Variation Law for Minimum Ignition Temperature of Coal Dust Layer
-
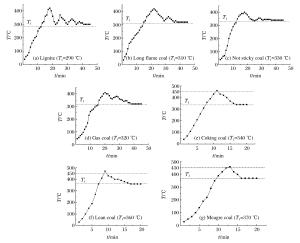
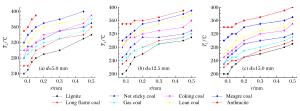
摘要: 为研究煤尘层最低着火温度随煤样变质程度、煤尘粒径及煤尘层厚度的变化规律,采用煤尘层最低着火温度测定系统进行实验研究,结果表明:随着煤样由褐煤到无烟煤变质程度逐渐增大,煤尘层最低着火温度由290℃上升到400℃以上,同时,褐煤、长焰煤、不粘煤、气煤煤尘层着火时观察到明显的火焰。随着煤尘粒径不断减小,不同煤质的煤尘层最低着火温度明显减小,煤尘层厚度为15 mm时,随着煤尘粒径由0.5 mm减小至0.075 mm,不同煤质煤尘层最低着火温度分别减小了31.0%、26.7%、28.1%、25.8%、28.6%、27.8%、18.9%和15.0%,煤尘粒径影响作用十分显著。随着煤尘层厚度的增大,不同煤质在不同粒径下的煤尘层最低着火温度都减小,其中无烟煤的变化最不明显。Abstract: In this paper we studied the variation of the minimum ignition temperature of coal dust layer with its metamorphism, particle size and thickness using the minimum ignition temperature measurement system.The results showed that, with the gradual increase of its degree of metamorphism, the minimum ignition temperature of coal dust layer varied from 290℃ to above 400℃; and that when the coal dust layer of lignite, long flame coal, non-stick coal, gas coal were ignited, an obvious flame was observed; and that, as the coal dust particle size decreased, the minimum ignition temperature of different kinds of the coal dust layer exhibited a significant reduction trend.It was found that when the thickness of the layer is 15 mm, with the particle size decreasing from 0.5 mm to 0.075 mm, the minimum ignition temperature decreased by 31.0%, 26.7%, 28.1%, 25.8%, 28.6%, 27.8%, 18.9% and 15.0%, respectively, indicating a very obvious effect of the coal dust particle size.With the increase of the layer's thickness, the minimum ignition temperature of different kinds of the coal dust layer exhibited a decreasing trend, while the trend of anthracite was the least significant.
-
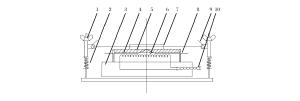
图 2 煤尘层最低着火温度测定装置结构
Figure 2. Structure of coal dust layer MIT tester
1.Thermocouple height adjustment knob; 2.Spring; 3.Heater base; 4.Recording thermocouple on hot plate surface; 5.Hot plate surface; 6.Heater; 7.Metal ring; 8.Control thermocouple on hot plate surface; 9.Dust layer thermocouple; 10.Heater leads
表 1 8种煤质的煤尘层最低着火温度
Table 1. Coal dust layer MIT of 8 kinds of coal quality
No. Coal quality Particle size/mm Thickness/mm Minimum ignition temperature/℃ Ignition type Ignition time/min 1 Lignite 0.2 5 290 a 18 2 Long flame coal 0.2 5 310 a 22 3 Not sticky coal 0.2 5 330 a 18 4 Gas coal 0.2 5 320 a 20 5 Coking coal 0.2 5 340 c 11 6 Lean coal 0.2 5 360 c 9 7 Meagre coal 0.2 5 370 c 13 8 Anthracite 0.2 5 >400 No fire >30 -
[1] 金龙哲.矿井粉尘防治理论[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:22-30.JIN L Z.Dust prevention theory in mine[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2010:22-30. [2] 毕明树.气体和粉尘爆炸防治工程学[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2012:39-48.BI M S.Gas and dust explosion prevention engineering sciences[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2012:39-48. [3] 毕明树, 李江波.密闭管内甲烷-煤粉复合爆炸火焰传播规律的实验研究[J].煤炭学报, 2010, 35(8):1298-1302. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4235181BI M S, LI J B.Experimental study on flame propagation law of methane-pulverized coal compound explosion in closed tube[J].Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(8):1298-1302. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4235181 [4] 宫广东, 刘庆明, 胡永利.管道中煤尘爆炸特性实验[J].煤炭学报, 2010, 35(4):609-612. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=mtxb201004020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQGONG G D, LIU Q M, HU Y L.Experimental study on explosion characteristics of coal dust in pipeline[J].Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(4):609-612. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=mtxb201004020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [5] 牛芳, 刘庆明, 白春华.甲烷-煤尘爆炸物火焰传播特性[J].高压物理学报, 2012, 26(4):455-461. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2012.04.015NIU F, LIU Q M, BAI C H.Flame propagation characteristics of methane-coal dust explosion[J].Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2012, 26(4):455-461. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2012.04.015 [6] 李雨成.矿井粉尘防治理论及技术[M].北京:煤炭工业出版社, 2015:35-56.LI Y C.Dust prevention theory and technology in mine[M].Beijing:Coal Industry Press, 2015:35-56. [7] 陈金健. 煤尘云最低着火温度及抑制技术研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10110-1016179809.htmCHEN J J. Study on lowest ignition temperature and suppression technology of coal dust cloud[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10110-1016179809.htm [8] 李润之.不同挥发分煤尘层最低着火温度变化规律研究[J].安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(3):954-957. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=aqhj201703029&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLI R Z.Study on variation law of minimum ignition temperature of different volatile coal dust[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(3):954-957. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=aqhj201703029&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [9] 司荣军, 王春秋.瓦斯对煤尘爆炸特性影响的实验研究[J].中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(12):86-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.12.016SI R J, WANG C Q.Experimental study on the effect of gas on coal dust explosion characteristics[J].China Safety Science Journal, 2006, 16(12):86-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.12.016 [10] 屈姣. 甲烷和煤尘爆炸特性实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2015. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D719360QU J. Study on explosion characteristics of gas and coal dust[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Technology University, 2015. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D719360 [11] 宋广朋. 瓦斯煤尘共存的爆炸特性与传播研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10424-1012276655.htmSONG G P. Study on ignition mechanism and experimental study of coal powder gas coupling system[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10424-1012276655.htm [12] 平洋. 煤粉瓦斯耦合体系着火机理和实验研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10145-1013116384.htmPING Y. Study on ignition mechanism and experimental study of coal powder gas coupling system[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10145-1013116384.htm -







 下载:
下载: