Characteristic Analysis of Acoustic Emission Signals Caused by Debris Cloud Impact
-
摘要: 为了掌握带防护屏的航天器结构受空间碎片超高速撞击时的声发射信号特征,利用二级轻气炮发射球形弹丸撞击铝合金双层板结构,获取了碎片云撞击铝合金板舱壁产生的声发射信号,并利用小波包技术和能量熵理论对信号进行了分析。实验结果表明:弹丸初始速度、防护屏厚度及弹丸直径是决定二次碎片云形态及声发射信号特征的重要因素;在本实验工况范围内,小波包能量熵值能够描述声发射信号频率的复杂程度;当弹丸初始速度处于破碎段(3~7 km/s)时,随着初始速度的增大,二次碎片云进一步细化,撞击产生的声发射信号幅值趋于减小、频率成分趋于复杂化,其小波包能量熵值逐渐增大;防护屏厚度对声发射信号的小波包能量熵值影响较大,弹丸直径对其影响较小。研究结果有助于实现对碎片云撞击舱壁结构的损伤模式识别。Abstract: In order to understand the characteristics of acoustic emission signals caused by hypervelocity space debris impacting spacecraft with shields, a two-stage light gas gun was used to launch sphere projectiles to impact an aluminum-alloy Whipple shield, the induced acoustic emission signals were acquired, and analyzed by wavelet packet technology and energy entropy theory.The experimental results indicate that, the initial velocity of projectile, bumper thickness and projectile diameter are important factors to decide the form of debris cloud and characteristics of acoustic emission signals.The wavelet packet energy entropy could be used to describe the frequency complexity of debris cloud impact signals.When the initial velocity of projectile increases in the broken section (3-7 km/s), along with which the projectile breaks more completely and the energy entropy of acoustic emission signals increases.Under the experimental conditions, the bumper thickness has greater influence on energy entropy values than the projectile diameter.The wavelet packet energy entropy is helpful to estimate the initial velocity of projectile and the maximum impact damage region, combined with the predicted curve from the Christiansen ballistic limit equation, the damage pattern recognition of the bulkhead could be assessed.
-
Key words:
- debris cloud /
- hypervelocity impact /
- acoustic emission /
- wavelet packet energy entropy
-
在航空航天研究领域中,弹道冲击试验作为研究材料抗冲击性能的重要途径被广泛应用。弹靶撞击问题是典型的非线性动态响应问题,试验结果不但与弹体和靶板的几何结构相关[1-2],且靶板的变形和破坏模式强烈依赖靶板材料的力学性能,而温度又是影响材料性能的重要因素之一[3]。GH4169镍基高温合金作为航天器中在高温高速工况下服役的常用零件材料,可以通过高温弹道冲击试验方法研究其在高温高速冲击载荷作用下的变形破坏机理和抗冲击性能。
目前,大多采用热辐射、热对流、接触热传导和电流焦耳热等技术开展高温弹道冲击试验。加热靶板的方法有电阻式加热炉法、接触式热惯性法、大电流加热法等,从而实现弹道冲击试验中靶板的高温试验条件。因弹道冲击试验中易产生沿弹体运动方向的高速破片,郑百林等[4]和Liu等[5-6]通过在靶板单侧设置加热炉形成可流通热空气的箱体,并通过风扇使热空气在箱体风道中循环,从而对靶板进行加热,成功实现了尺寸为180 mm×180 mm×1 mm的GH4169靶板600 ℃高温弹道冲击试验。Yang等[7]在靶板单侧布置了可移动的电加热高温板,通过高温板与目标靶板接触传热对尺寸为115 mm×115 mm×3 mm的C/SiC复合材料靶板进行加热,实现了900 ℃高温弹道冲击试验。然而,通过单侧加热装置对靶板进行加热势必会导致沿靶板厚度方向产生温度梯度,不利于保证靶板温度均匀,而且这种现象会随着靶板厚度的增加而越发明显。因此,有学者将靶板完全置于高温辐射炉内进行高温弹道冲击试验。例如:Erice等[8]通过可滑动支架结构将靶板置于环形高温炉中,待靶板加热至目标温度后撤掉高温炉两端隔温板,高速弹丸穿过高温炉腔后撞击置于高温炉腔内的靶板,由此对1.6 mm厚的Inconel 718靶板开展了700 ℃高温弹道冲击试验。由于高温加热装置并未与靶板分离,因此在试验过程中高速撞击产生的碎片可能会损坏高温加热装置,从而增加试验的难度和成本。Xie等[9]采用快速电加热系统,通过对C/C复合材料靶板两端施加电压,在靶板中产生10~5000 A的大电流,从而实现了靶板温度为1200 ℃的高温弹道冲击试验。然而,对金属材料施加大电流会导致电塑性效应引起材料原有性能发生改变[10]。另外,还有一些其他高温冲击试验方法。Zhong等[11]采用Zwick/Roell450摆锤冲击试验机对尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×55 mm 的ZA27合金试样进行了250 ℃高温冲击韧性试验,获得了不同温度下材料的冲击韧性。Rojacz等[12]采用落锤试验机对NiCrBSi金属基复合材料进行了冲击速度为1.79 m/s、冲击能量为8 J的700 ℃高温冲击试验。然而,落锤或摆锤试验并不便于实现大于100 m/s的高速冲击试验。上述不同高温冲击试验方法既存在优势又有弊端,因此建立一种既能够保证靶板实现均匀温度场,又能够方便地对不同材料类型和尺寸的靶板开展高温抗冲击性能研究的高温高速弹道冲击试验方法,仍需要开展进一步的研究工作。
本研究将采用对称式加热方法建立一种同步控制高温高速弹道冲击的试验方法,借鉴高温高应变率Hopkinson杆试验方法[13-14]中的同步组装试验技术,通过温度检测系统对试验过程中靶板的温度进行实时监测,分析冲击速度与靶板高温移除时间对靶板冲击时刻温度均匀性的影响。最后,采用此试验方法开展直径为24 mm的硬质弹丸对厚度为2 mm的GH4169镍基高温合金靶板在500 ℃高温及常温条件下的弹道冲击试验,分析GH4169镍基高温合金靶板受到冲击后的变形与破坏行为,并考察其在高温条件下的抗冲击性能。
1. 试验技术
1.1 高温冲击试验方法
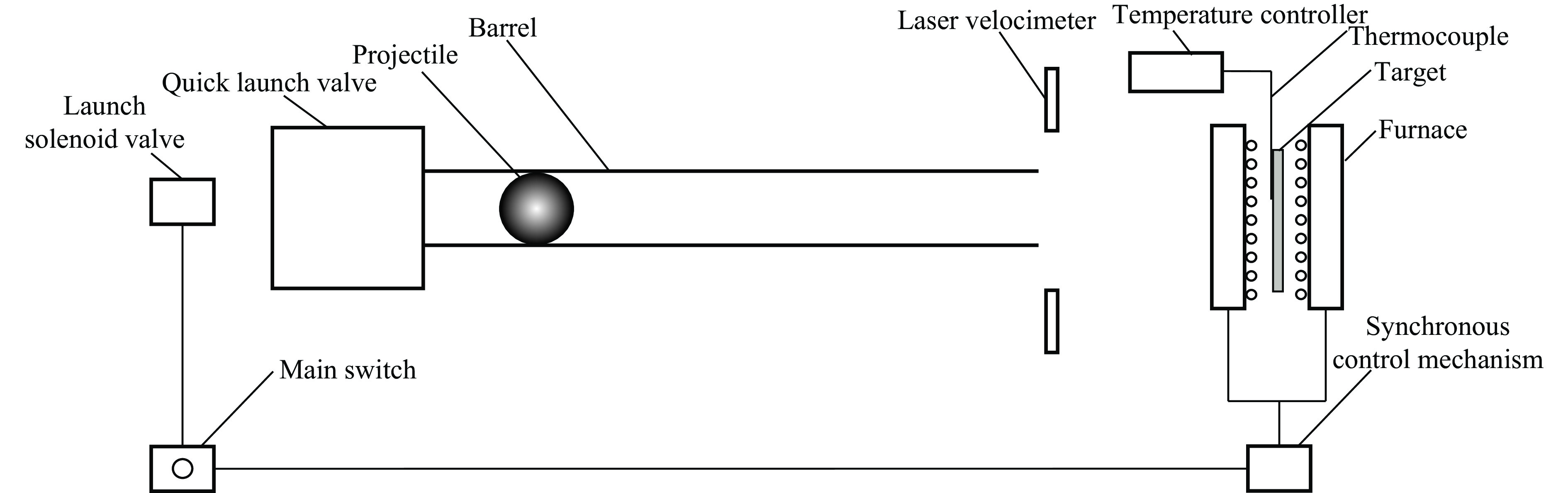
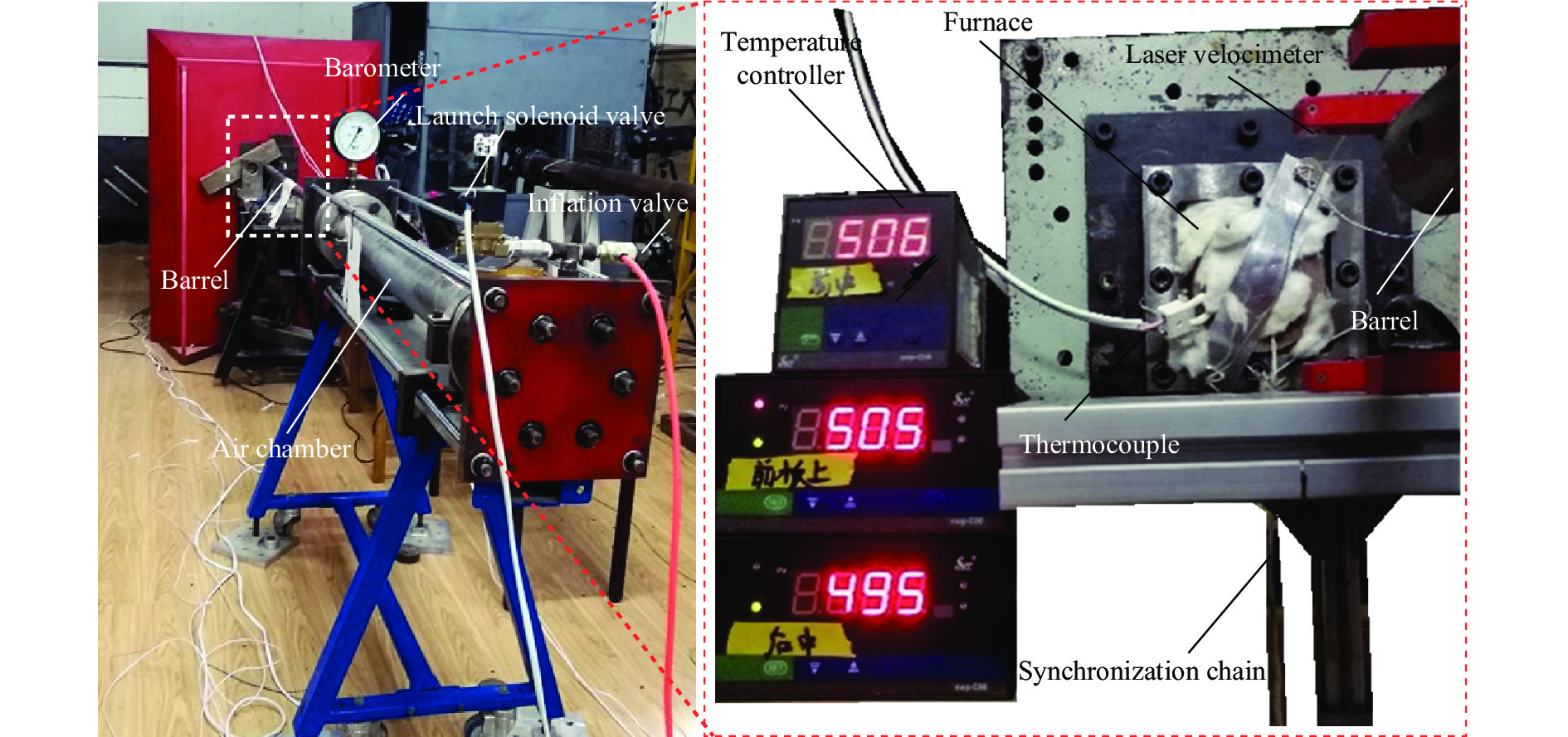
为了检测GH4169镍基高温合金靶板在高温高速冲击载荷作用下的抗冲击性能,建立了一种应用高温同步技术的弹道冲击试验方法。与文献[8]的试验方法不同,本研究以在线预加热方式加热固定靶板,并将高温炉设计为可移动形式。试验装置由弹体发射系统、可控式高温加热系统和同步控制系统3部分组成。弹体发射系统采用一级空气炮发射装置,推进气体介质可选择空气、氮气或氦气等高压气体,并采用激光测速仪测量弹体的冲击速度。可控式高温加热系统主要包含对称高温电阻加热炉、温控仪和调压器,在预加热过程中采用热电偶(K型)对靶板温度进行实时监控。为了保证试验中靶板撞击区域的温度场均匀,与文献[4-8]中采用的高温加热布置方式不同,本研究中在靶板正面与反面对称布置了两个高温电阻加热炉,使靶板完全处于高温环境中,从而避免靶板沿厚度方向产生温度梯度。同步控制系统主要由控制总开关、控制空气炮发射的电磁阀和高温炉控制移除装置组成。图1为高温冲击试验系统示意图,图2为高温弹道冲击靶板试验装置实物。
1.2 高温同步冲击控制技术
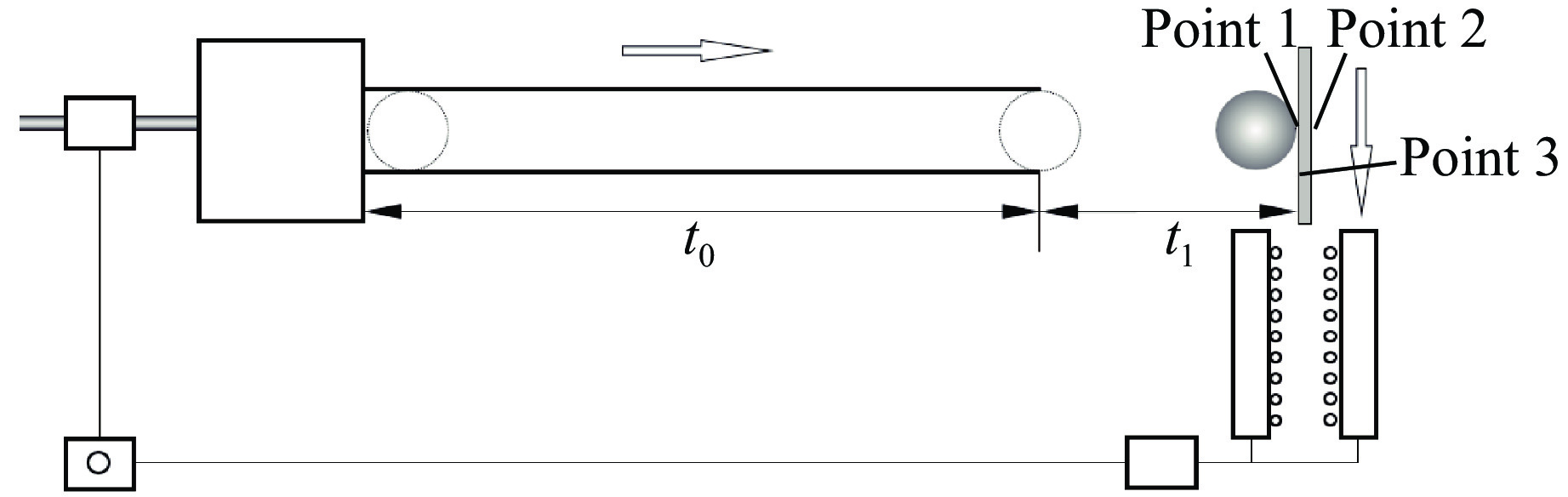
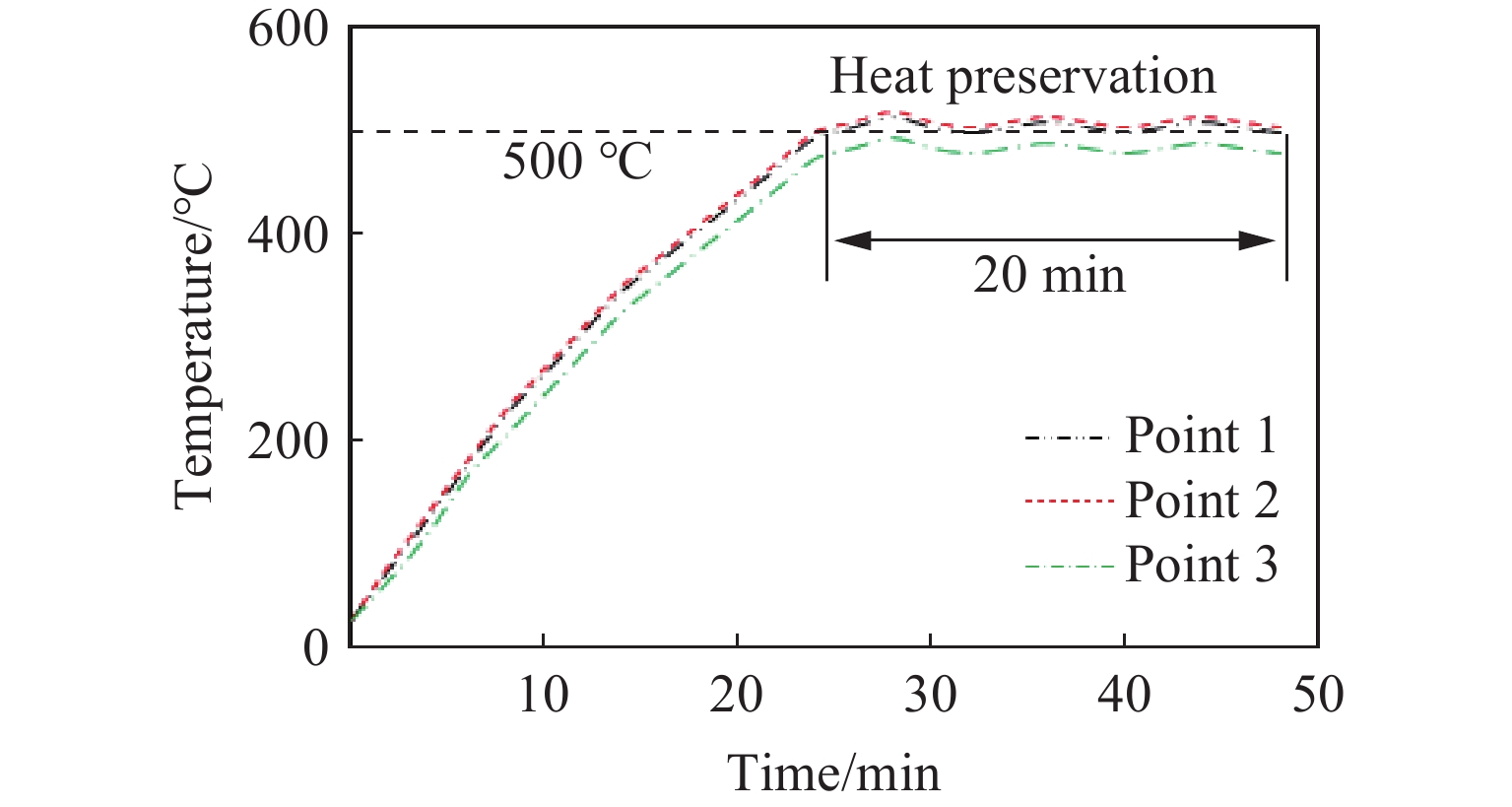
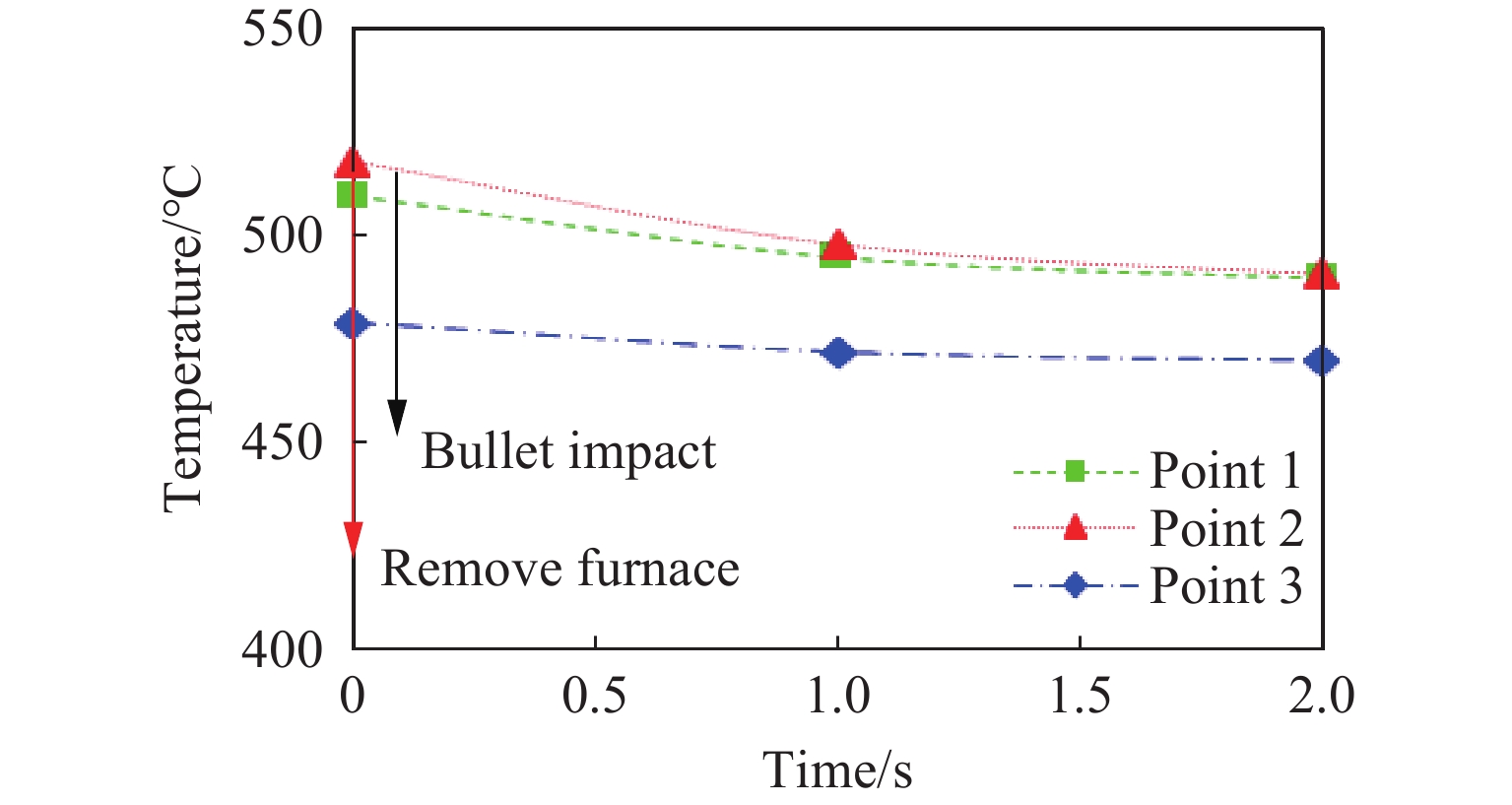
本研究中建立的高温弹道冲击试验方法采用对称布置电阻炉同时加热靶板两侧,保证试验前靶板正、背面温度均匀,高温炉布置方式见图1。通过试验装置中的温度调节控制系统控制温度,可使靶板在冲击试验开始前获得均匀的(500±5) ℃ 温度场试验条件。如图3所示,在靶板正面和背面布置3个温度测点,测点1和测点2的位置为靶板正面和背面的中心,测点3在测点1的面内且距离中心点30 mm。t0为弹丸在炮管中加速经历的时间,t1为弹体从炮口位置匀速运动到靶板经历的时间。靶板的目标加热温度为500 ℃,在升温过程中,3个测点的温度随时间变化情况见图4,持续加热25 min后靶板温度达到目标加热温度,保温20 min后进行弹道冲击试验。
高温弹道冲击试验中的高温同步冲击过程由电磁阀控制开关和高温炉移除装置控制,开启发射阀门开关后,高压气体推动弹丸做加速运动的同时,通过预先安装的高温炉装夹工装与联动控制结构将高温炉从靶板两侧移除,弹体运动和高温炉同步移除运动如图3所示。高温炉被移除后,靶板失去加热源并与空气直接接触,3个测点的温度随时间的变化情况如图5所示,可以发现,3个测点的温度随时间延长基本呈线性下降趋势。
为了获得弹丸冲击时靶板的实际温度,需要计算靶板停止加热至弹丸撞击靶板过程经历的时间tz,tz为弹体在炮管中加速过程所用的时间
t0 与弹体离开炮管后匀速运动至靶板所用的时间之和。弹体在炮管中的运动方程为dv/dt=a=pSf/m (1) 式中:v为弹体运动速度,t为弹体运动时间,a为弹体加速度,p为弹底气压,Sf为炮管内截面积,m为弹体质量。将炮膛内气体的膨胀过程视为等熵绝热过程[15],则
pczVγcq=p(Vcq+Sfx)γ (2) 式中:
pcz 为气室初始气压,Vcq 为气室体积,γ 为气体绝热指数,x 为弹体运动距离。联立式(1)和式(2)可得dvdt=SfpczVγcqφm(Vcq+Sfx)γ (3) φ=K+13Mm (4) M=pczVcqRTμg (5) 式中:
φ 为次要功系数,R为普适气体常数,T为温度,μg 为气体摩尔质量,K=1.05。设L为炮管长度,将式(3)进行变换,取定积分,得到∫t00dt=φm(Vcq+SfL)γSfpczVγcq∫v00dv (6) 由此获得弹丸在炮管中加速所经历的时间
t0 t0=v0φm(Vcq+SfL)γSfpczVγcq (7) 弹体匀速运动所用的时间
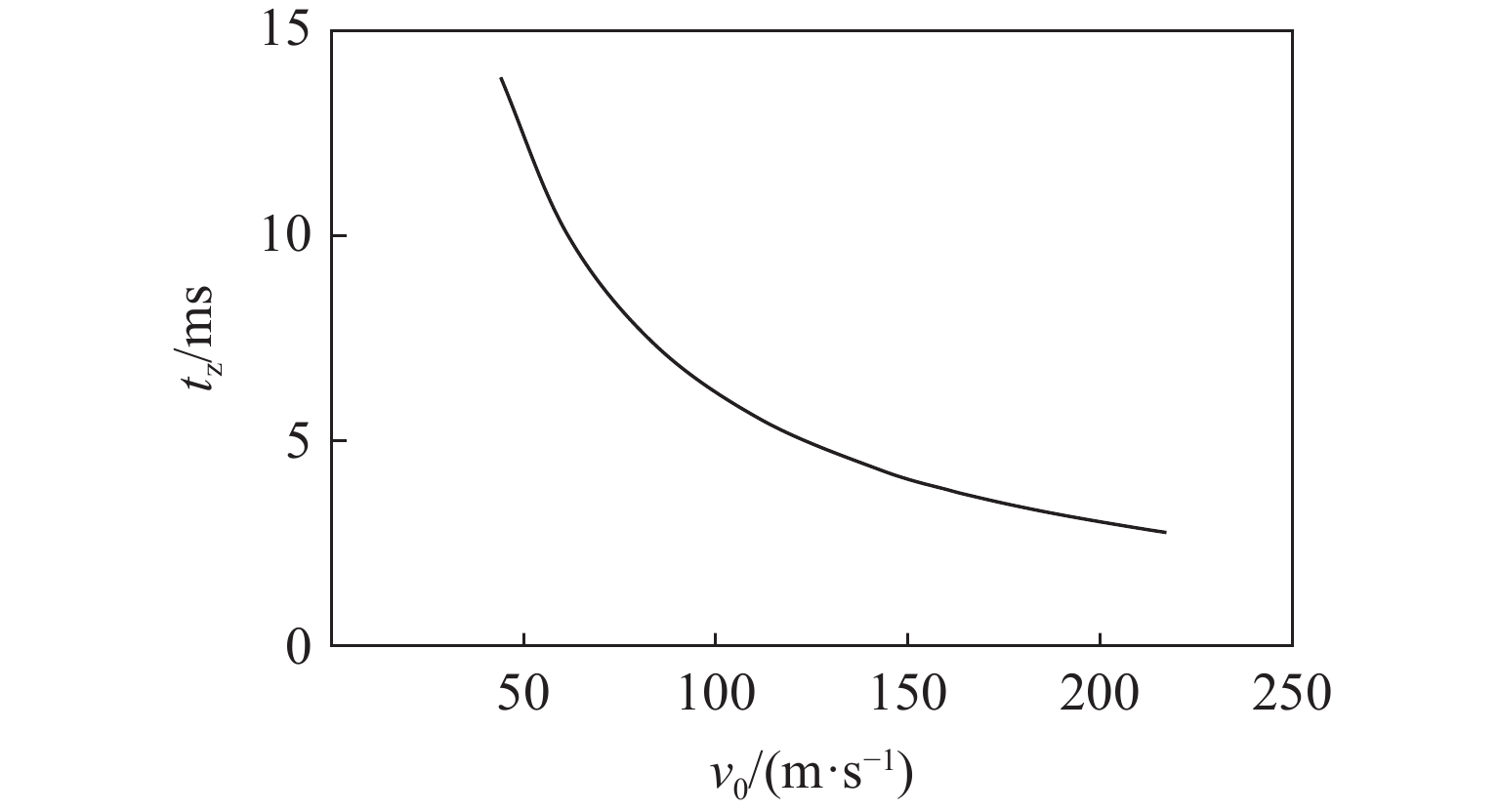
t1 可通过炮管端口与靶板的距离(L1=0.3 m)与弹丸的冲击速度计算得出。试验相关参数见表1。计算得到弹体冲击速度v与时间tz的关系,如图6所示,可见,当冲击速度高于50 m/s时,弹体的运动时间小于0.1 s。从图5中3个测点的温度随时间变化情况可知,撤除高温炉后0.1 s以内,靶板温度下降幅度小于3 ℃,靶板温度下降较小,从而保证了高温弹道冲击试验的有效性。设v0为弹体出膛速度,则有表 1 弹道冲击计算的相关参数Table 1. Calculation parameters of ballistic impactSf/m2 m/kg Vcq/m3 γ R/(J·mol−1·K−1) T/K μg /(kg·mol−1) L/m 4.91×10−4 0.054 2.18×10−2 1.41 8.31 300 2.8×10−2 5 tz=t0+Lv0 (8) 2. 试验结果和分析
2.1 同步时间
tz 对试验的影响在高温弹道冲击试验中最重要的两个参数是弹丸撞击靶板时刻的靶板温度和弹丸的冲击速度,是影响试验结果准确性最主要的因素。图5中,在移除高温炉后,靶板上3个测点的温度随时间变化曲线基本呈线性下降趋势,移除高温炉8 s后3个测点的温度分别下降了58、67和33 ℃。靶板撞击点的材料温度下降了11%以上,靶板材料的塑性流动应力随着温度下降而逐渐增强[16],表现出不同的抗冲击性能[8],从而影响试验结果的准确性。在考察C/SiC复合材料抗冲击性能的试验中,撤离高温炉后,10 s内复合材料板温度下降约15 ℃[7]。从试验结果可知,撤离高温炉后GH4169镍基高温合金的温度下降速率远远高于C/SiC复合材料,因此采用快速同步高温弹道冲击试验方法显得尤为重要。
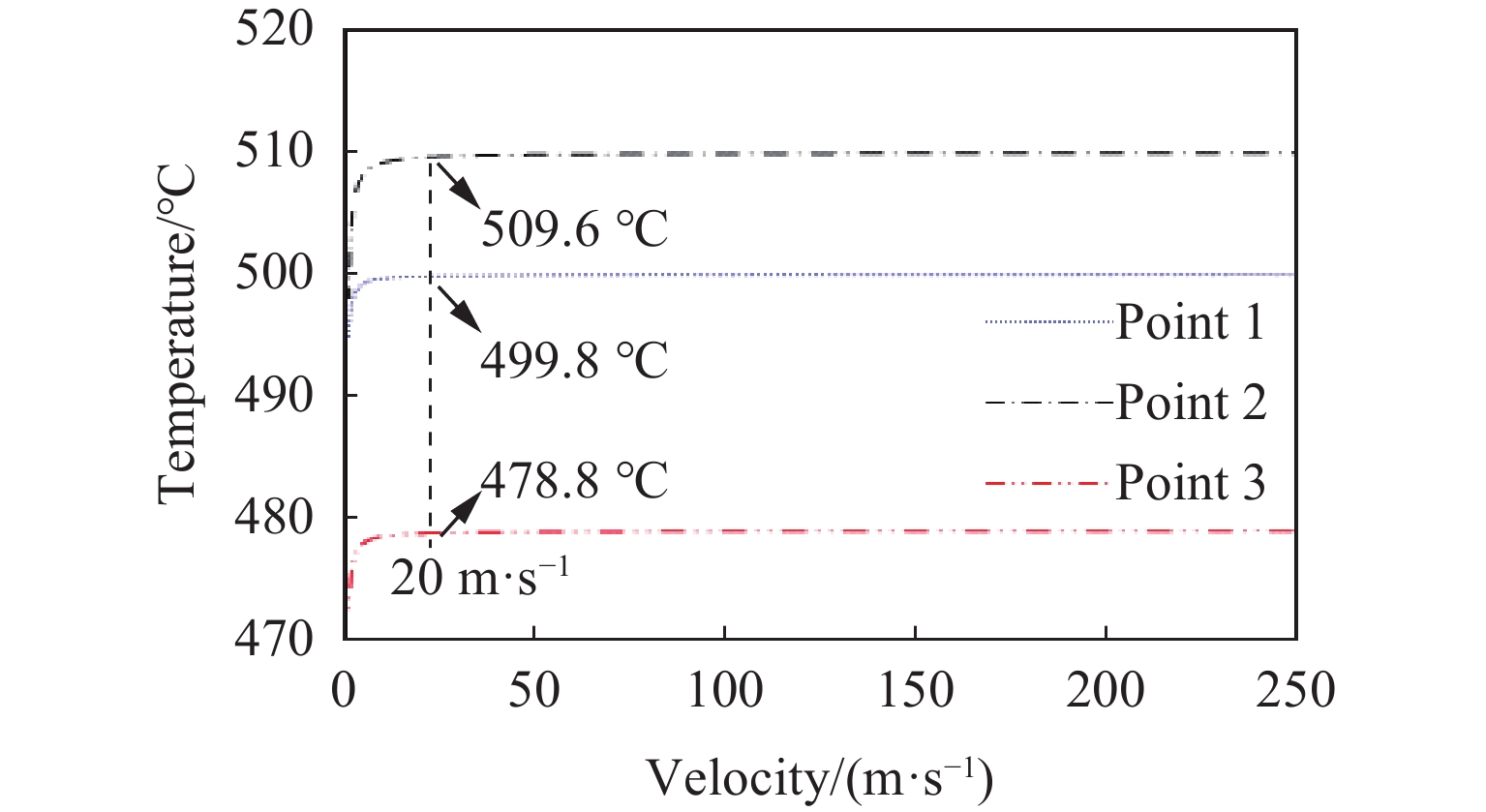
从图6可知,随着弹体撞击靶板前运动总时间tz的延长,弹体冲击速度呈幂指数下降趋势。若将此高温弹道冲击试验方法应用于其他类型材料的高温弹道冲击试验中,获得的冲击速度与弹体撞击靶板时靶板温度的关系可直观判断试验方法的可行性。弹丸发射和高温炉撤离为同一时刻,将图5中移除高温炉后测点温度随时间的变化曲线与图6中弹丸冲击速度v0与时间间隔tz的关系曲线整合并消除共同的时间变量,得到弹体冲击速度与靶板测点的温度变化曲线,如图7所示。由图7可知,随着弹体的冲击速度增大,靶板在冲击时刻的温度下降幅度变小,逐渐接近靶板的初始温度,因此在冲击速度较大的情况下,更容易保证靶板的试验目标温度条件。当弹体的冲击速度为20 m/s时,靶板3个测点的温度下降值均小于1 ℃,可以认为当冲击速度大于20 m/s时,通过该高温高速同步弹道冲击试验装置进行的弹道冲击试验是准确有效的。本试验方法也可应用于C/SiC复合材料[7]及其他高温合金或金属材料。
2.2 靶板变形与破坏
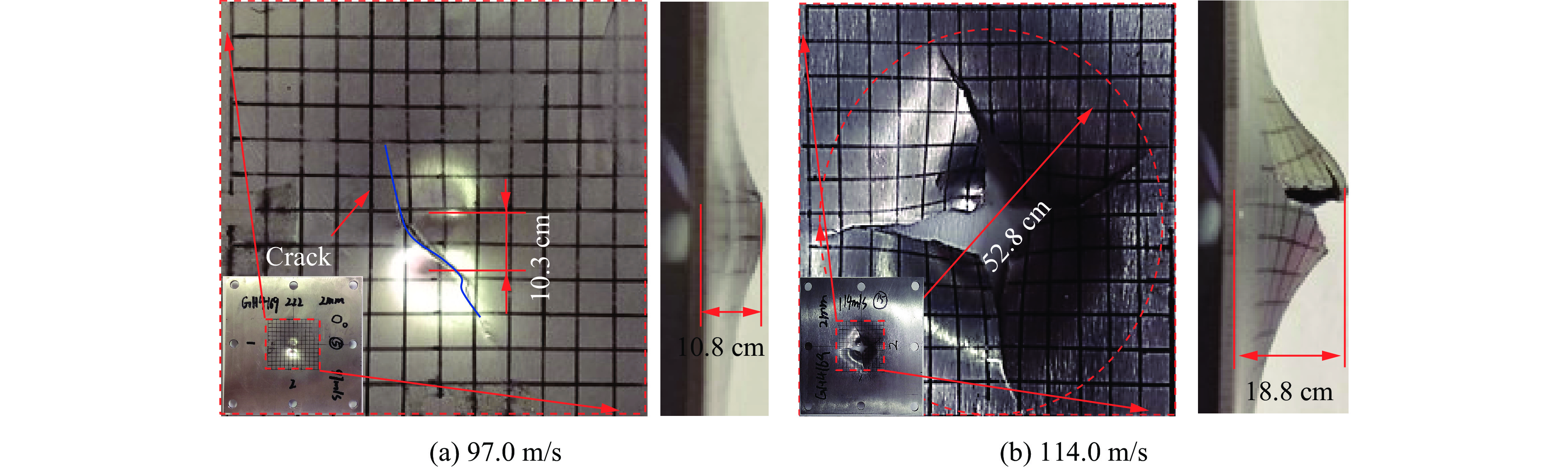
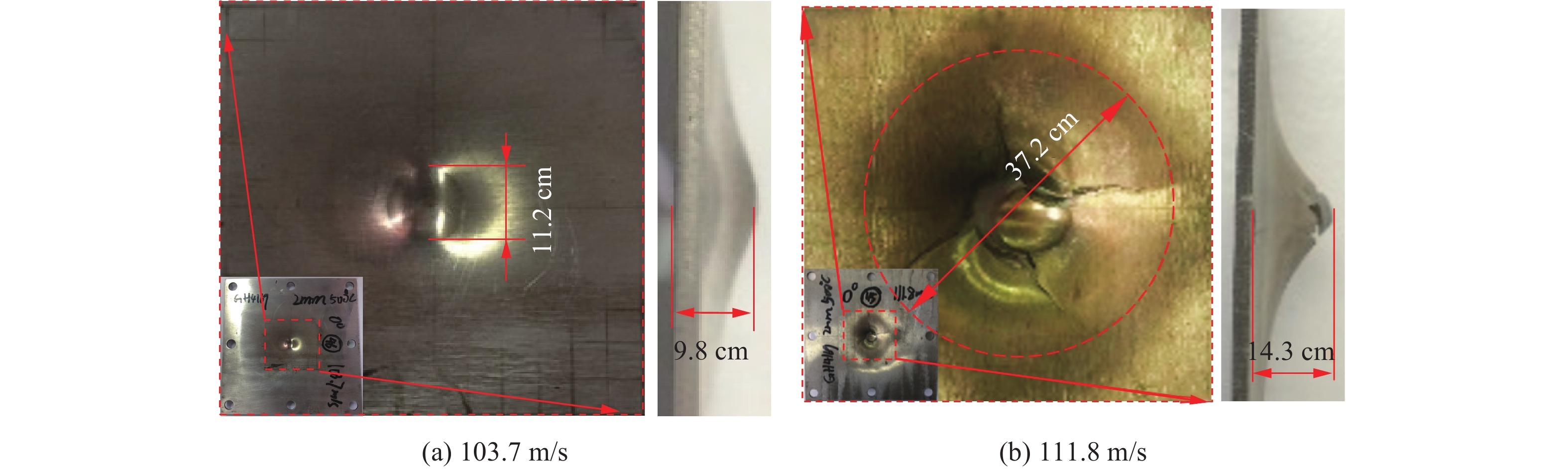
高温弹道冲击下靶板的变形和损伤形式与常温条件下的试验结果存在明显差异。图8(a)和图8(b)分别为常温下冲击速度为97.0和114.0 m/s时靶板正、侧面的变形和损伤情况,可以看到靶板出现了明显的弹坑和裂纹。图9(a)和图9(b)分别为500 ℃高温条件下弹丸以103.7和111.8 m/s的速度冲击靶板时靶板正、侧面的损伤情况。对比图8(a)与图9(a)中靶板的损伤结果可知,虽然高温使靶板材料的强度降低,但图9(a)中靶板并未产生明显的裂纹破坏,而图8(a)中靶板产生了一条长度为30 mm并贯穿整个靶板厚度方向的裂纹。对比相近速度条件下图8(b)与图9(b)中靶板的试验结果发现,高温条件下靶板的全局变形较常温试验结果低29.5%,表明高温使靶板材料软化,靶板变形更加集中在弹着区附近,Erice等[8]和Liu等[5]也得到了类似的试验结果。同时还发现常温条件下靶板的损伤裂纹长度是高温条件下的2倍左右,损伤形式更加剧烈。对比图8和图9中靶板的最大变形挠度可知,高温条件下靶板的最大变形挠度小于常温试验结果,推断产生这种现象的原因是高温条件增强了GH4169材料的塑性,使得材料的延伸率和失效应变均高于常温情况[17-18],另外由于镍基高温合金材料的塑性流动应力强度较常温情况有所下降但减小幅值较小,从而表现出在500 ℃高温条件下靶板的抗冲击性能优于常温条件下。同时,由图10可知,靶板的损伤裂纹首先产生在靶板背面并逐渐扩展到撞击正面,Erice等[8]的研究中也发现了同样的现象,表明靶板的主要冲塞失效机理是剪切破坏。
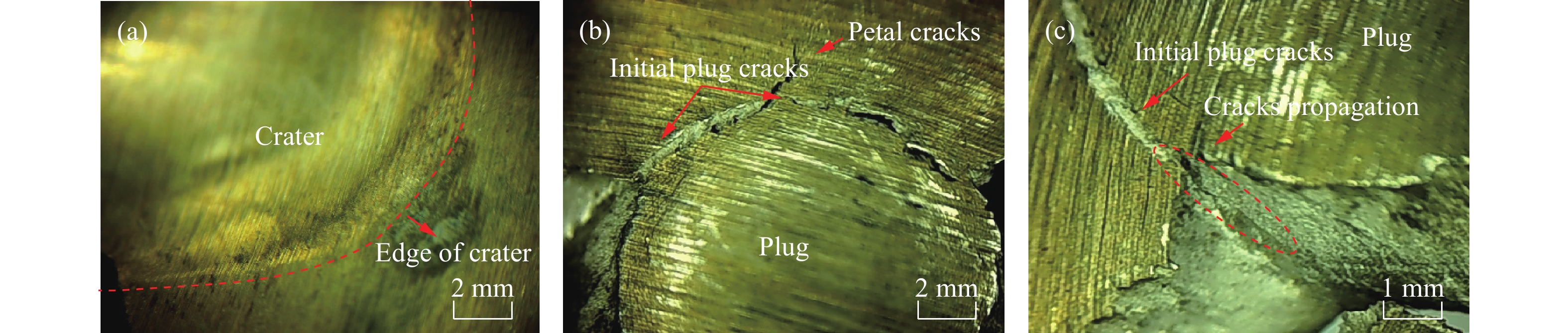
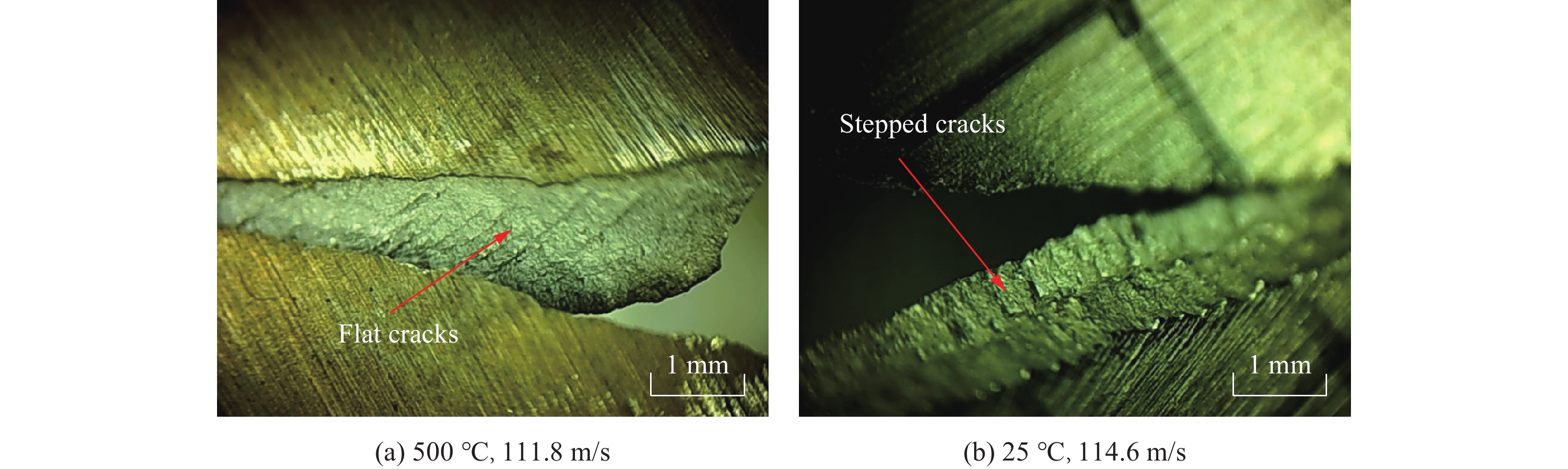
如图11所示,观察靶板的花瓣形损伤裂纹断口形貌可知,高温条件下的断口形貌与常温条件下明显不同。常温条件下断口粗糙,呈现分阶段破坏的层阶形式;而高温条件下的断口相对整齐,呈剪切破坏模式,断面与靶板平面呈45°,并且断面相对细腻平坦,与常温试验结果存在明显差异。花瓣形损伤裂纹是弹体穿过靶板过程中,靶板形成冲塞碎片后,弹体通过冲塞孔洞的扩孔行为导致冲塞孔周围靶板材料因发生径向弯曲变形[5]与周向拉伸变形而产生的。弹道冲击过程中靶板的应变率极高,可达到103 s−1以上,由于室温条件下GH4169材料在高速变形过程中其晶界不参与变形,晶界位置的晶体结构不规则,同时伴随着晶体缺陷、原子排列杂乱、晶格扭曲等,因此在形变时可阻止位错滑移[19],继而在断裂时形成如图11(b)所示的断口形貌;而在高温条件下,晶界参与变形,晶界位置薄弱[19],因此在破坏时呈现晶间断裂特征,如图11(a)所示。
3. 结 论
通过高温同步冲击控制技术建立了一套能够有效实现高温环境下靶板弹道冲击的试验方法,采用对称式加热法有效地解决了试验中靶板温度场均匀性的关键问题,并通过此试验方法对GH4169镍基高温合金靶板进行了常温和500 ℃高温条件下的弹道冲击试验,得到以下结论。
(1) 通过建立同步高温弹道冲击试验方法,实现了冲击速度超过320 m/s、温度高于500 ℃的弹道冲击试验。当冲击速度大于20 m/s时,靶板的温度下降幅度可控制在1 ℃以内。
(2) 设计了高温炉对称布置方式对靶板进行加热,当靶板的目标温度为500 ℃时,可将靶板正、背面温度梯度控制在0.1%以内,撞击区的靶板面内温度梯度小于2.6%。
(3) 在500 ℃高温条件下,冲击速度为111.8 m/s时,GH4169镍基高温合金材料的软化作用致使靶板全局变形范围较常温条件下小29.5%,但由于高温情况下材料的延伸率与失效应变均增大,使得以最大变形挠度和裂纹损伤程度为代表的靶板抗冲击性能获得提高。
(4) 常温条件下靶板的花瓣形裂纹损伤断口较粗糙,裂口损伤形貌呈阶梯状;高温条件下靶板断口的裂纹较光滑整齐,表现为剪切破坏模式,断面与靶板平面呈45°,总体呈现晶间断裂的特征。
本研究所建立的高温高速同步弹道冲击试验方法采用了可移动的对称式加热方式,利于保证靶板温度的均匀性。通过分析获得了弹体冲击速度与靶板温度之间的关系曲线,可得到不同冲击速度下靶板的温度情况,进而保证试验条件的准确性。通过设计不同尺寸及功率的加热炉,易于实现不同靶板材料及尺寸特征的高温高速弹道冲击试验,该试验方法将为其他高温弹道冲击试验提供参考。
-
表 1 实验工况及结果
Table 1. Experimental conditions and results
No. dp/
(mm)tb/
(mm)v/
(km/s)Dmax/
(mm)Damage of
the rear wall1 3.20 0.5 2.78 110 P 2 3.20 0.5 3.25 120 P 3 3.20 0.5 3.52 129 P 4 3.20 0.5 4.24 142 P 5 3.20 0.5 4.63 150 P 6 3.20 0.5 4.92 158 P 7 3.20 1.0 2.50 102 NP 8 3.20 1.0 3.05 126 P 9 3.20 1.0 3.65 133 NP 10 3.20 1.0 4.00 152 NP 11 3.20 1.0 4.45 159 NP 12 3.20 1.0 5.05 165 NP 13 3.20 1.5 2.81 120 NP 14 3.20 1.5 3.05 130 NP 15 3.20 1.5 3.73 148 NP 16 3.20 1.5 4.21 160 NP 17 3.20 1.5 4.46 165 NP 18 3.20 1.5 4.81 170 NP 19 3.97 1.0 2.65 120 P 20 3.97 1.0 3.25 138 P 21 3.97 1.0 3.57 148 P 22 3.97 1.0 4.15 160 NP 23 3.97 1.0 4.55 170 NP 24 3.97 1.0 4.85 180 NP 25 4.76 1.0 2.31 110 P 26 4.76 1.0 3.01 140 P 27 4.76 1.0 3.30 145 P 28 4.76 1.0 3.75 160 P 29 4.76 1.0 4.64 180 P 30 4.76 1.0 5.20 195 P Note: P-Penetration in the rear wall, NP-No perforated point in the rear wall. -
[1] Miyachi T, Hasebe N, Ito H, et al. Real-time detector for hypervelocity microparticles using piezoelectric material[J]. Adv Space Res, 2004, 34(5): 935-938. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.11.019 [2] Schäfer F, Janovsky R. Impact sensor network for detection of hypervelocity impacts on spacecraft[J]. Acta Astronaut, 2007, 61(10): 901-911. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2007.02.002 [3] Prosser W H, Gorman M R, Humes D H. Acoustic emission signals in thin plates produced by impact damage[J]. J Acoust Emiss, 1999, 17(1/2): 29-36. [4] 唐颀, 庞宝君, 韩增尧, 等.单层板超高速撞击声发射波的频谱特征分析[J].宇航学报, 2007, 28(4): 1059-1064.Tang Q, Pang B J, Han Z Y, et al. Analysis of frequency spectrum character of acoustic emission wave from hypervelocity impact on single-sheet plate[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2007, 28(4): 1059-1064. (in Chinese) [5] 刘武刚, 庞宝君, 韩增尧, 等.基于声发射的单层铝板高速撞击损伤类型识别[J].宇航学报, 2011, 32(3): 671-675.Liu W G, Pang B J, Han Z Y, et al. Damage identification of single aluminum plate produced by hypervelocity impact based acoustic emission[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(3): 671-675. (in Chinese) [6] 管永红, 胡八一, 黄超.基于小波包的爆炸容器振动分析[J].爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(5): 551-555.Guan Y H, Hu B Y, Huang C. Vibration analysis of an explosion vessel based on wavelet packet transform[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(5): 551-555. (in Chinese) [7] 凌同华, 廖艳程, 张胜.冲击荷载下岩石声发射信号能量特征的小波包分析[J].振动与冲击, 2010, 29(10): 127-130, 255.Ling T H, Liao Y C, Zhang S. Application of wavelet packet method in frequency band energy distribution of rock acoustic emission signals under impact loading[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2010, 29(10): 127-130, 255. (in Chinese) [8] 管公顺, 庞宝君, 哈跃, 等.铝合金Whipple防护结构高速撞击实验研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 2005, 25(5): 461-466.Guan G G, Pang B J, Ha Y, et al. Experimental investigation of high-velocity impact on aluminum alloy Whipple shield[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2005, 25(5): 461-466. (in Chinese) [9] Christiansen E L. Design and performance equations for advanced meteoroid and debris shields[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1993, 14(1): 145-156. [10] 唐颀.超高速撞击板波特性与声发射空间碎片在轨感知技术[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008: 56-76.Tang Q. Characteristics of plate waves induced by hypervelocity impact and onboard monitoring technique for detection of impact on spacecraft by space debris[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008: 56-76. (in Chinese) [11] Rosso O A, Blanco S, Yordanova J, et al. Wavelet entropy: A new tool for analysis of short duration brain electrical signals[J]. J Neurosci Meth, 2001, 105(1): 65-75. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0270(00)00356-3 [12] 印欣运, 何永勇, 彭志科, 等.小波熵及其在状态趋势分析中的应用[J].振动工程学报, 2004, 17(2): 49-53.Yin X Y, He Y Y, Peng Z K, et al. Study on wavelet entropy and its applications in trend analysis[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2004, 17(2): 49-53. (in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载:





























 下载:
下载: