Electronic Structure and Photoelectric Properties ofZnTe under High Pressure
-
摘要: 应用第一性原理平面波赝势计算方法,研究了闪锌矿ZnTe晶体在外界压力下的电子结构和光电性质, 并计算了介电函数和光学吸收系数随压力的变化情况。结果表明:在高压作用下,Te原子和Zn原子的态密度分布都向低能量方向移动,分布范围增大,Te 5p和Zn 3d电子轨道杂化变强。随着压力的增大,直接带隙逐渐增大,而间接带隙逐渐变小。当压力为10.7 GPa时,能带结构从直接带隙转变为间接带隙结构。压力增大,有利于Te 5p与Zn 3d电子间的跃迁,光吸收系数增大,产生更多的电子-空穴对,材料导电能力增强。Abstract: The electrons structure and photoelectric properties of zinc-blende structural ZnTe were investigated under high pressure, using first-principles plane-wave pseudo-potential method.The dielectric function and optical absorption coefficient were also predicted under high pressure.The results show that the distributions of density of states of Te and Zn atoms under high pressure shift towards lower energy direction and cover wider range.High pressure leads to stronger hybridization between Te 5p and Zn 3d electrons.The direct band gap increases gradually with pressure while the indirect band gap decreases.The direct band gap structure becomes an indirect one when the ambient pressure reaches 10.7 GPa.High pressure helps the transitions between Te 5p and Zn 3d electrons.The optical absorption coefficient increases, which leads to more electron-hole pairs and enhances the conductivity.
-
1. 引言
ZnTe是Ⅱ-Ⅳ族中一种直接带隙宽禁带半导体材料[1-4], 室温下带隙宽度为2.39 eV, 常压下是立方闪锌矿结构, 可以广泛应用于各种光电子器件中, 如绿光发光二极管, 电光探测器, 太阳能电池。同时, 由于ZnTe二阶非线性系数和电光系数较大, 在(110)晶面方向800 nm左右的激光脉冲作用下相位匹配最好, 产生、探测太赫兹辐射的效率较高, 目前已成为产生和探测太赫兹辐射最常用的电光材料[5-6]。自从金刚石对顶砧(Diamond Anvil Cell, DAC)技术发明以来, 各种功能材料在高压下的性质成为研究热点, 主要包括高压下的电学、磁性、光电、压电和热电研究等方面[7]。早期, Samara等人[8]发现, 高压下ZnTe的电阻率会急剧下降, 当压力超过14 GPa时, 甚至会向金属相转变。San-miguel等人[9]利用X射线吸收和衍射的方法实验研究了ZnTe晶体在高压下的结构情况。Franco等人[10]从理论上进行了高压下ZnTe的抗压性研究。最近, 吕冉等人[11]利用第一性原理平面波赝势方法并结合准谐德拜模型, 计算了闪锌矿结构ZnTe在高温高压下的弹性及热力学性质, 计算结果与实验结果符合较好。
关于ZnTe材料在高压下的性质已有了一定的研究基础, 但是高压下ZnTe的电子结构变化, 以及高压对电子跃迁、光吸收系数和导电能力等光电性质的影响还鲜有报道。本研究运用第一性原理平面波赝势方法, 着力研究闪锌矿ZnTe在高压下的电子结构, 以及高压对其光电性质的影响。
2. 计算方法和模型
ZnTe在常温常压下是闪锌矿结构, 空间群为F-43M(216), Zn原子在(0, 0, 0)处, Te原子在(0.25, 0.25, 0.25)处。本研究基于密度泛函理论下的平面波赝势方法, 交换-关联能用广义梯度近似(General Gradient Approximation, GGA)[12]描述, 离子实和价电子之间的相互作用用超软赝势描述。此方法已成功运用于材料的高压特性研究[13]。理论上, ZnTe从闪锌矿结构到朱砂相结构转变的相变点为11.9 GPa[10], 故在0~12 GPa压力范围内进行几何优化, 并在此基础上计算电子结构和光电性质。
为确保计算速度并保证足够的精度, 取平面波截止能量(Cutoff Energy)为400 eV, Monkhorst-Pack网格大小为5×5×5, 原子间相互作用力的收敛标准为0.01 eV/nm, 能量收敛标准为10 μeV/atom。计算采用VASP(Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package)[14-16]量子力学模块完成, 参与计算的价态电子:Te为5s25p4, Zn为3d104s2。所有计算结果都是在绝对零度下的理论值。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 几何结构优化
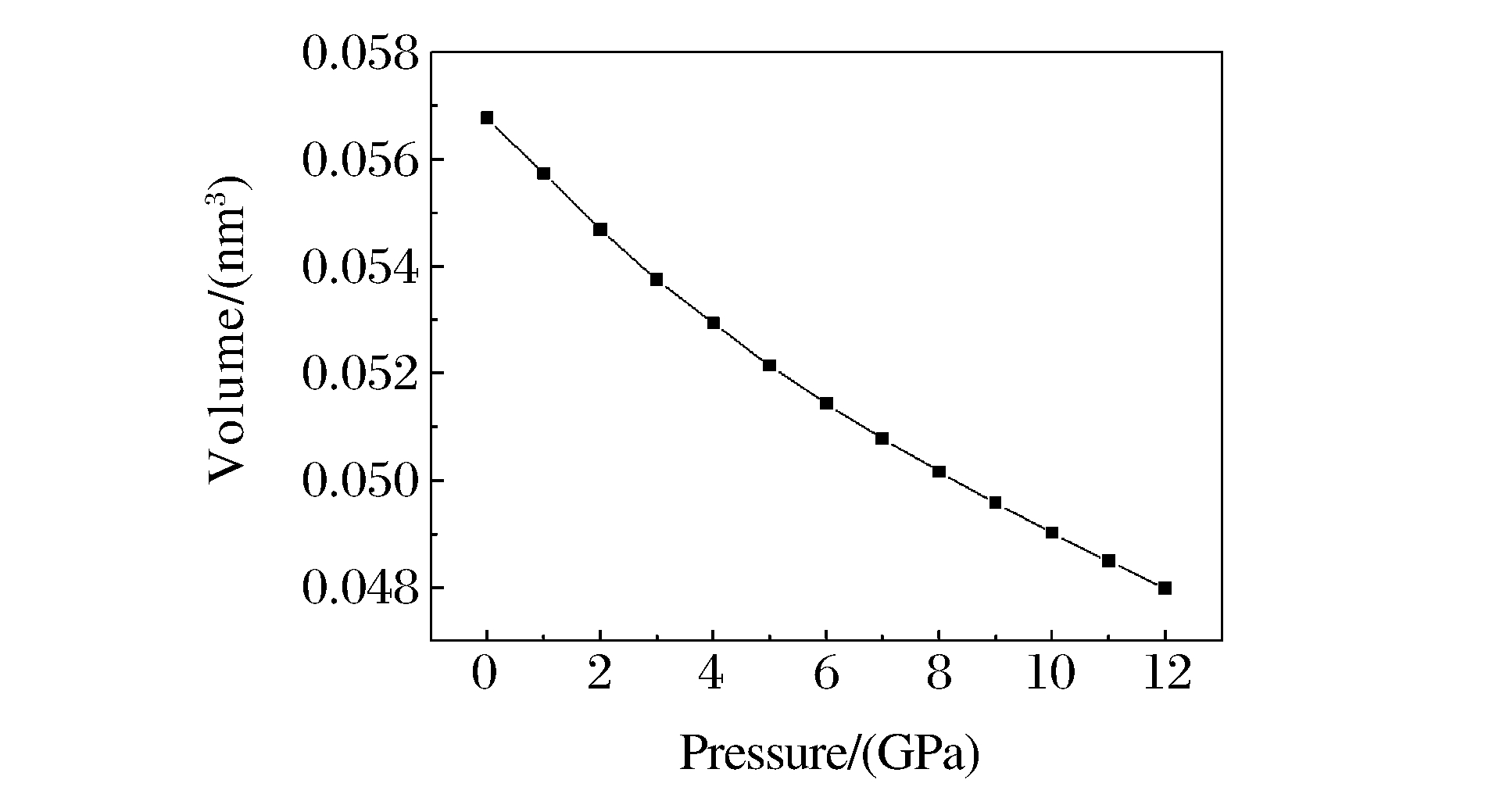
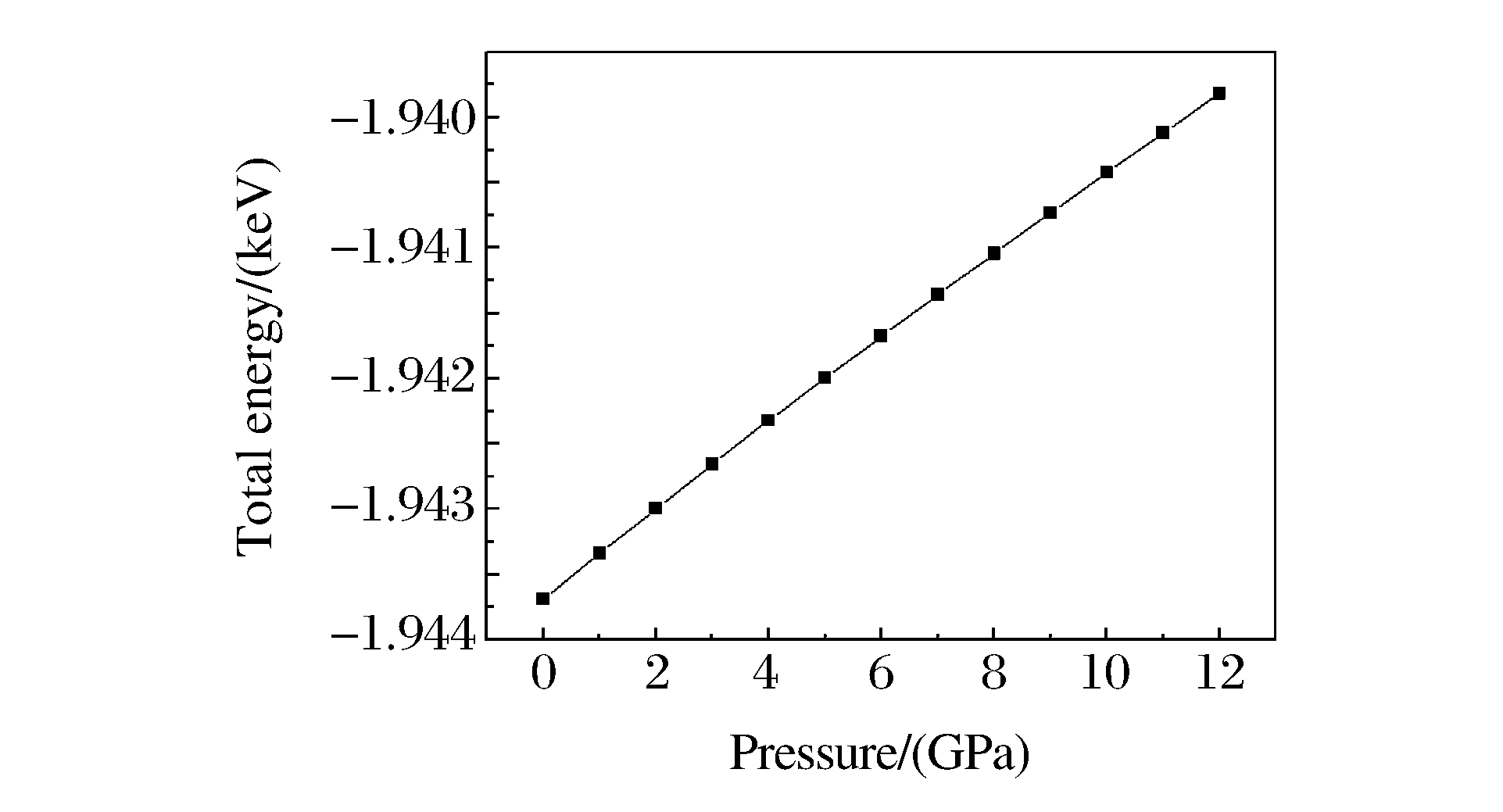
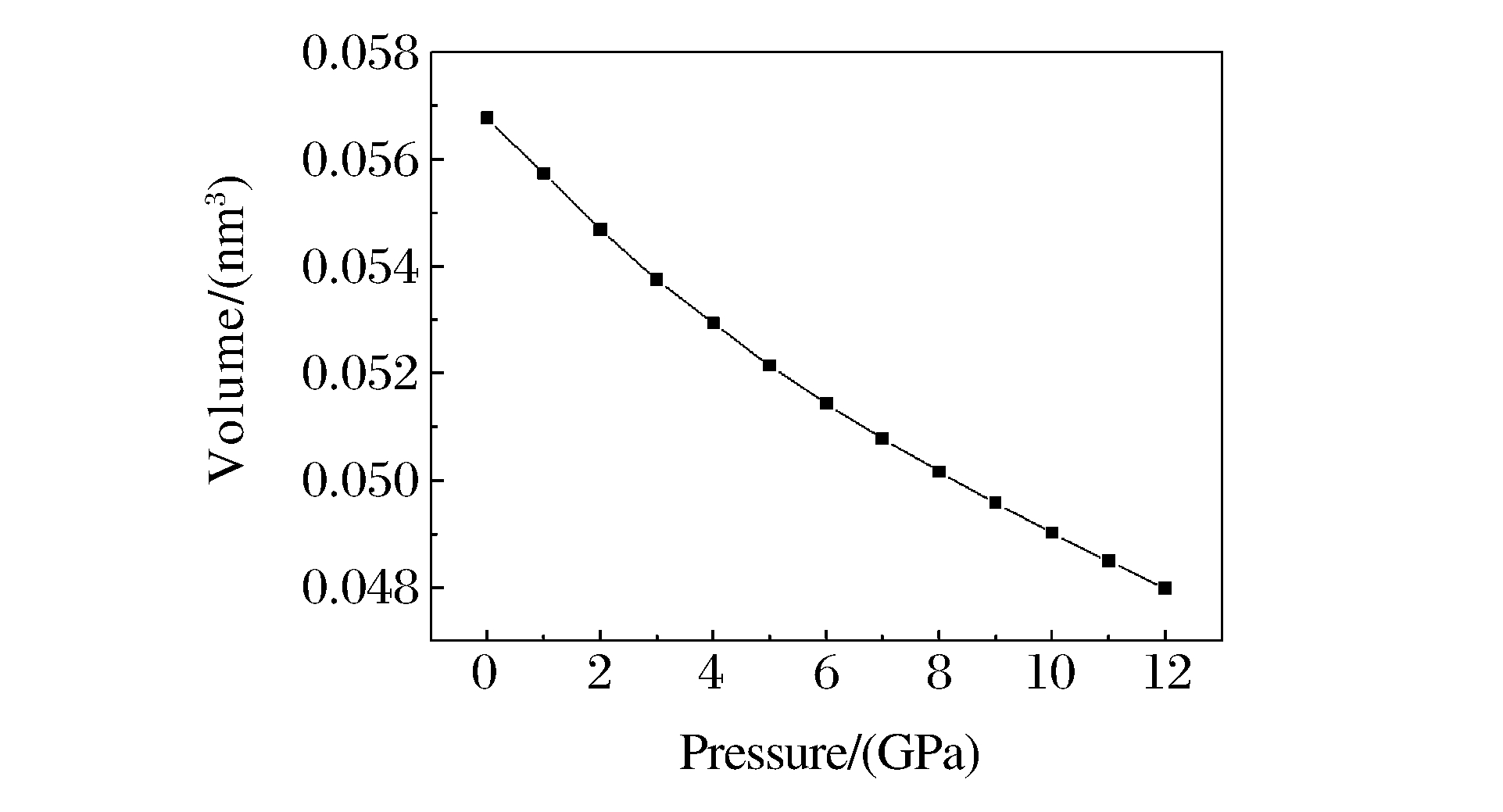
在没有加压的情况下, 优化后的Zn-Te键键长为0.264 nm, 和实验结果[9]及理论值[17]符合得很好。随着压力的增大, 晶体处于压缩状态, 键长逐渐变小, 相应的晶体体积变小, 如图 1所示。图 2为ZnTe总能量随压力变化的关系图。结果表明, 随着压力的增大, 系统总能量逐渐增加, 而且是随着压力线性变化的。加压几何优化后, 晶体中各原子都达到了最稳定的平衡状态, 但压力会导致各原子间的相互作用力增大而处于挤压状态, 晶体势能逐渐增加, 总能量逐渐变大。
3.2 电子结构
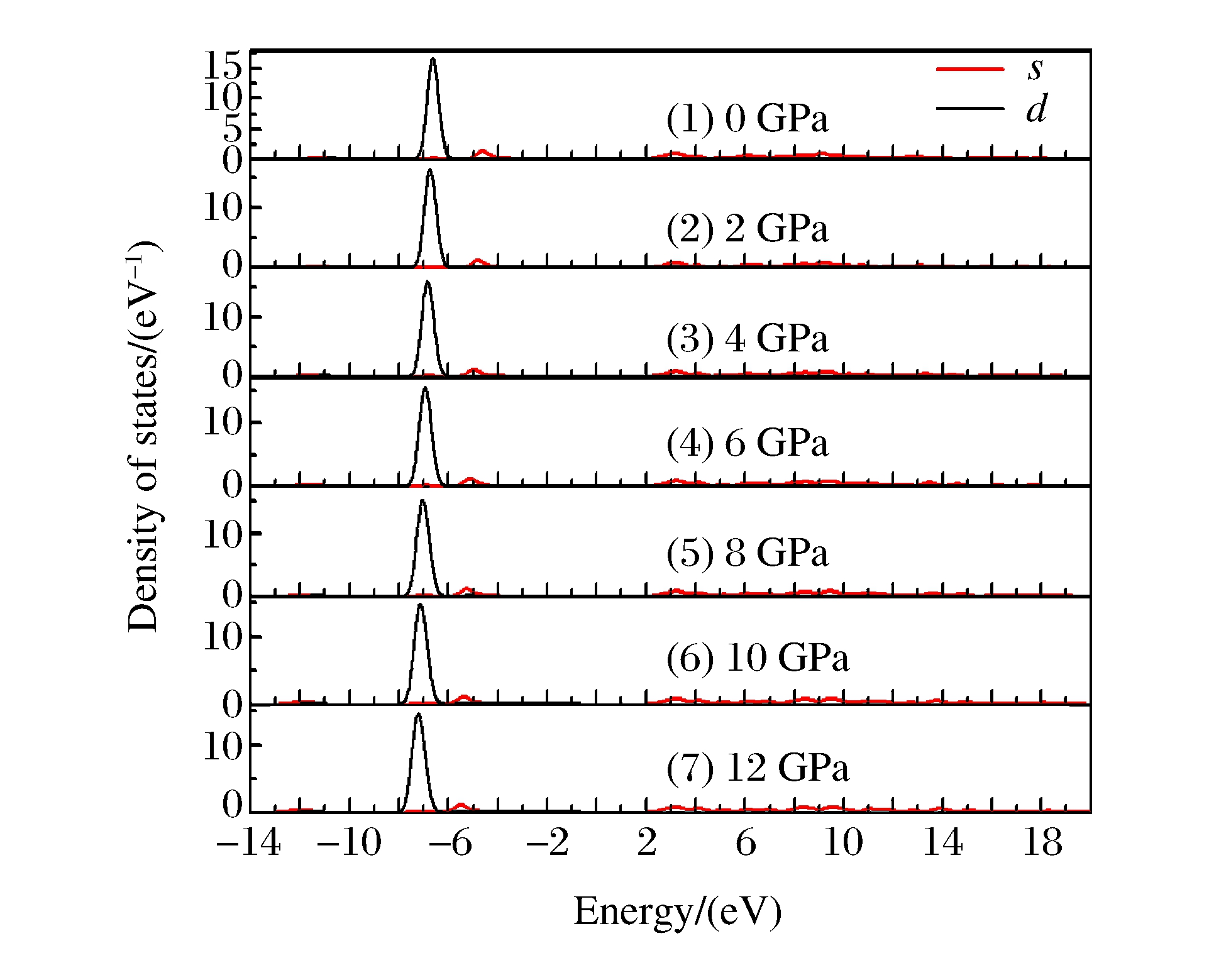
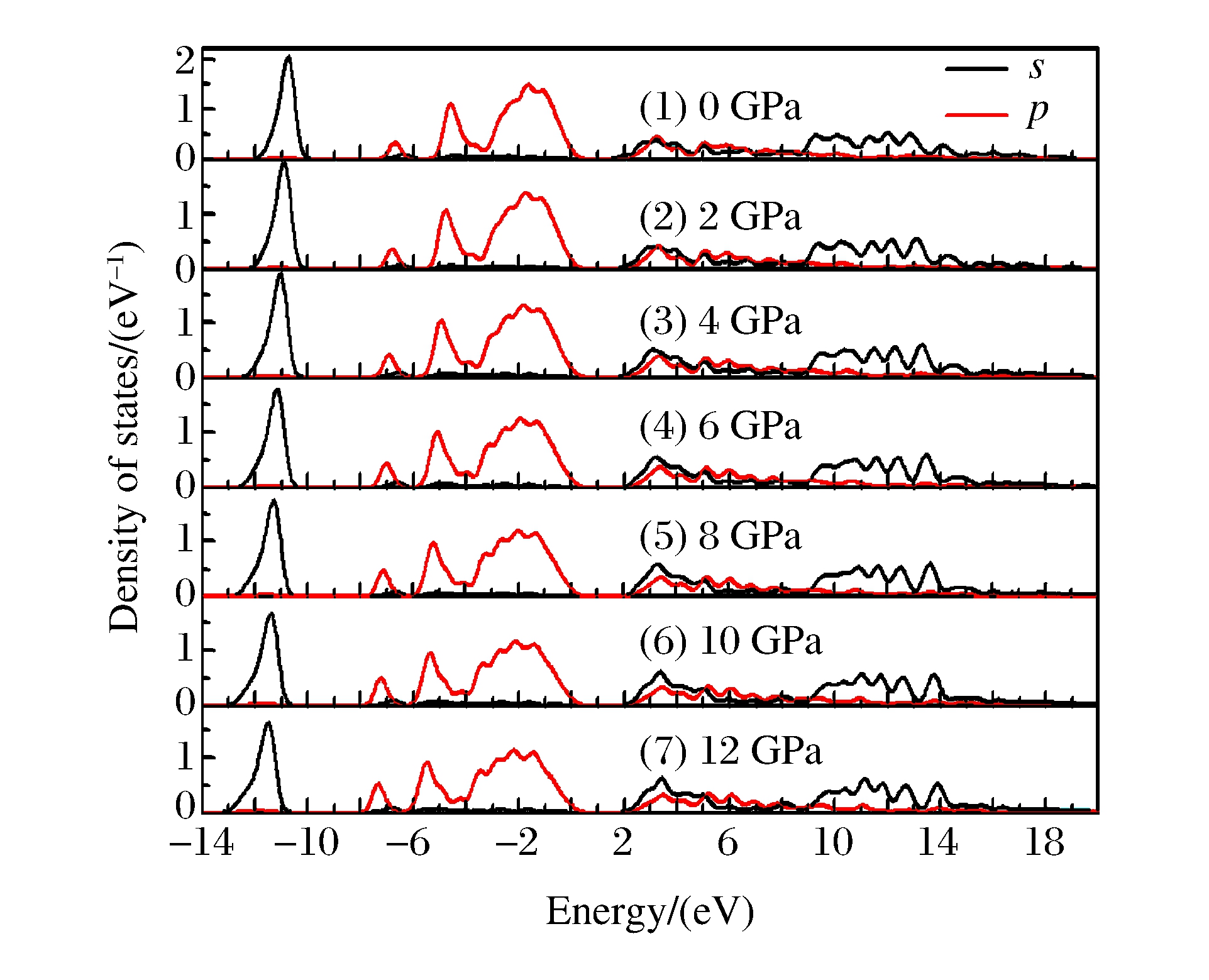
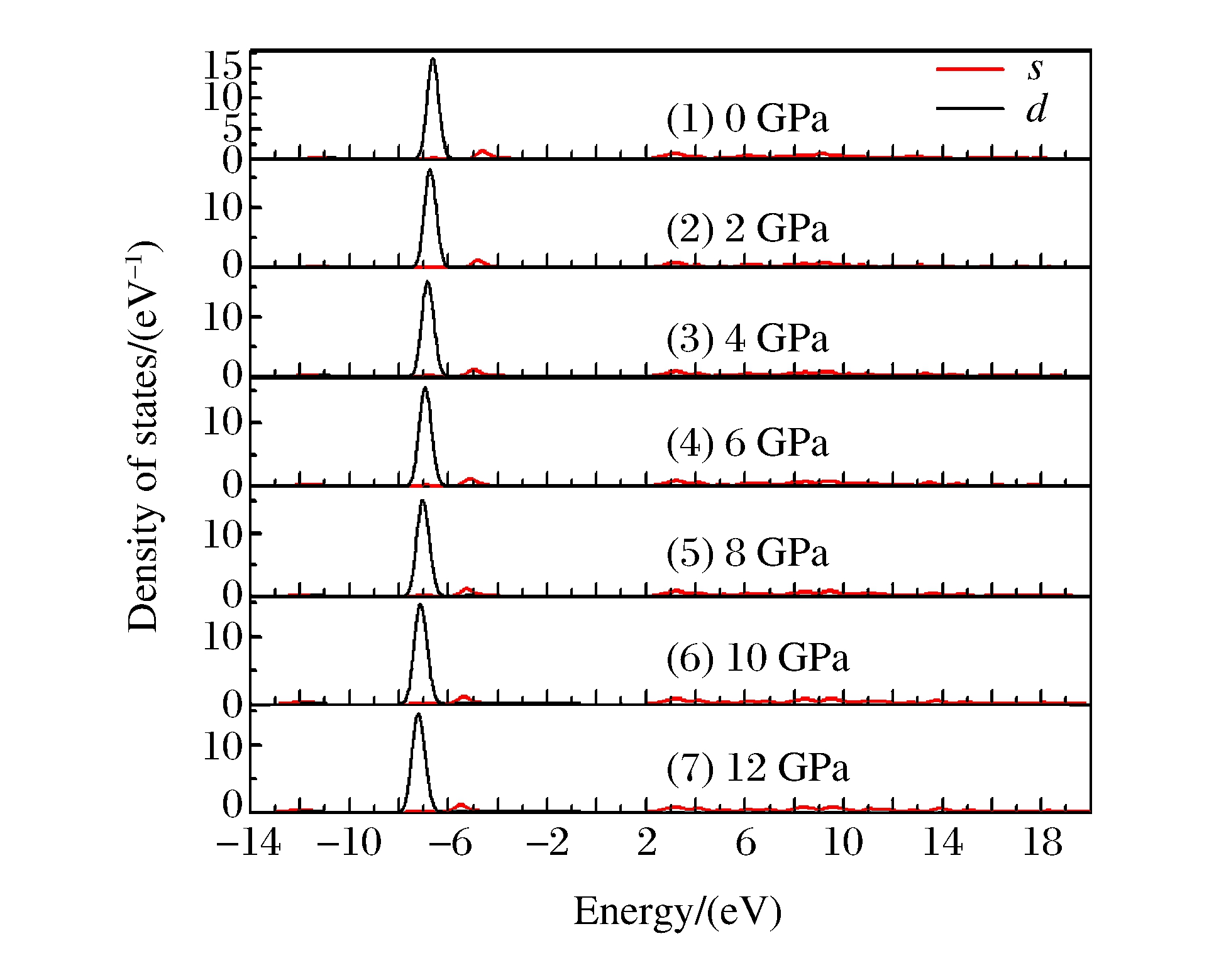
图 3和图 4分别给出了在外界压力为0、2、4、6、8、10、12 GPa时, Te原子和Zn原子态密度的分布情况。从图 3和图 4中可以看出:当外界压力为0 GPa时, Te原子的s电子主要分布在下价带区域-12.2~-9.8 eV范围内, 能带比较狭窄, 表现出较强的定域性, 与价带内其它能级间没有明显的相互作用; p电子主要分布在从-7.3 eV到价带顶的范围内, 还有一小部分p电子对导带也有一定贡献, 表现出明显的非定域性; Zn原子的d电子主要分布在价带区域-7.4~-5.9 eV范围内。当压力为12 GPa时, Te原子的s电子主要分布在-13.2~-10.6 eV范围内, 能量分布范围比0 GPa时增加了0.2 eV; Zn原子的d电子分布在-8.0~-6.3 eV范围内, 能量分布范围也比0 GPa时增加了0.2 eV。无论Te原子的s电子和p电子, 还是Zn原子的d电子, 高压下它们的态密度峰都向低能量方向移动, 分布范围变大。
再来分析峰形的变化。在0 GPa时, Te原子的p电子态密度分布曲线呈现出3个清晰的峰, 从低能量向高能量的方向看过去, 峰值依次增加。当压力逐渐增大时, 左边的峰逐渐上升, 右边的峰逐渐下降, 而且演化出越来越多的峰, 表现出更加明显的非定域性。从整体上看, 随着压力的增大, Te 5p和Zn 3d电子的分布出现了更大范围的重叠, 说明压力导致了更多的价键重叠和轨道杂化, 这也是ZnTe在高压下能够稳定存在的原因。压力的直接作用是减小晶体体积, 从而减小原子间距, 增加电子波函数的直接交叠, 导致态密度峰蓝移和分布增宽。
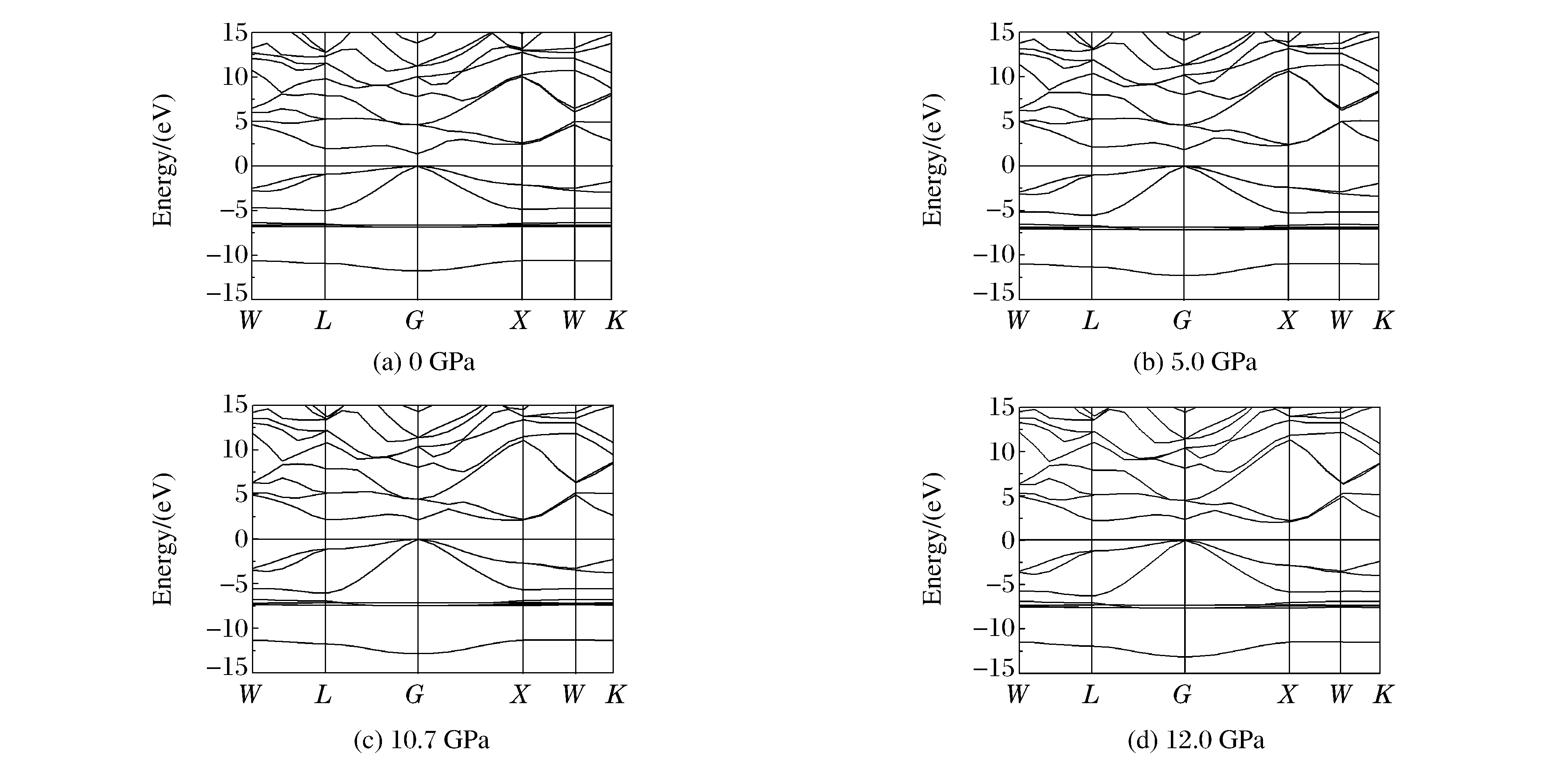
为了进一步分析高压对电子结构的影响, 图 5给出了几种典型情况下的能带结构。从图 5(a)中可以看出, 没有加压时, ZnTe是一种典型的直接带隙半导体, 在布里渊区高对称点G处, 直接带隙宽度为1.39 eV, 比实验值2.39 eV[18]小1.00 eV, 间接带隙宽度(从G点到X点)为2.45 eV, 比实验值3.30 eV[18]小0.85 eV, 但是二者均略大于其他文献报道的计算值[19-20]。总体而言, 计算结果比实验值偏小, 这主要是由于采用密度泛函理论中的GGA计算基态能级所致[21-22], 但布里渊区内的能量色散关系不受影响, 能带基本特征与文献[22]一致。
结合图 3和图 4, 从图 5(a)~图 5(d)中可以看出:ZnTe的导带底能级主要来自Te 5s和Te 5p电子的贡献; 价带由3个明显的区域构成, 上价带主要来自Te 5p电子, 中间价带-6.0~-8.0 eV区域的能级变化比较平缓, 主要来自Te 5p和Zn 3d电子, 价带底主要来自Te 5s电子的贡献。当压力逐渐增大时, 能带结构的色散关系未发生明显变化, 但导带底和价带顶的能级位置发生了一定的变化, 导致带隙大小发生变化。
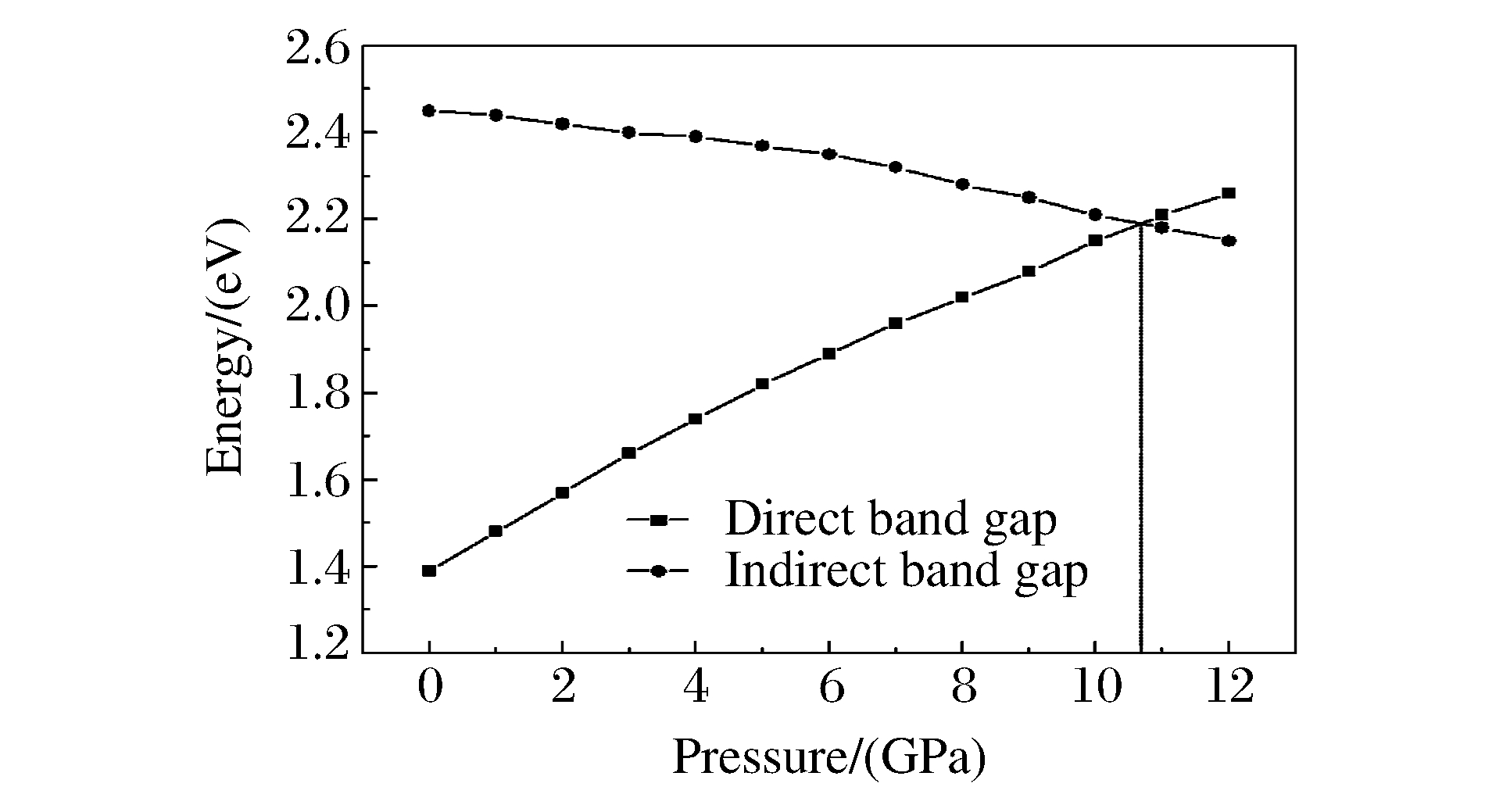
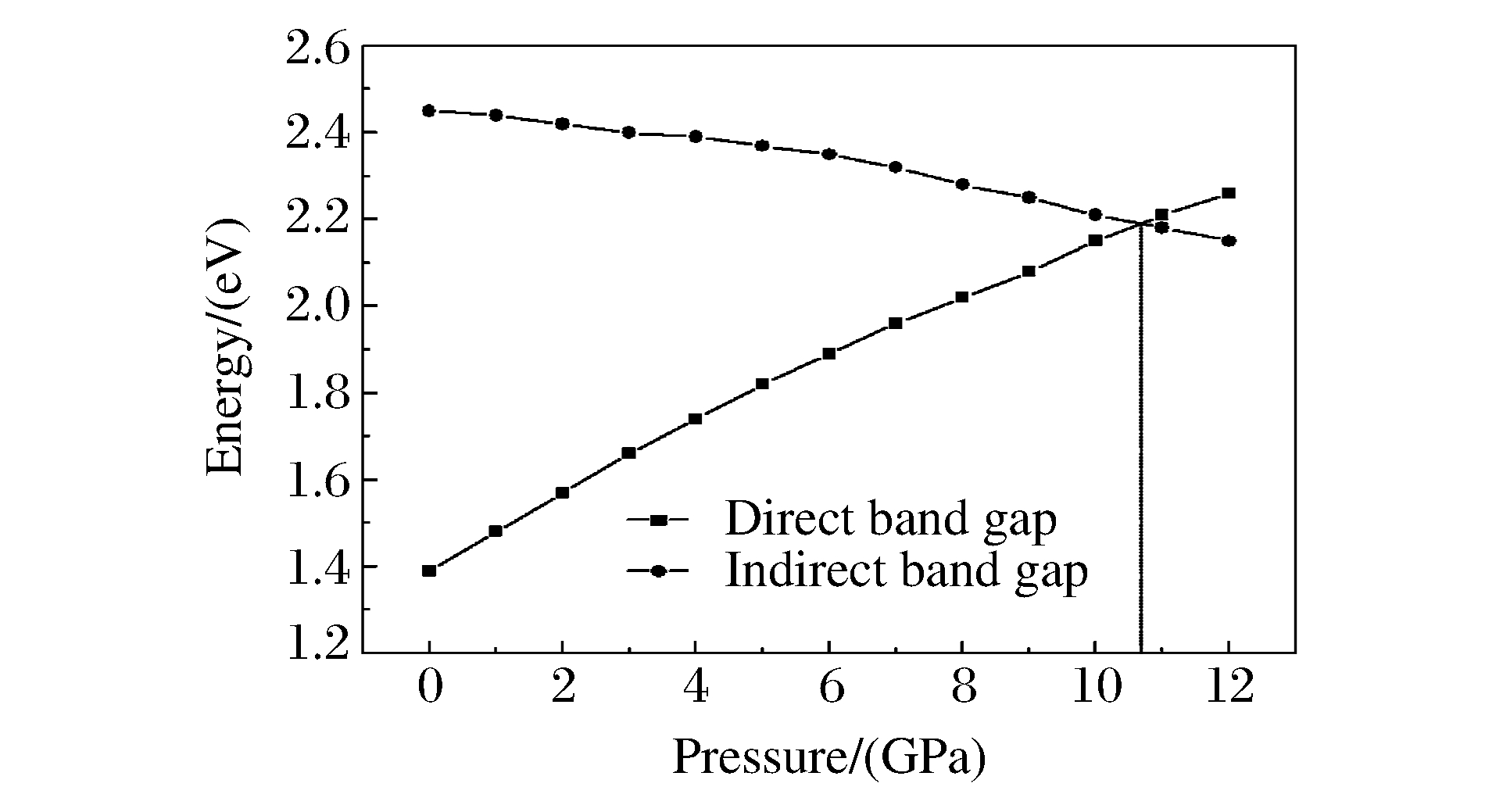
如图 6所示, 随着压力的增加, 直接带隙逐渐增大, 间接带隙逐渐减小, 两者呈现出完全不同的变化趋势。当压力增加至10.7 GPa时, 从G点竖直方向跃迁形成的直接带隙和非竖直方向跃迁(从G点到X点)形成的间接带隙大小相等, 此时直接带隙结构变成了间接带隙结构, 临界压力为10.7 GPa。如图 5(d)所示, 当压力增加至12.0 GPa时, 直接带隙大小为2.26 eV, 而间接带隙大小为2.15 eV, 间接带隙结构特征更加明显。不同压力下带隙的对比如表 1所示。
表 1 ZnTe在不同压力下的直接带隙和间接带隙Table 1. Direct and indirect band gaps of ZnTe under different pressuresPressure/
(GPa)E1/(eV) E2/(eV) Present Calc.[19] Calc.[20] Exp.[18] Present Calc.[19] Exp.[18] 0 1.39 1.28 1.10 2.39 2.45 2.11 3.30 1.0 1.48 1.35 - - 2.44 2.07 - 2.0 1.57 1.42 - - 2.42 2.04 - 3.0 1.66 1.49 - - 2.40 2.00 - 4.0 1.74 1.56 - - 2.39 1.97 - 5.0 1.82 1.63 - - 2.37 1.93 - 6.0 1.89 1.70 - - 2.35 1.90 - 7.0 1.96 1.77 - - 2.32 1.86 - 8.0 2.02 1.84 - - 2.28 1.82 - 9.0 2.08 1.91 - - 2.25 1.79 - 10.0 2.15 1.98 - - 2.21 1.76 - 10.7 2.19 - - - 2.19 - - 11.0 2.21 2.05 - - 2.18 1.72 - 12.0 2.26 2.12 - - 2.15 1.68 - Note:E1 and E2 represent the direct and indirect band gaps,respectively. 3.3 光电性质
电磁波在介质中传播, 当需要考虑吸收的影响时, 介电函数应写成复数形式ε(ω)=ε1(ω)+i ε2(ω), 式中:ε1(ω)=n2(ω)-k2(ω), ε2(ω)=2n(ω)k(ω), n、k分别为材料复折射率的实部、虚部, ω为圆频率。可以用ε1、ε2或者n、k来描述晶体的光学性质。利用Kramers-Krönig关系, 可以推导出晶体介电函数的实部ε1、虚部ε2、吸收系数α及反射系数R等[23-24]
ε1(ω)=1+2πp∫∞0ε2(ω)ss2−ω2ds (1) ε2(ω)=−2ωπp∫∞0ε1(ω)s2−ω2ds (2) n(ω)=√√ε21(ω)+ε22(ω)+ε1(ω)2 (3) α(ω)=2ωk(ω)c=ε2(ω)ωn(ω)c (4) R(ω)=|1−N1+N|2=(n−1)2+k2(n+1)2+k2 (5) 式中:p为积分主值,

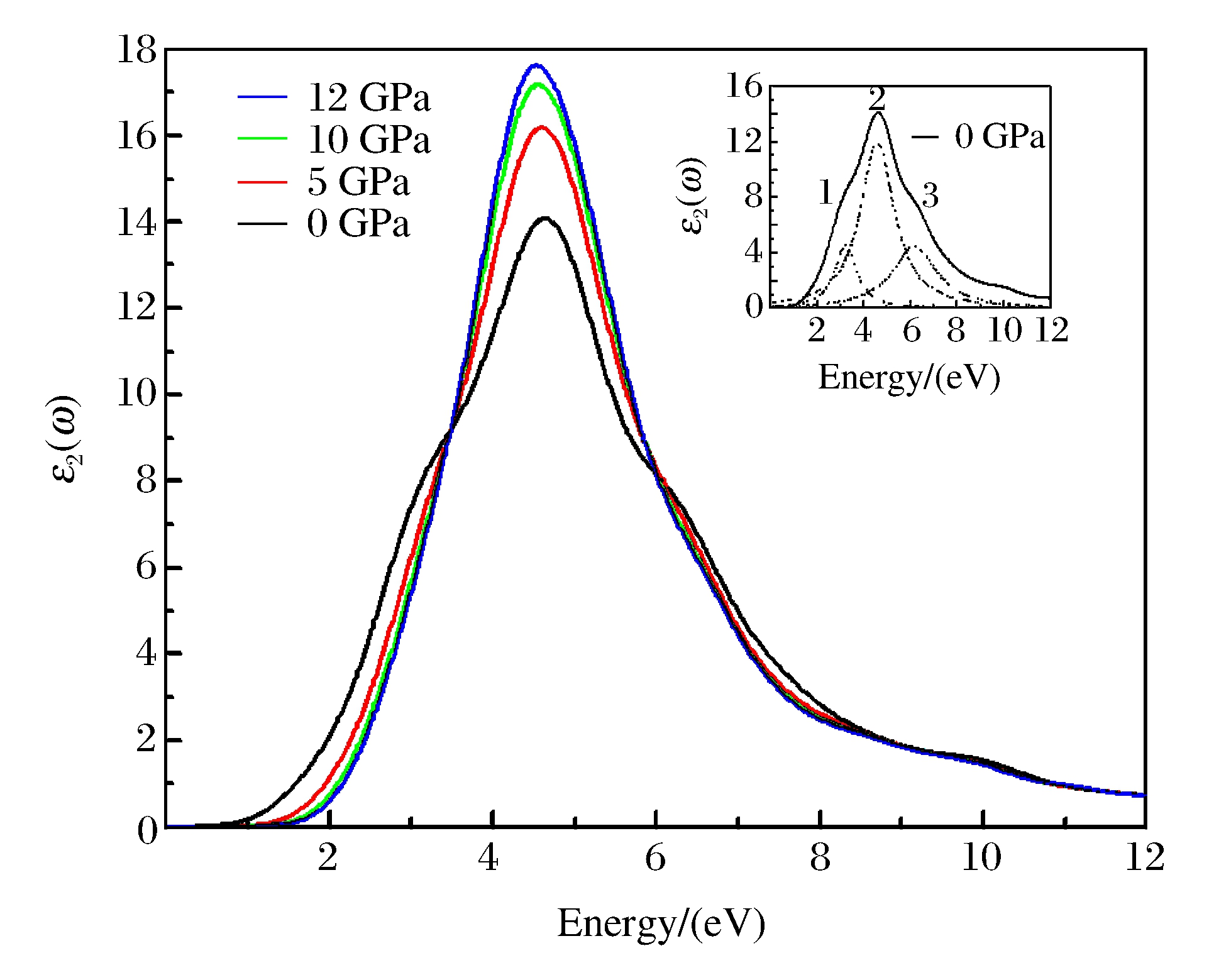
从介电函数虚部出发, 可以推导出复折射率、吸收系数、反射系数等光学常数, 因此介电常数虚部反映了能级间电子跃迁产生光谱的机理, 体系在较小波矢下对光场的线性响应由复介电常数的虚部ε2(ω)决定[25]。从某种意义上说, 介电函数虚部比宏观光学常数更能表征材料的物理特性, 更容易和物理过程的微观模型及固体的微观电子结构联系起来[26]。图 7为介电函数虚部随压力变化的关系图。当压力为0 GPa时, 介电函数在0~8.0 eV区域内出现了3个峰, 其中第2个峰最明显。结合态密度和能带结构图, 可以看出第1个峰约为3.2 eV, 来自Zn 5s与Te 5p电子之间的跃迁; 第2个峰约为4.6 eV, 来自Te 5p与Zn 3d电子间的跃迁; 第3个峰约为6.1 eV, 主要来自Te 5s与Zn 3d电子间的跃迁。随着压力的增加, 第1个和第3个峰逐渐减弱, 第2个峰逐渐增强, 说明压力增大有利于Te 5p与Zn 3d电子间的跃迁。
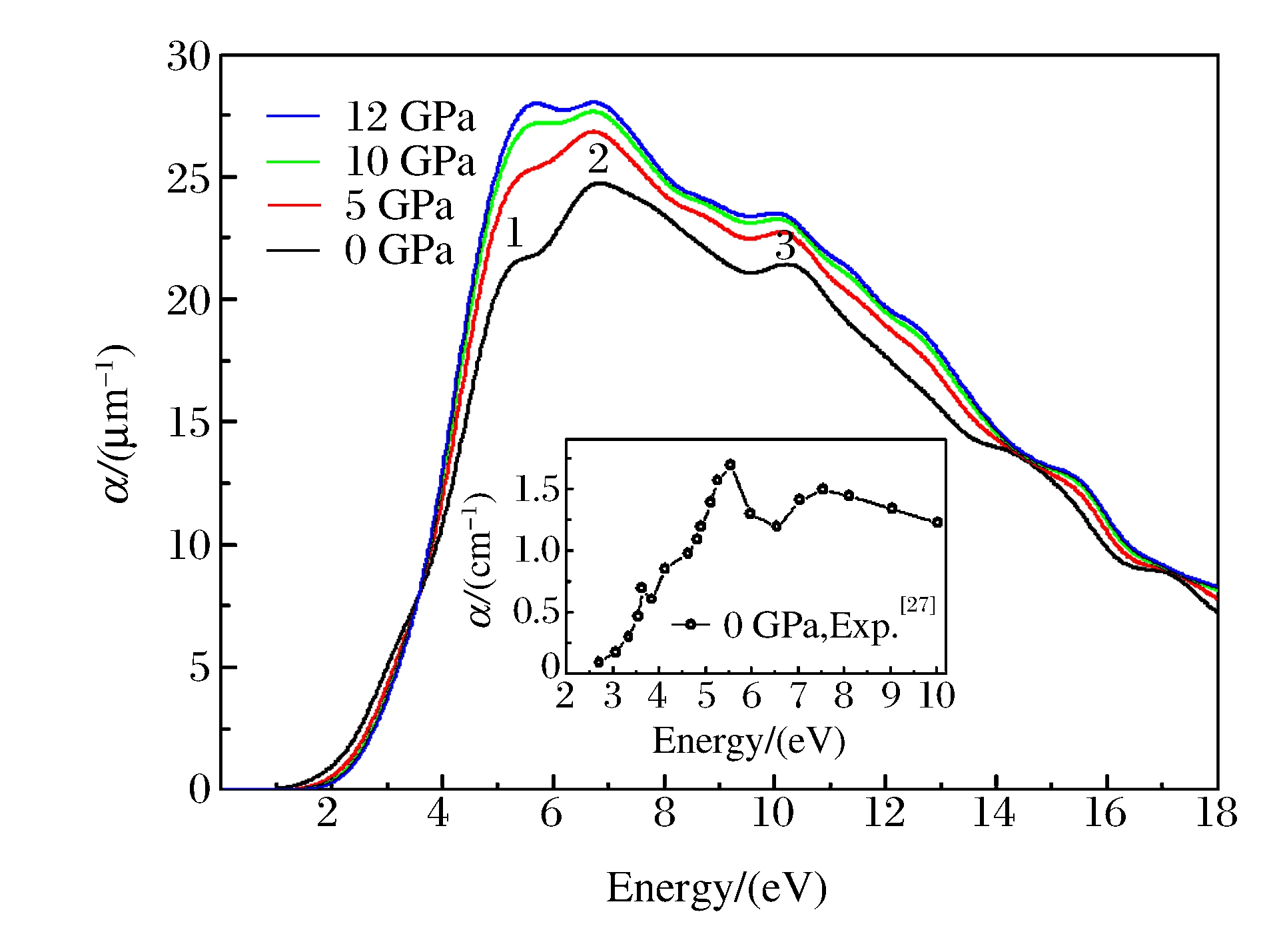
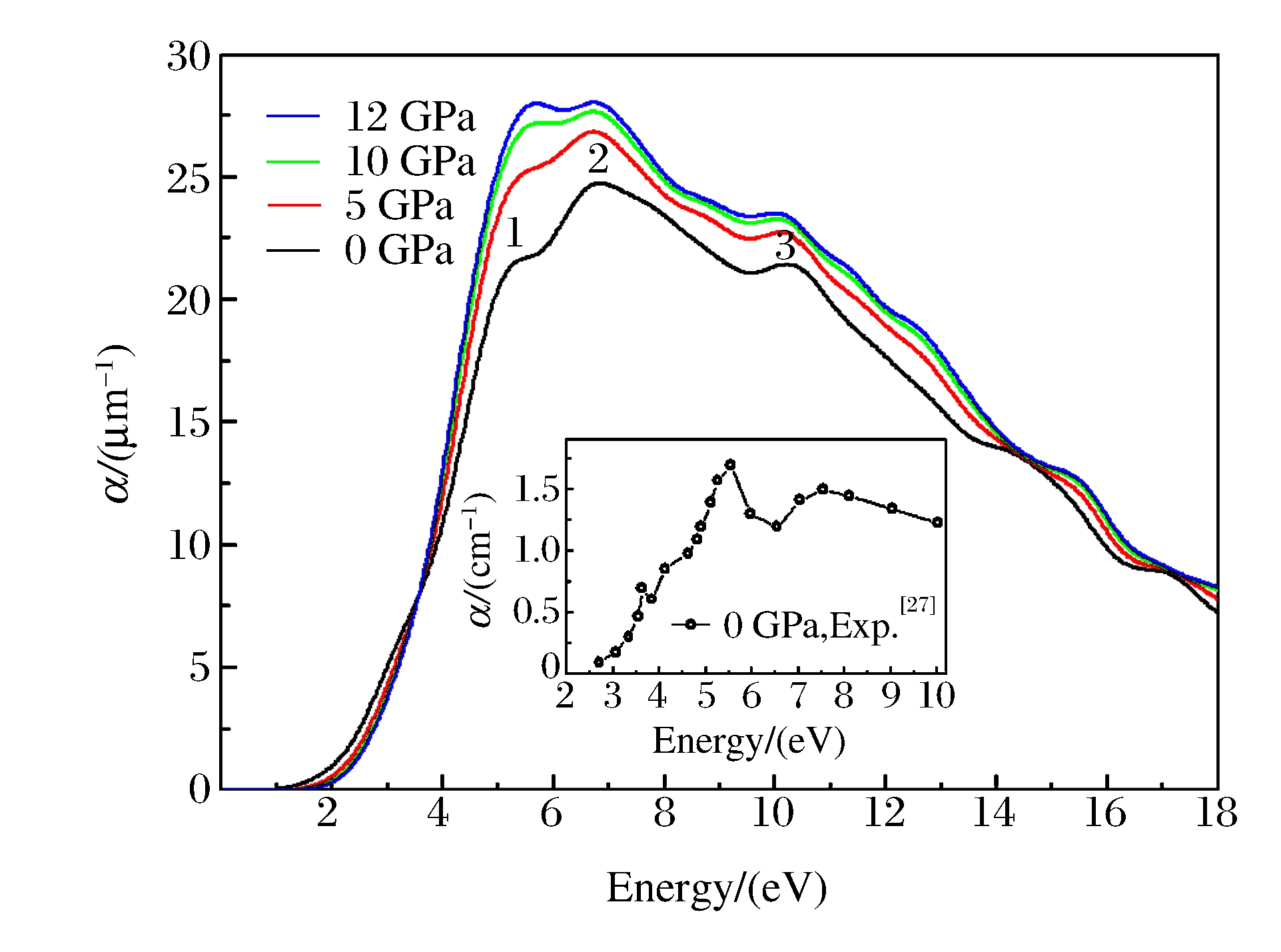
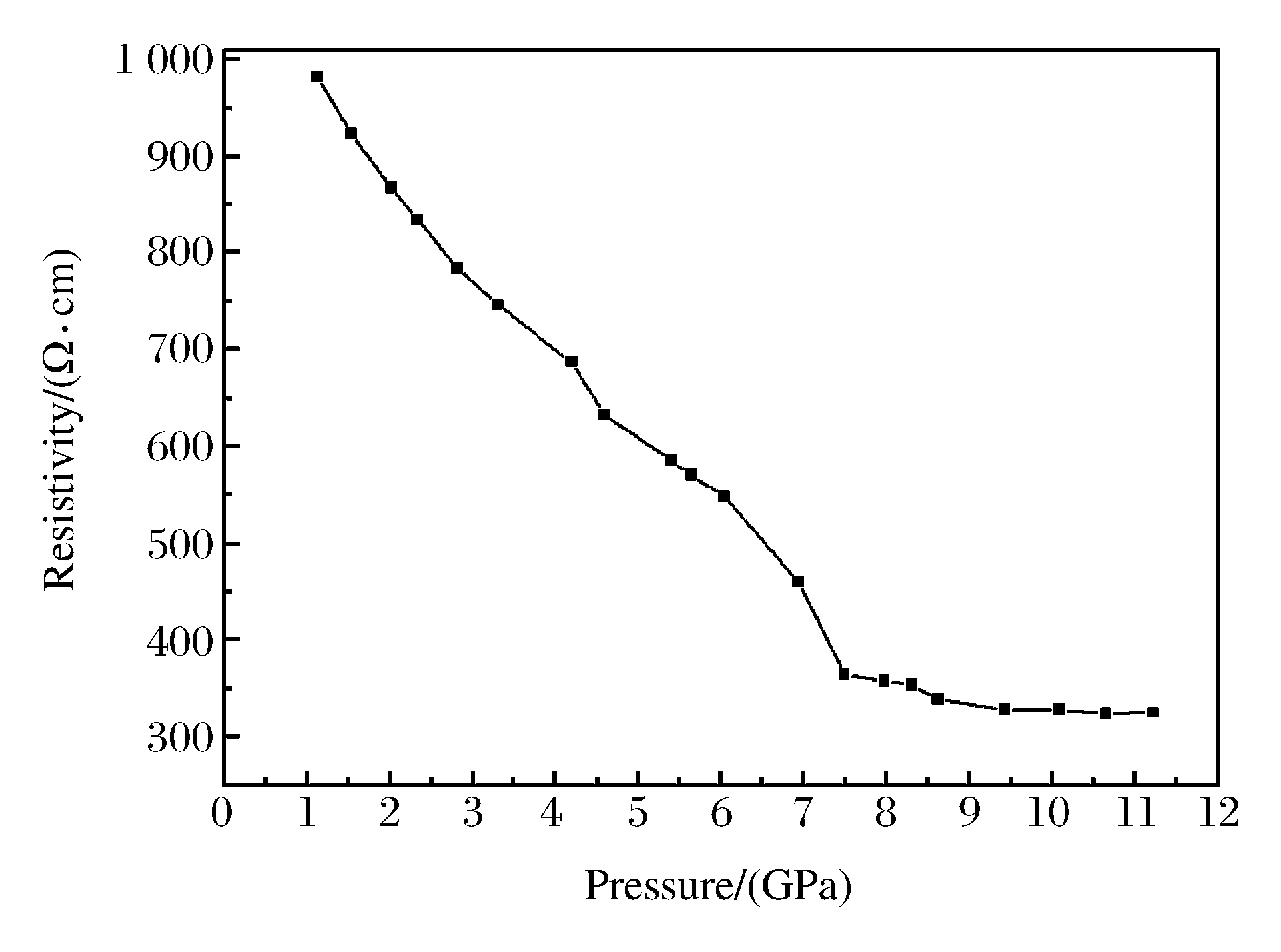
图 8为光学吸收系数随压力变化的关系图。从图 8中可以看出, 最佳光谱响应区主要位于紫外和可见光波段, 来源于价带电子吸收光子跃迁至导带, 产生电子-空穴对; 吸收系数高达105 cm-1, 表现出良好的光电性能。当外界压力为0 GPa时, 本征吸收限为1.28 eV, 该值和带隙宽度相对应, 与前人计算结果[22]及实验结果[27]都符合得很好; 吸收谱上出现了3个明显的光学吸收峰, 分别位于5.20、6.78和10.20 eV处。随着压力的增大, 吸收系数明显增大, 第1个峰的变化尤其明显, 这是因为轨道杂化加强后, Te 5p与Zn 3d电子间跃迁的几率更高。从整体来看, 电子在高压下更容易发生受激跃迁, 产生更多的电子-空穴对, 大大提高载流子浓度, 从而提高半导体材料ZnTe的导电能力, 这正好解释了实验上ZnTe在高压作用下导电能力增强的现象[28], 如图 9所示。
4. 结论
利用密度泛函理论下的平面波赝势和广义梯度近似(GGA)方法, 对闪锌矿ZnTe在高压下进行了电子结构和光电性质计算。结果表明:(1)高压对Zn原子和Te原子的态密度峰分布均有不同程度的影响, Te 5p与Zn 3d电子间出现了更加明显的轨道杂化现象; (2)当压力为10.7 GPa时, ZnTe由直接带隙半导体转变为间接带隙半导体, 能带结构对光电性质有决定性的影响, 故这一发现将为ZnTe在高压下的光电性质和应用研究方面提供重要参考意义; (3)压力增大有利于杂化轨道间电子的跃迁和光吸收能力的提高, 很好地解释了高压下ZnTe导电能力增强的实验现象, 该研究结果为高压实验以及高压下光电器件的制作提供了一些理论依据和参考。
-
表 1 ZnTe在不同压力下的直接带隙和间接带隙
Table 1. Direct and indirect band gaps of ZnTe under different pressures
Pressure/
(GPa)E1/(eV) E2/(eV) Present Calc.[19] Calc.[20] Exp.[18] Present Calc.[19] Exp.[18] 0 1.39 1.28 1.10 2.39 2.45 2.11 3.30 1.0 1.48 1.35 - - 2.44 2.07 - 2.0 1.57 1.42 - - 2.42 2.04 - 3.0 1.66 1.49 - - 2.40 2.00 - 4.0 1.74 1.56 - - 2.39 1.97 - 5.0 1.82 1.63 - - 2.37 1.93 - 6.0 1.89 1.70 - - 2.35 1.90 - 7.0 1.96 1.77 - - 2.32 1.86 - 8.0 2.02 1.84 - - 2.28 1.82 - 9.0 2.08 1.91 - - 2.25 1.79 - 10.0 2.15 1.98 - - 2.21 1.76 - 10.7 2.19 - - - 2.19 - - 11.0 2.21 2.05 - - 2.18 1.72 - 12.0 2.26 2.12 - - 2.15 1.68 - Note:E1 and E2 represent the direct and indirect band gaps,respectively. -
[1] Mitchell D W, Das T P, Potzel W, et al. First-principles investigation of 67Zn isomer shifts in ZnF2 and the chalcogenides ZnO, ZnS, ZnSe, and ZnTe[J]. Phys Rev B, 1993, 48(22): 16449-16462. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.48.16449 [2] Bozzini B, Baker M A, Cavallotti P L, et al. Electrodeposition of ZnTe for photovoltaic cells[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2000, 361(2): 388-395. [3] Ishizaki T, Ohtomo T, Fuwa A. Structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnTe thin films electrochemically deposited from a citric acid aqueous solution[J]. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2004, 37(2): 255-258. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/37/2/014 [4] 邵军. Ti掺杂ZnTe体材料的优化光致发光光谱[J].物理学报, 2003, 52(7): 1743-1747.Shao J. Optimal photoluminescence spectrum from Ti-doped ZnTe[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2003, 52(7): 1743-1747. (in Chinese) [5] Sinyukov A M, Hayden L M. Generation and detection of terahertz radiation with multilayered electro-optic polymer films[J]. Opt Lett, 2002, 27(1): 55-57. doi: 10.1364/OL.27.000055 [6] Löffler T, Hahn T, Thomson M, et al. Large-area electro-optic ZnTe terahertz emitters[J]. Opt Express, 2005, 13(14): 5353-5362. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.005353 [7] 王月.高压下ZnX(S、Se、Te)和TiO2的电学性质[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2010: 2-4.Wang Y. The electrical properties of ZnX(S, Se, Te)and TiO2 under high pressure[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2010: 2-4. (in Chinese) [8] Samara G A, Drickamer H G. Pressure induced phase transitions in some Ⅱ-Ⅵ compounds[J]. J Phys Chem Solids, 1962, 23(5): 457-461. doi: 10.1016/0022-3697(62)90086-0 [9] San-miguel A, Polian A, Gauthier M, et al. ZnTe at high pressure: X-ray-absorption spectroscopy and X-ray-diffraction studies[J]. Phys Rev B, 1993, 48(12): 8683-8693. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.48.8683 [10] Franco R, Mori-Sanchez P, Recio J M, et al. Theoretical compressibilities of high-pressure ZnTe polymorphs[J]. Phys Rev B, 2003, 68(19): 195208-195212. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.195208 [11] 吕冉, 高涛, 李喜波, 等.闪锌矿ZnTe高温高压下的弹性及热力学性质[J].物理化学学报, 2010, 26(1): 13-17.Lü R, Gao T, Li X B, et al. Elastic and thermodynamic properties of zinc-blende ZnTe under high temperature and pressure[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2010, 26(1): 13-17. (in Chinese) [12] Perdew J P, Levy M. Physical content of the exact Kohn-Sham orbital energies: Band gaps and derivative discontinuities[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1983, 51(20): 1884-1887. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.51.1884 [13] 何开华, 郑广, 陈刚, 等.高压下氧化镉弹性性质、电子结构和光学性质的第一性原理研究[J].高压物理学报, 2007, 21(3): 299-304.He K H, Zheng G, Chen G, et al. First principles study of the elastic, electronic and optical properties of CdO under pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2007, 21(3): 299-304. (in Chinese) [14] Kresse G, Hafner J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals[J]. Phys Rev B, 1993, 47(1): 558-561. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.558 [15] Kresse G, Hafner J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal-amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium[J]. Phys Rev B, 1994, 49(20): 14251-14269. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.49.14251 [16] Kresse G, Furthmuller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Comput Mater Sci, 1996, 6(1): 15-50. doi: 10.1016/0927-0256(96)00008-0 [17] Nassour A. First-principles calculations of structural properties and lattice dynamics in ZnSexTe1-x alloys[J]. Comput Mater Sci, 2013, 77(1): 403-407. [18] Lempert R G, Hass K C, Ehrenreich H. Molecular coherent-potential approximation for zinc-blende pseudobinary alloys[J]. Phys Rev B, 1987, 36(2): 1111-1129. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.36.1111 [19] Khenata R, Bouhemadou A, Sahnoun M, et al. Elastic, electronic and optical properties of ZnS, ZnSe and ZnTe under pressure[J]. Comput Mater Sci, 2006, 38(1): 29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2006.01.013 [20] Sheetal S, Verma A S, Sarkar B K, et al. FP-LAPW+lo calculations for the structural, electronic, optical and mechanical properties of ZnX(X=S, Se and Te)[C]//Proceeding of the 56th DAE Solid Physics Symposium. Atlanta: American Institute of Physics, 2012: 849-850. [21] Stampfl C, van de Walle C G. Density-functional calculations for Ⅲ-Ⅴ nitrides using the local-density approximation and the generalized gradient approximation[J]. Phys Rev B, 1999, 59(8): 5521-5535. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.5521 [22] Karazhanov S Z, Ravindran P, Kjekshus A, et al. Electronic structure and optical properties of ZnX(X=O, S, Se, Te): A density functional study[J]. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75(15): 155104-155117. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.75.155104 [23] 黄昆, 韩汝琦.固体物理学[M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 1988: 438-440.Huang K, Han R Q. Solid-State Physics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1988: 438-440. (in Chinese) [24] 沈学础.半导体光谱和光学性质[M].北京: 科学出版社, 1992: 7-10.Shen X C. Spectrum and Optical Property of Semiconductor[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1992: 7-10. (in Chinese) [25] 冯晶, 肖冰, 陈敬超. CuInSe2电子结构与光学性质的第一性原理计算[J].物理学报, 2007, 56(10): 5990-5995.Feng J, Xiao B, Chen J C. Electronic and optical properties of CuInSe2 from ab-initio calculations[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56(10): 5990-5995. (in Chinese) [26] 郭建云, 郑广, 何开华, 等. Al, Mg掺杂GaN电子结构及光学性质的第一性原理研究[J].物理学报, 2008, 57(6): 3740-3746.Guo J Y, Zheng G, He K H, et al. First-principles study on electronic structure and optical properties of Al and Mg doped GaN[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2008, 57(6): 3740-3746. (in Chinese) [27] Adachi S. Optical Constants of Crystalline and Amorphous Semiconductors: Numerical Data and Graphical Information[M]. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1999: 473-478. [28] Cui X Y, Hu T J, Yang J, et al. The electrical properties of ZnTe under high pressure and moderate temperature[J]. Phys Status Solidi C, 2011, 8(5): 1676-1679. doi: 10.1002/pssc.201000609 -








 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: