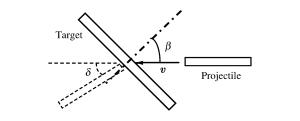
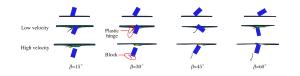
Numerical Study of the Oblique Perforation of Single Thin Metallic Plates
-
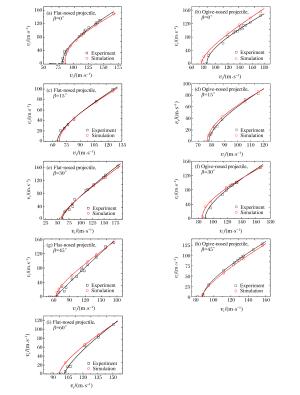
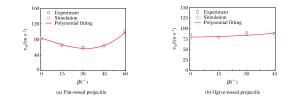
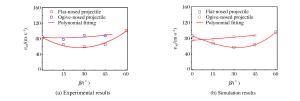
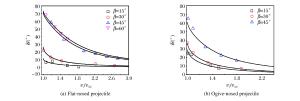
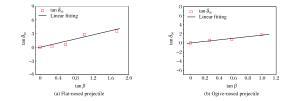
摘要: 通过调用ABAQUS子程序引入修正的靶板J-C本构模型和修正的应力三轴度三分段式失效准则,开展了平头、卵形弹0°~60°斜撞击单层Q235钢薄靶的数值仿真计算,分析了弹体头部形状、撞击角度对靶板防护性能及失效模式的影响,同时对弹体击穿靶板后的角度偏转问题进行了分析,并提出了一个改进的角度偏转半理论模型。结果发现:平头弹在各个撞击角度下较卵形弹更容易击穿靶板;靶板的防护性能与弹体造成的靶板损伤及失效模式紧密相关,单层靶板在平头弹以同一角度分别低速和高速斜撞击后具有不同的失效模式,而在卵形弹斜撞击下失效模式相差不大;仿真与实验结果吻合较好。Abstract: In this study, we conducted numerical simulations of the oblique perforation of single 1 mm-thick Q235 steel plates subjected to flat-and ogive-nosed projectiles at 0°~60° by invoking the ABAQUS subroutine to introduce a modified J-C constitutive model and a modified three-section failure criterion of stress triaxiality, and examined the effects of the projectile nose shape and the obliquity on the ballistic resistance and failure modes of the targets.We also investigated the angle-deflection of the projectiles perforating targets and proposed a modified semi-theoretical model to describe the angle-deflection laws.The results show that the target perforation by flat-nosed projectiles is easier than that by ogive-nosed projectiles at each oblique angles; the ballistic resistance of targets is closely related to the target damages induced by projectile impact; the target has different failure modes as impacted by flat-nosed projectiles at low and high velocities in the same oblique angle respectively, while the failure modes of single target due to impact of ogive-nosed projectiles at different angles do not show much difference.The results of numerical simulation agree well with those of experiments.
-
Key words:
- failure criterion /
- oblique impact /
- ballistic resistance /
- failure mode /
- angle deflection /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 弹体的材料参数
Table 1. Material constants of projectile
Density/(kg·m-3) E/GPa Possion's ratio σ0/MPa Et/GPa 7 850 204 0.33 1 900 15 表 2 Q235钢的本构模型及失效模型相关参数
Table 2. Material constants for Q235 steel
Density/(kg·m-3) E/GPa Possion's ratio Tr/K Tm/K A/MPa 7 800 200 0.33 293 1 795 293.8 B/MPa n C m1 m2 cp/(J·kg-1·K-1) 230.2 0.578 0.065 2 1.762 1.278 469 χ D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 0.9 0.472 18.73 -7.805 -0.019 3 13.017 D6 D01 D02 D03 ${{\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0}}$/s-1 2.338 0.511 -6.80 4.047 2.1×10-3 表 3 平头弹和卵形弹斜撞击单层靶的弹道极限及相应模型参数
Table 3. Ballistic limits and other model constants for single target obliquely impacted byflat- and ogive-nosed projectiles
β Flat-nosed projectile Ogive-nosed projectile a p v50/(m·s-1) a p v50/(m·s-1) 0° 0.95 2.68 86.10 1.06 1.69 75.76 15° 0.92 1.93 67.04 1.01 1.93 76.75 30° 0.99 1.61 57.44 0.97 2.16 84.90 45° 0.99 1.68 63.50 1.14 1.48 86.90 60° 1.18 1.51 95.91 -
[1] BØRVIK T, LANGSETH M, HOPPERSTAD O S, et al.Perforation of 12mm thick steel plates by 20mm diameter projectiles with flat, hemispherical and conical noses:Part Ⅰ:experimental study[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27:19-35. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00034-3 [2] BØRVIK T, HOPPERSTAD O S, BERSTAD T, et al.Perforation of 12mm thick steel plates by 20mm diameter projectiles with flat, hemispherical and conical noses:Part Ⅱ:numerical simulations[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27:37-64. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00035-5 [3] GUPTA N K, IQBAL M A, SEKHON G S.Experimental and numerical studies on the behavior of thin aluminum plates subjected to impact by blunt and hemispherical-nosed projectiles[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 32:1921-1944. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.06.007 [4] GUPTA N K, IQBAL M A, SEKHON G S.Effect of projectile nose shape, impact velocity and target thickness on deformation behavior of aluminum plates[J].International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44:3411-3439. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.09.034 [5] ZHOU D W, STRONGE W J.Ballistic limit for oblique impact of thin sandwich panels and spaced plates[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35:1339-1354. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.08.004 [6] GOLDSMITH W.Non-ideal projectile impact on targets[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1999, 22(2/3):95-395. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/non-ideal-projectile-impact-on-targets-5Ud62WhB2Q [7] IQBAL M A, GUPTA G, GUPTA N K.3D numerical simulations of ductile targets subjected to oblique impact by sharp nosed projectiles[J].International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2010, 47(2):224-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2009.09.032 [8] IQBAL M A, CHAKRABARTI A, BENIWAL S, et al.3D numerical simulations of sharp nosed projectile impact on ductile targets[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(2):185-195. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.09.008 [9] IQBAL M A, SENTHIL K, MADHU V, et al.Oblique impact on single, layered and spaced mild steel targets by 7.62 AP projectile[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 110:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.04.011 [10] GUPTA P K, IQBAL M A, MOHAMMAD Z, et al. Energy absorption in thin metallic targets subjected to oblique projectile impact: a numerical study[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018[2018-01-09]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2017.08.005. [11] BØRVIK T, OLOVSSON L, DEY S, et al.Normal and oblique impact of small arms bullets on AA6082-T4 aluminium protective plates[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(7):577-589. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.02.001 [12] 陈刚, 陈忠富, 张方举, 等.截锥形弹体侵彻薄靶板实验研究[J].弹箭与制导学报, 2005, 25(4):888-890. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=djyzdxb200504285CHEN G, CHEN Z F, ZHANG F J, et al.Experimental study on the penetration of thin plates by truncated conical projectiles[J].Missiles and Guidance, 2005, 25(4):888-890. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=djyzdxb200504285 [13] 陈刚, 陈忠富.截锥形空心弹体侵彻薄靶板的数值模拟[J].弹箭与制导学报, 2008, 28(6):99-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=djyzdxb200806028CHEN G, CHEN Z F.Numerical study on the penetration of thin plates by truncated hollow conical projectiles[J].Missiles and Guidance, 2008, 28(6):99-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=djyzdxb200806028 [14] 张青平, 陈刚, 屈明.截锥型战斗部斜穿靶数值模拟研究[J].含能材料, 2005, 13(4):222-224. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hncl200504006ZHANG Q P, CHEN G, QU M.Numerical study on the oblique perforation of targets by truncated conical warhead[J].Energetic Materials, 2005, 13(4):222-224. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hncl200504006 [15] 黄涛, 吴卫国, 李晓彬, 等.截锥形弹体斜穿甲花瓣型破坏模型[J].振动与冲击, 2010, 29(2):125-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zdycj201002028HUANG T, WU W G, LI X B, et al.Oblique armor-piercing effect of a truncated cylindroconical projectile[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2010, 29(2):125-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zdycj201002028 [16] 徐双喜, 吴卫国, 李晓彬, 等.锥头弹小斜角侵彻薄板剩余速度理论分析[J].弹道学报, 2010, 22(3):58-62. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92261X/201003/35442697.htmlXU S X, WU W G, LI X B, et al.Theoretical analysis on residual velocity of conical projectile after penetrating thin plate at low oblique angle[J].Journal of Ballistics, 2010, 22(3):58-62. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92261X/201003/35442697.html [17] BAO Y B, WIERZBICKI T.On fracture locus in the equivalent strain and stress triaxiality space[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2004, 46(1):81-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2004.02.006 [18] 肖新科. 双层金属靶的抗侵彻性能和Taylor杆的变形与断裂[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D268956XIAO X K. The ballistic resistance of double-layered metallic target and deformation & fracture of Taylor rod[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D268956 [19] 郭子涛, 高斌, 郭钊, 等. 基于J-C模型的Q235钢的动态本构关系研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(4)[2018-01-09]. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/10.11883/bzycj-2016-0333.DOI:10.11883/bzycj-2016-0333.GUO Z T, GAO B, GUO Z, et al. Study on the J-C model based dynamic constitutive relation of Q235 steel[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(4)[2018-01-09]. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/10.11883/bzycj-2016-0333.DOI:10.11883/bzycj-2016-0333. [20] 郭子涛. 弹体入水特性及不同介质中金属靶的抗侵彻性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D241209GUO Z T. Research on characteristics of projectile water entry and ballistic resistance of targets under different mediums[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2012. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D241209 [21] RECHT R, IPSON T W.Ballistic perforation dynamics[J].Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1963, 30(3):384-390. doi: 10.1115/1.3636566 [22] IPSON T W, RECHT R.Ballistic penetration resistance and its measurement[J].Experimental Mechanics, 1975, 15(7):249-257. doi: 10.1007/BF02318057 -







 下载:
下载: