Stress Distribution and Propagation Mechanism of Crack Tip in Directional Fracturing Blasting under the Influence of Free Boundary
-
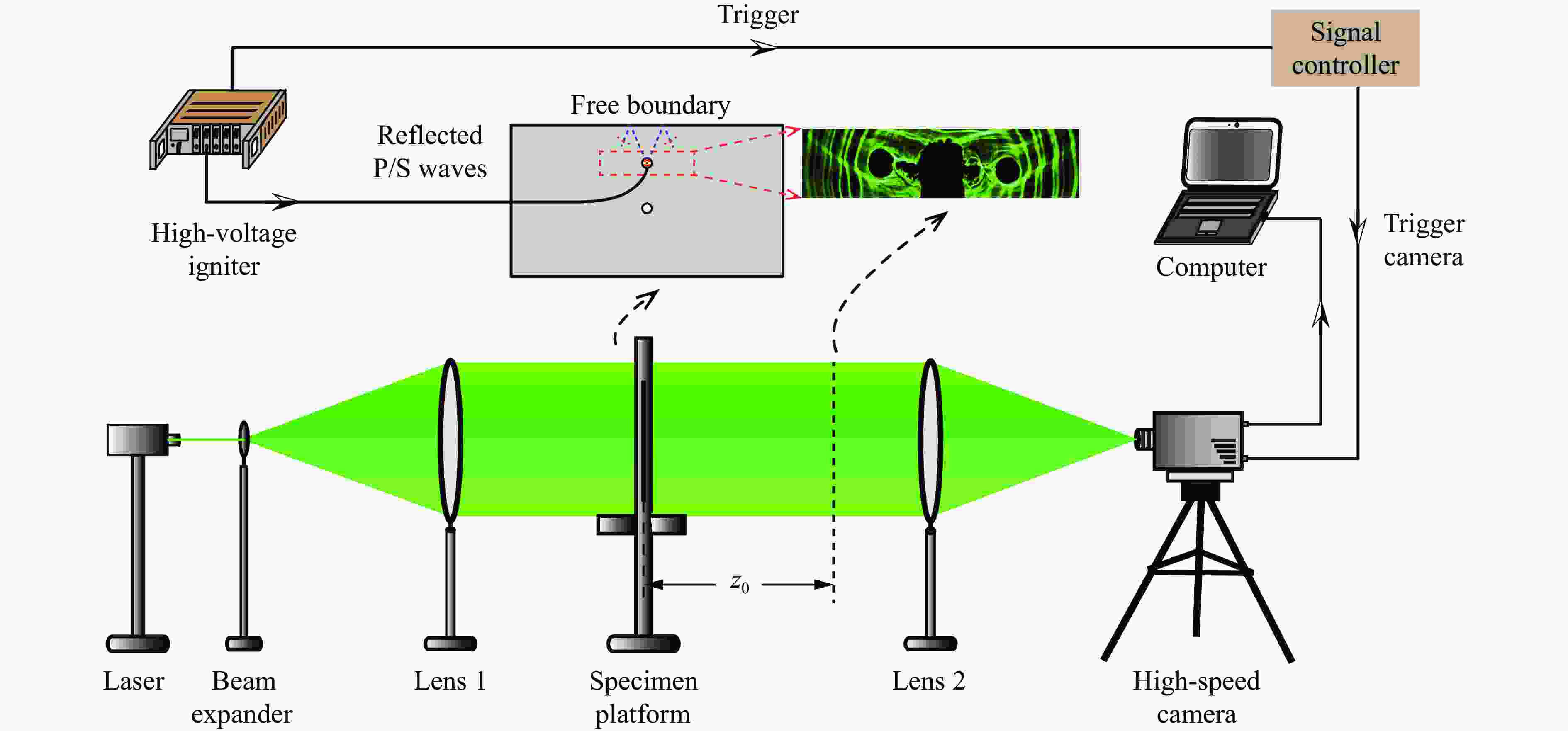
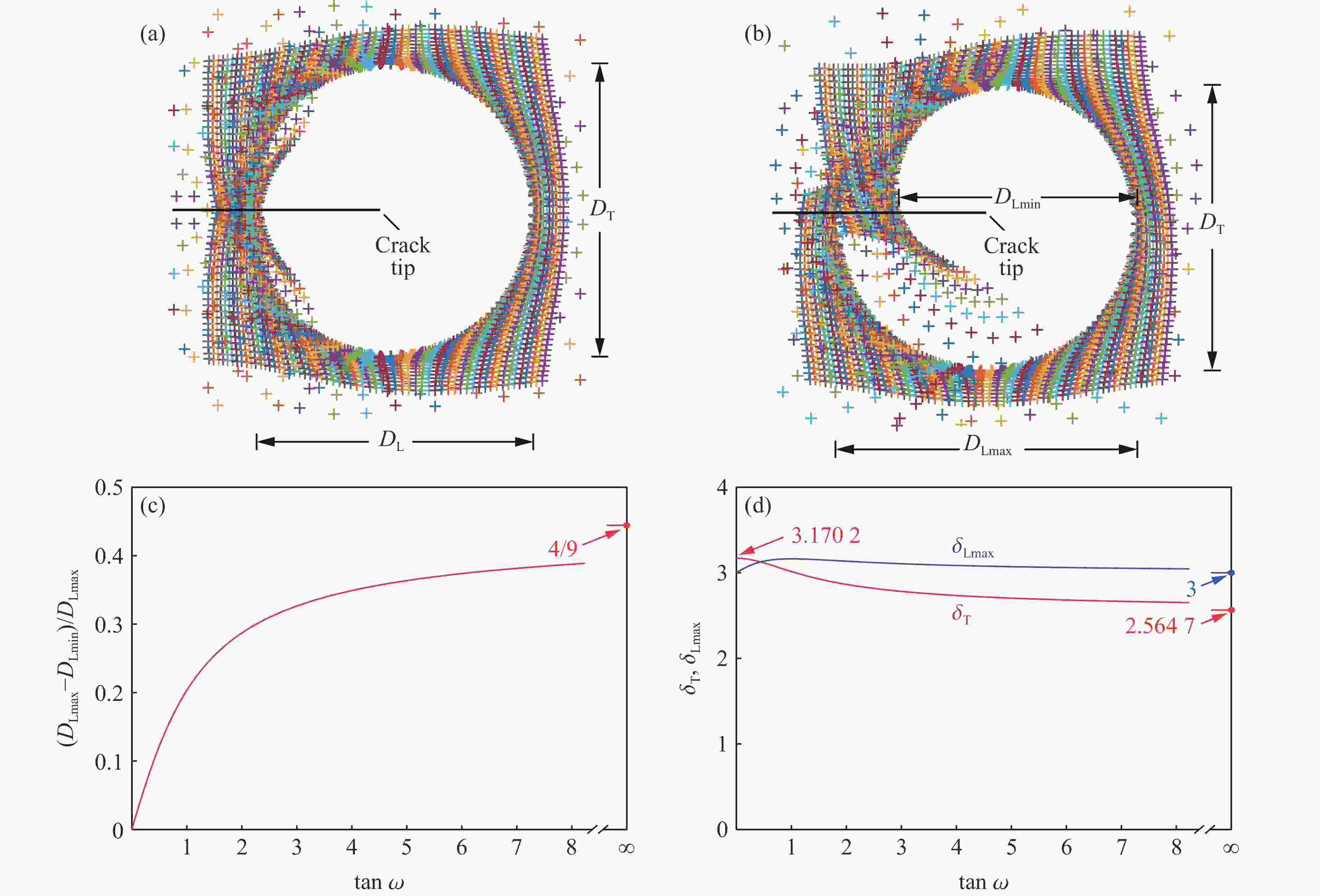
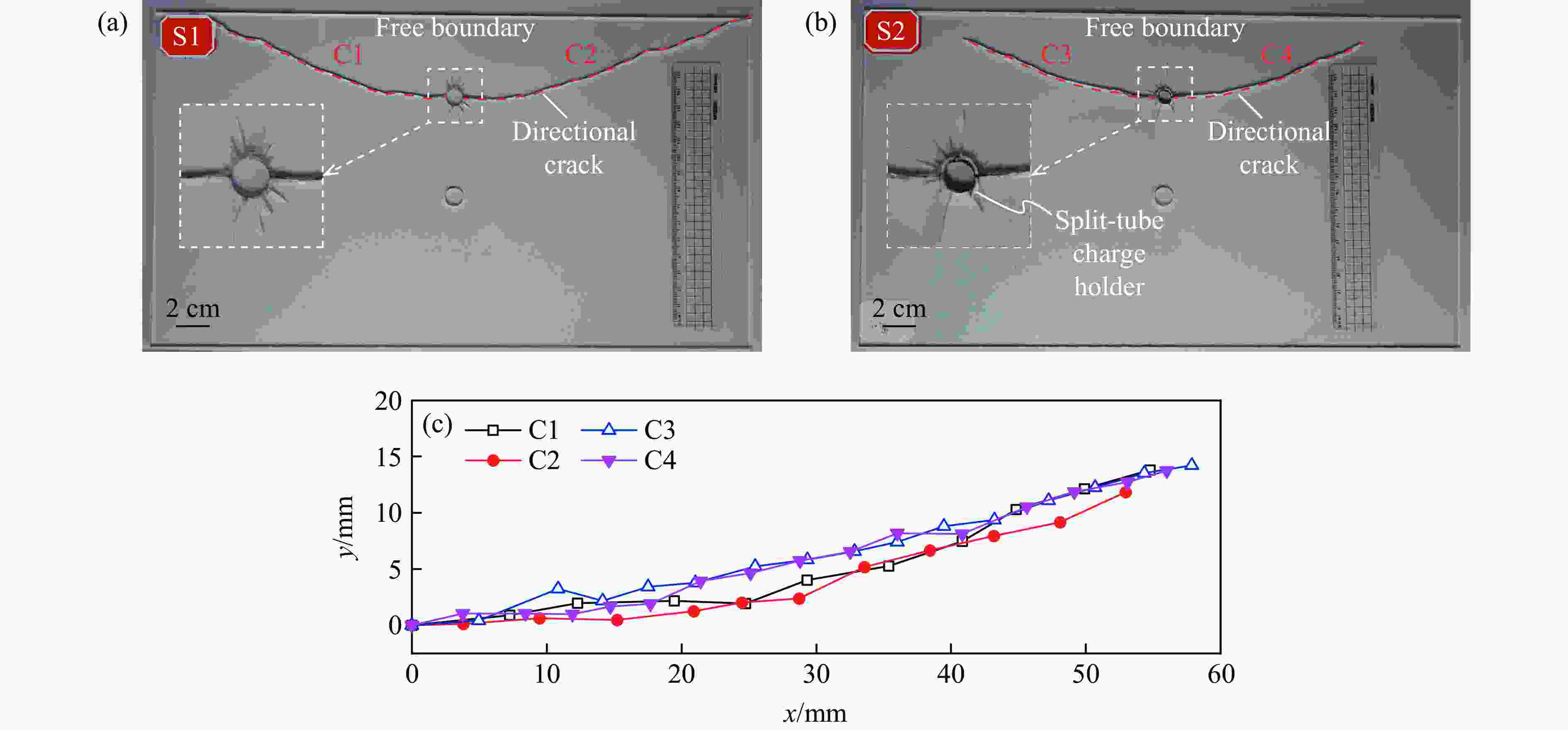
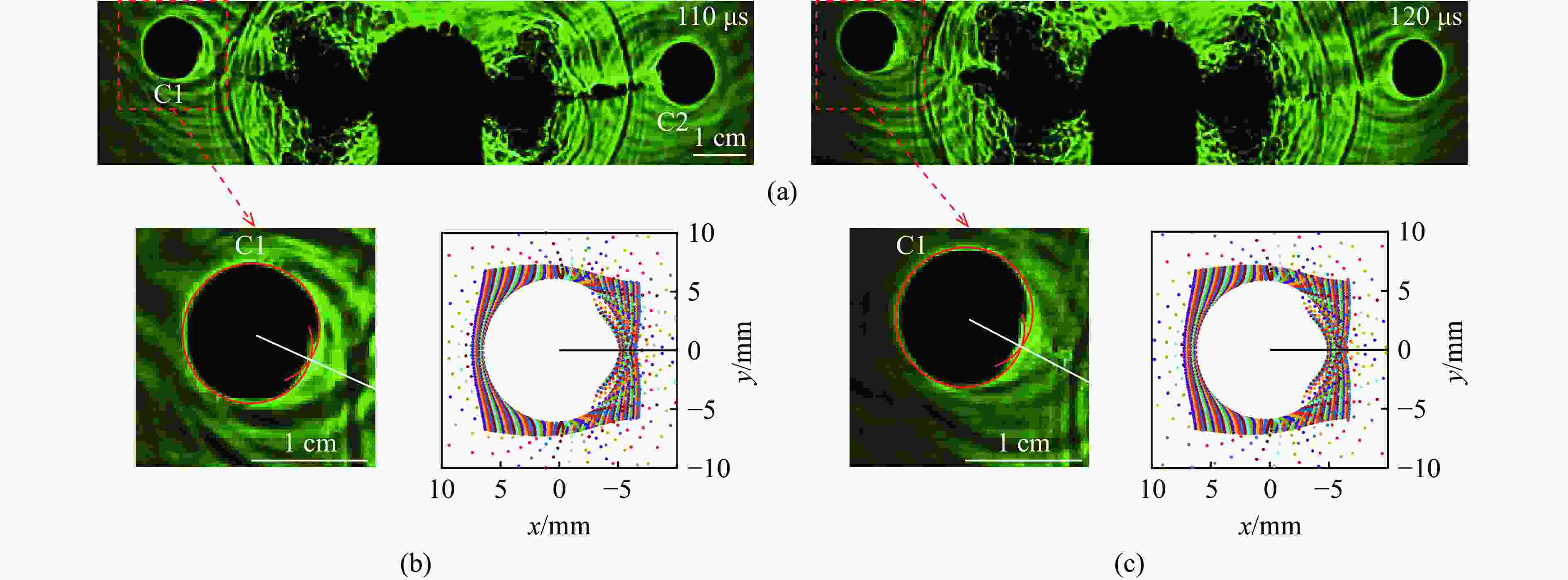
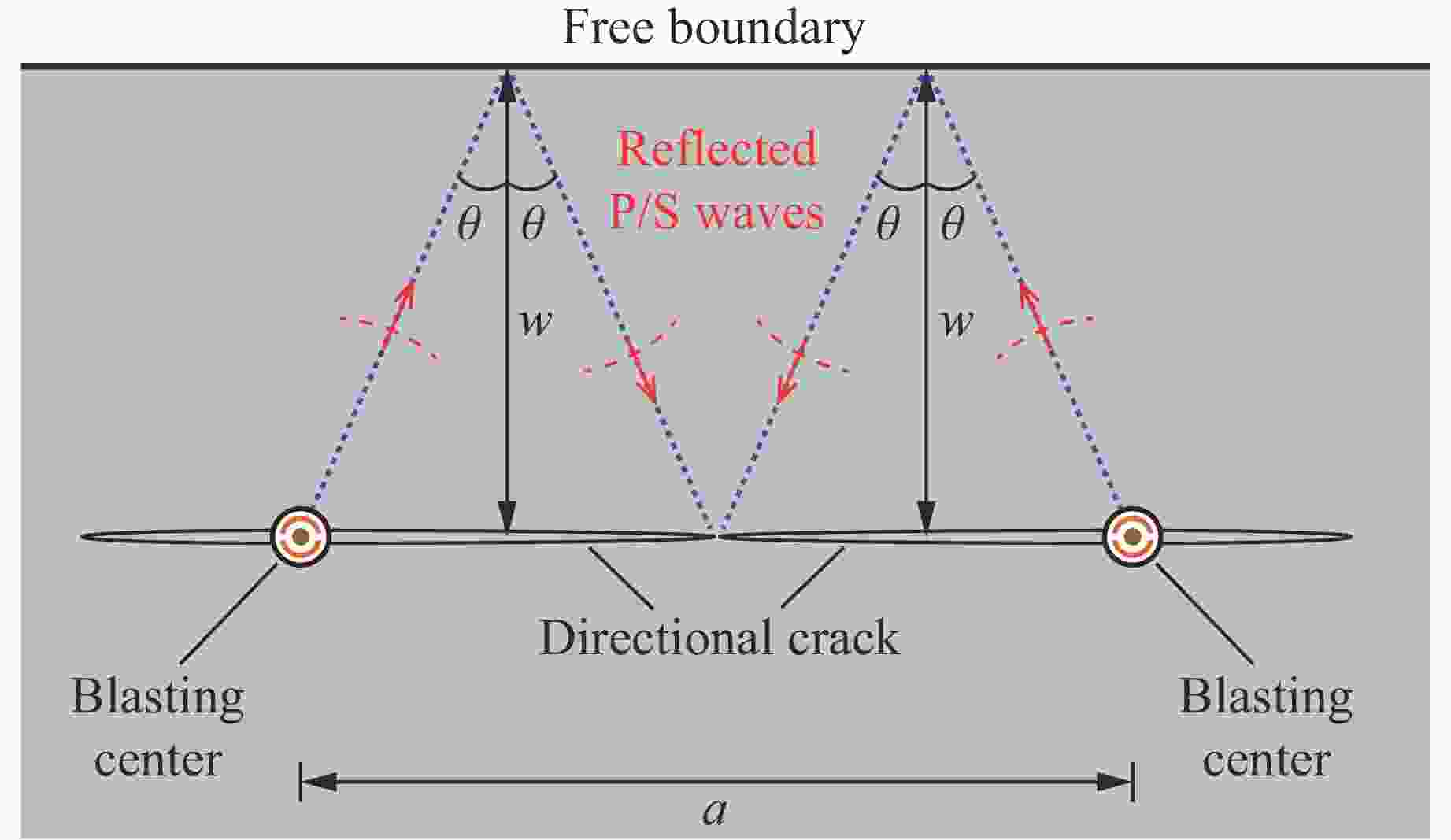
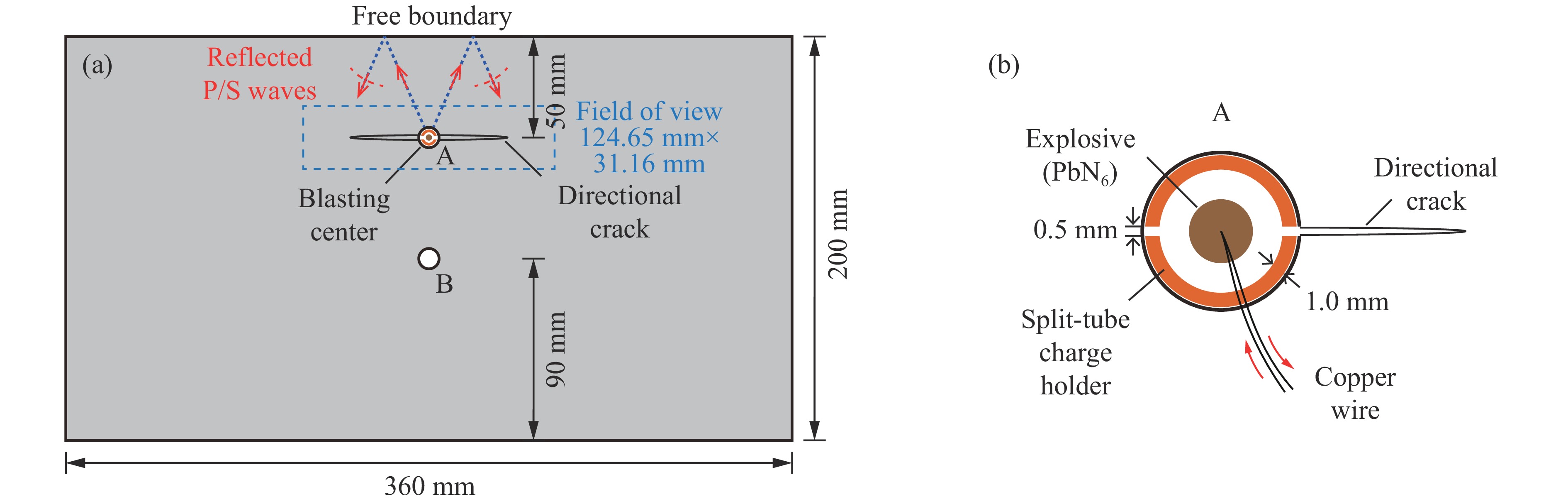
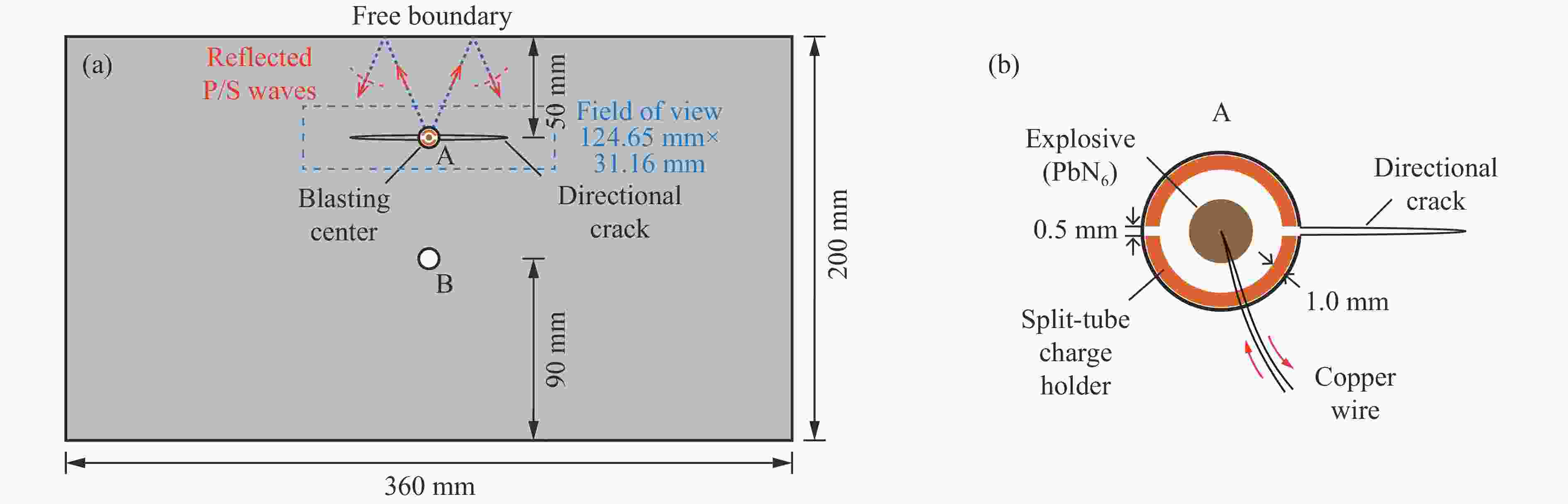
摘要: 天然岩体常含自由边界,对定向断裂爆破产生干扰。为探究自由边界对定向断裂爆破的影响,采用爆炸焦散线方法和高速摄影技术,研究了含自由边界时定向爆炸裂纹尖端的应力分布和扩展机理。自由边界的反射P/S波作用于定向爆炸裂纹,改变了裂尖应力分布,产生了“弧线形”裂纹扩展路径。定向爆炸裂纹扩展可分为3个阶段。(1) 反射波作用前:裂尖受爆生气体“气楔”作用,产生Ⅰ型断裂,并沿直线扩展。(2) 反射波作用时:反射P/S波均使裂尖受张拉-剪切作用,产生Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型断裂,裂纹偏转趋向自由边界;在反射P波的作用下裂尖产生畸变焦散斑,裂尖应力由K场主导变为非K场主导,而在反射S波的作用下裂尖应力恢复为K场主导。(3) 反射波作用后:裂尖在惯性作用下恢复为Ⅰ型断裂,沿直线扩展。在明确反射P/S波对定向爆炸裂纹作用的基础上,推导了自由边界影响下定向断裂爆破炮孔间距的计算公式,可为精细化定向断裂爆破提供理论参考。Abstract: Natural rock masses often contain free boundaries, which can interfere with directional fracturing blasting. To investigate effects of free boundary on directional fracturing blasting, the caustics method and high-speed photography were used to study the crack-tip stress distribution and propagation of directional blast-induced cracks. The reflected P/S waves from the free boundary act on a directional blast-induced crack, and change the crack-tip stress distribution and generate an “arc shaped” crack path. Directional blast-induced crack propagation can be divided into three stages. Stage one: before the action of reflected waves, the crack tip is subjected to the action of a blast-induced gas wedge, resulting in a mode Ⅰ crack that propagates along a straight line. Stage two: under the action of reflected waves, both reflected P and S waves cause the crack tip to be subjected to tension and shear action, resulting in a mixed mode Ⅰ-Ⅱ crack which deflects towards the free boundary. Under reflected P waves, the crack tip produces distorted caustics, and crack-tip stress changes from K-dominated field to non-K-dominated field, while under reflected S waves, crack-tip stress returns to K-dominated field. Stage three: after the action of reflected waves, the crack tip is subjected to inertial action and then returns to a mode Ⅰ crack which propagates along a straight line. On the basis of clarifying effects of reflected P/S waves on the tip of directional blast-induced cracks, a calculation formula for the distance between two directional fracturing blasting holes under the influence of free boundary is derived, providing a theoretical basis for refined directional fracturing blasting.
-
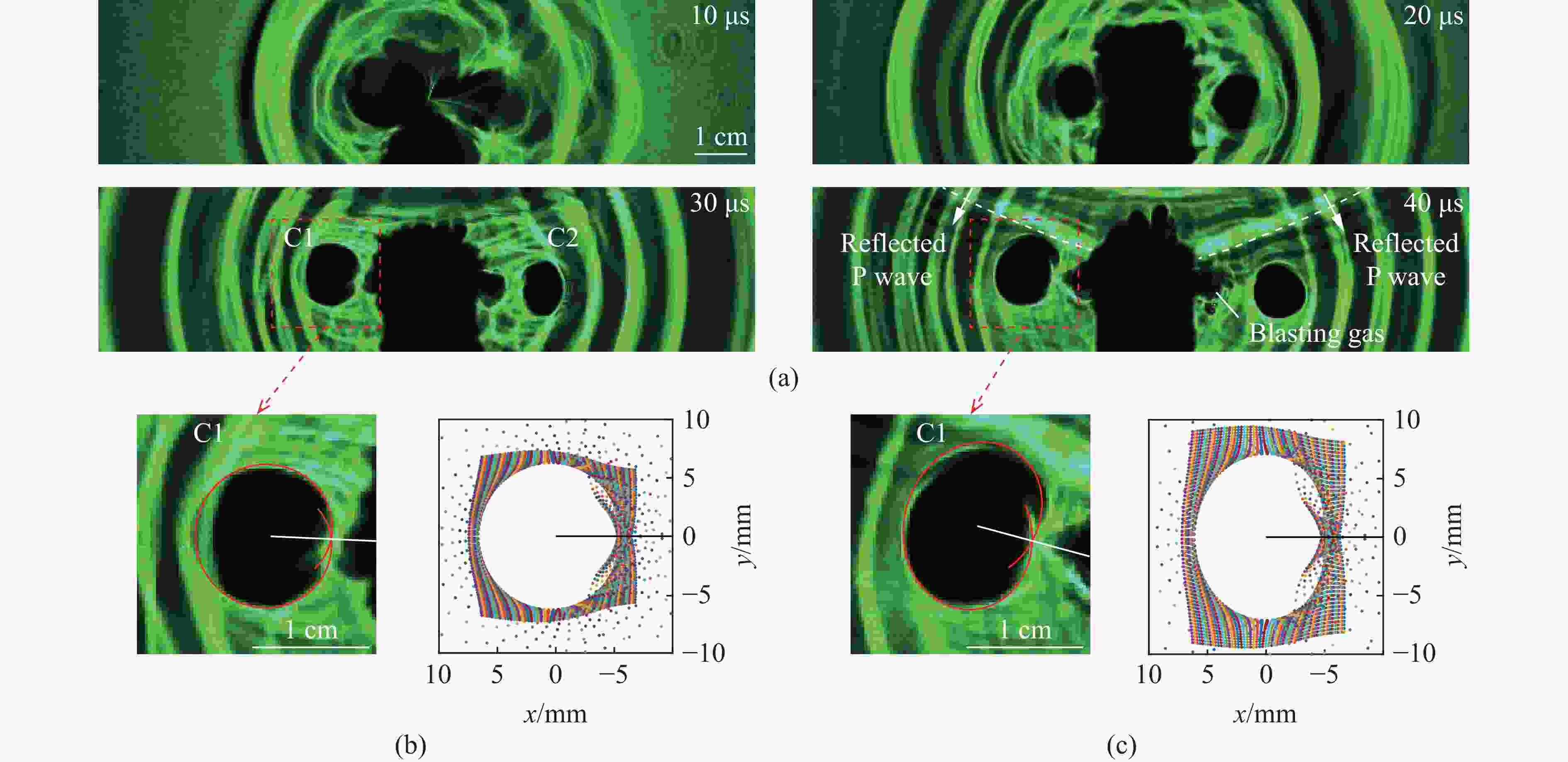
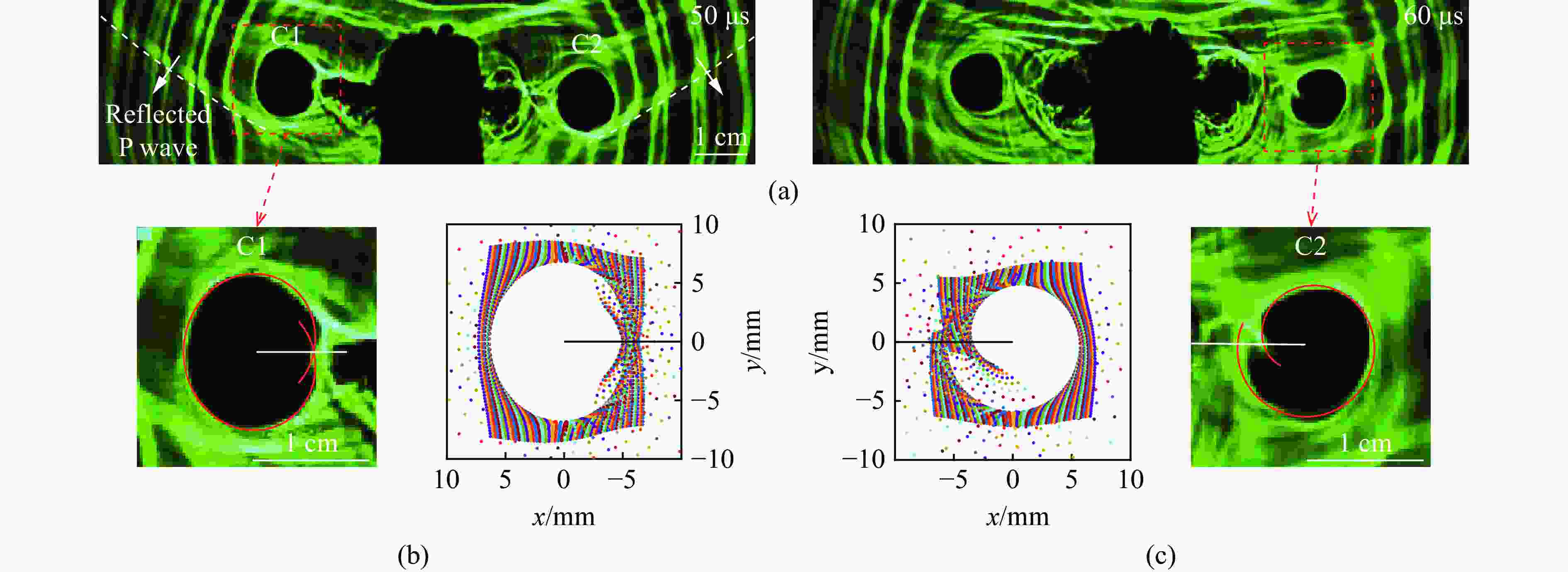
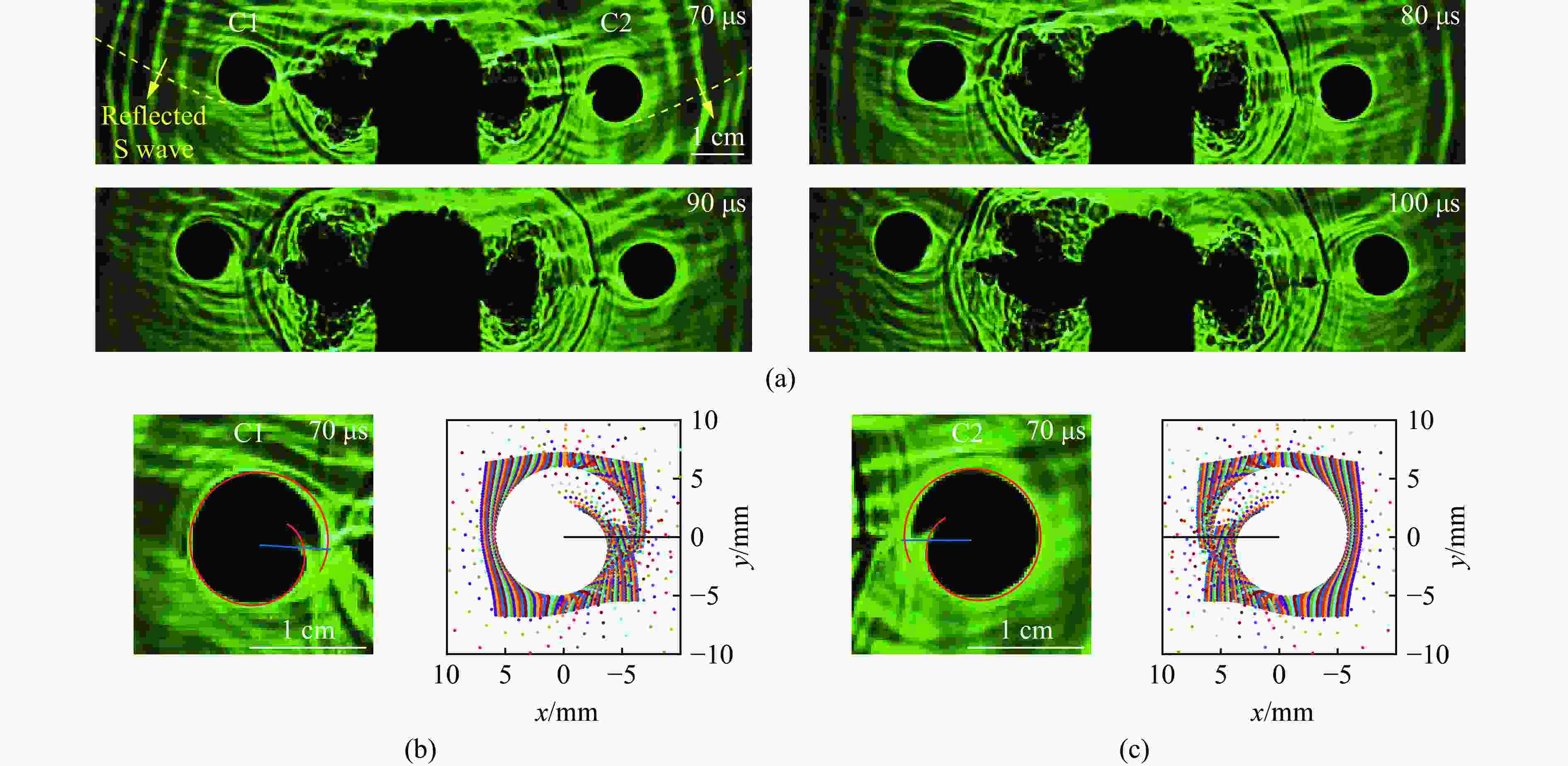
图 7 反射S波作用时:(a) 爆炸焦散斑图像,(b) t=70 μs 时C1裂纹尖端的Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型焦散斑,(c) t=70 μs时C2裂纹尖端的Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型焦散斑
Figure 7. Under action of reflected S wave: (a) blast-induced caustics patterns; (b) mixed Ⅰ-Ⅱ mode caustics pattern at the tip of crack C1 at 70 μs; (c) mixed Ⅰ-Ⅱ mode caustics pattern at the tip of crack C2 at 70 μs
-
[1] 赵晓明, 杨玉民, 蒋楠, 等. 深埋引水隧洞光面爆破周边孔装药结构优化试验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(4): 045301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220503ZHAO X M, YANG Y M, JIANG N, et al. Optimization of charging structure of surrounding holes in smooth blasting of deep diversion tunnel [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(4): 045301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220503 [2] 杨仁树, 李成孝, 陈骏, 等. 我国煤矿岩巷爆破掘进发展历程与新技术研究进展 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(1): 224–241.YANG R S, LI C X, CHEN J, et al. Development history and new technology research progress of rock roadway blasting excavation in coal mines in China [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 224–241. [3] 何满潮. 无煤柱自成巷开采理论与110工法 [J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2023, 40(5): 869–881.HE M C. Theory and engineering practice for non-pillars mining with automagical entry formation and 110 mining method [J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2023, 40(5): 869–881. [4] 乔国栋, 刘泽功, 高魁, 等. 切缝药包超前预裂爆破厚硬顶板矿压与瓦斯综合防治试验研究 [J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2024, 53(2): 334–345, 376.QIAO G D, LIU Z G, GAO K, et al. Experimental study on the control of mine pressure and gas governance in thick and hard roof by pre-blasting of slotted cartridge [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2024, 53(2): 334–345, 376. [5] 杨国梁, 毕京九, 董智文, 等. 定向断裂控制爆破下层理页岩的致裂机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(6): 061001.YANG G L, BI J J, DONG Z W, et al. Fracturing mechanism of bedding shale under directional fracture-controlled blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(6): 061001. [6] 杨仁树, 丁晨曦, 杨立云, 等. 含缺陷PMMA介质的定向断裂控制爆破试验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(3): 690–696.YANG R S, DING C X, YANG L Y, et al. Experimental study on controlled directional fracture blasting on PMMA mediums with flaws [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(3): 690–696. [7] 岳中文, 郭洋, 许鹏, 等. 定向断裂控制爆破爆生裂纹扩展机理的实验研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(2): 50–58. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.09.0816YUE Z W, GUO Y, XU P, et al. Controlled blasting experimental study on the mechanism of blast-induced crack propagation under directional fracture [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(2): 50–58. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.09.0816 [8] 岳中文, 郭洋, 许鹏, 等. 定向断裂控制爆破的空孔效应实验分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(3): 304–311. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455-(2015)03-0304-08YUE Z W, GUO Y, XU P, et al. Analysis of empty hole effect in directional fracture controlled blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(3): 304–311. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455-(2015)03-0304-08 [9] 王雁冰, 商禹智, 石震鑫, 等. 定向断裂双孔爆破含缺陷介质裂纹扩展的动焦散试验 [J]. 爆破, 2018, 35(1): 15–20, 48. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2018.01.003WANG Y B, SHANG Y Z, SHI Z X, et al. Dynamic caustics experiment on crack propagation in defective medium by directional breaking with double hole blasting [J]. Blasting, 2018, 35(1): 15–20, 48. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2018.01.003 [10] 许鹏, 陈程, 郭洋, 等. 含垂直层理介质在切缝药包爆破下裂纹扩展行为的试验研究 [J]. 矿业科学学报, 2019, 4(6): 498–505.XU P, CHEN C, GUO Y, et al. Experimental study on crack propagation of slit charge blasting in media with vertical bedding plane [J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2019, 4(6): 498–505. [11] 费鸿禄, 山杰, 包士杰, 等. 节理几何特征对爆破裂纹扩展的数值模拟研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2023, 29(5): 12–21.FEI H L, SHAN J, BAO S J, et al. Numerical simulation study of joint geometric characteristics for explosion crack propagation [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2023, 29(5): 12–21. [12] 郭德勇, 张慧杰, 吕鹏飞, 等. 断层对深孔聚能爆破煤层增透的影响 [J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2014, 36(10): 1281–1286.GUO D Y, ZHANG H J, LYU P F, et al. Effect of fault on deep-hole cumulative blasting to improve coal bed permeability [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2014, 36(10): 1281–1286. [13] QIU P, YUE Z W, YANG R S, et al. Effects of vertical and horizontal reflected blast stress waves on running cracks by caustics method [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2019, 212: 164–179. [14] QIU P, YUE Z W, JU Y, et al. Characterizing dynamic crack-tip stress distribution and evolution under blast gases and reflected stress waves by caustics method [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2020, 108: 102632. [15] QIU P, YUE Z W, YANG R S, et al. Modified mixed-mode caustics interpretation to study a running crack subjected to obliquely incident blast stress waves [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 150: 103821. [16] 吴延梦, 李洪伟, 苏洪, 等. 单向围压下切槽爆破裂纹扩展规律研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(6):129–139.WU Y M, LI H W, SU H, et al. Crack propagation law of notch blasting under unidirectional confining pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(6):129–139. [17] 邱鹏. 爆炸应力波与裂纹相互作用机理研究 [D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京), 2019.QIU P. Mechanisms of the interaction between blast stress waves and cracks [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2019. [18] THEOCARIS P S. Elastic stress intensity factors evaluated by caustics [M]//SIH G C. Experimental evaluation of stress concentration and intensity factors. Netherlands: Springer, 1981: 189–252. [19] PAPADOPOULOS G A. Fracture mechanics: the experimental method of caustics and the det.-criterion of fracture [M]. London: Springer-Verlag, 1993. [20] 李庆扬, 王能超, 易大义. 数值分析 [M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2008.LI Q Y, WANG N C, YI D Y. Numerical analysis [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2008. [21] ANDERSON T L. Fracture mechanics: fundamentals and applications [M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2005. [22] 范天佑. 断裂动力学原理与应用 [M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2006.FAN T Y. Principles and applications of fracture dynamics [M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2006. -






 下载:
下载: