Stress Waves Propagation in Layered Graded CellularMaterials under Dynamic Crush Loading
-
摘要: 以一维应力波传播理论为基础,建立了3层金属泡沫材料受到刚性块撞击时的理论模型,研究了刚性块撞击3层泡沫圆杆时的动力响应过程,从理论上给出了刚性块在撞击过程中的速度衰减规律数值解。利用ANSYS/LS-DYNA分析了受刚性块撞击时塑性应力波在3层泡沫材料中的传播过程,比较了刚性块以及层间界面处节点速度的变化规律。通过对比有限元结果与理论结果发现:理论模型能够较好地预测冲击载荷下分层泡沫材料各界面的速度衰减规律;3层梯度泡沫材料比相同质量的单层均质泡沫材料具有更加高效的吸能和缓冲能力。由于理论假设忽略了反射波以及泡沫材料应变硬化效应的影响,理论解与有限元模拟结果之间存在一定的误差。Abstract: The theoretical mode of velocity attenuation of rigid mass and the stress wave propagation in layered cellular materials under dynamic impact loading has been proposed based on the 1-D wave theory and the dynamic response process of a foam rod strike by a rigid mass has been studied. A finite element (FE) validation has been conducted by employing ANSYS/LS-DYNA software, agreeing well with the theoretical results. The compared results show that the triple layered graded foam material has better impact reduction and energy absorption capacity than the uniform foam with the same mass. Due to the reflected wave and the strain hardening effects not considered in the theoretical model, there are some acceptable errors between the theoretical and FE results.
-
Key words:
- layered cellular material /
- dynamic crushing /
- stress wave /
- theoretical model
-
多孔材料因其压缩应力-应变曲线包含一段较长的平台区域,在受到冲击载荷时能够吸收较多的能量,起到缓冲减震的功能,在航空航天、交通运输等领域具有广泛的应用。然而受工业生产中金属发泡工艺本身的限制,泡沫材料的厚度、平台应力以及密实化应变有限,压缩效率较低,单层泡沫材料作为吸能填充层在爆炸冲击中的缓冲和能量吸收能力受到制约[1]。分层泡沫材料在用作防护层时没有厚度限制,可以根据载荷工况进行梯度及分层优化设计[2],合理的分层泡沫组合能够对冲击波产生有效的衰减作用,提高结构的抗冲击能力[3-4]。与均质多孔材料相比,梯度和分层设计可以便捷地对不同性质的材料进行有序的组合,并结合不同材料的特点,充分发挥材料的吸能特性,使之具有更加优越的性能,因此分层梯度金属多孔材料及结构冲击动力学行为引起了广泛的关注[5-7]。
本研究以一维应力波传播理论为基础,建立了3层梯度金属泡沫材料受到刚性块撞击时的理论模型,分析各层界面速度的衰减规律,并利用ANSYS/LS-DYNA分析受刚性块撞击时应力波在3层泡沫材料中的传播过程,再与理论结果进行对比。
1. 理论模型
Reid等[8]最早运用波阵面上的动量守恒条件,研究了应力波在木头圆杆中的传播特性,提出了有关应力波在多孔材料中传播的刚性理想塑性锁定模型(RPPL模型)。Tan等[9]通过对冲击载荷下金属泡沫铝的动态压缩性能实验研究,提出了有关泡沫铝材料在冲击作用下的冲击模型。Karagiozova[10]针对刚性质量块撞击单层和双层梯度泡沫圆杆的动力响应及应力波传播问题,利用能量守恒原理,结合波阵面上的质量守恒及动态连续条件,分析了质量块速度变化及衰减特征。
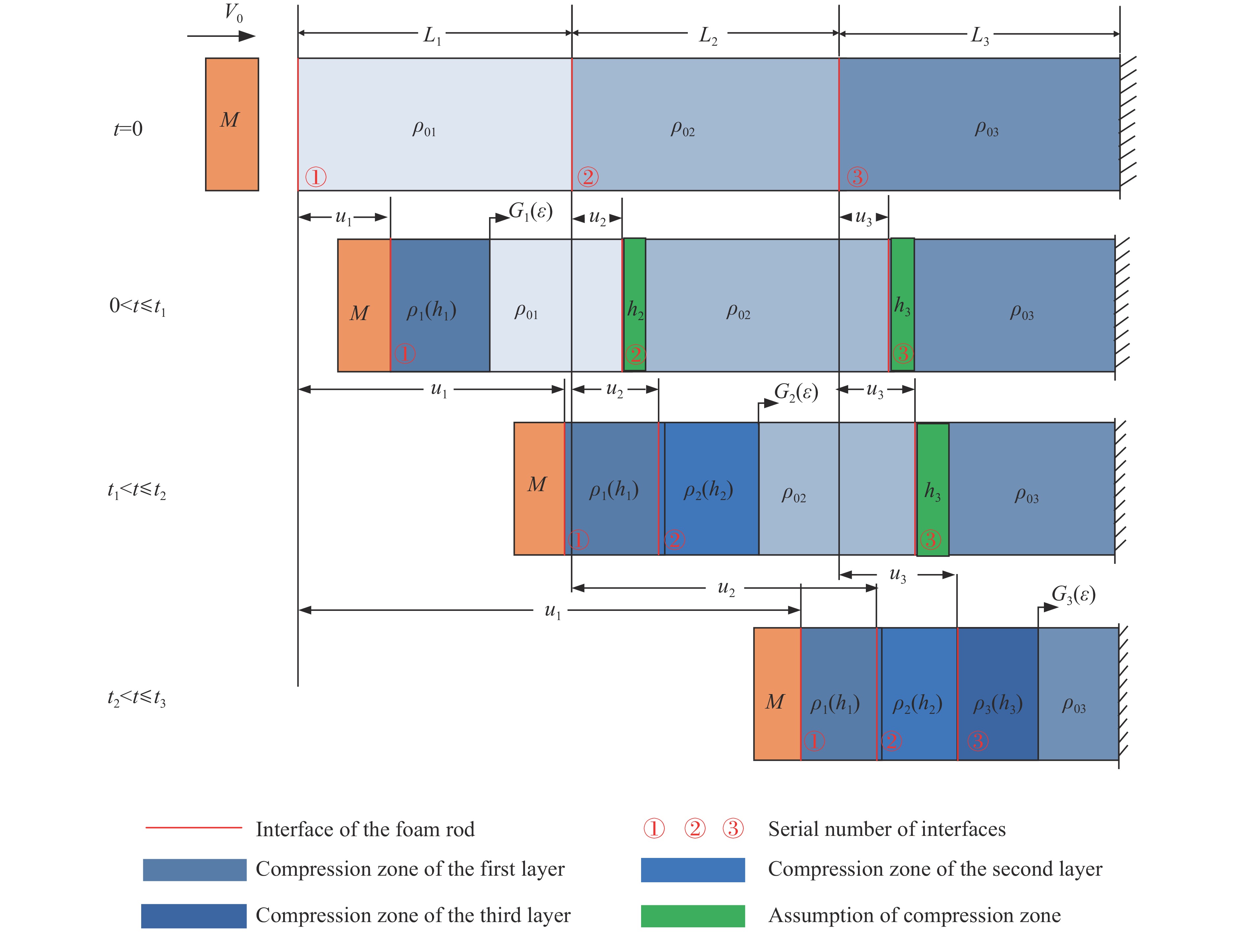
本研究以一维应力波传播理论为基础,建立质量为M的刚性质量块撞击一端固定的3层泡沫圆杆的理论模型,设泡沫圆杆的截面积为A0,时间为t,撞击过程如图1所示。假设整个过程分为3个相互耦合的阶段:第1阶段(
0<t⩽t1 )为塑性冲击波通过第1层泡沫之前;第2阶段 (t1<t⩽t2 )为塑性冲击波通过第1层泡沫至通过第2层泡沫之前;第3阶段(t2<t⩽t3 )为塑性冲击波通过第2层泡沫至到达固定端之前。由于各层之间的波阻抗发生间断,压缩过程中前驱波可能导致各层之间的耦合压缩作用,这种耦合作用通过假设层间压缩区(Assumption of Compression Zone,如图1所示)来描述。理论模型中忽略泡沫材料界面间的反射作用,并且假设每层泡沫都符合RPPL模型[8]。假设刚性质量块的初始速度为V0,3层泡沫圆杆的初始密度分别为
ρ01 、ρ02 、ρ03 ,初始长度分别为L1、L2、L3,初始平台屈服应力分别为σY1 、σY2 、σY3 ,泊松比均假设为零。根据波阵面上的质量守恒及动量守恒定律[8, 11],得到如下结果。(1)第1阶段。当
0⩽t⩽t1 时,初始条件为:各界面速度V1(0)=V0 ,V2(0)=0 ,V3(0)=0 ;各压缩区长度h1(0)=0 ,h2(0)=0 ,h3(0)=0 ;各界面位移u1(0)=0 ,u2(0)=0 ,u3(0)=0 ;压缩过程中假设自由端速度V1=du1/dt,第1界面处速度为V2=du2/dt,第2界面处速度为V3=du3/dt。对刚性质量块和第1层泡沫杆压缩区域(压缩长度为h1,如图1(b)所示)列动量守恒方程{M/A0+ρ01[u1+δu1+h1+δh1−(u2+δu2)]}(V1+δV1)−[M/A0+ρ01(u1+h1−u2)]V1−ρ01(δu1+δh1−δu2)V2=−σY1δt (1) 即
[M/A0+ρ01(u1+h1−u2)]δV1+ρ01(V1−V2)(δu1+δh1−δu2)=−σY1δt (2) 由于
dh1dt=G1−(V1−V2) ,冲击波波速G1(ε)=V1−V2ε1 ,ε1 为第1层泡沫材料的密实化应变,所以当δt→0 时,(2)式可写为[M/A0+ρ01(u1+h1−u2)]dV1dt+ρ01(V1−V2)du1+dh1−du2dt=[M/A0+ρ01(u1+h1−u2)]dV1dt+ρ01(V1−V2){[G1−(V1−V2)]+V1−V2}=[M/A0+ρ01(u1+h1−u2)]dV1dt+ρ01(V1−V2)2ε1=−σY1 (3) 于是
dV1dt=−[σY1+ρ01(V1−V2)2ε1]1M/A0+ρ01A0(u1+h1−u2) (4) 在此阶段,可以记②号界面(如图1所示)上的压力为
p1 ,通过假设右侧第2层泡沫杆压缩段的长度为h2来考虑耦合压缩作用,对第2层泡沫杆压缩段列动量守恒方程ρ02[h2+u2+δh2+δu2+(u3+δu3)](V2+δV2)−ρ02(h2+u2−u3)V2=(p1−σY2)δt (5) 当
δt→0 时ρ02(h2+u2−u3)dV2dt+ρ02V2d(h2+u2−u3)dt=p1−σY2 (6) 同样有如下关系:
dh2dt=G2−(V2−V3) ,冲击波波速G2(ε)=V2−V3ε2 ,ε2 为第2层泡沫材料的密实化应变,V3=du3dt 。代入(6)式,可得ρ02(h2+u2−u3)dV2dt=p1−(σY2+ρ02V2G2) (7) 由于惯性效应,压缩区动态应力符合如下关系
σd2=σY2+ρ02(V2−V3)G2 (8) 联合(7)式和(8)式,得到
ρ02(h2+u2−u3)dV2dt=p1−σd2 (9) 对第1层泡沫杆未压缩段列动量守恒方程
ρ01[L1−(h1+u1−u2)]δV2−ρ01(V1+δV1)(δh1+δu1−δu2)+ρ01V2(δh1+δu1−δu2)=(σd1−p1)δt (10) 略去无穷小量
(δh1δV1+δu1δV1−δu2δV1) ,则ρ01[L1−(h1+u1−u2)]dV2dt−ρ01V1d(h1+u1−u2)dt+ρ01V2d(h1+u1−u2)dt=σd1−p1 (11) 式中:
σd1=σY1+ρ01(V1−V2)G1 。由此可得dV2dt=−[σY2+ρ02(V2−V3)2ε2−σY1]⋅1ρ02(h2+u2−u3)+ρ01[L1−(u1+h1−u2)] (12) 同样,在此阶段记③号界面上的压力为
p2 ,通过假设右侧第3层泡沫杆压缩段的长度为h3来考虑耦合压缩作用,对第3层泡沫杆压缩段列动量守恒方程ρ03(h3+u3+δh3+δu3)(V3+δV3)−ρ03(h3+u3)V3=(p2−σY3)δt (13) 当
δt→0 时ρ03(h3+u3)dV3dt+ρ03V3d(h3+u3)dt=p2−σY3 (14) 因为
dh3dt=G3−V3 ,冲击波波速G3(ε)=V3ε3 ,ε3 为第3层泡沫材料的密实化应变,V3=du3dt ,则σd3=σY3+ρ03V3G3 (15) 联合(14)式和(15)式,有
ρ03(h3+u3)dV3dt=p2−σd3 (16) 对第2层泡沫杆未压缩段列动量守恒方程
ρ02[L2−(h2+u2−u3)]δV3−ρ02(V2+δV2)(δh2+δu2−δu3)+ρ02V3(δh2+δu2−δu3)=(σd2−p2)δt (17) 略去无穷小量
(δh1δV1+δu1δV1−δu2δV1) ,则ρ02[L2−(h2+u2−u3)]dV3dt−ρ02V2d(h2+u2−u3)dt+ρ02V3d(h2+u2−u3)dt=σd2−p2 (18) 所以有
dV3dt=−(σY3+ρ03V23ε3−σY2)⋅1ρ03(h3+u3)+ρ02[L2−(u2+h2−u3)] (19) (2)第2阶段。
t1<t⩽t2 ,V1=V2 ,dh2dt=G2−(V2−V3) ,G2(ε)=V2−V3ε2 ,du2dt=V2 ,du3dt=V3 ,根据波阵面上的动量守恒条件{M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02[u2+δu2+h2+δh2−(u3+δu3)]}(V2+δV2)−[M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02(u2+h2−u3)]V2−ρ02(δu2+δh2−δu3)V3=−σY2δt (20) [M/A0+ρ01(u1+h1−u2)δV1+ρ01(V1−V2)(δu1+δh1−δu2)=−σY1δt (21) [M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02(u2+h2−u3)]dV2dt+ρ02(V2−V3)du2+dh2−du3dt=[M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02(u2+h2−u3)]dV2dt+ρ02(V2−V3){[G2−(V2−V3)]+V2−V3}=[M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02(u2+h2−u3)]dV2dt+ρ02(V2−V3)2ε2=−σY2 (22) 可得
dV2dt=−[σY2+ρ02(V2−V3)2ε2]1M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02A0(u2+h2−u3) (23) dV3dt=−(σY3+ρ03V32ε3−σY2)⋅1ρ03(h3+u3)+ρ02[L2−(u2+h2−u3)] (24) 其中初始条件:
V2(t1)=V1(t1) ,h2(t1)=0 ,h3(t1)=0 ,u2(t1)=ˉu2 ,u3(t1)=ˉu3 。(3)第3阶段。
t2<t⩽t3 ,V1=V2=V3 时dV3dt=−(σY3+ρ03V23ε3)1M/A0+ρ01L1+ρ02L2+ρ03(u3+h3) (25) dh3dt=G3−V3,G3(ε)=V3ε3,du3dt=V3 (26) 初始条件:
V3(t2)=V2(t2) ,h3(t2)=0 ,u3(t2)=¯¯u3 。利用Runge-Kutta方法,将各阶段初始条件代入(4)式、(12)式、(19)式、(23)式、(24)式和(25)式,可求得各界面速度随时间变化规律的数值解。
2. 有限元计算
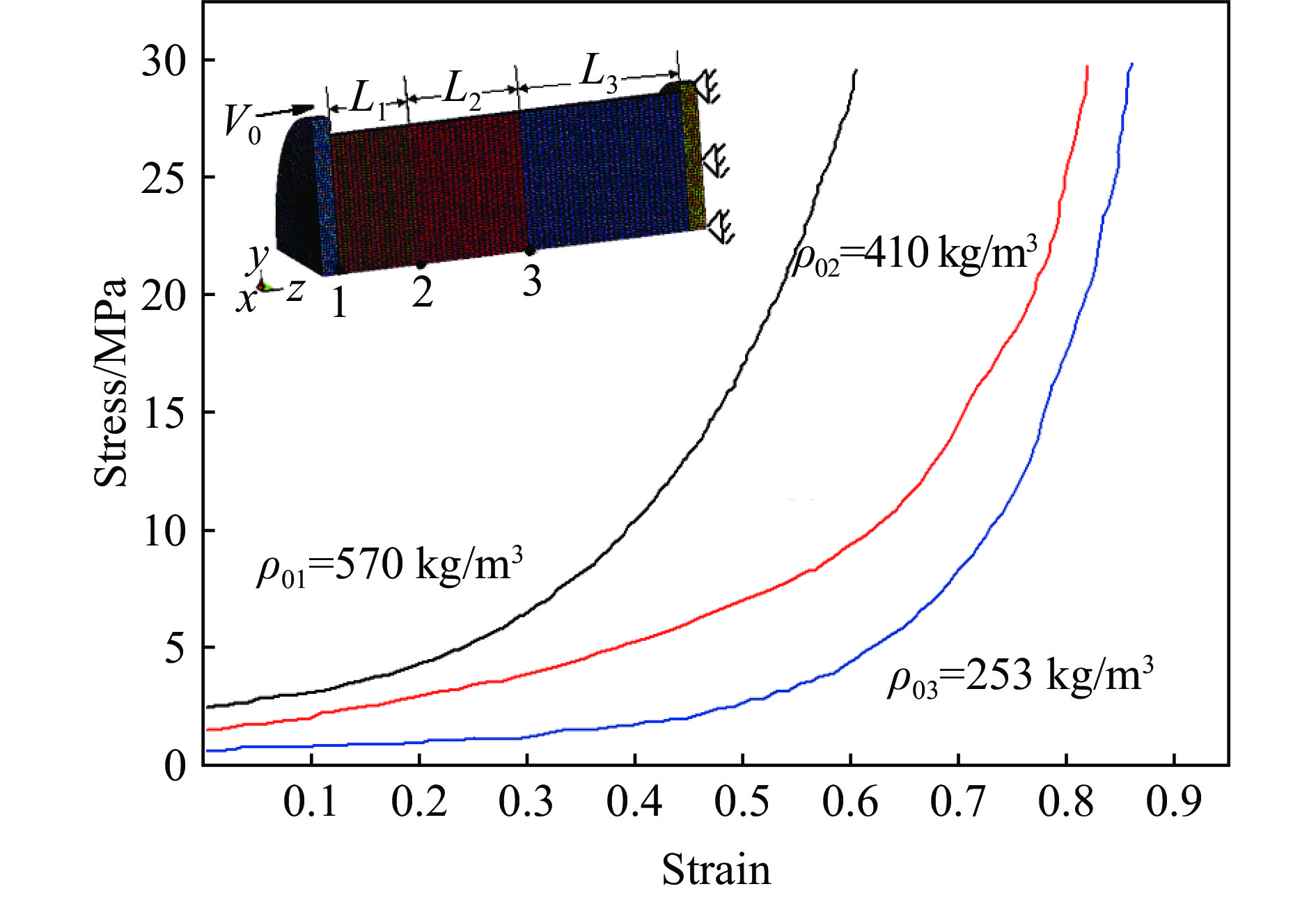
为了验证理论模型的可靠性,建立如图2所示的有限元模型(1/4模型)。刚性块的质量M为370 g,泡沫杆直径为100 mm,3层泡沫杆的参数如表1所示。
表 1 泡沫杆参数Table 1. Parameters of the foam rodL1/mm L2/mm L3/mm ρ01/(kg·m–3) ρ02/(kg·m–3) ρ03/(kg·m–3) 30 40 60 570 410 253 在有限元计算中,泡沫材料通过Crushable Foam模型模拟其压缩变形,图2给出了3种不同密度的Cymat泡沫铝的准静态压缩应力-应变曲线。为了记录压缩过程中各界面的速度变化规律,分别在刚性块与第1层泡沫杆及中间泡沫杆界面处选择节点1、2、3,记录压缩过程中层间界面的速度时程曲线。
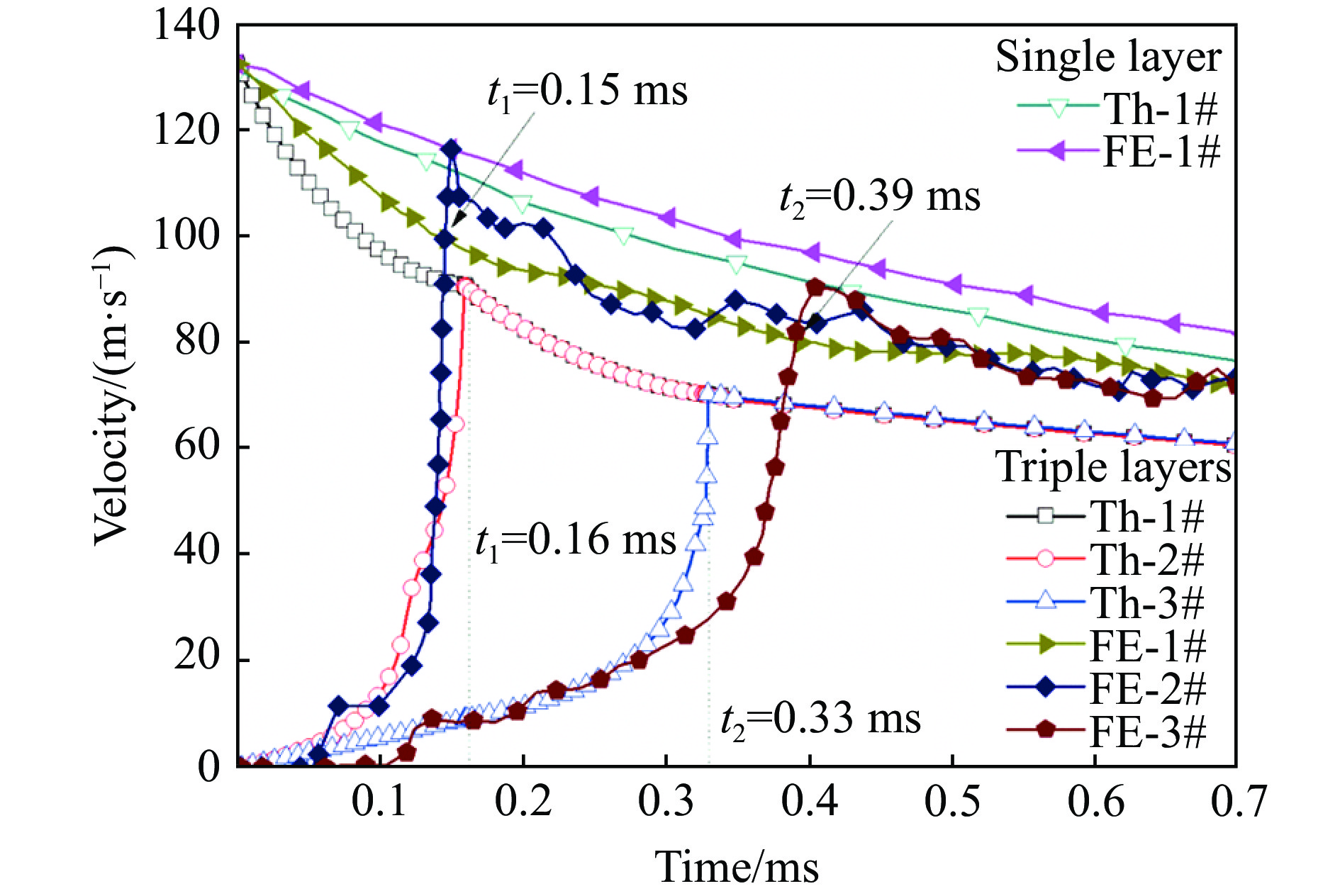
图3对比了有限元模拟结果和理论模型计算结果,并且与相同质量的单层泡沫圆杆(单层泡沫杆长度L1=200 mm,密度
ρ =253 kg/m3)的理论和有限元结果进行了比较。从图3可以看出,理论结果与有限元模拟结果吻合较好,说明理论模型能够较好地预测冲击载荷下分层泡沫材料各界面的速度衰减规律。由图3可知,在整体质量一定的情况下,增加泡沫材料的层数时,理论结果与有限元模拟结果之间的相对偏差增加。这是由于:理论计算中将连续的压缩过程假设为相互耦合的3个阶段,各阶段之间的计算误差不断累积;并且在有限元计算中泡沫铝材料的应力-应变关系为单轴压缩实验曲线,随着应变的增加有明显的硬化现象,而理论计算并未考虑应变硬化的影响,压缩过程中平台应力保持恒定,所以在整个压缩过程中刚性块速度的有限元结果略高于理论结果。从图3中还可以看出,在理论模型中第1阶段和第2阶段对应的时间分别为t1=0.16 ms和t2=0.33 ms,数值模拟中则分别为t1=0.15 ms和t2=0.39 ms。在3层泡沫材料的有限元结果中,节点2的速度与节点1速度相等之后会略微超越节点1的速度,节点3也有类似情况,这是由于:冲击波在截面处发生反射,反射波抑制了波阵面后方节点的运动,而在理论计算中并未考虑界面处反射波的作用。
比较单层和3层泡沫材料节点1的结果发现:在相同的冲击速度下,3层梯度泡沫材料对刚性块的衰减作用更明显,且相同质量的3层泡沫材料的总长度更短,所以分层梯度泡沫材料具有更高的压缩效率[11]以及更有效的吸能和缓冲效果。
3. 结 论
在理论分析刚性质量块撞击分层梯度泡沫材料的动力响应过程的基础上,利用ANSYS/LS-DYNA建立了相应的有限元模型,分析了受刚性块撞击时应力波在3层泡沫材料中的传播过程,比较了层间界面的速度变化规律。根据波阵面上动量守恒关系与一维应力波传播理论,建立了刚性块撞击分层泡沫材料时各界面速度衰减规律的理论模型,利用Runge-Kutta方法给出了理论模型的数值解,理论计算结果与有限元模拟结果吻合较好,说明理论模型能够较好地预测冲击载荷下分层梯度泡沫材料各界面的速度衰减规律。然而,由于在理论计算中忽略了反射波以及泡沫材料应变硬化效应的影响,理论解与有限元模拟结果之间存在一定偏差。从有限元结果还发现,在相同质量和冲击速度下,与单层泡沫材料相比,3层梯度泡沫材料具有更高效的吸能和缓冲能力。
-
表 1 泡沫杆参数
Table 1. Parameters of the foam rod
L1/mm L2/mm L3/mm ρ01/(kg·m–3) ρ02/(kg·m–3) ρ03/(kg·m–3) 30 40 60 570 410 253 -
[1] MA G W, YE Z Q. Energy absorption of double-layer foam cladding for blast alleviation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(2): 329–347. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.07.012 [2] GARDNER N, SHUKLA A. The blast response of sandwich composites with a functionally graded core and polyurea interlayer [M]//Dynamic Behavior of Materials. New York: Springer, 2011: 215–223. [3] WANG E, GARDNER N, SHUKLA A. The blast resistance of sandwich composites with stepwise graded cores [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2009, 46(18/19): 3492–3502. [4] LI S, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Sandwich panels with layered graded aluminum honeycomb cores under blast loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 173: 242–254. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.04.037 [5] LI S, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Finite element analysis of sandwich panels with stepwise graded aluminum honeycomb cores under blast loading [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 80: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.09.025 [6] LIU X, TIAN X, LU T J, et al. Blast resistance of sandwich-walled hollow cylinders with graded metallic foam cores [J]. Composite Structures, 2012, 94(8): 2485–2493. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.02.029 [7] ZHANG L, HEBERT R, WRIGHT J T, et al. Dynamic response of corrugated sandwich steel plates with graded cores [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 65: 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.11.011 [8] REID S R, PENG C. Dynamic uniaxial crushing of wood [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(5/6): 531–570. [9] TAN P J, REID S R, HARRIGAN J J, et al. Dynamic compressive strength properties of aluminium foams. Part II—‘shock’ theory and comparison with experimental data and numerical models [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2005, 53(10): 2206–2230. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2005.05.003 [10] KARAGIOZOVA D. Velocity attenuation and force transfer by a single-and double-layer claddings made of foam materials [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2011, 2(4): 417–437. doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.2.4.417 [11] GURUPRASAD S, MUKHERJEE A. Layered sacrificial claddings under blast loading Part I—analytical studies [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(9): 957–973. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00004-X -







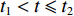
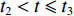

 下载:
下载:
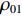
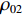
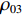
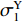
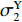
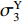
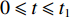
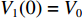
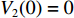

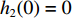
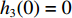
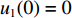
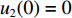

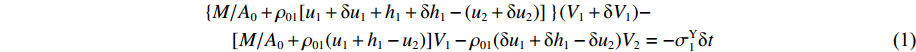
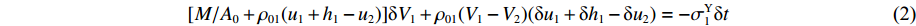
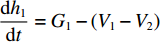

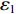
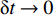
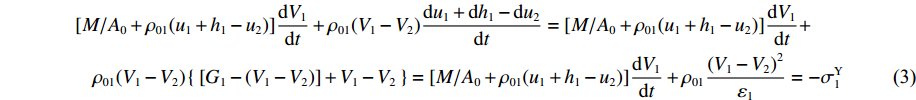
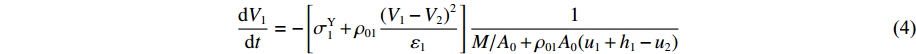
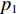
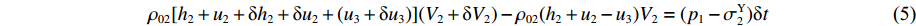

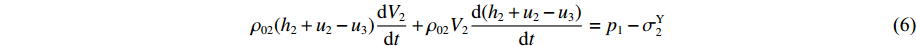
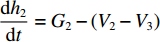
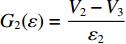
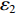
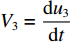
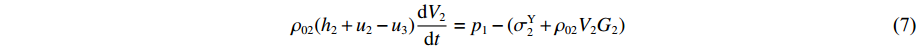
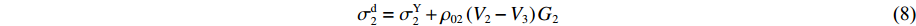
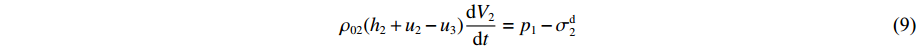
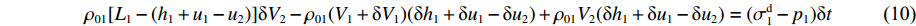
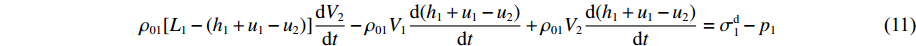

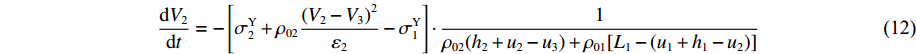
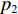
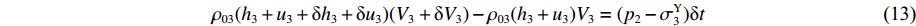
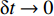
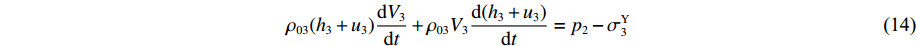

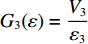
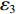
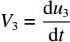
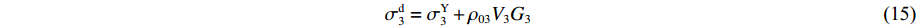
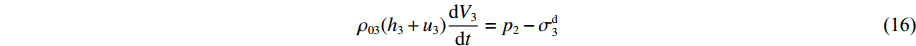
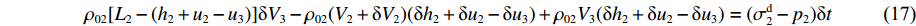

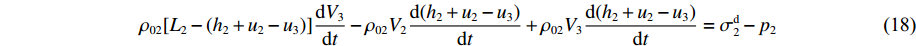
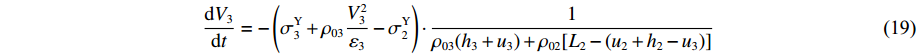
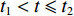
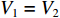
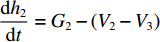
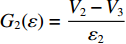
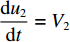
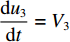
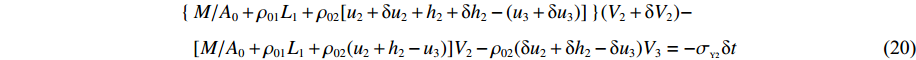
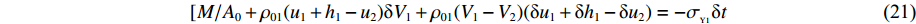
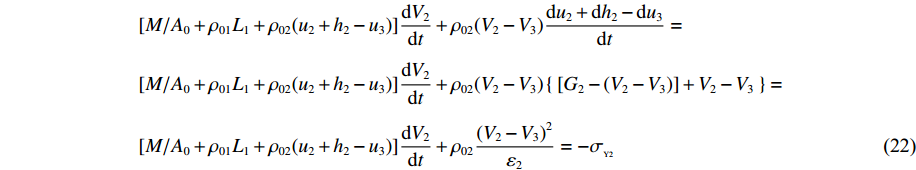
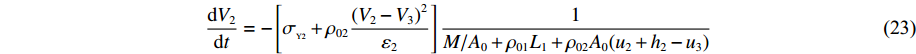
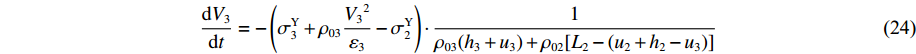

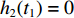

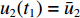
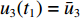

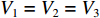
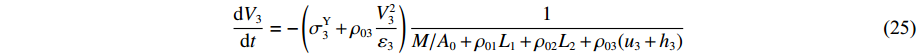
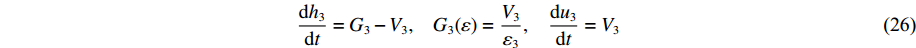
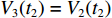
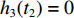
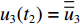




 下载:
下载: