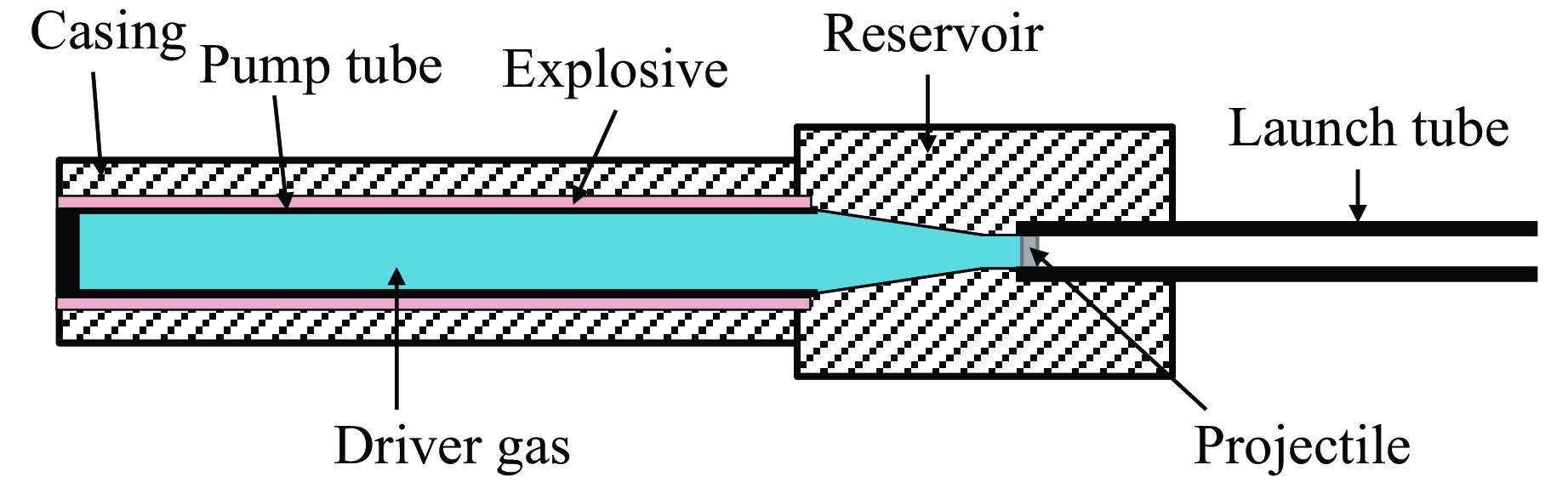
Preliminary Simulation and Experimental Study on Implosion-Driven Hypervelocity Launching Technology
-
摘要: 为获得10 km/s左右的超高速发射能力,以内爆发射器为研究对象,利用AUTODYN 2D软件对口径为8 mm的内爆发射器进行有限元仿真分析,获得了典型状态下的弹丸发射速度。研制了口径为8 mm的内爆发射器,并在压缩管中填充5 MPa氦气进行实验,分别获得了0.55 g铝合金弹丸7.95 km/s和0.37 g镁合金弹丸10.28 km/s的发射速度,与有限元仿真计算结果的速度偏差分别为15.3%和3.7%。结果表明,设计的内爆发射器具备10 km/s发射能力,满足空间碎片撞击和防护研究的超高速发射需求。Abstract: For achieving the hypervelocity launching of about 10 km/s, an implosion-driven launcher with the caliber of 8 mm diameter was analyzed using the AUTODYN 2D software. The projectile launching velocities under typical operation condition were obtained. Based on numerical simulation results, several tests of the implosion-driven launcher with the caliber of 8 mm diameter were carried out. The driven gas of helium with the pressure of 5 MPa was filled in the compressed pipe. The experimental results show that the 0.55 g aluminum and 0.37 g magnesium projectiles could be launched to the velocity of 7.95 km/s and 10.28 km/s, respectively, and the relative deviations between the numerical and experimental results are 15.3% and 3.7%, respectively. Consequently, the designed implosion-driven launcher can realize the launching of the projectiles to 10 km/s or even higher which could provide a new ground-test method for investigating the impact features of orbital debris and corresponding shield technologies.
-
Key words:
- launching technique /
- hypervelocity /
- implosion-driven
-
表 1 不同弹丸材料和充气压力下仿真计算参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of launchers with different projectile materials and filling pressure
No. Material of projectile Filling pressure/MPa Diameter of launch tube/mm Diameter of pump tube/mm Muzzle velocity/(km·s–1) 1 Aluminum alloy 4 8 16 8.62 2 Aluminum alloy 5 8 16 9.17 3 Aluminum alloy 6 8 16 9.25 4 Magnesium alloy 5 8 16 10.66 表 2 内爆发射器实验相关参数
Table 2. Parameters of the implosion-driven launchers in tests
No. Material of projectile Mass of projectile/g Filling pressure/MPa Diameter of launch tube/mm Diameter of pump tube/mm Maximum velocity/(km·s–1) ILT04 Aluminum alloy 0.55 5 8 16 7.26 ILT07 6.96 ILT14 7.95 ILT08 Magnesium alloy 0.37 5 8 16 9.73 ILT09 10.28 ILT11 9.36 ILT12 9.77 -
[1] HUNEAULT J, LOISEAU J, HIGGINS A J. Coupled lagrangian gasdynamic and structural hydrocode solvers for simulating an implosion-driven hypervelocity launcher [C]//51st AIAA Aerospace Science Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Grapevine, 2013: 1–21. [2] 王翔, 王青松, 彭建祥, 等. 三级炮超高速发射技术在空间碎片防护研究中的初步应用 [C]//第八届全国空间碎片学术交流会. 北京, 2015: 350–358.WANG X, WANG Q S, PENG J X, et al. Preliminary application of three-stage gas gun hypervelocity launcher techniques in space debris protection research [C]//8th National Symposium on Space Debris. Beijing, 2015: 350–358. [3] 张旭平, 谭福利, 王桂吉, 等. 基于CQ4的磁驱动10 km/s以上超高速飞片发射 [C]//第八届全国空间碎片学术交流会. 北京, 2015: 385–390.ZHANG X P, TAN F L, WANG G J, et al. Magnetically driven flyer plates to velocities above 10 km/s on CQ4 [C]//8th National Symposium on Space Debris. Beijing, 2015: 385–390. [4] 文尚刚, 赵锋, 王建, 等. 气炮加载下炸药强爆轰驱动技术的初步实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2011, 25(1): 36–40. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2011.01.006WEN S G, ZHAO F, WANG J, et al. Primary experimental study on driving technique of strong detonation using gas gun [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2011, 25(1): 36–40. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2011.01.006 [5] 赵士操, 宋振飞, 姬广富, 等. 一种基于二级轻气炮平台的超高速弹丸发射装置设计 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2011, 25(6): 557–564. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2011.06.012ZHAO S C, SONG Z F, JI G F, et al. A novel design of a hypervelocity launcher based on two-stage gas gun facilities [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2011, 25(6): 557–564. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2011.06.012 [6] 邢柏阳, 刘荣忠, 郭锐, 等. 强爆轰驱动超高速碎片发射装置设计因素分析 [J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2018(4): 151–158.XING B Y, LIU R Z, GUO R, et al. Analysis on design factors of hypervelocity fragment launcher using strong detonation drive [J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2018(4): 151–158. [7] 林俊德, 张向荣, 朱玉荣, 等. 超高速撞击实验的三级压缩气炮技术 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(5): 483–489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1455.2012.05.006LIN J D, ZHANG X R, ZHU Y R, et al. The technique of three-stage compressed-gas gun for hypervelocity impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(5): 483–489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1455.2012.05.006 [8] 王青松, 王翔, 郝龙, 等. 三级炮超高速发射技术研究进展 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2014, 28(3): 340–345.WANG Q S, WANG X, HAO L, et al. Progress on hypervelocity launcher techniques using a three-stage gun [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2014, 28(3): 340–345. [9] MOORE J E T. Explosive hypervelocity launchers: PIFR-051 [R]. Physics International Company, 1968. [10] WATSON J D. High-velocity explosively driven guns: CR-1533 [R]. Physics International Company, NASA, 1970. [11] LOISEAU J, HUNEAULT J, HIGGINS A J. Development of a linear implosion-driven hypervelocity launcher [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2013, 58: 77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2013.05.011 [12] HUNEAULT J, LOISEAU J, HILDEBRAND M, et al. Down-bore velocimetry of an explosively driven light-gas gun [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 103: 230–236. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.04.031 [13] HILDEBRAND M, HUNEAULT J, LOISEAU J, et al. Down-bore two-laser heterodyne velocimetry of an implosion-driven hypervelocity launcher [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1793: 160009. [14] 田杨萌, 王莹. 炸药爆轰驱动高速击波管发射技术 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2003, 23(3): 221–224.TIAN Y M, WANG Y. A propulsion technology of the fast shock tube driven by high explosive [J]. Journal of Projectiles Rockets Missiles and Guidance, 2003, 23(3): 221–224. [15] 北京工业学院八系. 爆炸及其作用(上册) [M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1979: 214–219.No.8 Department of Beijing Industrial College. Explosion and its application [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industrial Press, 1979: 214–219. -







 下载:
下载: