Compression Stability of Multi-Layer Composite Close-Wound Solenoid Driven by Explosive Implosion
-
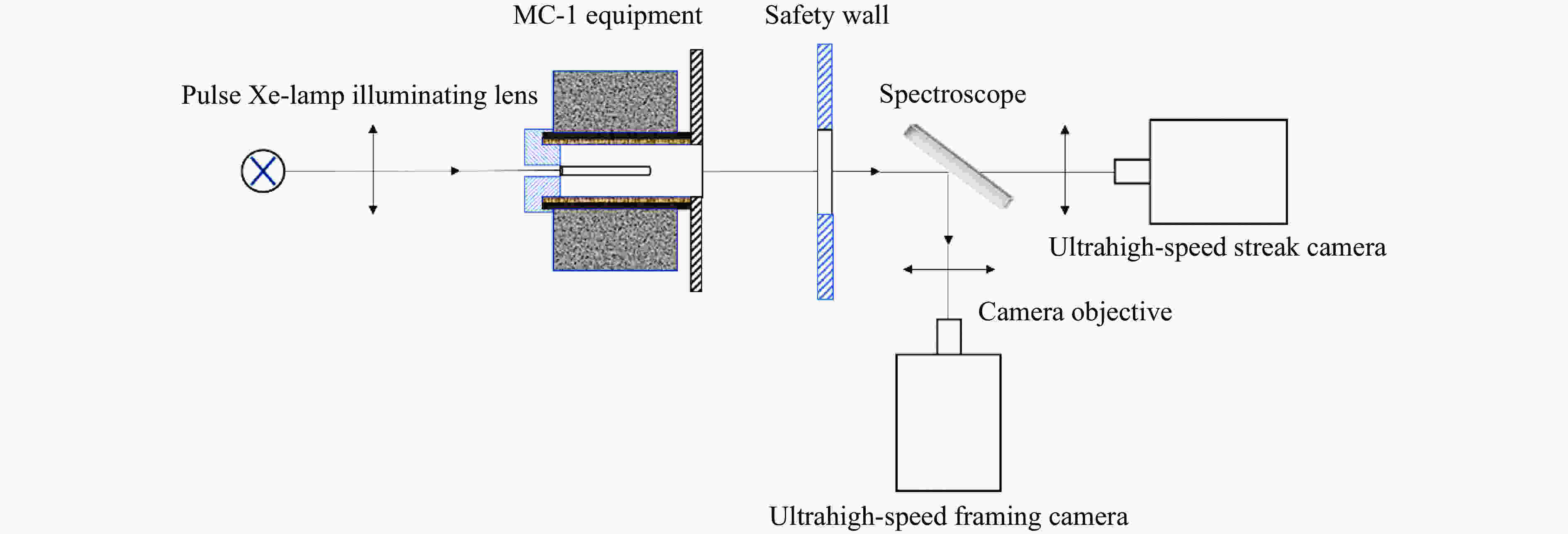
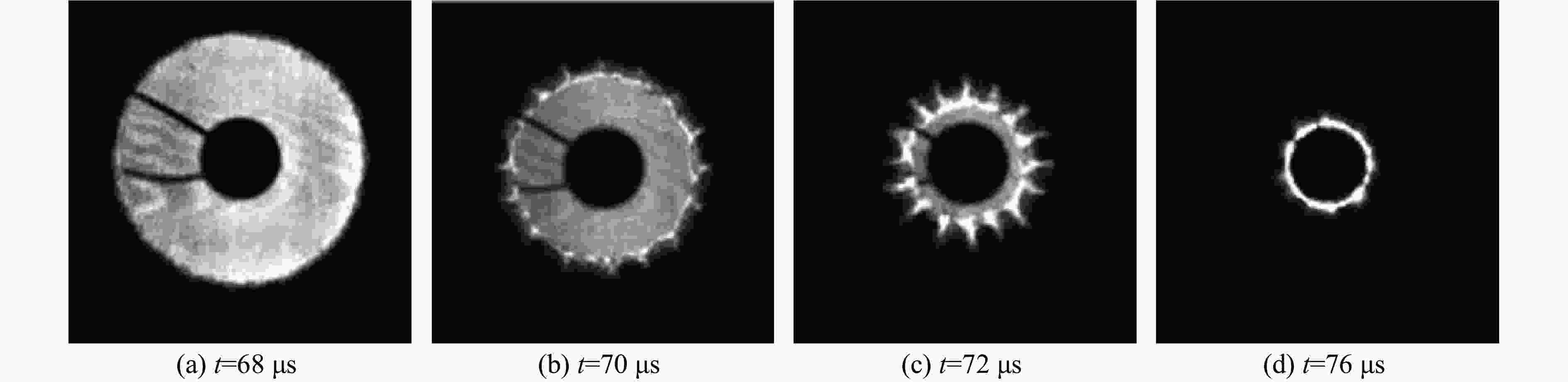
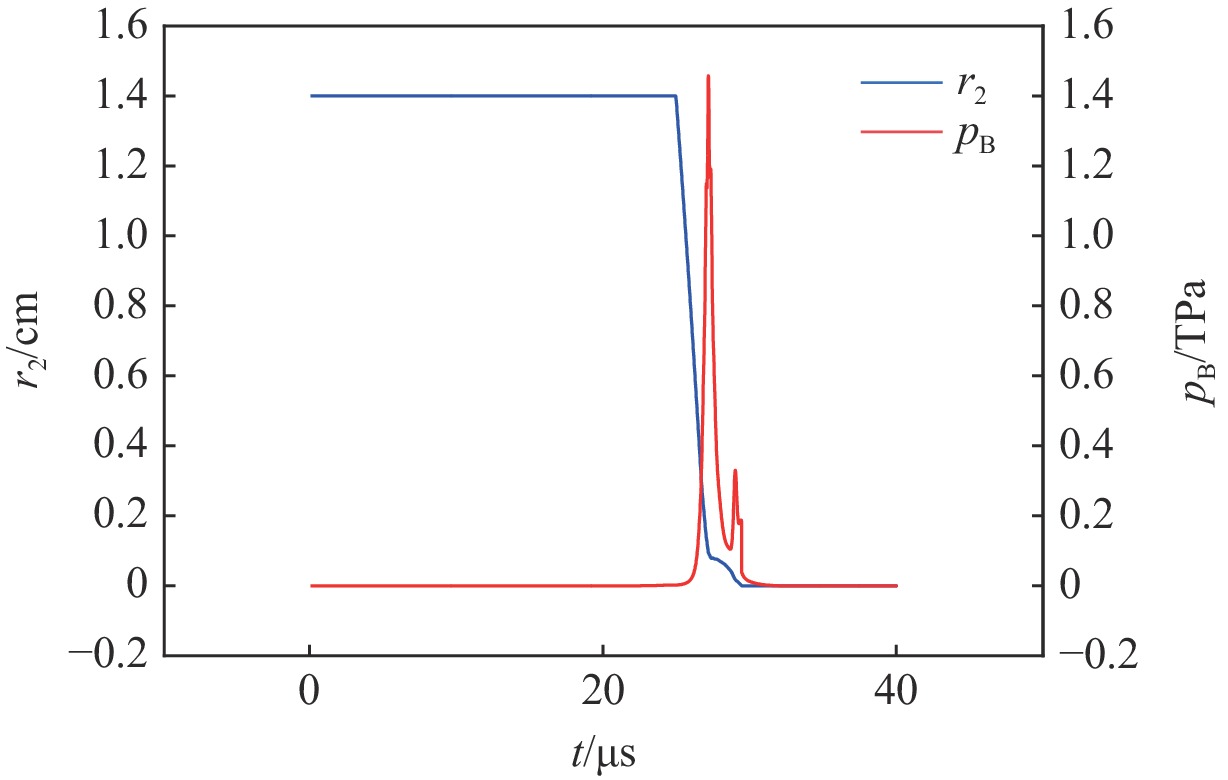
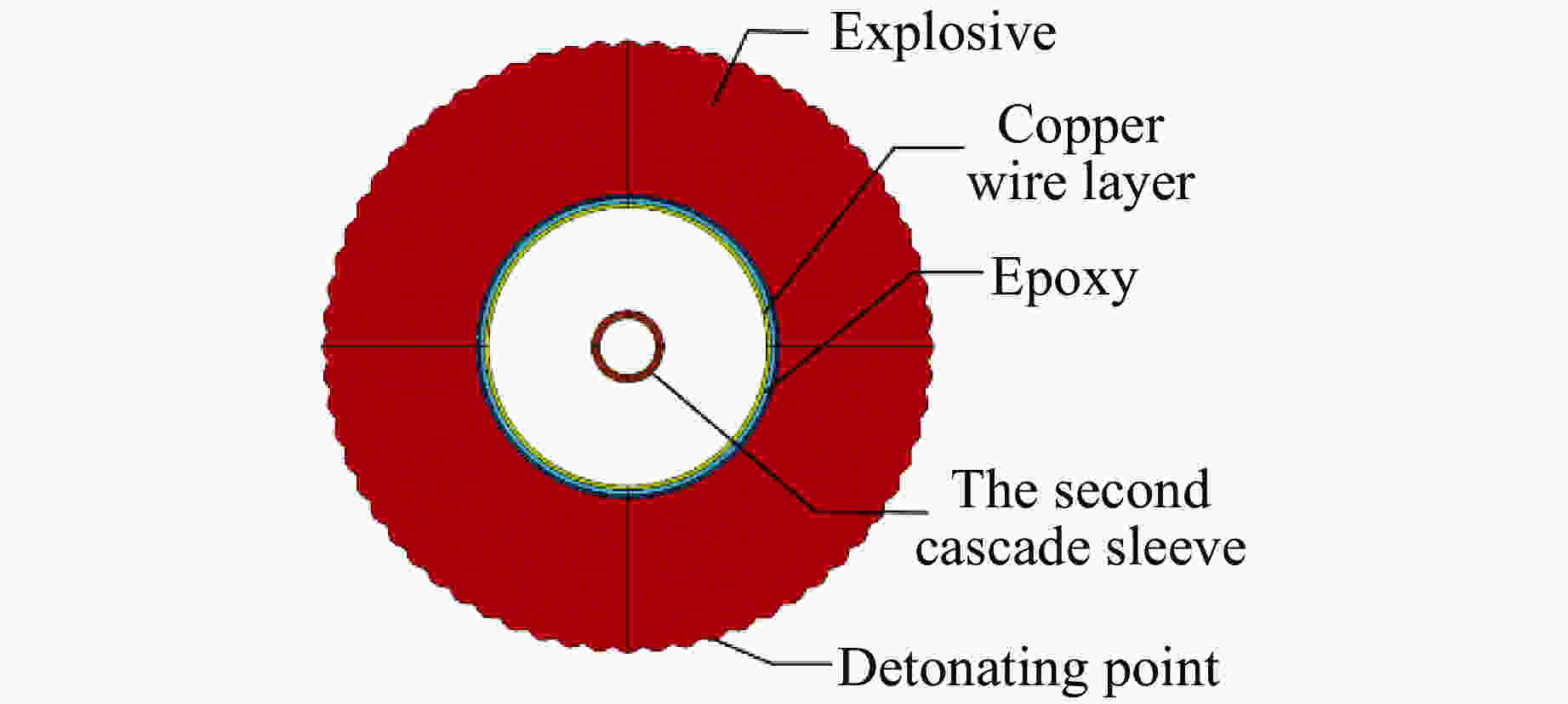
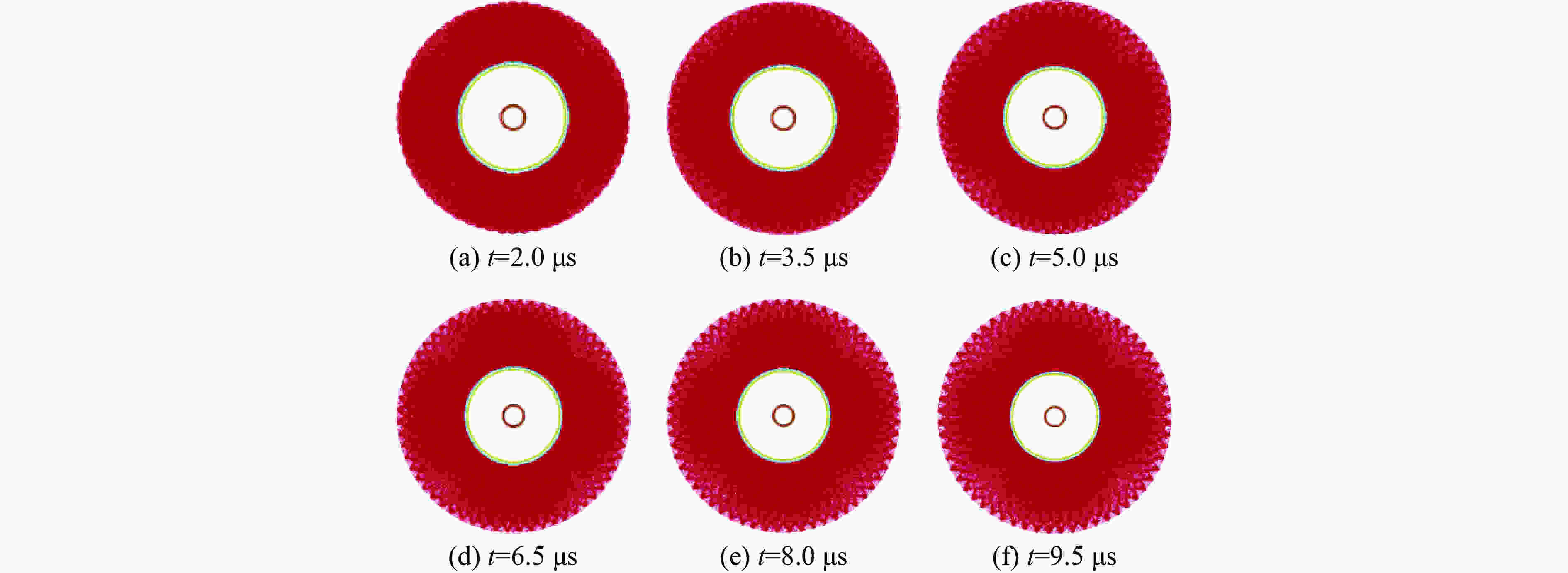
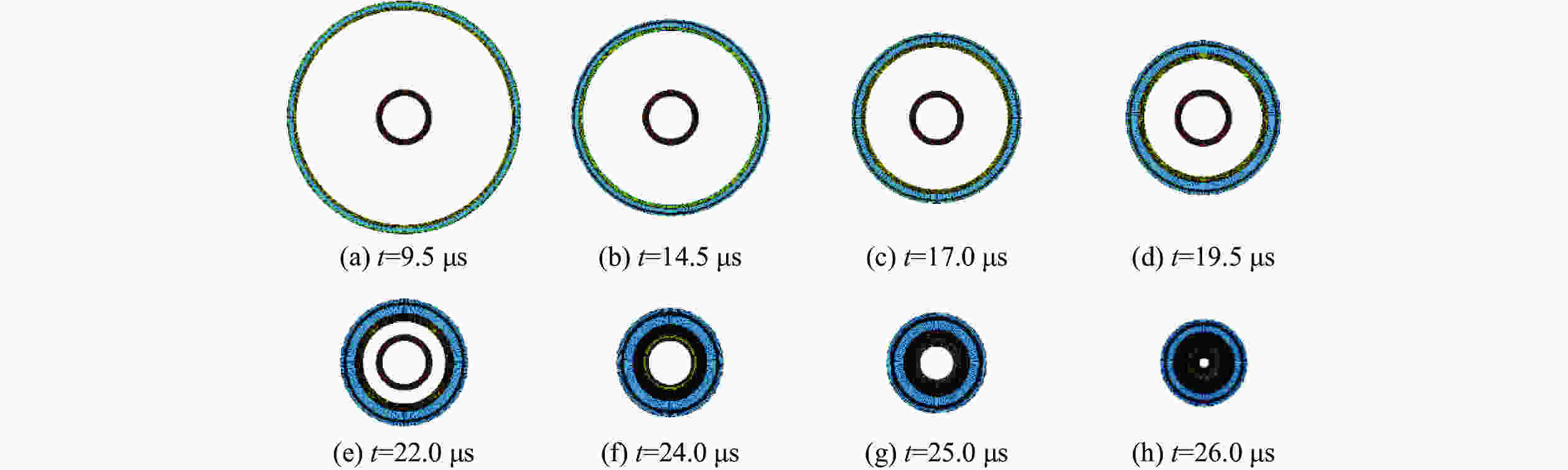
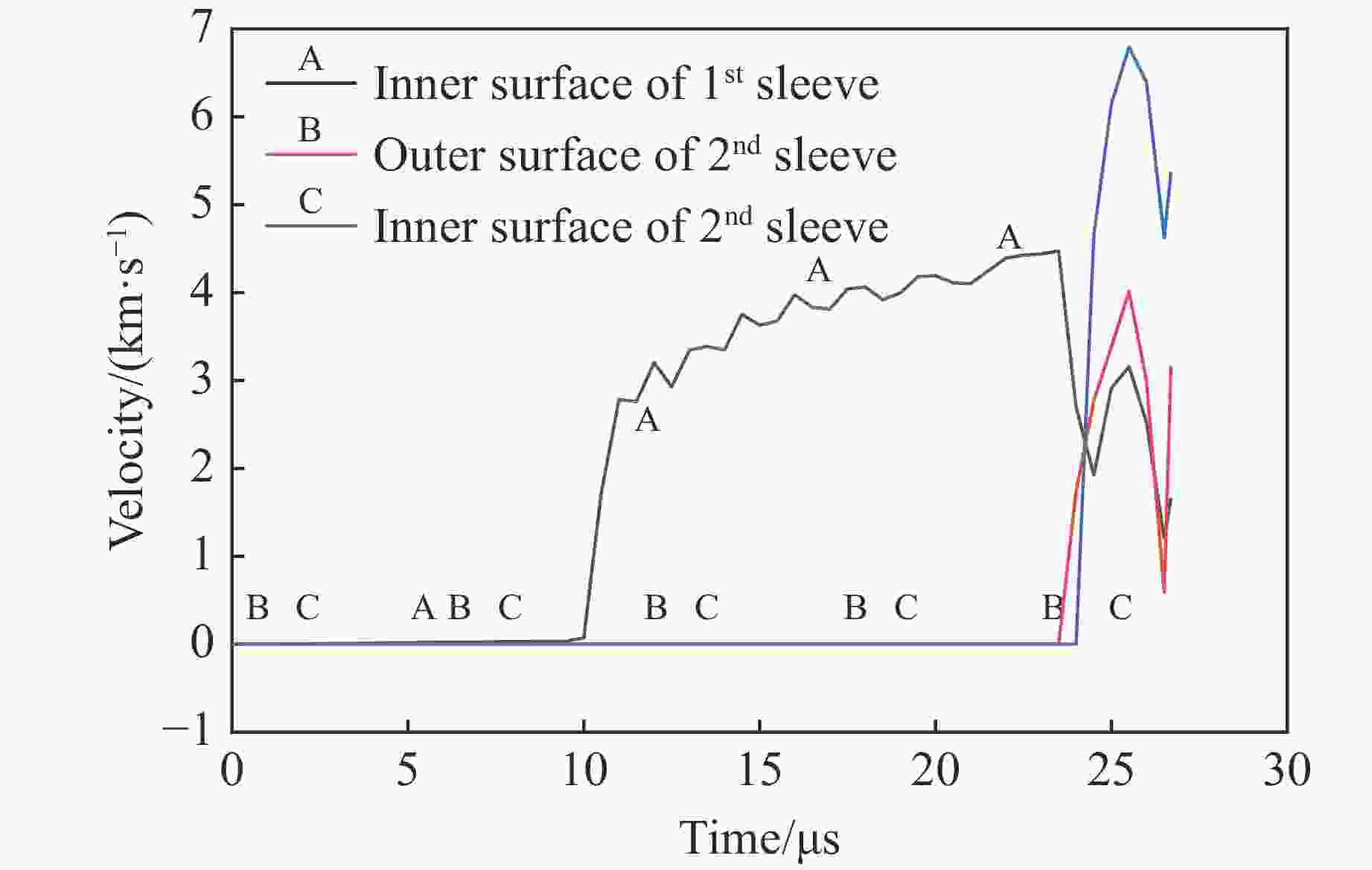
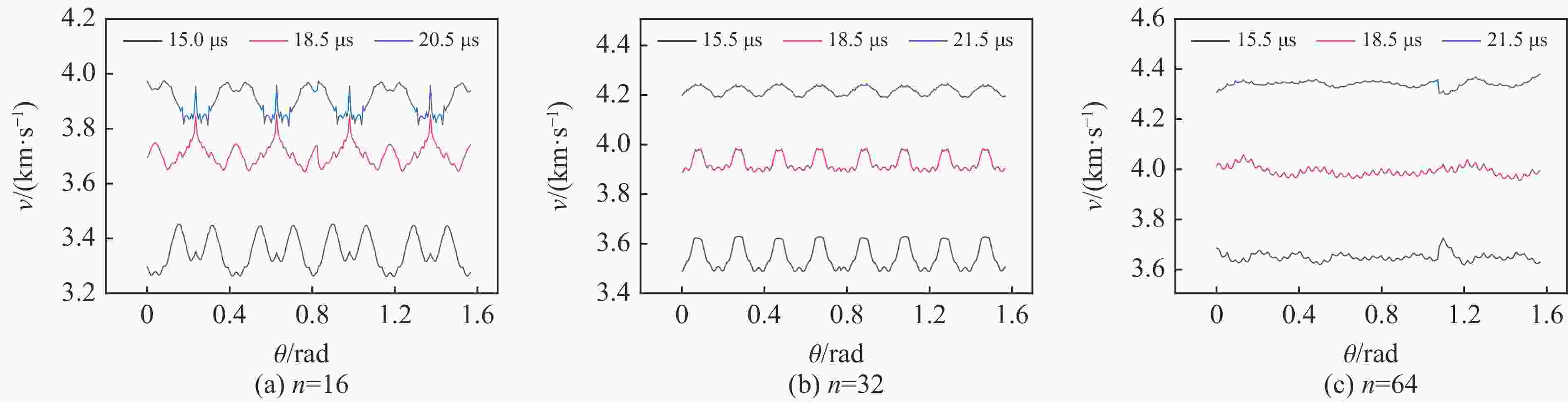
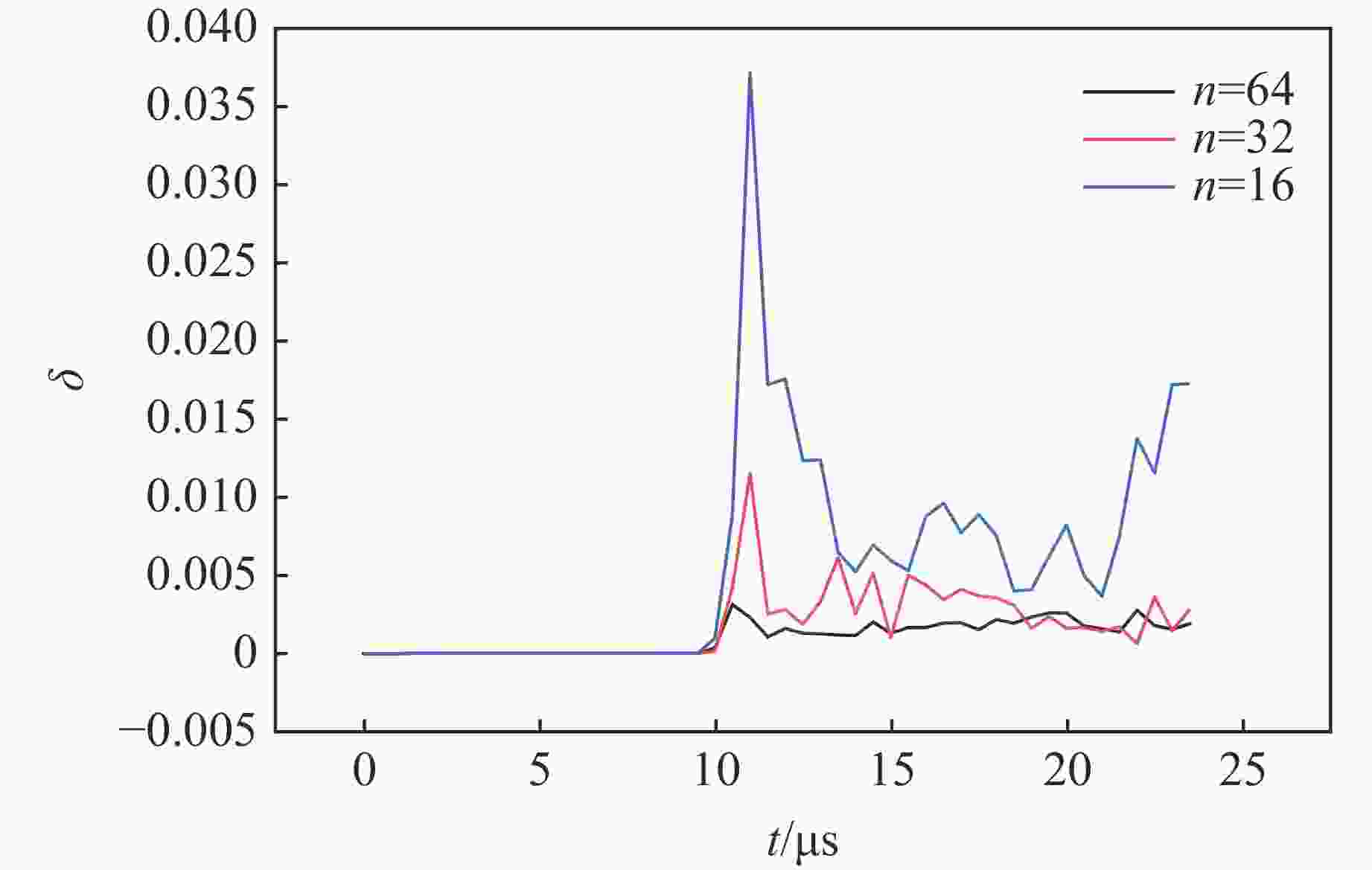
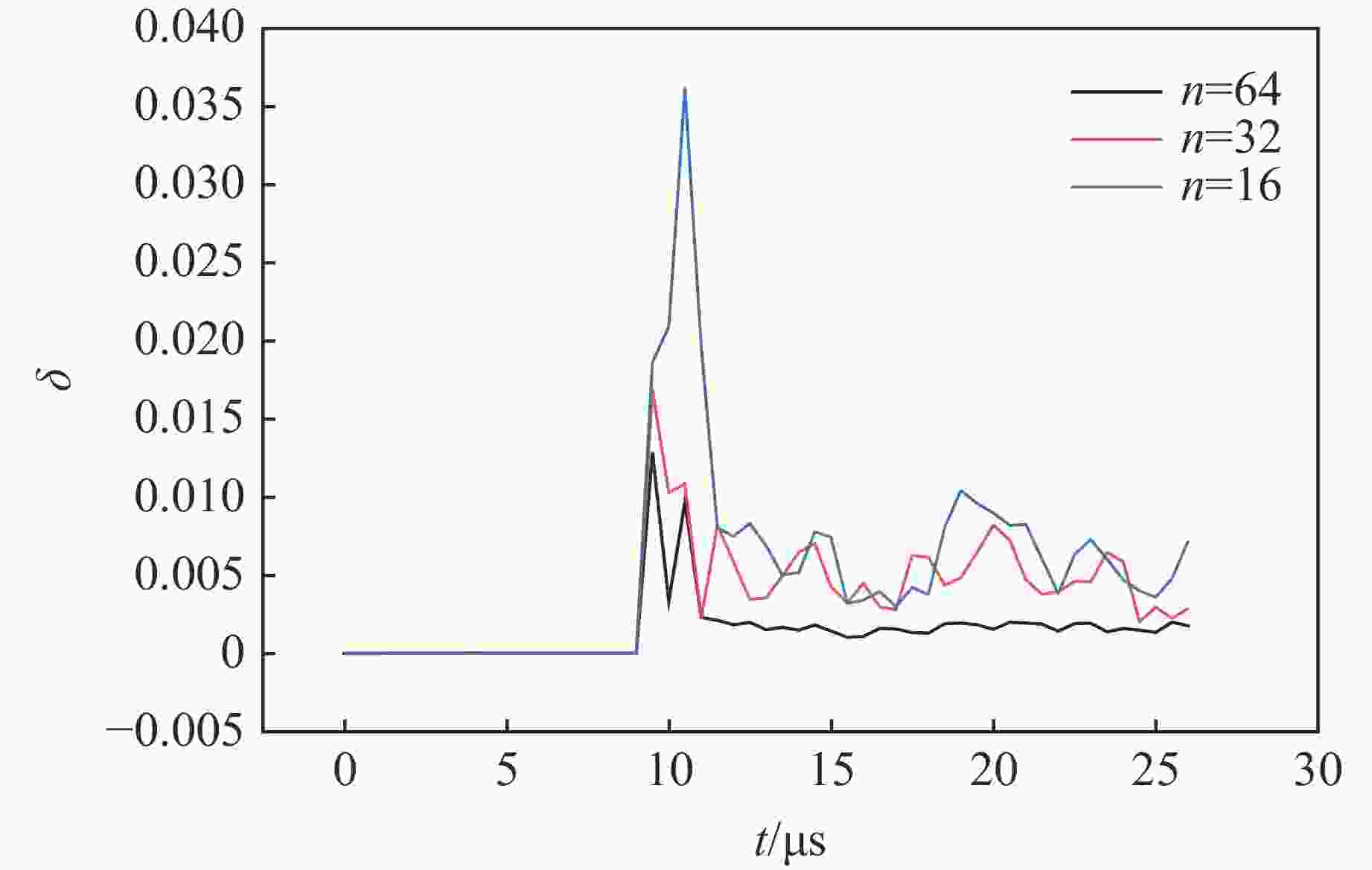
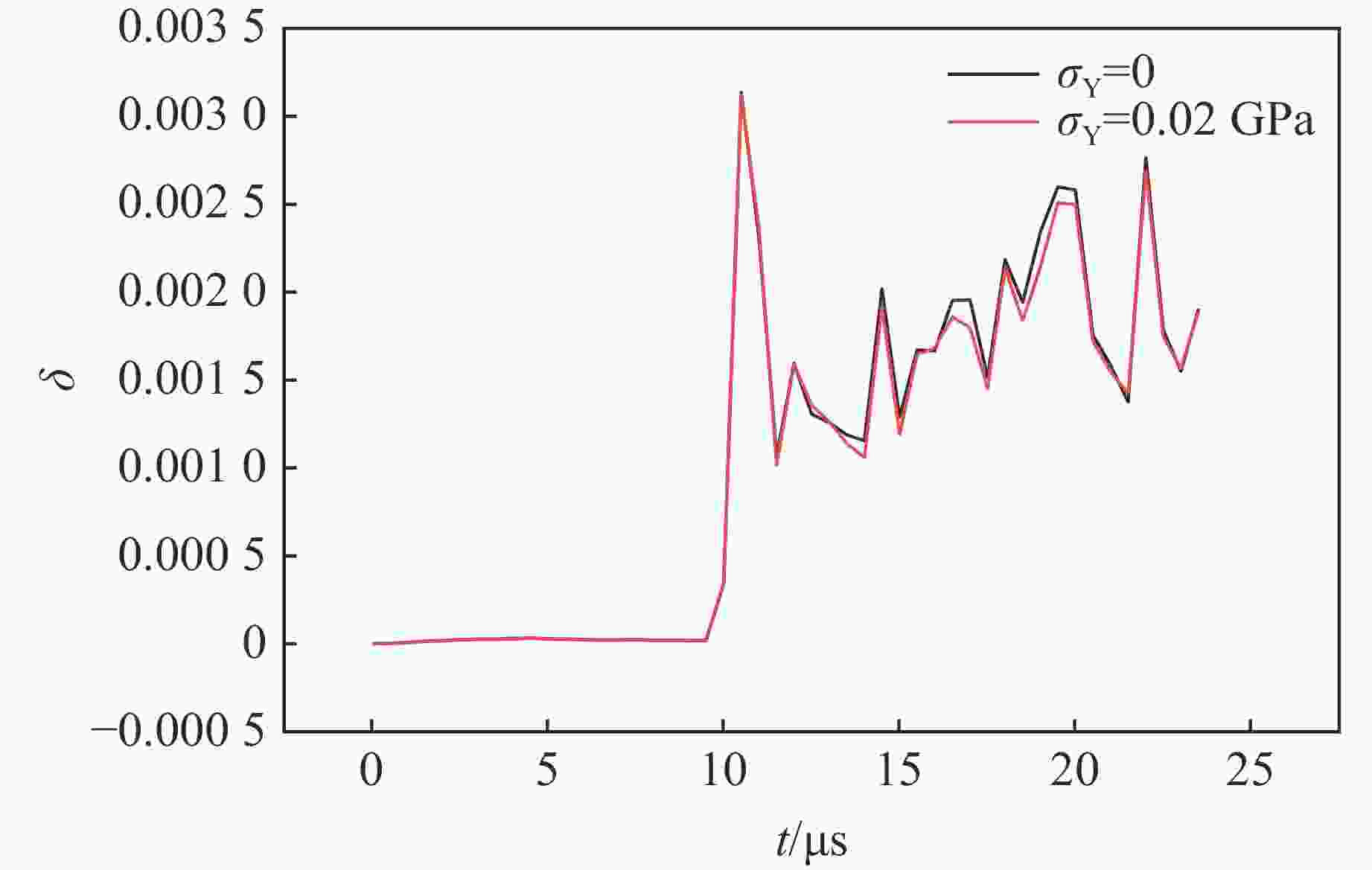
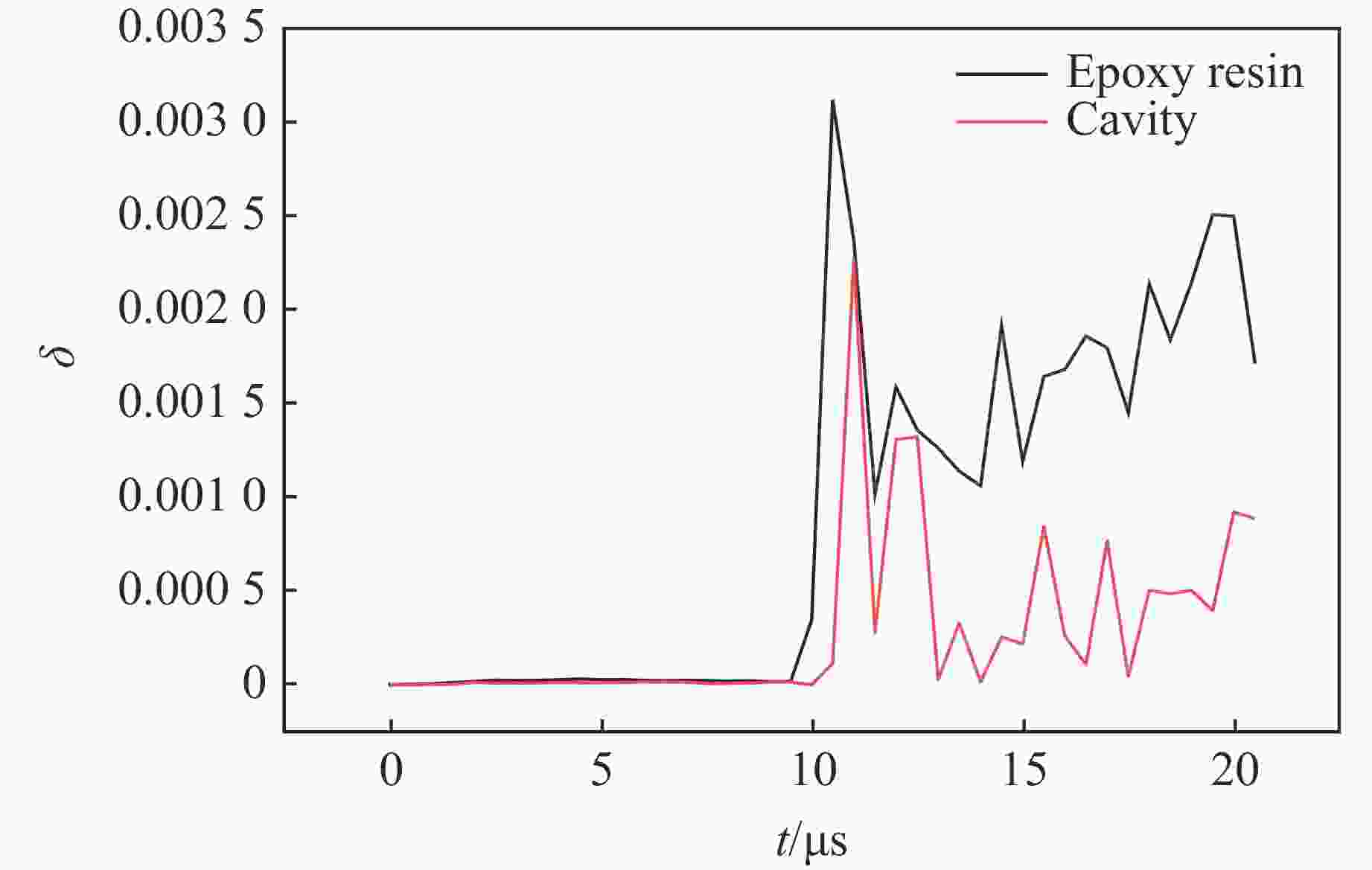
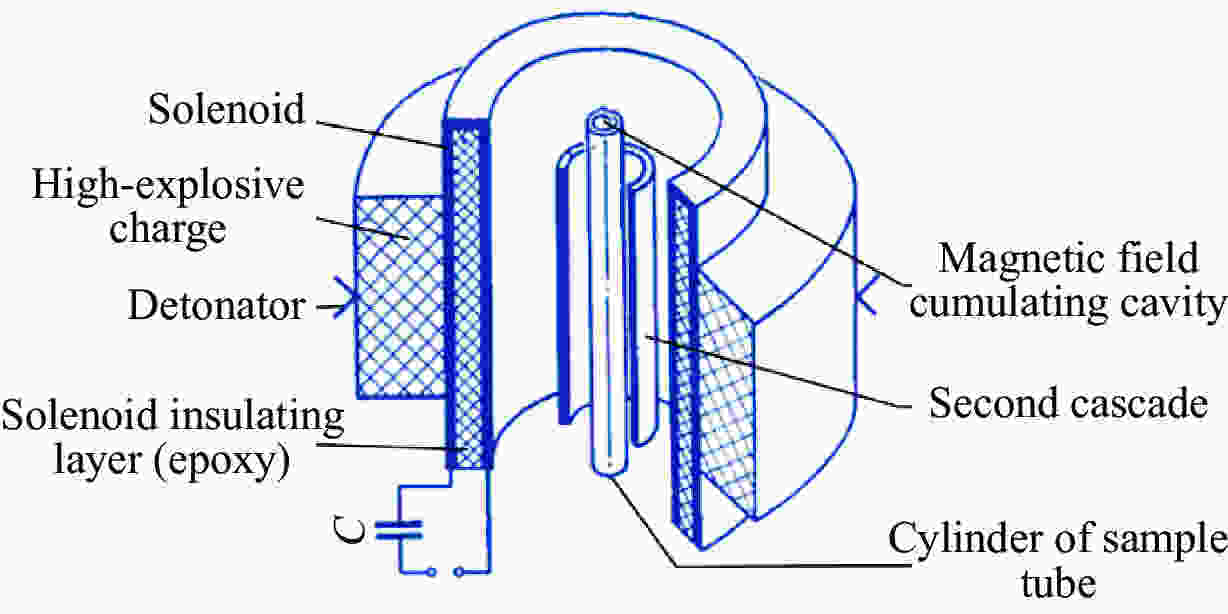
摘要: 多层密绕螺线管是炸药柱面内爆磁通量压缩多级MC-1装置的核心构件。设计了一套内爆磁通量压缩装置,初步开展了两级内爆压缩多层密绕螺线管实验,得到了较为清晰的高速摄影图像。密绕螺线管在炸药强爆轰驱动下的界面不稳定性发展是能否获取超高磁场和超高磁压力的关键因素。高速摄影实验结果显示,多层密绕螺线管在内爆过程中没有出现垮塌,套筒内界面仍保持对称性,外界面出现强爆轰导致的周期扰动。为此建立了考虑磁压力的二维有限元内爆数值计算模型,系统研究了密绕螺线管在炸药内爆驱动下的稳定性问题。计算结果表明,炸药网络板多点起爆方式对套筒冲击不稳定性的发展影响较大,网络起爆点数量的增加可以有效抑制套筒界面不稳定性的增长。相比于环氧缓冲层,在炸药与螺线管套筒之间添加1~2 mm的间隙可以更有效地衰减爆轰波引入的周期扰动。Abstract: The tightly wound solenoid is the core component of a cascade explosive cylindrical implosion magnetic flux compression device. We designed a solenoid cylinder with composite structure, and carried out two-cascade implosion magnetic flux compression experiment. It is known that the growth of interfacial instability of the solenoid cylinder will determine the amplification of the magnetic field and/or magnetic compressive stress. In the implosion compression event, the projection images of the solenoid by high-speed photography revealed that the inner surface kept in a circle without visible collapse, but cyclic disturbances were observed on the outer surface resulting from explosive detonation. A 2D finite element model was built to study the instability growth of the solenoid under the explosive implosion. The simulation results displayed that the multi-point network detonation of the explosive played an important role on the solenoid instability. The instability growth can be effectively inhibited by both increasing the number of detonation points and introducing a 1–2 mm thick cavity between the explosive cylinder and the solenoid.
-
表 1 Comp B炸药的模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of Comp B explosive
$\;\rho $/(g·cm−3) D/(km·s−1) A/GPa B/GPa R1 R2 $\omega$ E/MPa pCJ/GPa V 1.717 7.98 524.23 7.68 4.2 1.1 0.34 85 29.5 1 表 2 环氧材料模型参数
Table 2. Model parameters of epoxy material
$\;\rho $/(g·cm−3) G/GPa $\sigma$Y/GPa C/(km·s−1) S1 S2 S3 ${ {\gamma } }$0 V 1.186 2.32 0.15 0.257 1.624 0 0 0.85 1 表 3 漆包铜线排布层模型参数
Table 3. Model parameters of enameled copper wire arrangement layer
$\;\rho $/(g·cm−3) G/GPa $\sigma$Y/GPa C/(km·s−1) S1 S2 S3 ${ {\gamma } }$0 V 7.268 24 0.02 0.394 1.490 0 0 2.02 1 -
[1] ALTGILBERS L L, BROWM M D J, GRISHNAEV I, 等. 磁通量压缩发生器 [M]. 孙承纬, 周之奎译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008.ALTGILBERS L L, BROWM M D J, GRISHNAEV I, et al. Magnetocumulative generators [M]. Translated by SUN C W, ZHOU Z K. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2008. [2] PAVLOVSKII A I. Reproducible generation of multimegagauss magnetic fields [C]//TURCHI P J. Megagauss Physics and Technology. New York: Plenum Press, 1980: 627. [3] 谷卓伟, 罗浩, 张恒第, 等. 炸药柱面内爆磁通量压缩实验技术研究 [J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(17): 176–181.GU Z W, LUO H, ZHANG H D, et al. Experimental research on the technique of magnetic flux compression by explosive cylindrical implosion [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(17): 176–181. [4] BYKOV A I, DOLOTENKO M I. An MC-1 cascade magnetocumulative generator of multimegagauss magnetic fields: ideas and their realization [J]. Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2015, 58(4): 531–538. doi: 10.1134/S0020441215040284 [5] 张恒第. MC-1型爆磁压缩发生器一维内爆: 磁流体力学模拟[D]. 绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2012.ZHANG H D. 1D implosion and MHD simulation of MC-1 flux compression generator [D]. Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2012. -






 下载:
下载: