Effects of Truncated Ovate Nose Diameter of the Penetration Warhead on the Ballistic Deflection
-
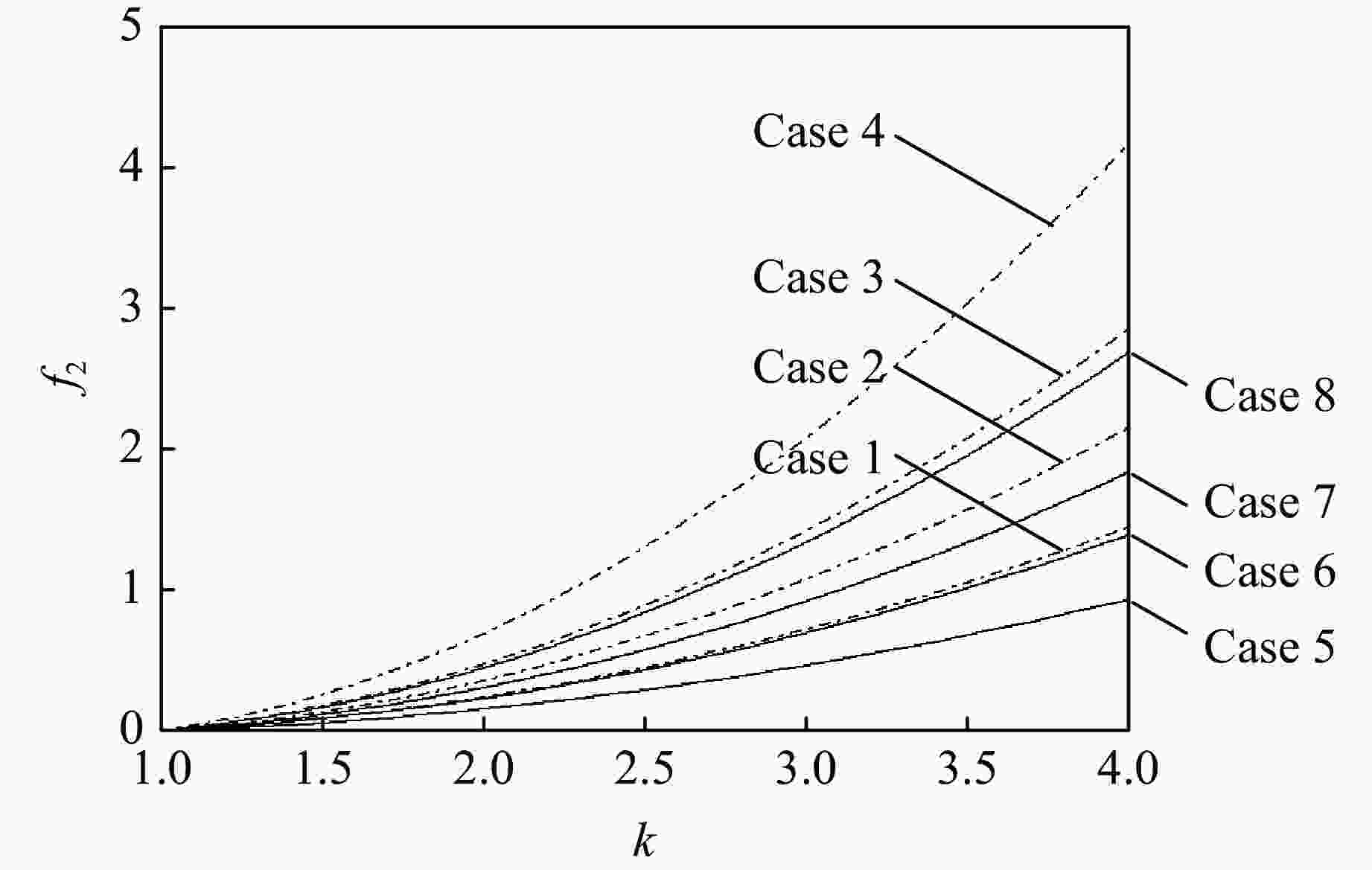
摘要: 针对截卵形头部弹体斜侵彻靶标时弹道发生初始偏转的问题,建立了分析截卵平台直径对初始弹道偏转影响的理论和数值仿真计算模型,计算了相同侵彻条件下不同截卵平台直径时,头部侵彻产生的偏转函数和偏转角速度。结果表明:截卵平台头部侵彻产生的偏转力矩会减小弹轴与靶标法线之间的夹角,且随着截卵平台直径的增大,偏转力矩增大,偏转角速度增大,当截卵平台直径增大到1.5倍时,偏转力矩增大到约1.2倍,当截卵平台直径增大到2.0倍时,偏转力矩增大到约2倍;相同截卵平台直径下,随着头部形状系数的减小,偏转力矩和偏转角速度增大。Abstract: In order to study the problem of preliminary ballistic deflection when a penetration warhead with truncated ovate nose penetrates target obliquely, the theoretical model and simulation model are set up to analyze the effects of truncated ovate nose diameter on the preliminary ballistic deflection of penetration. The defection function and deflection angular velocity of warhead penetrating target are calculated in the same penetration condition with different truncated ovate nose diameters. It is concluded that the angle between axis of warhead and normal of target decreases with the action of deflection moment caused by the warhead of truncated ovate nose penetrating target. Both the deflection moment and the deflection angular velocity increase with the increase of truncated ovate nose diameter. When the truncated ovate nose diameter increases to 1.5 times, the deflection moment will increase to about 1.2 times. When the truncated ovate nose diameter increases to 2.0 times, the deflection moment will increase to about 2 times. Under the condition of the same truncated ovate nose diameter, the defection moment and the deflection angular velocity are increased with the shape coefficient of warhead.
-
Key words:
- penetration /
- ballistic /
- ballistic deflection /
- deflection moment
-
表 1 计算工况
Table 1. Conditions of calculation
Case No. $\theta $/(°) $\varphi $/(°) Case No. $\theta $/(°) $\varphi $/(°) 1 25 10 5 35 10 2 25 15 6 35 15 3 25 20 7 35 20 4 25 30 8 35 30 $\;\rho $/(g·cm−3) E/GPa $\;\mu$ $\sigma $/MPa Et/MPa $\;\beta$ fs 7.85 210 0.2 1900 0 1 0.8 $\rho $/(g·cm−3) G/GPa A B C N fc/MPa 2.44 11.147 0.79 1.6 0.007 0.61 40 T/MPa ${\dot \varepsilon }$0/s−1 ${\sigma {_{ {\rm{fmin} } }} }$ Sfmax pc/MPa ${\;\mu {_{\rm c}} }$ pL/MPa 3.28 1 0.01 7 9.34 0.008 800 ${\mu {_{\rm{L} }} }$ D1 D2 K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa ${f }$s 0.116 0.04 1 85 −171 208 0.1 表 4 仿真算例参数
Table 4. Parameters of simulation examples
Case Lp/mm dp/mm mp/kg $\theta $/(°) d/mm S/mm Ix/(kg·m2) Iy/(kg·m2) Iz/(kg·m2) A 1534.4 300 400 25 40 828.5 5.63 80.52 80.52 A1 1534.4 300 400 35 40 828.1 5.64 80.60 80.60 B 1535.3 300 400 25 60 828.9 5.63 80.39 80.39 C 1532.0 300 400 25 80 828.9 5.64 79.85 79.85 -
[1] 刘坚成, 黄风雷, 皮爱国, 等. 异型头部弹体增强侵彻性能机理研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(4): 409–414. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)04-0409-06LIU J C, HUANG F L, PI A G, et al. On enhanced penetration performance of modified nose projectiles [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(4): 409–414. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)04-0409-06 [2] 彭永, 方秦, 吴昊, 等. 不同头部形状弹体侵彻混凝土靶体的终点弹道参数分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(Suppl 2): 128–134.PENG Y, FANG Q, WU H, et al. Theoretical analyses for terminal ballistic of the projectiles with different nose geometries penetrating into concrete targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(Suppl 2): 128–134. [3] 葛超, 董永香, 陆志超, 等. 弹丸头部对斜侵彻弹道偏转影响研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(2): 255–262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.02.010GE C, DONG Y X, LU Z C, et al. Ballistic deflection on oblique penetration of projectiles with different noses [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(2): 255–262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.02.010 [4] 贺登高, 贺虎成. 基于Teland模型的截卵形弹丸侵彻混凝土计算分析 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33(5): 78–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.05.021HE D G, HE H C. Calculation and analysis of rigid truncated-ogive-nosed projectile penetrating into concrete based on Teland force model [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33(5): 78–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.05.021 [5] 展婷变, 吕淑芳, 黄德雨. 截卵形弹体正侵彻加强筋结构靶的理论分析 [J]. 弹道学报, 2012, 24(1): 52–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2012.01.011ZHAN T B, LÜ S F, HUANG D Y. Theoretical analysis on normal penetration of truncated oval-nosed projectile into stiffened plate [J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2012, 24(1): 52–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2012.01.011 [6] 杨华伟, 王志华, 晋小超. 高速侵彻混凝土弹体在横向非对称作用下的动态响应 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2017, 31(1): 73–80. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.01.011YANG H W, WANG Z H, JIN X C. Dynamic response of high-speed projectiles penetrating into concrete target by asymmetric load [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(1): 73–80. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.01.011 [7] 郭子涛, 张伟, 郭钊, 等. 截卵形弹水平入水的速度衰减及空泡扩展特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(4): 727–733. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0727-07GUO Z T, ZHANG W, GUO Z, et al. Characteristics of velocity attenuation and cavity expansion induced by horizontal water-entry of truncated-ogive nosed projectiles [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(4): 727–733. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0727-07 [8] 吴昊, 方秦, 龚自明. 考虑刚性弹弹头形状的混凝土(岩石)靶体侵彻深度半理论分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(6): 573–580. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)06-0573-08WU H, FANG Q, GONG Z M. Semi-theoretical analyses for penetration depth of rigid projectiles with different nose geometries into concrete (rock) targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(6): 573–580. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)06-0573-08 [9] 赵军, 陈小伟, 金丰年, 等. 考虑头形磨损变化的动能弹侵彻深度研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2010, 42(2): 212–218. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2010-2-2009-009ZHAO J, CHEN X W, JIN F N, et al. Studying on the penetration depth of penetrator with including the effect of mass abrasion [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2010, 42(2): 212–218. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2010-2-2009-009 [10] 邓佳杰, 张先锋, 葛贤坤, 等. 基于局部相互作用理论的侵彻弹头部形状优化及仿真 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(4): 611–620. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0611-10DENG J J, ZHANG X F, GE X K, et al. Nose-shape optimization and simulation of projectiles penetrating into concrete target based on local interaction theory [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(4): 611–620. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0611-10 [11] 张丁山, 谷鸿平, 吕永柱, 等. 战斗部后端盖结构强度的数值仿真及应力波分析方法 [J]. 探测与控制学报, 2018, 40(5): 21–25.ZHANG D S, GU H P, LÜ Y Z, et al. Numerical simulation of structure strength calculation and stress waves analysis [J]. Journal of Detection and Control, 2018, 40(5): 21–25. -







 下载:
下载: