Numerical Simulation of Penetration in Concrete Sheet Based on SPH Method
-
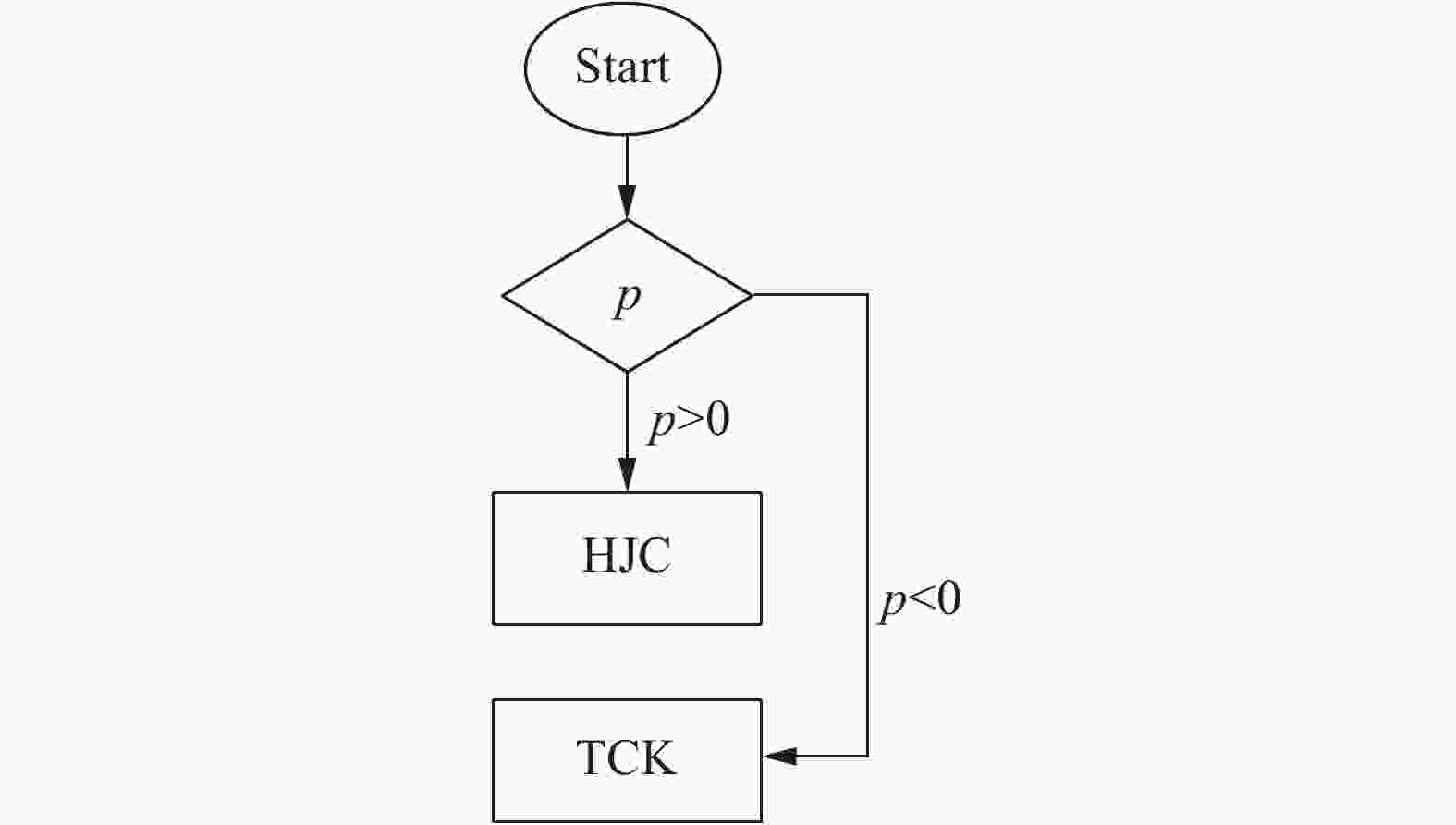
摘要: 随着混凝土结构强度的不断提高,越来越多的防护工事选择混凝土作为主要建筑材料。在光滑粒子流体动力学方法的基础上,提出了TCK-HJC复合本构模型,对锥形弹刚性侵彻过程中混凝土薄板的变形损伤进行数值模拟,采用拟流体模型处理失效的混凝土碎片,分析了不同侵彻角(0°,60°)下锥形弹侵彻混凝土薄板的变形过程,得到了薄板的压力分布以及失效混凝土碎片的飞散角度,并与实验进行对比。结果表明,数值模拟方法是合理的,为进一步研究脆性材料的力学性能奠定了技术基础。
-
关键词:
- 混凝土 /
- TCK-HJC复合本构模型 /
- 光滑粒子流体动力学方法 /
- 脆性材料
Abstract: As the continuous improvement of the strength of concrete structure, more and more protective fortifications have chosen concrete as the main building material. On the basis of the smooth particle hydrodynamics method, the TCK-HJC composite constitutive model is proposed to simulate the deformation damage of the concrete target during the penetration process of the rigid conical projectile, and the pseudo-fluid model is used to describe the failed concrete fragments. The deformation process of the conical projectile penetrating into the concrete target under different penetration angles (0°, 60°) were analyzed, and the pressure on the surface of the target was also obtained. The scattering angles of the broken concrete fragments were obtained, and the comparison with experiment shows the simulation result is robust and accurate, which lays a technical foundation for further simulation of the mechanical properties of brittle materials. -
表 1 混凝土的状态方程和本构方程参数
Table 1. Parameters of equation-of-state equation and constitutive equation of concrete
G/GPa $ \rho $/(kg·m–3) $A$ $B $ $ N $ $ {\dot \varepsilon _0} $/s–1 $ C $ $ {f'_{\rm{c}}} $/MPa $ {S_{\max }} $ 14.8 2450 0.79 1.6 0.61 1.0 0.007 48 7.0 pl/MPa pc/MPa $ {\varepsilon _{\rm{f}}}$ $ {\mu _{\rm{c}}}$ $ {D_1} $ $ {D_2} $ $ {\mu _{{1}}} $ T/MPa K1/GPa 800 16.0 0.01 0.001 0.04 1.0 0.1 5 85 K2/GPa K3/GPa $v $ $\;\beta $ K/(1026 m–3) m $ {K_{{\rm{IC}}}}$/(MPa·m1/2) –171 208 0.27 0.5 1.1452 6 2.758 -
[1] HOLMQUIST T J, TEMPLETON D W, BISHNOI K D. Constitutive modeling of aluminum nitride for large strain, high-strain rate, and high-pressure applications [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(3): 211–231. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00046-4 [2] 孙炜海, 鞠桂玲, 杨班权. 平头弹丸侵彻B4C陶瓷/金属复合靶板的数值模拟 [J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报, 2014, 28(2): 45–48SUN W H, JU G L, YANG B Q. Numerical simulation on penetration of B4C ceramic/metal composite targets struck by flat-ended projectiles [J]. Journal of Academy of Armored Force Engineering, 2014, 28(2): 45–48 [3] BACKMAN M E, GOLDSMITH W. The mechanics of penetration of projectiles into targets [J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 1978, 16(1): 1–99. doi: 10.1016/0020-7225(78)90002-2 [4] 钱伟长. 穿甲力学 [M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 1984.QIAN W C. Penetration mechanics [M]. Beijing: High Education Press, 1984. [5] CORBETT G G, REID S R, JOHNSON W. Impact loading of plates and shells by free-flying projectiles: a review [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(2): 141–230. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00023-4 [6] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, et al. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 465–476. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00048-F [7] LI Q M, REID S R, WEN H M, et al. Local impact effects of hard missiles on concrete targets [J]. International Journal of impact engineering, 2005, 32(1): 224–284. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.04.005 [8] 陈小伟. 穿甲/侵彻问题的若干工程研究进展 [J]. 力学进展, 2009, 39(3): 316–351 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2009.03.006CHEN X W. Advances in the penetration/perforation of rigid projectiles [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2009, 39(3): 316–351 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2009.03.006 [9] LI Q M, CHEN X W. Dimensionless formulae for penetration depth of concrete target impacted by a non-deformable projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(1): 93–116. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00037-4 [10] GEBBEKEN N, GREULICH S, PIETZSCH A. Hugoniot properties for concrete determined by full-scale detonation experiments and flyer-plate-impact tests [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 32(12): 2017–2031. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.08.003 [11] 梁斌. 动能攻坚战斗部对混凝土靶侵爆效应研究 [D].绵阳:中国工程物理研究院, 2009.LIANG B. Research on invading explosion effect of concrete target by kinetic energy [D]. Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2009. [12] 黄民荣.刚性弹体对混凝土靶的侵彻与贯穿机理研究 [D].南京:南京理工大学, 2011.HUANG M R. Penetration and perforation mechanism of rigid projectile into the concrete target [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2011. [13] 邓佳杰, 张先锋, 葛贤坤, 等. 基于局部相互作用理论的侵彻弹头部形状优化及仿真 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(4): 611–620 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0611-10DENG J F, ZHANG X F, GE X K, et al. Nose-shape optimization and simulation of projectiles penetrating into concrete target based on local interaction theory [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(4): 611–620 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0611-10 [14] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HICKERSON J P, et al. Penetration of concrete targets with deceleration-time measurements [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(5): 479–497. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00108-2 [15] 王成, 王万军, 宁建国. 聚能装药对混凝土靶板的侵彻研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2015, 47(4): 672–684WANG C, WANG W J, NING J G. Investigation on shaped charge penetrating into concrete targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2015, 47(4): 672–684 [16] 薛建锋, 沈培辉, 王晓鸣. 弹体斜侵彻混凝土靶的实验研究及其数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(3): 536–543 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0536-08XUE J F, SHEN P H, WANG X M. Experimental study and numerical simulation of projectile obliquely penetrating into concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(3): 536–543 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0536-08 [17] KONG X Z, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Projectile penetration into mortar targets with a broad range of steiking velocities: test and analyses [J]. International of Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 106: 18–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.02.022 [18] GUPTA N K, AITMAN B S, CARGILE J D, et al. Normalimpact of ogive nosed projectiles on thin plates [J]. International of Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(7): 641–660. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00003-3 [19] WARREN T L, FOSSUM A F, FREW D J. Penetration into low-strength (23 MPa) concrete: target characterization andsimulations [J]. International of Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(5): 477–503. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(03)00092-7 [20] 董军, 邓国强, 杨科之, 等. 弹丸对混凝土薄板的冲击破坏效应 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(4): 713–720 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.04.029DONG J, DENG G Q, YANG K Z, et al. Damage effect of thin concrete slabs subjected to projectile impact [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(4): 713–720 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.04.029 [21] 强洪夫, 范树佳, 陈福振, 等. 基于SPH 方法的聚能射流侵彻混凝土靶板数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(4): 516–524 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0516-09QIANG H F, FAN S J, CHEN F Z, et al. Numerical simulation on penetration of concrete target by shaped charge jet with SPH method [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(4): 516–524 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0516-09 [22] 张馨予, 吴艳青, 黄风雷. PBX装药弹体侵彻混凝土薄板的数值模拟 [J]. 含能材料, 2018, 26(1): 101–108ZHANG X Y, WU Y Q, HUANG F L. Numerical simulation on the dynamic damage of PBX charges filled in projectiles during penetrating thin concrete targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2018, 26(1): 101–108 [23] 武海军, 黄风雷, 付跃升, 等. 钢筋混凝土中爆炸破坏效应数值模拟分析 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2007, 27(3): 200–204 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0645.2007.03.004WU H J, HUANG F L, FU Y S, et al. Numerical simulation of reinforced concrete breakage under internal blast loading [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2007, 27(3): 200–204 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0645.2007.03.004 [24] SWEGLE J W, ATTAWAY S W. On the feasibility of using smoothed particle hydrodynamics for underwater explosion calculations [J]. Computational Mechanics, 1995, 17(3): 151–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00364078 [25] LIBERSKY L D, PETSCHEK A G, CARNEY T C, et al. High strain Lagrangian hydrodynamics: a three-dimensional SPH code for dynamic material response [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1993, 109(1): 67–75. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1993.1199 [26] MONAGHAN J J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics [J]. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1992, 30(1): 543–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.30.090192.002551 [27] JOHNSON G R, COOK W. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures [C]// Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Ballistics. The Hague, 1983: 541–547. [28] QIANG H, WANG K, GAO W. Numerical simulation of shaped charge jet using multi-phase SPH method [J]. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2008, 14(1): 495–499. [29] 强洪夫, 孙新亚, 陈福振, 等. 钻地弹侵爆多层混凝土建筑物的SPH 数值模拟 [J/OL]. 爆炸与冲击(2018–06–02) [2018–09–14].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1148.O3.20180531.1019.034.html.QIANG H F, SUN X Y, CHEN F Z, et al. Numerical simulation of earth penetrating weapon penetration and explosion multi-layer concrete structures with SPH method [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves (2018–06–02) [2018–09–14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1148.O3.20180531.1019.034.html. [30] 陈福振, 强洪夫, 高巍然. 气粒两相流传热问题的光滑离散颗粒流体动力学方法数值模拟 [J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(23): 230206 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.230206CHEN F Z, QIANG H F, GAO W R. Numerical simulation of heat transfer in gas-particle two-phase flow with smoothed discrete particle hydro dynamics [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(23): 230206 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.230206 [31] 强洪夫, 高巍然. 完全变光滑长度SPH法及其实现 [J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(5): 569–575 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2008.05.008QIANG H F, GAO W R. SPH method with fully variable smoothing lengths and implementation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2008, 25(5): 569–575 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2008.05.008 [32] 强洪夫.光滑例子流体动力学方法及应用 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 246–287. [33] 金乾坤. 混凝土动态损伤与失效模型 [J]. 兵工学报, 2006, 27(1): 10–14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2006.01.003JIN Q K. Dynamic damage and failure model for concrete materials [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2006, 27(1): 10–14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2006.01.003 -







 下载:
下载: