 3.0×10−5 3.0×10−6 Break compressive
strain rate/s–1Break tensile
strain rate/s–1Compressive strain rate
dependence exponentTensile strain rate
dependence exponent3.0×1025 3.0×1025 0.0085 0.012 Pressure influence on
plastic flow in tensionCompressive yield
surface parameterTensile yield surface
parameterShear modulus
reduction factor0.001 0.40 0.70 0.48 Damage parameter D1 Damage parameter D2 Minimum damaged
residual strainResidual surface
parameter AF0.042 1.0 0.012 1.60 Residual surface
parameter NFGrüneisen parameter γ Hugoniot polynomial
coefficient A1/GPaHugoniot polynomial
coefficient A2/GPa0.60 0 47.10 79.13 Hugoniot polynomial
coefficient A3/GPaCrush pressure/MPa Compaction pressure/GPa Porosity exponent 48.36 50.0 6.0 4.0 Initial porosity 1.01 表 4 网格尺寸与侵彻深度
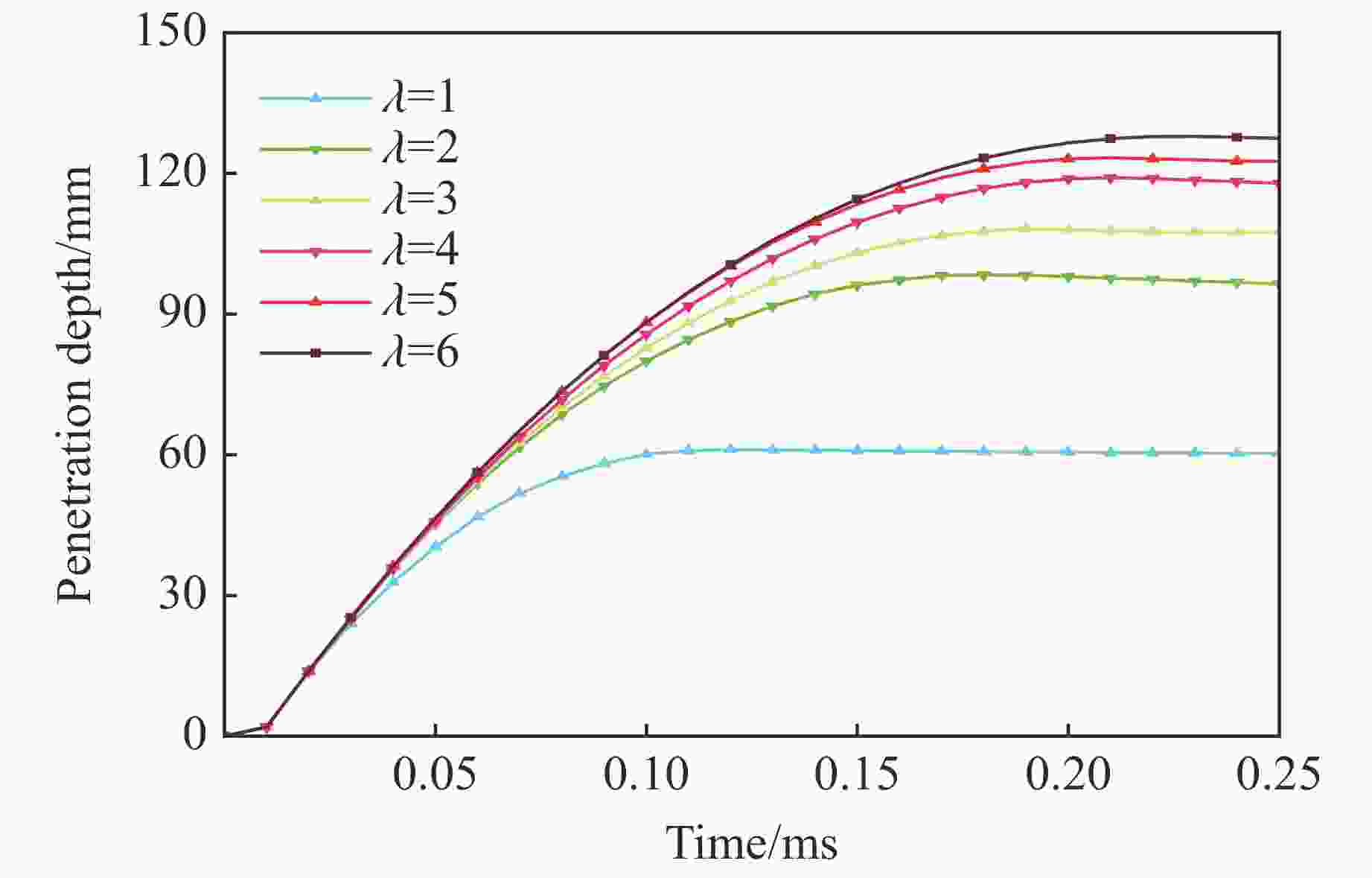
Table 4. Mesh size and penetration depth
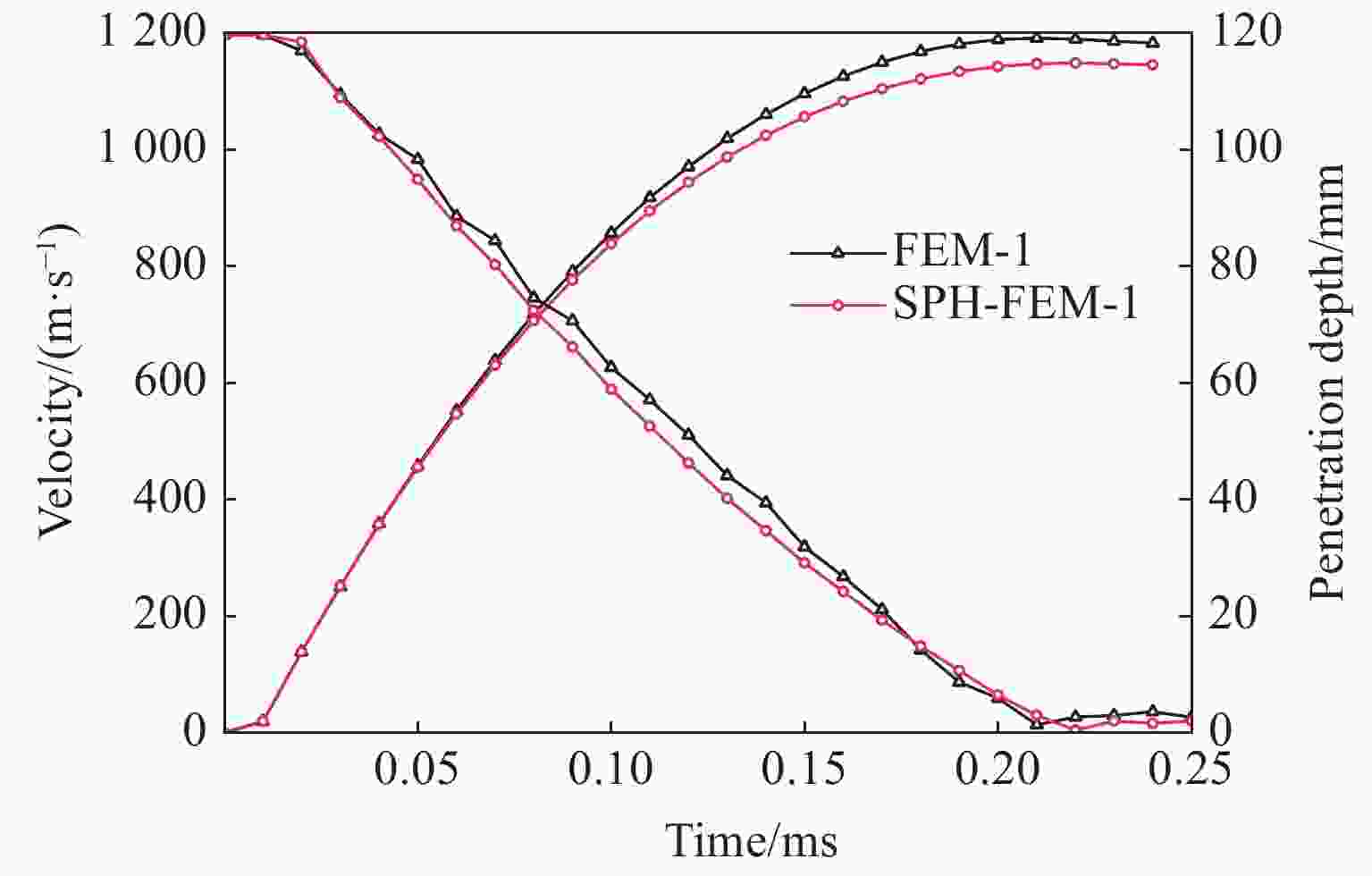
No. Mesh size Penetration depth/mm No. Mesh size Penetration depth/mm 1 1∶1 60.98 4 1∶4 119.07 2 1∶2 98.37 5 1∶5 123.33 3 1∶3 108.15 6 1∶6 126.50 -
[1] 沈俊, 徐翔云, 何翔, 等. 弹体高速侵彻岩石效应试验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(Suppl 2): 4207–4212.SHEN J, XU X Y, HE X, et al. Experimental study of effect of rock targets penetrated by high-velocity projectiles [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(Suppl 2): 4207–4212. [2] FREW D J, FORRESTAL M J, HANCHAK S J. Penetration experiments with limestone targets and ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2000, 67(4): 841–845. [3] 张德志, 张向荣, 林俊德, 等. 高强钢弹对花岗岩正侵彻的实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(9): 1612–1618.ZHANG D Z, ZHANG X R, LIN J D, et al. Penetration experiments for normal impact into granite targets with high-strength steel projectile [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(9): 1612–1618. [4] BERNARD R S. Empirical analysis of projectile penetration in rock: AD-A047989 [R]. Vicksburg, US: Soils and Pavements Laboratory, US Amry Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, 1977. [5] 李干, 宋春明, 邱艳宇, 等. 超高速弹对花岗岩侵彻深度逆减现象的理论与实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(1): 60–66.LI G, SONG C M, QIU Y Y, et al. Theoretical and experimental studies on the phenomenon of reduction in penetration depth of hyper-velocity projectiles into granite [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 60–66. [6] 王延斌, 张西前, 俞茂宏, 等. 长杆弹对岩石靶的侵彻分析 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(8): 1301–1307.WANG Y B, ZHANG X Q, YU M H, et al. Penetration analysis of long rod projectiles on rock targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(8): 1301–1307. [7] YOUNG C W. Penetration equations: SAND97-2426 [R]. Albuquerque, NM: Sandia National Laboratories, 1997: 4–12. [8] 王明洋, 谭可可, 吴华杰, 等. 岩石中侵彻深度计算新原理与方法 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(9): 1863–1869. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.09.018WANG M Y, TAN K K, WU H J, et al. New method of calculation of projectile penetration into rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(9): 1863–1869. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.09.018 [9] 王明洋, 邱艳宇, 李杰, 等. 超高速长杆弹对岩石侵彻、地冲击效应理论与实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3): 564–572.WANG M Y, QIU Y Y, LI J, et al. Theoretical and experimental study on rock penetration and ground impact effects of hypervelocity long rod projectiles [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 564–572. [10] WARREN T L, HANCHAK S J, POORMON K L. Penetration of limestone targets by ogive-nosed VAR 4340 steel projectiles at oblique angles: experiments and simulations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(10): 1307–1331. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2003.09.047 [11] THAM C Y. Numerical and empirical approach in predicting the penetration of a concrete target by an ogive-nosed projectile [J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2006, 42(14/15): 1258–1268. [12] 强洪夫, 张国星, 王广, 等. SPH方法在宽速域岩石侵彻问题中的应用 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33(5): 055105.QIANG H F, ZHANG G X, WANG G, et al. Application of SPH method for problem of rock penetration within the wide-ranged velocity [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33(5): 055105. [13] 王凤英, 刘迎彬, 刘天生, 等. 强冲击载荷下氧化铝陶瓷靶破坏过程的SPH数值模拟 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2012, 26(4): 415–420.WANG F Y, LIU Y B, LIU T S, et al. Numerical simulation of the destructive process of shock-loaded alumina ceramics using smoothed particle hydrodynamics [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2012, 26(4): 415–420. [14] 孔祥振, 方秦. 基于SPH方法对强动载下混凝土结构损伤破坏的数值模拟研究 [J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50(2): 25–33.KONG X Z, FANG Q. Numerical predictions of failures in concrete structures subjected to intense dynamic loadings using the smooth particle hydrodynamics method [J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2020, 50(2): 25–33. [15] 卞梁, 王肖钧, 章杰. SPH/FEM耦合算法在陶瓷复合靶抗侵彻数值模拟中的应用 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2010, 24(3): 161–167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2010.03.001BIAN L, WANG X J, ZHANG J. Numerical simulations of anti-penetration of confined ceramic targets by SPH/FEM coupling method [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2010, 24(3): 161–167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2010.03.001 [16] 傅学金, 强洪夫, 杨月诚. 固体介质中SPH方法的拉伸不稳定性问题研究进展 [J]. 力学进展, 2007, 37(3): 375–388.FU X J, QIANG H F, YANG Y C. Advances in the tensile instability of smoothed particle hydrodynamics applied to solid dynamics [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2007, 37(3): 375–388. [17] 尹冠生, 高艳, 赵庭. 基于SPH算法的刚性弹丸侵彻的数值模拟 [J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(3): 74–79.YIN G S, GAO Y, ZHAO T. Numerical simulation for penetration of rigid projectile based on SPH method [J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 34(3): 74–79. [18] LI J, WANG M Y, CHENG Y H, et al. Analytical model of hypervelocity penetration into rock [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 384–394. [19] LS-DYNA. Keyword user’s manual. Version 971 [M]. Livermore, CA: Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), 2006: 1071–1078. [20] CHEN X G, LU F Y, ZHANG D. Penetration trajectory of concrete targets by ogived steel projectiles-experiments and simulations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 120: 202–213. [21] JOHNSON G R, HOLMQUIST T J. An improved computational constitutive model for brittle materials [C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 1993. [22] 姜华, 王君杰. 弹体垂直侵彻钢筋混凝土数值模拟 [J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(4): 557–563.JIANG H, WANG J J. Numerical simulation of projectile perforation reinforced concrete perpendicularly [J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2010, 38(4): 557–563. [23] 李洪超. 岩石RHT模型理论及主要参数确定方法研究 [D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2016: 6–77.LI H C. Study on theory and main parameters determination of rock RHT model [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016: 6–77. [24] LIU K W, HAO H, LI X B. Numerical analysis of the stability of abandoned cavities in bench blasting [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2017, 92: 30–39. -






 下载:
下载: