Diffusion of Helium in Calcite and Aragonite:A First-Principles Study
doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180698
-
摘要: 研究碳酸盐矿物中氦的扩散行为对理解地球脱气过程中的物理化学性质和动力过程具有重要意义。基于密度泛函理论研究了氦在方解石和文石矿物中的扩散机理,计算了氦在地表和地幔条件下的扩散路径、激活能(Ea)和频率因子(v)。计算结果表明:氦在方解石中的扩散具有明显的各向异性,沿a(b)轴方向的扩散更快;文石呈现中等的各向异性,沿c轴的扩散速率低于a轴。在高压条件下,文石的激活能随压力的增大而增大。方解石晶体在[010]方向的封闭温度为–54~–25 ℃,沿[100]方向的封闭温度为 –12~23 ℃。在地表条件下,氦在文石中的滞留能力比在方解石中强,与以往的实验研究结果一致。Abstract: Helium diffusion in carbonate minerals is important for studying the physical and chemical properties and dynamic processes of Earth’s degassing. This paper discussed helium incorporation and diffusion mechanism in crystals of calcite and aragonite based on density functional theory calculations. The diffusion pathways, activation energies (Ea), and frequency factors (v) of helium under the surface and mantle condition were calculated. Calculations show an apperant anisotropy of helium diffusion in calcite, with more energetically favorable directions along a(b) axis. The moderate anisotropy of helium diffusion is showed in aragonite, in which the diffusion rate along c axis is slower than that along a axis. Under high pressure conditions, the activation energies of helium diffusion in aragonite increase with pressure. The closure temperature for calcite crystal varies from −54 ℃ to −25 ℃ in the direction [010], and for aragonite varies from −12 ℃ to 23 ℃ in [100]. Aragonite may be more retentive for helium than calcite under surface condition, which agrees well with previous experimental studies.
-
Key words:
- helium diffusion /
- calcite /
- aragonite /
- ab initio /
- pressure effect
-
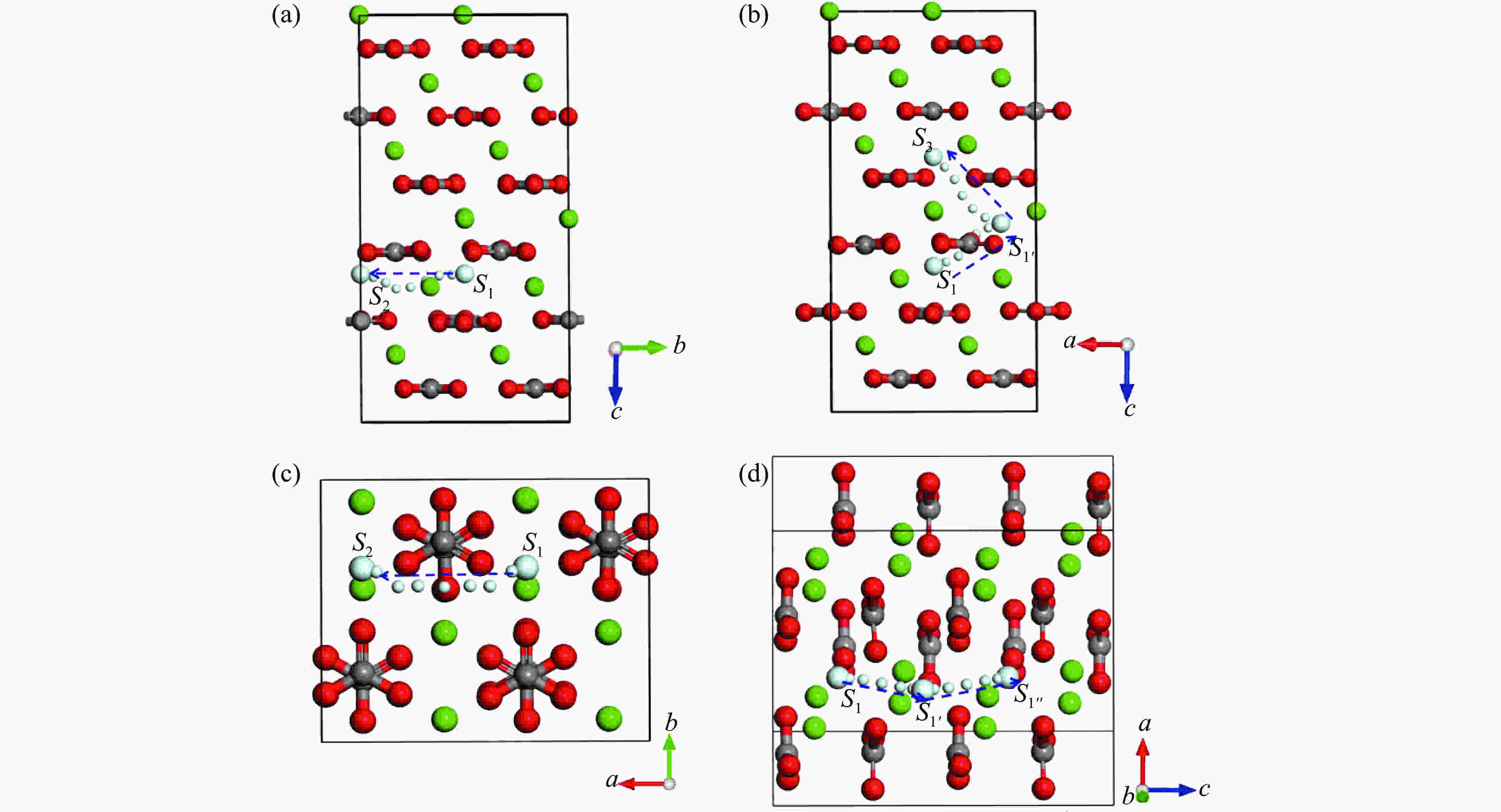
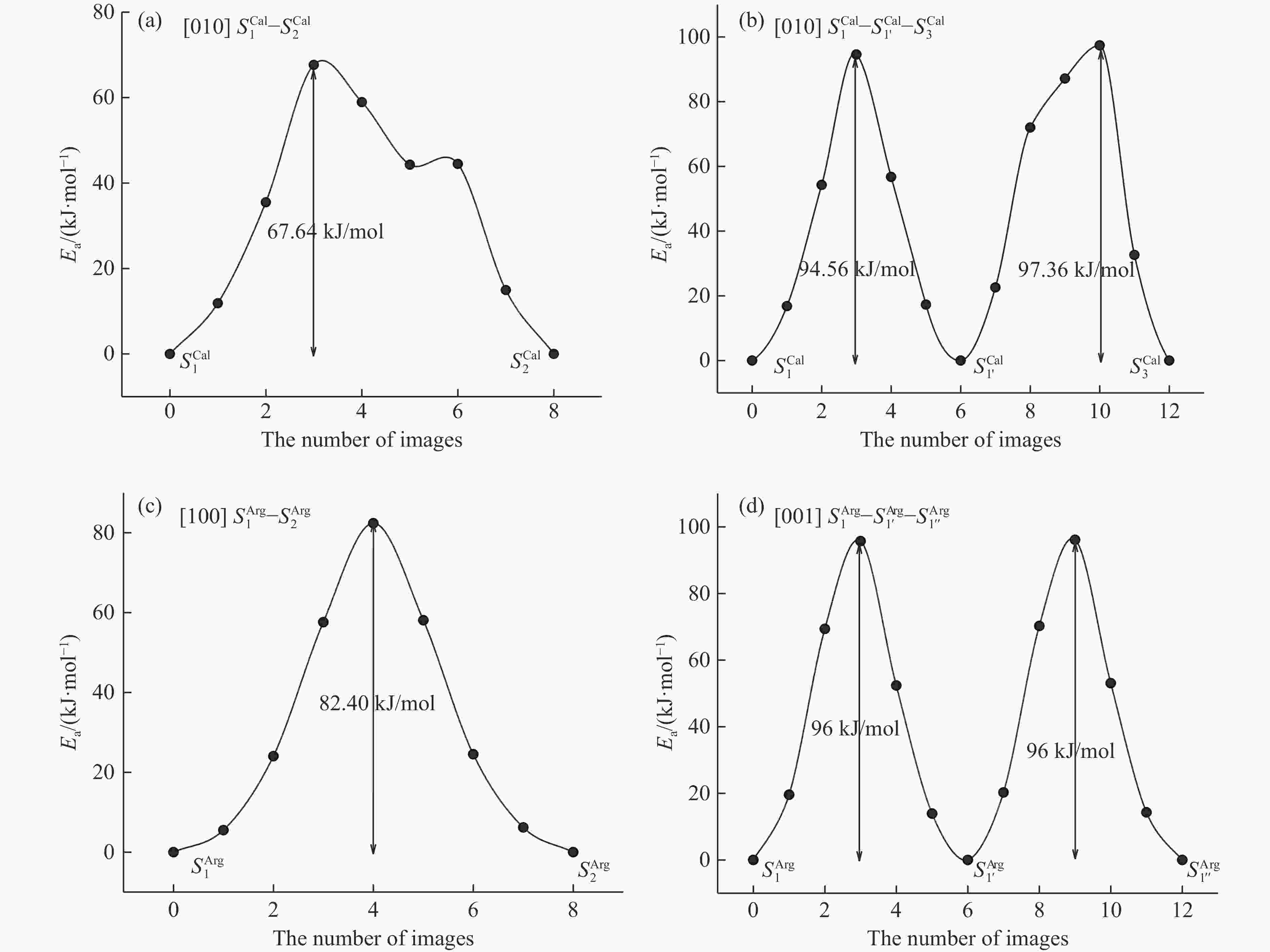
Figure 3. Energy barriers of different paths for helium diffusion in calcite: (a)
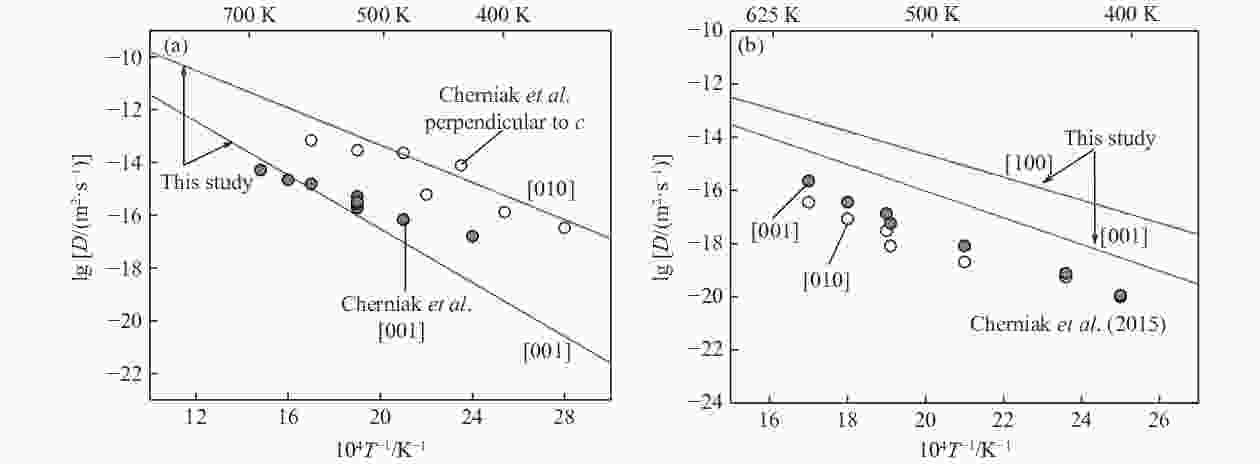
${S_1^{\rm Cal}- S_2^{\rm Cal}}$ path in the [010] direction, (b)${S_1^{\rm Cal}- S_{1'}^{\rm Cal}-S_3^{\rm Cal}}$ path in the [001] direction; in aragonite: (c)${S_1^{\rm Arg}- S_2^{\rm Arg}}$ path in the [100] direction, (d)${S_1^{\rm Arg}- S_{1'}^{\rm Arg}-S_{1''}^{\rm Arg}}$ path in the [001] directionFigure 4. Comparisons of our Arrhenius relations for calcite (a) and aragonite (b) with the data of Cherniak et al.[4] (He diffusion in calcite displays marked anisotropy, while in aragonite shows moderate anisotropy.)
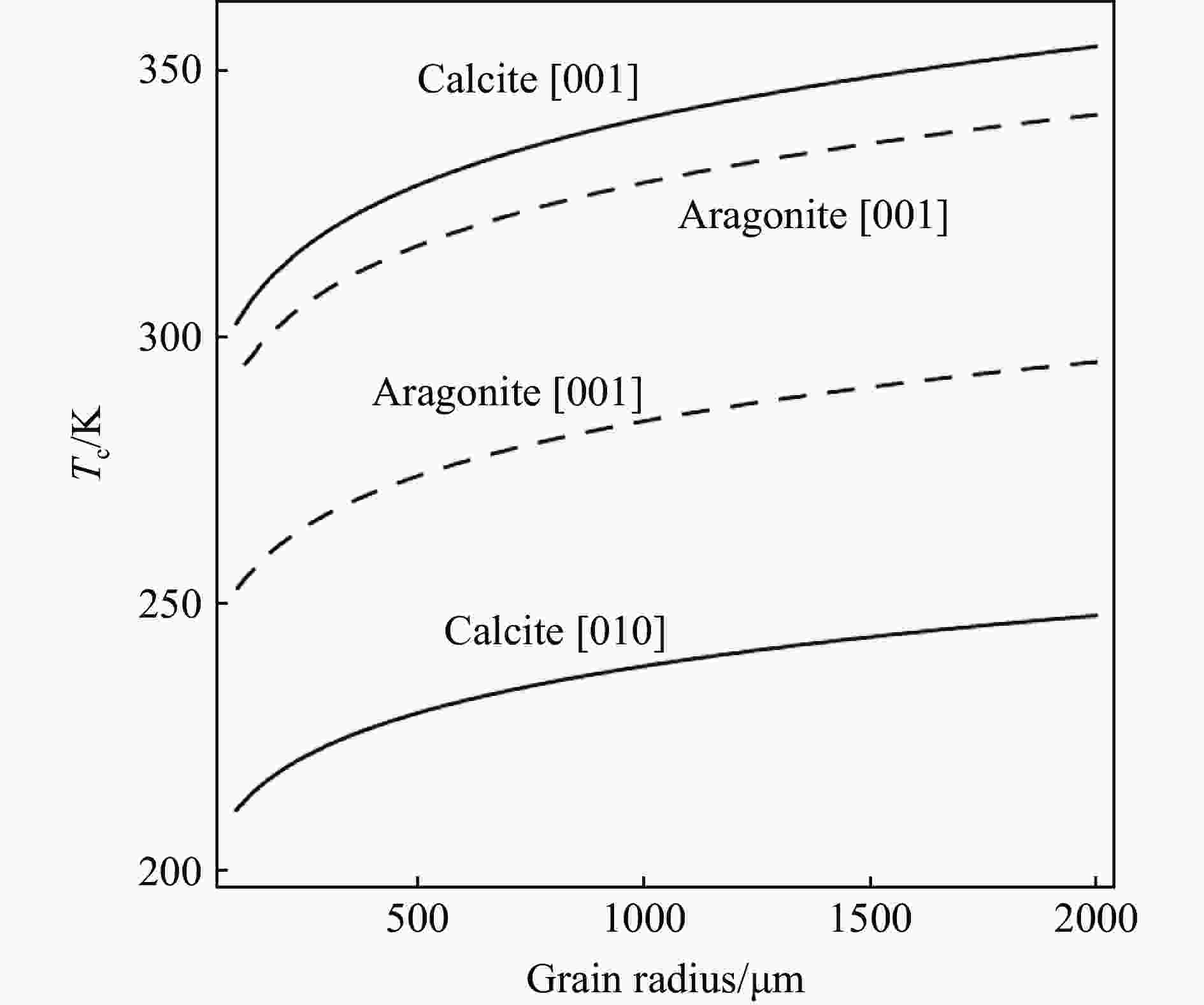
Figure 6. Calculated closure temperature (Tc) as a function of grain radius (a) along different directions in calcite and aragonite (Closure temperature are plotted for assuming spherical geometry (A=55) of the crystals. Helium in each carbonate composition using Dodson’s (1973) equation and a cooling rate of 10 ℃/Ma.)
Table 1. Calculated structural parameters of calcite and aragonite in comparison with previous theoretical and experimental values
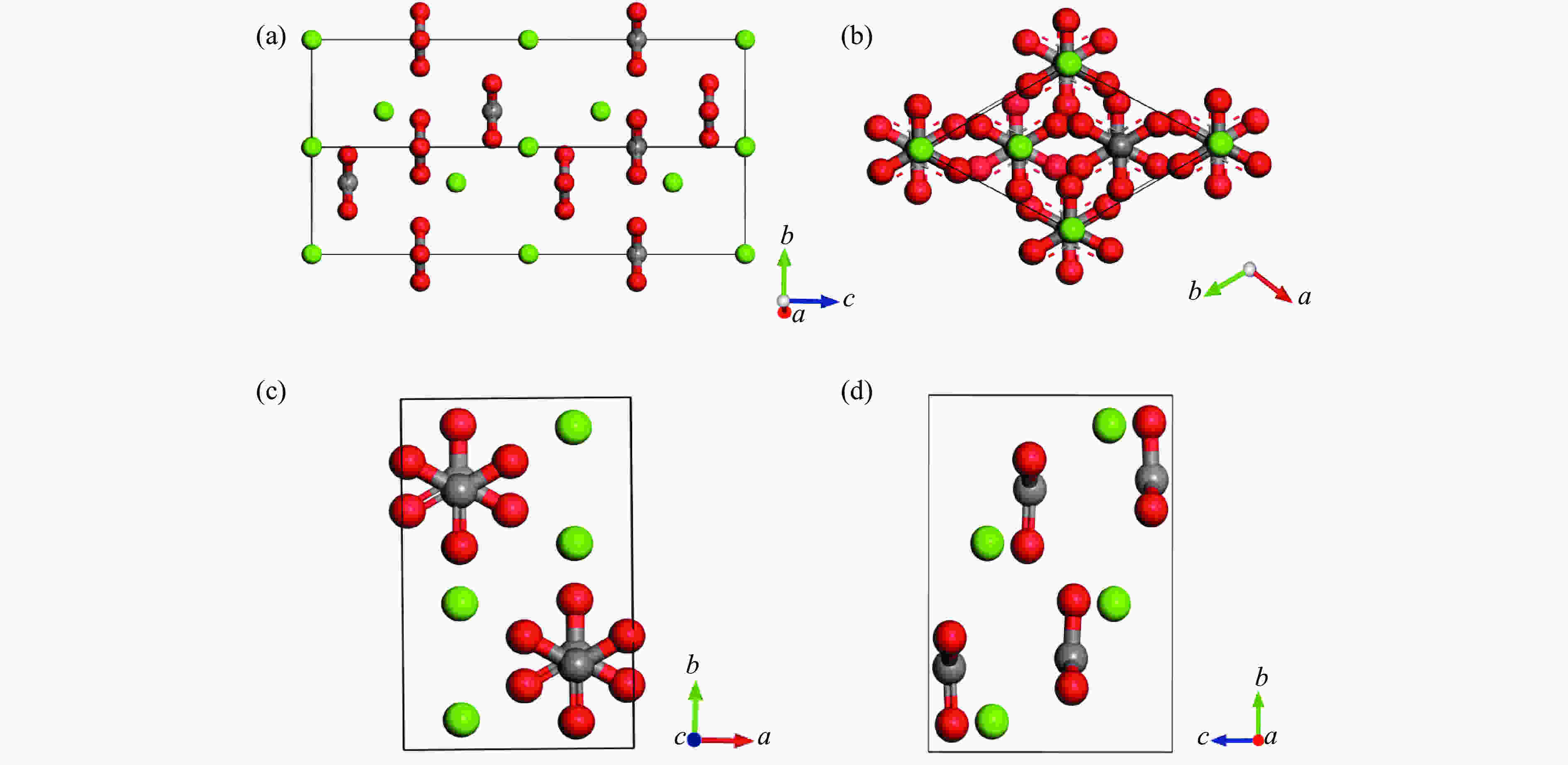
Mineral Data source Unit cell volume/nm3 a/nm b/nm c/nm C-O bond distance/nm Ca-O bond distance/nm Calcite This work 379.58 5.05 17.21 1.299 2.383 Calculation[22] 383.20 5.05 17.33 1.291 2.397 Experiment[23] 368.10 4.99 17.06 1.284 2.359 Aragonite This work 232.58 5.01 8.01 5.79 1.291 2.469 Calculation[24] 233.84 5.02 8.04 5.80 1.292 2.440 Experiment[25] 226.65 4.96 7.96 5.74 1.284 2.414 Table 2. Calculated parameters for helium diffusion in calcite and aragonite under ambient and high pressures
Mineral Pressure/GPa Direction Ea/(kJ·mol–1) v/THz l/nm D0/(m2·s–1) Calcite 0 [010] 67.64 4.29 5.05 5.46×10–7 0 [001] 97.36 4.19 4.71 4.65×10–7 0 [100] 82.40 7.71 5.00 9.64×10–7 0 [001] 96.00 6.34 5.79 1.06×10–6 3 [100] 110.57 7.11 4.98 8.82×10–7 3 [001] 125.43 6.57 5.68 1.06×10–6 Aragonite 6 [100] 115.78 7.03 4.95 8.61×10–7 6 [001] 133.63 6.85 5.85 1.17×10–6 10 [100] 139.42 7.54 4.90 9.05×10–7 10 [001] 160.17 7.56 5.47 1.13×10–6 14 [100] 154.38 7.01 4.86 8.28×10–7 14 [001] 174.45 8.41 5.36 1.21×10–6 Table 3. Summary of the characteristic bond distances of activated states in calcite and aragonite under different pressure conditions (All bond distances are the smallest distances.)
Mineral Pressure/GPa Direction Ca-O bond distance/nm C-O bond distance/nm He-O bond distance/nm Calcite 0 [010] 2.261 1.299 2.033 0 [001] 2.241 1.295 1.922 0 [100] 2.356 1.296 2.141 0 [001] 2.412 1.287 2.042 3 [100] 2.358 1.294 2.067 3 [001] 2.379 1.294 2.002 Aragonite 6 [100] 2.351 1.289 2.026 6 [001] 2.317 1.284 1.970 10 [100] 2.340 1.278 1.982 10 [001] 2.290 1.274 1.927 14 [100] 2.334 1.277 1.951 14 [001] 2.265 1.270 1.909 -
[1] CHERNIAK D J, WATSON E B, THOMAS J B. Diffusion of helium in zircon and apatite [J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(1): 155–166. [2] REICH M, EWING R C, EHLERS T A, et al. Low-temperature anisotropic diffusion of helium in zircon: implications for zircon (U–Th)/He thermochronometry [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(12): 3119–3130. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.033 [3] REINERS P W. Zircon (U-Th)/He thermochronometry [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy Geochemistry, 2005, 58(1): 151–179. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2005.58.6 [4] CHERNIAK D J, AMIDON W, HOBBS D, et al. Diffusion of helium in carbonates: effects of mineral structure and composition [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 165: 449–465. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.06.033 [5] COPELAND P, WATSON E B, URIZAR S C, et al. Alpha thermochronology of carbonates [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(18): 4488–4511. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.004 [6] COPELAND P, COX K, WATSON E B. The potential of crinoids as (U+Th+Sm) /He thermochronometers [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 42: 1–10. [7] CROS A, GAUTHERON C, PAGEL M, et al. 4He behavior in calcite filling viewed by (U-Th)/He dating, 4He diffusion and crystallographic studies [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 125: 414–432. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.09.038 [8] AMIDON W H, HOBBS D, HYNEK S A, et al. Retention of cosmogenic 3He in calcite [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 27: 172–184. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.03.004 [9] BENGTSON A, EWING R C, BECKER U. He diffusion and closure temperatures in apatite and zircon: a density functional theory investigation [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 86: 228–238. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.004 [10] WANG K, BRODHOLT J, LU X. Helium diffusion in olivine based on first principles calculations [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 156: 145–153. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.01.023 [11] BALOUT H, ROQUES J, GAUTHERON C, et al. Helium diffusion in pure hematite (α-Fe3O3) for thermochronometric applications: a theoretical multi-scale study [J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2017, 1099: 21–28. doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2016.11.001 [12] SONG Z, WU H, SHU S, et al. A first-principles and experimental study of helium diffusion in periclase MgO [J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2018, 45(7): 641–654. doi: 10.1007/s00269-018-0949-y [13] DODSON M H. Closure temperatures in cooling geological and petrological systems [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy Petrology, 1973, 40(3): 259–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00373790 [14] HOHENBERG P, KOHN W. Inhomogenous electron gas [J]. Physical Review, 1964, 136: 864–871. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.136.B864 [15] KOHN W, SHAM L J. Quantum density oscillations in an inhomogeneous electron gas [J]. Physical Review, 1965, 137: 1697–1705. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.137.A1697 [16] KRESSE G, FURTHMULLER J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Computational Materials Science, 1996, 6(1): 15–50. doi: 10.1016/0927-0256(96)00008-0 [17] KRESSE G, HAFNER J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid-metals [J]. Physical Review B, 1993, 47(1): 558–561. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.558 [18] BLÖCHL P E. Projected augmented-wave method [J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 50(24): 17953–17979. [19] KRESSE G, JOUBERT D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758–1775. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758 [20] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865–3868. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 [21] CHADI D J. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations [J]. Physical Review B, 1977, 16(4): 1746–1747. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.16.1746 [22] BRIK M G. First-principles calculations of structural, electronic, optical and elastic properties of magnesite MgCO3 and calcite CaCO3 [J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2011, 406(4): 1004–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2010.12.049 [23] MALSEN E N, STRELTSOV V A, STRELTSOVA N R, et al. X-ray study of the electron density in calcite, CaCO3 [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Science, 1993, 49(4): 636–641. doi: 10.1107/S0108768193002575 [24] OGANOV A R, GLASS C W, ONO S. High-pressure phases of CaCO3: crystal structure prediction and experiment [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(1): 95–103. [25] DICKENS B, BOWEN J S. Refinement of the crystal of the aragonite phase of CaCO3 [J]. Physics and Chemistry A, 1971, 75(1): 27–32. [26] HENKELMAN G. Improved tangent estimate in the nudged elastic band method for finding minimum energy paths and saddle points [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2000, 113(22): 9978–9985. doi: 10.1063/1.1323224 [27] VINEYARD G H. Frequency factors and isotope effects in solid state rate processes [J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1957, 3(1/2): 121–127. [28] BENDER M L. Helium-uranium dating of corals [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, 37(5): 1229–1247. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90058-6 -






 下载:
下载: