Effect of Temperature on Grüneisen Parameters of Aluminum and Sodium Chloride by Rapid Compression Method
-
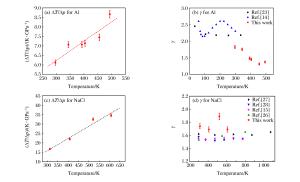
摘要: 根据Grüneisen状态方程导出的偏导关系式γ=(KS/T)(∂T/∂p)S(其中KS是绝热体积弹性模量),采用快速增压方法结合中值定理分别在297~494 K和312~608 K温度范围内研究了铝和氯化钠的Grüneisen参数γ随温度的变化关系。在平面对顶压砧模具上设计了内加热的样品组装方式,测量了不同温度下快速增压过程中样品的温升曲线和压力变化曲线,并对温升曲线进行了温度修正,使所得结果更接近绝热压缩过程。实验结果表明:铝和氯化钠在实验温度范围内、压力分别为2.17 GPa和1.46 GPa下,其ΔT/Δp值随着温度的升高而增大;γ值随着温度的升高表现为波动的变化趋势,与温度没有明显的变化关系。
-
关键词:
- Grüneisen参数 /
- 高温高压 /
- 快速增压 /
- 氯化钠 /
- 铝
Abstract: In this work, we measured the Grüneisen parameter γ of aluminum in 297-494 K under 2.17 GPa and the γ of sodium chloride in 312-608 K under 1.46 GPa, based on the Grüneisen differential equation γ=(KS/T)(∂T/∂p)S (where KS is the adiabatic elastic bulk modulus), combining the rapid compression method with the mean value theorem.A setup for internal heating was designed to produce high temperature in the sample chamber and the rapid compression on sample at different temperatures was carried out in a Bridgman anvil by a self-made rapid compression apparatus.The curves of temperature and pressure rise of the sample were recorded during rapid compression.For compensating the heat loss due to heat conduction, the temperature-rise curve was modified according to the cooling rate of the sample during the pressure-holding process.The temperature-rise curve after compensation is closer to that of adiabatic compression.It was found that for aluminum under 2.17 GPa and sodium chloride under 1.46 GPa, the ΔT/Δp increases with the increasing temperature while the Grüneisen parameters fluctuate, showing no obvious relationship with temperature in the experimental temperature range.-
Key words:
- Grüneisen parameter /
- high temperature high pressure /
- rapid compression /
- NaCl /
- Al
-
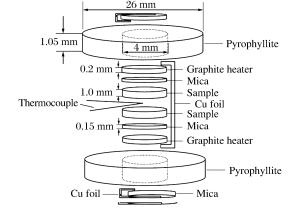
图 2 室温下快速增压过程中样品铝的压力、温度随时间变化曲线(a),以及修正前、后的温升曲线(b);380K温度下快速增压过程中样品铝的压力、温度随时间变化曲线(c),以及修正前、后的温升曲线(d)
Figure 2. T(t), p(t) curves of Al during rapid compression at room temperature (a) and the recorded and corrected T(t) curves (b); T(t), p(t) curves of Al during rapid compression at 380K (c) and the recorded and corrected T(t) curves (d)
图 4 室温下快速增压过程中氯化钠样品的压力、温度随时间变化曲线(a),以及修正前、后的温升曲线(b);488K温度下快速增压过程中氯化钠样品的压力、温度随时间变化曲线(c),以及修正前、后的温升曲线(d)
Figure 4. T(t), p(t) curves of NaCl during rapid compression at room temperature (a) and the recorded and corrected T(t) curves (b); T(t), p(t) curves of NaCl during rapid compression at 488K (c) and the recorded and corrected T(t) curves (d)
表 1 样品铝的实验参数及γ值
Table 1. Experimental parameters and γ values of Al
No. T1/
KT2/
KTm/
KΔp/
GPapm/
GPaKS[32-33]/
GPa$ \frac{{\Delta T}}{{\Delta p}}/\left( {{\rm{K}} \cdot {\rm{GP}}{{\rm{a}}^{ - 1}}} \right)$ γ 1 287 307 297 3.27 2.30 88.16±0.21 6.12±0.14 1.82±0.05 2 331 357 344 3.68 2.17 85.25±0.20 7.07±0.16 1.75±0.04 3 380 406 393 3.68 2.00 82.04±0.20 7.07±0.16 1.48±0.04 4 391 417 404 3.64 2.10 82.04±0.20 7.14±0.16 1.45±0.04 5 443 469 456 3.49 2.23 80.24±0.19 7.45±0.17 1.31±0.03 6 479 509 494 3.46 2.19 78.23±0.19 8.67±0.20 1.37±0.03 表 2 样品氯化钠的实验参数及γ值
Table 2. Experimental parameters and γ value of NaCl
No. T1/
KT2/
KTm/
KΔp/
GPapm/
GPaKS[26]/
GPa$ \frac{{\Delta T}}{{\Delta p}}/\left( {{\rm{K}} \cdot {\rm{GP}}{{\rm{a}}^{ - 1}}} \right)$ γ 1 291 332 312 2.45 1.43 32.54±0.08 16.73±0.38 1.74±0.04 2 385 431 408 2.09 1.42 31.42±0.08 22.01±0.51 1.69±0.04 3 488 553 521 2.00 1.46 30.41±0.07 32.50±0.75 1.89±0.05 4 566 649 608 2.40 1.54 29.70±0.07 34.58±0.80 1.69±0.04 -
[1] 经福谦.实验物态方程导引[M].第2版.北京:科学出版社, 1999:25-29.JING F Q.Introduction to experimental equation of state[M]. 2nd ed.Beijing:Science Press, 1999:25-29. [2] 吴强.金属材料高压物态方程及Grünesisen系数的研究.绵阳:中国工程物理研究院, 2004:69-79. http://www.docin.com/p-243112213.htmlWU Q.Studies on equation of state and Grüneisen parameter for metals at high pressures and temperatures.Mianyang:China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2004:69-79. http://www.docin.com/p-243112213.html [3] 谢鸿森.地球深部物质科学导论[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997:104-110.XIE H S.Introduction to earth interior material science[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1997:104-110. [4] 汤文辉, 张若棋.物态方程理论及计算概论[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2008:1-306.TANG W H, ZHANG R Q.Introduction to theory and calculation of equation of state[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press, 2008:1-306. [5] IRVINE R D, STACEY F D.Pressure dependence of the thermal Grüneisen parameter, with application to the Earth's lower mantle and outer core[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1975, 11:157-165. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(75)90009-6 [6] 张万箱.固体的特征频率及系数的普遍表达式[J].物理学报, 1984, 33(8):1120-1128. doi: 10.7498/aps.33.1120ZHANG W X.General expressions of the characteristic frequency and Grüneisen coeffcient for solids[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 1984, 33(8):1120-1128. doi: 10.7498/aps.33.1120 [7] QUARENI F, MULARGIA F.The validity of the common approximate expressions for the Grüneisen parameter[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1988, 93:505-519. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1988.tb03877.x [8] VASCHENKO V Y, ZUBAREV V N.Concerning the Grüneisen constant[J]. Soviet Physics-Solid State, 1963, 5:653-655. [9] VǑCADLO N L, PRICE G D.The Grüneisen parameter-computer calculations via lattice dynamics[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1994, 82(3):261-270. [10] ANDERSON O L.The Grüneisen ratio for the last 30 years[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2000, 143(2):279-294. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2000.01266.x [11] WU Q, JING F Q, LI X Z.Behaviour of Grüneisen parameter at high pressure and temperature inferred from shock compression data[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 19(4):528-530. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231115116_Behaviour_of_Gruneisen_Parameter_at_High_Pressure_and_Temperature_Inferred_from_Shock_Compression_Data [12] GAUSTER W B.Low-temperature Grüneisen parameters for silicon and aluminum[J]. Physical Review B, 1971, 4(4):1288-1296. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.4.1288 [13] BOEHLER R, RAMAKRISHNAN J.Experimental results on the pressure dependence of the Grüneisen parameter:a review[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 1980, 85(B12):6996-7002. doi: 10.1029/JB085iB12p06996 [14] BANDYOPADHYAY J, GUPTA K P.Low temperature lattice parameters of Al and Al-Zn alloys and Grüneisen parameter of Al[J]. Cryogenics, 1978, 18(1):54-55. doi: 10.1016/0011-2275(78)90141-8 [15] BIRCH F.Equation of state and thermodynamic parameters of NaCl to 300 kbar in the high-temperature domain[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1986, 91(B5):4949-4954. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB05p04949 [16] 王筑明, 谢鸿森, 郭捷, 等.高压下铝的Grüneisen参数的实验测量[J].高压物理学报, 1998, 12(1):54-58. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.1998.01.009WANG Z M, XIE H S, GUO J, et al.Measurement of Grüneisen parameter of aluminium at high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 1998, 12(1):54-58. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.1998.01.009 [17] BOEHLER R, GETTING I C, KENNEDY G C.Grüneisen parameter of NaCl at high compressions[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1977, 38(3):233-236. doi: 10.1016/0022-3697(77)90095-6 [18] RAMAKRISHNAN J, BOEHLER R, HIGGINS G H, et al.Behavior of Grüneisen parameter of some metals at high pressures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1978, 83(B7):3535-3538. doi: 10.1029/JB083iB07p03535 [19] HONG S M, CHEN L Y, LIU X R, et al.High pressure jump apparatus for measuring Grüneisen parameter of NaCl and studying metastable amorphous phase of poly (ethylene terephthalate)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2005, 76(5):053905. doi: 10.1063/1.1899443 [20] 陈丽英. 快速大幅度增压法测量NaCl的Grüneisen参数. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006.CHEN L Y. Measuring Grüneisen parameter of NaCl by double-quick and larger range comperssion. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2006. [21] HUANG D H, LIU X R, SU L, et al.Measuring Grüneisen parameter of lead by pressure-jump method[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2007, 24(8):2441-2443. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/24/8/078 [22] HUANG D H, LIU X R, SU L, et al.Measuring Grüneisen parameter of iron and copper by an improved pressure-jump method[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2007, 40:5327-5330. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/40/17/047 [23] TOLPADI S.Isobaric and isochoric Grüneisen parameters of Al and Cu[J]. Solid State Communications, 1975, 16(7):937-939. doi: 10.1016/0038-1098(75)90898-4 [24] HUZAN E, ABBISS C P, JONES G O.Thermai expansion of aluminium at low temperatures[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1961, 6(62):277-285. doi: 10.1080/14786436108243317 [25] SINGH V P, HEMKAR M P.Dynamical study for the Grüneisen parameters in FCC metals[J]. Journal of Physics F:Metal Physics, 1977, 7(5):760-768. [26] SPETZLER H, SAMMIS C G, O'CONNELL R J.Equation of state of NaCl:ultrasonic measurements to 8 kbar and 800℃ and static lattice theory[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1972, 33(9):1727-1750. [27] BOEHLER R.Adiabats (∂T/∂P)s and Grüneisen parameter of NaCl up to 50 kilobars and 800℃[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(B8):7159-7162. doi: 10.1029/JB086iB08p07159 [28] CAI L C, CHEN Q F, CUI S X, et al.The Grüneisen parameter of NaCl at high pressures and temperatures:a molecular dynamics study[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2005, 22(2):514-516. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/22/2/069 [29] CUI S X, CAI L C, HU H Q, et al.Melting behavior and the Grüneisen parameter of NaCl at high pressures:a molecular dynamical study[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2010, 24(3):331-341. doi: 10.1142/S0217979210053604 [30] CHENG V M, ALLEN P C, LAZARUS D.Pressure coefficient of thermoelectric power of platinum/platinum-10% rhodium and Chromel/Alumel thermocouples[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1975, 26(1):6-7. doi: 10.1063/1.87967 [31] 陈丽英. 快速增压发测量物质的等熵压缩曲线及W-J参数. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014.CHEN L Y. Measuring of the isentropic compression curve and W-J parameter via a pressure jump method. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. [32] SUTTON P M.The variation of the elastic constants of crystalline aluminum with temperature between 63 K and 773 K[J]. Physical Review B, 1953, 91(4):816-821. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.91.816 [33] SCHMUNK R E, SMITH C S.Pressure derivatives of the elastic constants of aluminum and magnesium[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1959, 9(2):100-112. doi: 10.1016/0022-3697(59)90200-8 [34] 张书霞. 高温高压合成实验所用传压介质的研究. 成都: 四川大学, 2006.ZHANG S X. A study on pressure medium for high pressure and high temperature experiment. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2006. [35] ZHANG T, WU M Q, HE M, et al.A study and comparison of calculating Grüneisen parameter using different methods[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 146/147:1102-1107. https://www.scientific.net/amr.146-147.1102.pdf -






 下载:
下载: