Effects of Sintering Pressure on the Vickers Hardness of TaC
-
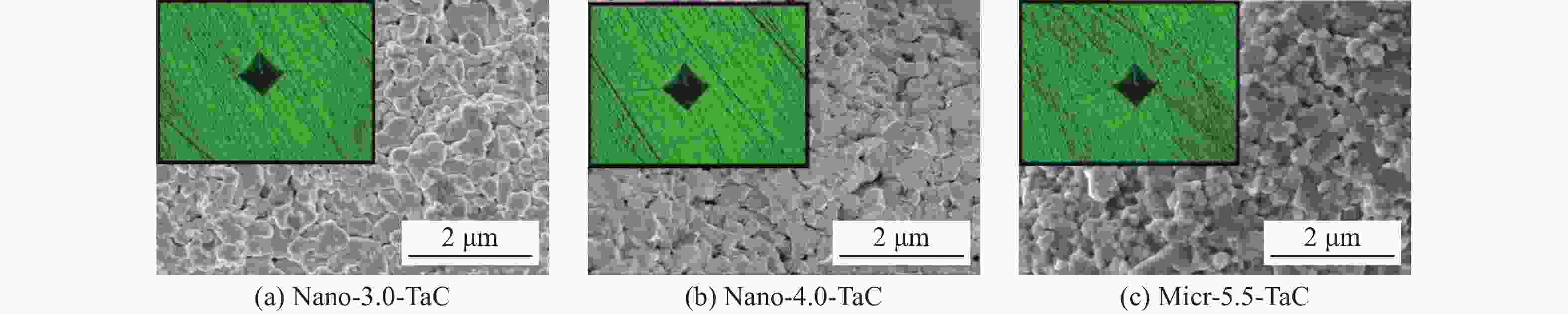
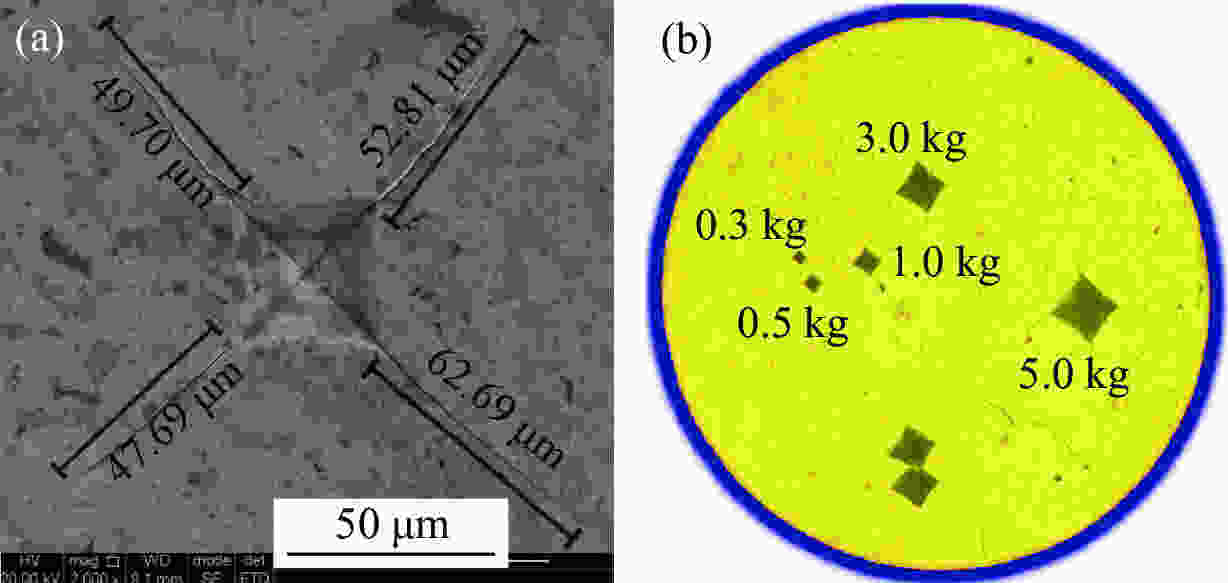
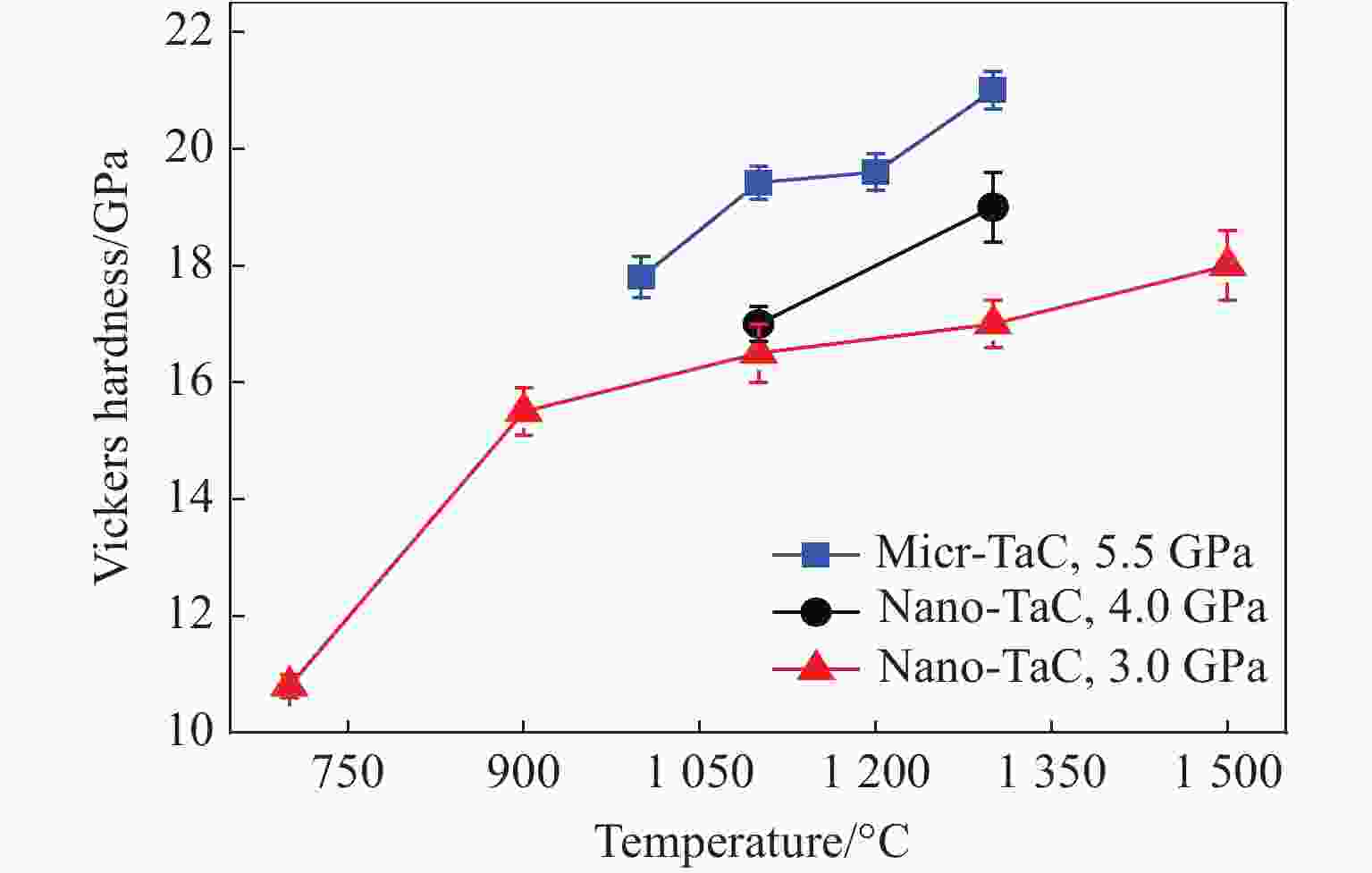
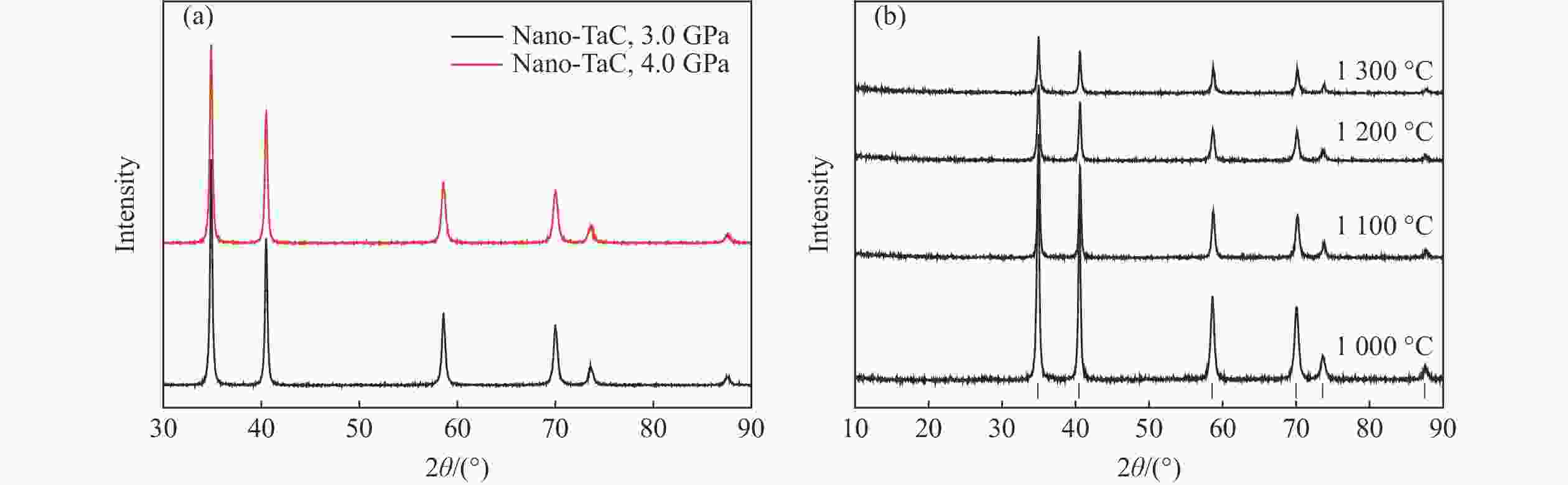
摘要: 为了探究烧结压力对不同晶粒尺寸碳化钽(TaC)力学性能的影响,通过高温高压技术对纳米、微米尺寸TaC粉末进行高温高压烧结,制备不同烧结条件下的块状TaC陶瓷。利用X射线衍射等表征方法对烧结样品的物相、元素分布、压痕形态进行表征,结果表明:TaC在烧结过程中物相稳定,且无杂质渗入。利用维氏硬度计对不同烧结压力(3.0、4.0和5.5 GPa)条件下的3种陶瓷样品进行维氏硬度测试,并进行微观结构分析,结果表明:随着烧结压力由3.0 GPa提升到5.5 GPa,微米尺寸TaC的维氏硬度(21.0 GPa)优于3.0、4.0 GPa下的纳米尺寸TaC维氏硬度(17.5、19.2 GPa)。此外,研究发现,测试维氏硬度时,3.0 kg应用载荷对测试TaC维氏硬度更加精确。研究结果对结构陶瓷烧结和超高温陶瓷硬度研究具有指导意义。Abstract: To study the effects of the sintering pressure on the mechanical properties of TaC with various grain sizes, nano- and micro-sized TaC powders are sintered at high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) to acquire bulk TaC ceramics under different sintering conditions. Different characterization approaches, such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), are used to observe phase, elements distribution, and indentation state. The observations reveal that the TaC phase is stable during the sintering process and there is no impurity infiltration. Three ceramic samples at the various sintering pressures (3.0, 4.0, 5.5 GPa) are measured by the Vickers hardness tester and their microstructures are also analyzed. The results show that as the sintering pressure increases from 3.0 GPa to 5.5 GPa, the Vickers hardness of Micro-5.5-TaC (21.0 GPa) is higher than that of Nano-3.0-TaC (17.5 GPa) and Nano-4.0-TaC (19.2 GPa). In addition, it is found that 3.0 kg is the most accurate load for measuring the Vickers hardness. This study has a guiding significance for sintering structural ceramics and exploring the Vickers hardness of ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs).
-
Key words:
- high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) sintering /
- TaC /
- Vickers hardness /
- grain size
-
表 1 实验与其他过渡金属碳化物的机械性能
Table 1. Mechanical parameters of TaC and other TMCs
-
[1] CHENG Q, TANG S, LIU C, et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Li4- xMgxTi5O12 as anode materials for lithium-ion battery [J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2017, 722: 229–234. [2] SUN W, KUANG X, LIANG H, et al. Mechanical properties of tantalum carbide from high-pressure/high-temperature synthesis and first-principles calculations [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020, 22(9): 5018–5023. doi: 10.1039/C9CP06819H [3] CASTLE E, CSANÁDI T, GRASSO S, et al. Processing and properties of high-entropy ultra-high temperature carbides [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 8609. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26827-1 [4] ZHAO E, MENG J, MA Y, et al. Phase stability and mechanical properties of tungsten borides from first principles calculations [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2010, 12(40): 13158–13165. doi: 10.1039/c004122j [5] ZHANG C, GUPTA A, SEAL S, et al. Solid solution synthesis of tantalum carbide-hafnium carbide by spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(5): 1853–1862. doi: 10.1111/jace.14778 [6] KIM H, YOON J, DOH J, et al. Rapid sintering process and mechanical properties of binderless ultra fine tungsten carbide [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 435: 717–724. [7] CHEN H H, BI Y, CHENG Y, et al. Elastic stability and electronic structure of tantalum boride investigated via first-principles density functional calculations [J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2012, 73(10): 1197–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2012.05.007 [8] GLECHNER T, MAYRHOFER P H, HOLEC D, et al. Tuning structure and mechanical properties of Ta-C coatings by N-alloying and vacancy population [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 17669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35870-x [9] ZHANG Z G, LIANG H, CHEN H, et al. Exploring physical properties of tantalum carbide at high pressure and temperature [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2020, 59(3): 1848–1852. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b03055 [10] LIN Z J, ZHANG J Z, LI B S, et al. Superhard diamond/tungsten carbide nanocomposites [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(12): 121914. doi: 10.1063/1.3570645 [11] CEDILLOS-BARRAZA O, GRASSO S, AL NASIRI N, et al. Sintering behaviour, solid solution formation and characterisation of TaC, HfC and TaC–HfC fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7): 1539–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.02.009 [12] ZHANG X, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Densification and mechanical properties of TaC-based ceramics [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2009, 501(1/2): 37–43. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.09.024 [13] CHEN C, HE D, KOU Z, et al. B6O-based composite to rival polycrystalline cubic boron nitride [J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(23): 4288–4291. doi: 10.1002/adma.200700836 [14] LIANG H, PENG F, CHEN C, et al. High-pressure sintering of bulk MoSi2: microstructural, physical properties and mechanical behavior [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 711: 389–396. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.11.016 [15] CHEN H, LIANG H, LIU L, et al. Hardness measurements for high-pressure prepared TaB and nano-TaC ceramics [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 3859–3862. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2017.10.006 [16] KIM B R, WOO K D, DOH J M, et al. Mechanical properties and rapid consolidation of binderless nanostructured tantalum carbide [J]. Ceramics International, 2009, 35(8): 3395–3400. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.06.012 [17] ZHANG X, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, et al. Hot pressing of tantalum carbide with and without sintering additives [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(2): 393–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01416.x [18] CEDILLOS-BARRAZA O, MANARA D, BOBORIDIS K, et al. Investigating the highest melting temperature materials: a laser melting study of the TaC-HfC system [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 [19] ANSTIS G R, CHANTIKUL P, LAWN B R, et al. A critical evaluation of indentation techniques for measuring fracture toughness: Ⅰ, direct crack measurements [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1981, 64(9): 533–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1981.tb10320.x [20] KIM B R, WOO K D, YOON J K, et al. Mechanical properties and rapid consolidation of binderless niobium carbide [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 481(1/2): 573–576. [21] SCITI D, GUICCIARDI S, NYGREN M. Densification and mechanical behavior of HfC and HfB2 fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(5): 1433–1440. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.02248.x [22] KRZANOWSKI J E, LEUCHTNER R E. Chemical, mechanical, and tribological properties of pulsed-laser-deposited titanium carbide and vanadium carbide [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1997, 80(5): 1277–1280. -






 下载:
下载: