Numerical Simulation on the Performance of Shaped Charge with Explosively Welded Aluminum Copper Liner
-
摘要: 为提高射流侵彻性能,根据聚能射流装置的射流形成特点,设计了爆炸复合铝铜金属体作为药型罩的聚能射流装置。此装置依据已有的锥角为42°的聚能装药紫铜药型罩改进而来。利用LS-DYNA软件中的MMALE多物质算法,对此装置的射流形成、侵彻金属靶体全过程进行数值模拟。在保持装药量不变的情况下,计算了当铝铜药型罩锥角分别为36°、38°、40°和42°时的射流形成及侵彻过程。结果表明:射流头部速度随着铝铜药型罩锥角的减小而增大;且锥角为38°时射流穿深最大。相比单纯金属铜药型罩情况,射流头部速度提高了13.2%,侵彻深度提高了14.5%。Abstract: According to the character of jet formation in shaped charge device, a new type of charge assembly, with metallic liner of aluminum-copper bond fabricated by explosively welding technique, has been proposed in order to acquire the improvement on penetration capability from such charge. The device is modified from the available conical shaped charge with single copper liner material and 42° conical apex angle. Multi-material arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (MMALE) method in LS-DYNA software package is employed as the numerical simulation tool to fulfill the calculations for the whole processes involving jet formation and ensuing penetration into target. Charges with apex angles varying from 36°, 38°, 40°, and 42° respectively have been calculated for comparison. The results show that the head velocity of the jet increases with the decreasing value of apex angle. Furthermore, 38° apex angle charge reaches maximum penetration depth. Compared to shaped charge with single copper liner, such design of the charge presents 13.2% improvement in jet head velocity and 14.5% rising in penetration depth.
-
Key words:
- shaped charge /
- penetration /
- welded aluminum copper liner /
- LS-DYNA
-
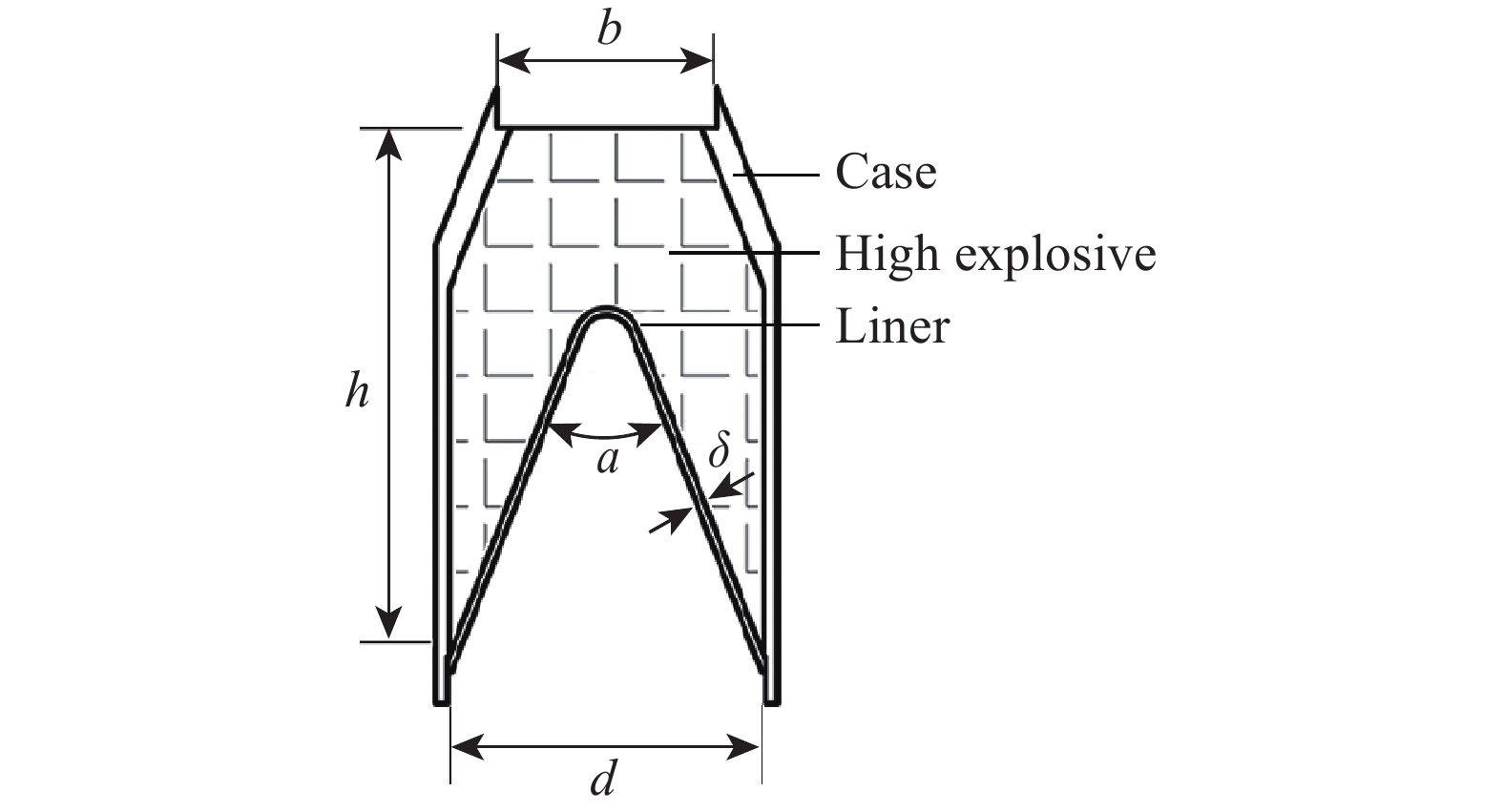
表 1 模型几何参数
Table 1. Geometrical parameters in shaped charge configuration
δ/cm h/cm d/cm α/(°) b/cm 0.21 15.24 8.38 42 5.86 Note: δ, h, d, α, b are liner thickness, height of charge, diameter, apex angle, and top diameter, respectively. ρ0/(g·cm–3) D/(km·s–1) pCJ/GPa E0/(J·m–3) ω 1.821 8.48 34.2 9.6 0.38 A/GPa B/GPa C/GPa R1 R2 748.6 13.38 1.167 4.50 1.20 Note: ω, A, B, C, R1 and R2 are JWL EOS parameters; ρ0, D, pCJ and E0 are density, detonation velocity, CJ presure, and explosive energy per volume, respectively. 表 3 铝和铜的Grüneisen状态方程参数[16]
Table 3. Parameters in Grüneisen equation of state of aluminum and copper[16]
Material ρ0/(g·cm–3) C0/(km·s–1) S Γ Troom/K cv/(J·kg–1·K–1) Aluminum 2.78 5.39 1.339 1.97 300 884 Copper 8.93 3.94 1.489 2.02 300 383 Note: S is constant; C0, Γ, Troom, cv are sound velocity, Grüneisen coefficient, room temperature, and specific heat capacity at constant volume, respectively. 表 4 铝和铜材料的Steinberg强度模型参数[17]
Table 4. Parameters in Steinberg strength model of aluminum and copper[17]
Material ρ0/(g·cm–3) G0/GPa Y0/GPa β n (${-G'_r/G_0}$)×103/K–1 Aluminum 2.78 27.6 0.29 125 0.10 0.62 Copper 8.93 47.7 0.12 36 0.45 0.38 Note: β and n are constants; G0, Y0 and are shear modulus, yield strength, and ${G'_r}$ shear modulus per time derivative,respectively. 表 5 钢靶弹塑性随动硬化模型参数[19]
Table 5. Target material parameters in elastic-plastic-kinematic strength model[19]
Material ρ0/(g·cm–3) Ep/GPa μ Y/GPa Ce Pe/s–1 ɛeff Steel 7.83 2.07 0.3 0.011 1 6 500 4 0.7 Note: Pe, Ce and ɛeff are constants; Ep, μ and Y are platic modulus, Poisson’s ratio and yield strength, respectively. 表 6 纯铜药型罩射流侵彻计算和实验结果对比
Table 6. Comparison on computational and experimental results of jet and penetration by charge with single copper liner
Jet head velocity/(km·s–1) Penetration depth/cm Experiment This calculation Experiment This calculation 8.30 8.23 38.58–40.23 41.15 表 7 不同锥角铝铜药型罩与纯铜药型罩射流计算结果对比
Table 7. Computational results on penetration by aluminum-copper liner with various apex angels
Material α/(°) Penetration depth/cm Cu 42° 41.15 Al-Cu 42° 40.01 40° 44.23 38° 47.01 36° 44.02 表 8 锥角38°铝铜药型罩射流各分段速度分布及总动能
Table 8. Jet velocity values at different locations along its elongation and total jet kinetic energy from the charge with aluminum copper welded liner at 38° apex angle
Portion i Velocity/(km·s–1) va/(km·s–1) r/cm l/cm Evi/kJ Ev/kJ 1 2.0–3.0 2.5 0.54 0.45 11.50 454.71 2 3.0–7.0 5.0 0.28 6.09 167.43 454.71 3 7.0–8.0 7.5 0.23 2.29 95.58 454.71 4 8.0–9.6 8.8 0.17 5.74 180.19 454.71 表 9 单层铜药型罩射流各分段速度分布及总动能
Table 9. Jet velocity values at different locations along jet elongation and total jet kinetic energy from the charge with single copper liner
Portion i Velocity/(km·s–1) va/(km·s–1) r/cm l/cm Evi/kJ Ev/kJ 1 2.0–3.0 2.5 0.58 1.21 35.68 414.13 2 3.0–7.0 5.0 0.28 8.83 242.76 414.13 3 7.0–8.0 7.5 0.21 3.40 118.30 414.13 4 7.0–8.3 7.7 0.11 1.75 17.38 414.13 -
[1] 谭多望, 孙承纬. 成型装药研究新进展 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(1): 50–51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.01.009TAN D W, SUN C W. Progress in studies on shaped charge [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(1): 50–51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.01.009 [2] 戴兰宏. 工程科学前沿的拓荒者——郑哲敏 [J]. 力学进展, 2013, 43(3): 265–294. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-033DAI L H. A pioneer in the frontier of engineering science—Zhe-Min Zheng [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2013, 43(3): 265–294. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-033 [3] 龚柏林, 李明, 初哲, 等. 贫铀合金药型罩聚能破甲性能实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(3): 035102.GONG B L, LI M, CHU Z, et al. Penetration performance of depleted uranium alloys liner [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(3): 035102. [4] 龚柏林, 初哲, 王长利, 等. 基于贫铀合金药型罩的聚能弹破甲后效实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(6): 065104.GONG B L, CHU Z, WANG C L, et al. Experimental research on armor penetration aftereffect produced by depleted uranium alloys liner shaped charge [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(6): 065104. [5] 潘文强, 付代轩, 赖康华, 等. 含能射孔弹双层药型罩穿孔性能研究 [J]. 爆破器材, 2017, 46(2): 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2017.02.007PAN W Q, FU D X, LAI K H, et al. Study on penetration performance of Bi-layer liner in energetic penetrating charge [J]. Explosive Materials, 2017, 46(2): 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2017.02.007 [6] DIL’’DIN Y M, KOLMAKOV A I, LADOV L V, et al. Effect of the width of the diffusion zone in multilayer lining of shaped charges on the shaping effect [J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 1980, 16(6): 660–663. [7] LAROCCA E W, STRIKE R. Method of making a bimetallic shaped charge liner: 4807795 [P]. 1989-02-28. [8] 臧涛成, 胡焕性, 邵琦. 破甲弹复合罩性能研究 [J]. 火炸药学报, 1998(4): 44–47.ZANG T C, HU H X, SHAO Q. The performance study of shaped charge liner [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 1998(4): 44–47. [9] 郑宇, 王晓鸣, 李文彬, 等. 双层药型罩侵彻半无限靶板的数值仿真研究 [J]. 南京理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(3): 313–317.ZHENG Y, WANG X M, LI W B, et al. Numerical simulation on double-layered shaped charge liner penetration into semi-infinite target [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2008, 32(3): 313–317. [10] 乔金超, 吴越, 贾磊朋. 双层线型药型罩侵彻靶体的数值分析 [J]. 兵工自动化, 2017, 36(9): 27–30.QIAO J C, WU Y, JIA L P. Numerical analysis of double-layer composite linear liner penetrate target [J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2017, 36(9): 27–30. [11] LS-DYNA Manual R.9448 [CP]. Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2018. [12] DIPERSIO R, SIMON J, MERENDINO A B. Penetration of shaped-charge jets into metallic targets [R]. Maryland: Ballistics Research Laboratory, 1965. [13] LEE E L, HORNIG H C, KURY J W. Adiabatic expansion of high explosive detonation products: UCRL-50422 [R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Report, 1968. [14] DOBRATZ B M, CRAWFORD P C. LLNL explosive handbook [M]. California: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1987: 8–22. [15] MEYERS M A. Dynamic behavior of materials [M]. John Wiley & Sons, 1994: 124. [16] KATAYAMA M. Numerical and experimental study on the shaped charge for space debris assessment [J]. Acta Astronautica, 2001, 48(5): 363–372. [17] STEINBERG D J, COCHRAN S G, GUINAN M W. A constitutive model for metals applicable at high-strain rate [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(3): 1498–1504. doi: 10.1063/1.327799 [18] KRIEG R D, KEY S W. Implementation of a time dependable plasticity theory into structural computer programs, constitutive of equations in viscoplasticity: computational and engineering aspects [M]. New York: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1976: 125–137. [19] 时党勇, 李裕春, 张胜民. 基于ANSYS/LS-DYNA 8.1进行显示动力分析 [M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005: 313–326.SHI D Y, LI Y C, ZHANG S M. Explicit dynamic analysis based on ANSYS/LS-DYNA 8.1 [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005: 313–326. -







 下载:
下载: