Dynamic Response of Equipment Cabin Bottom Plate of High-Speed Train Subjected to Ballast Impact
-
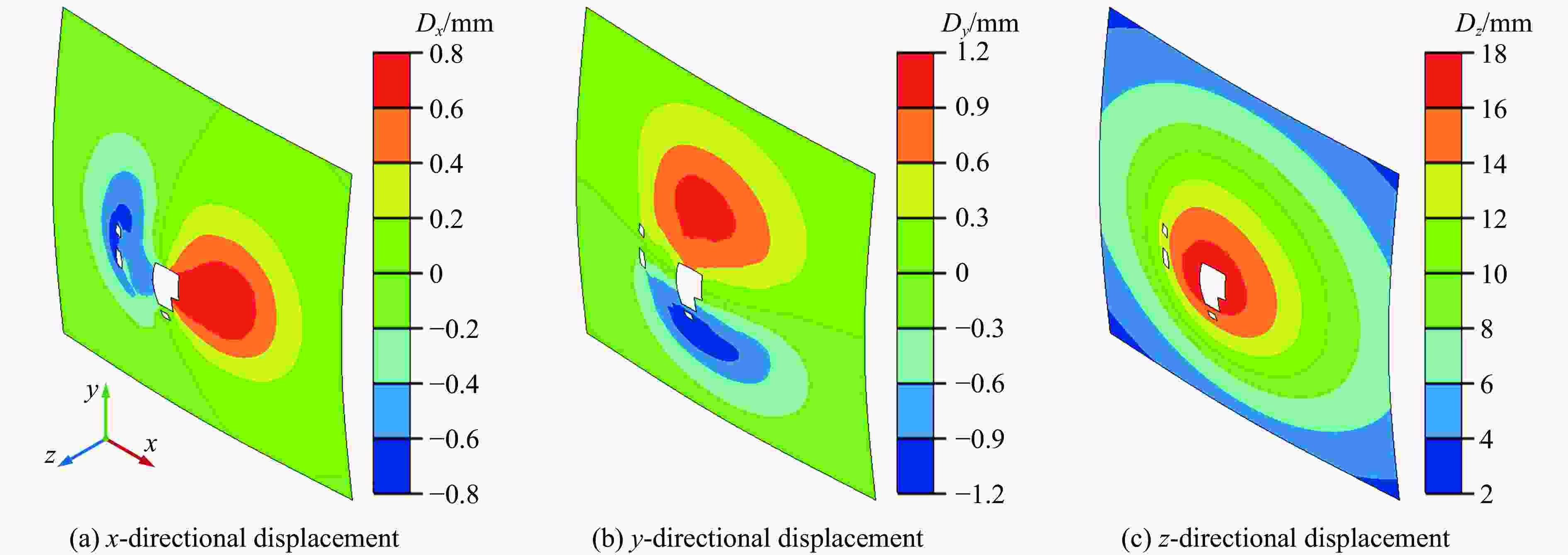
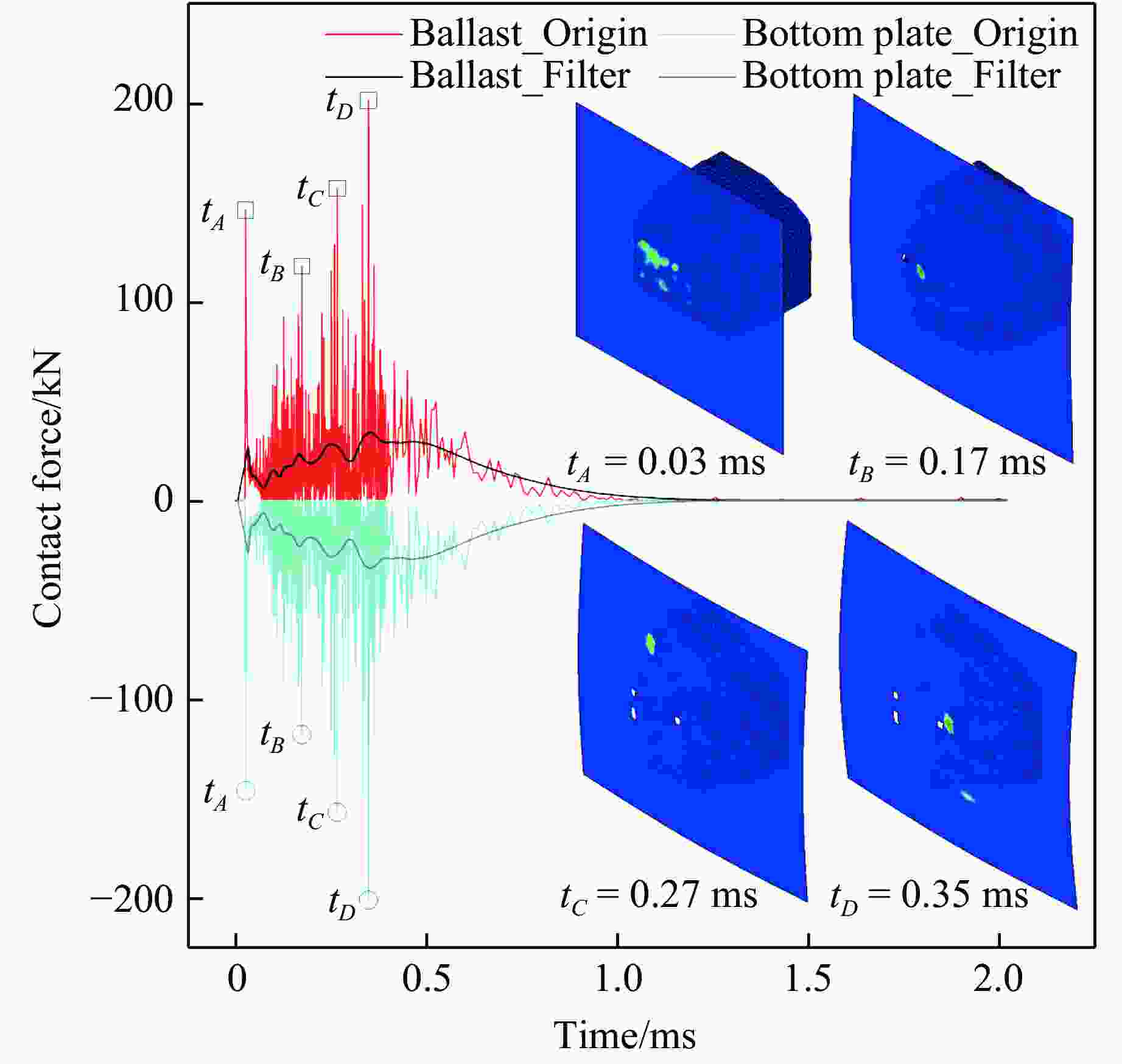
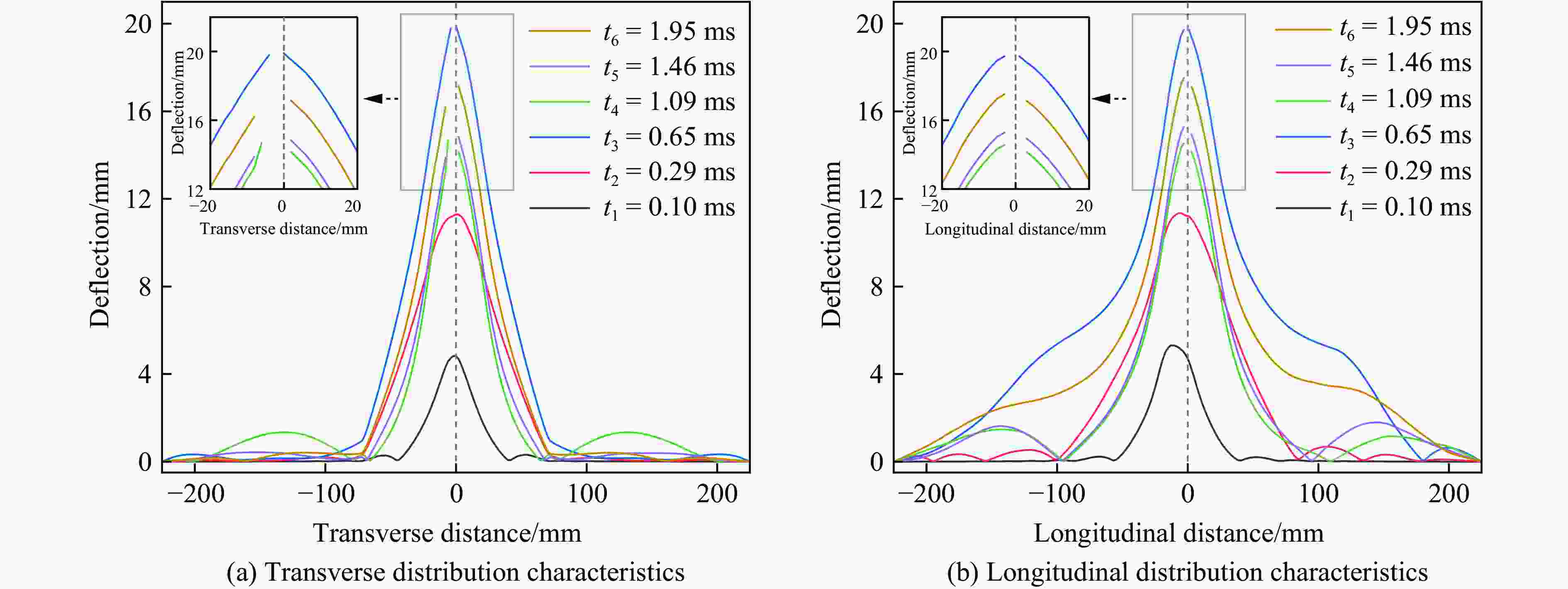
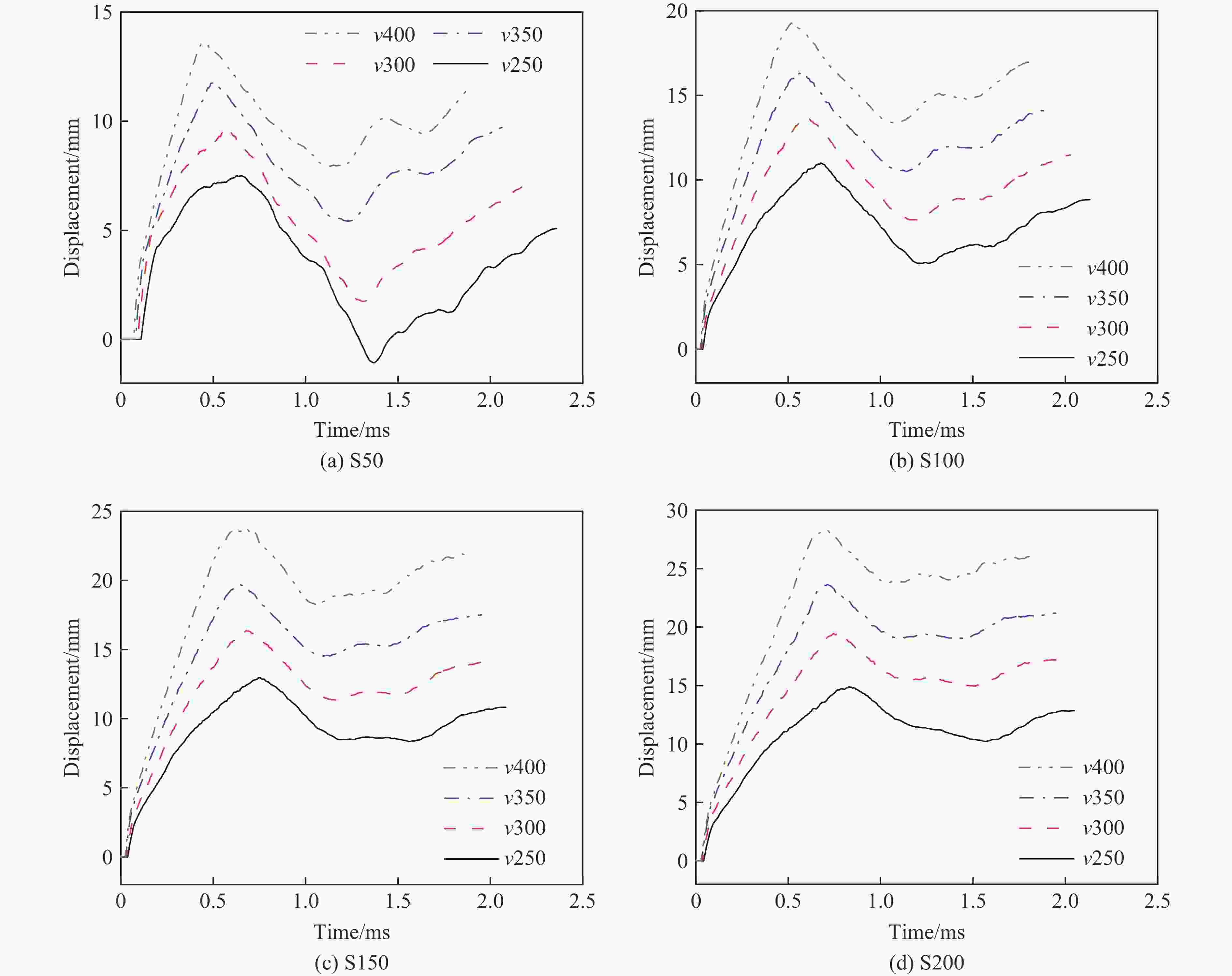
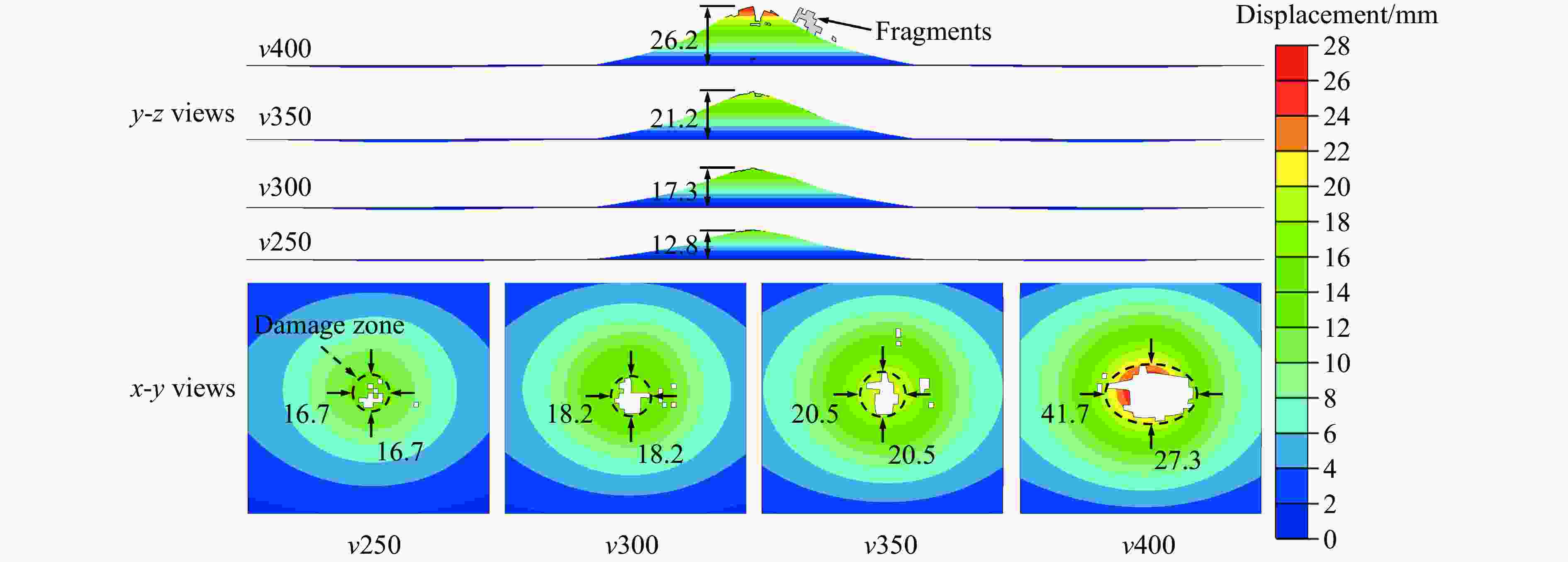
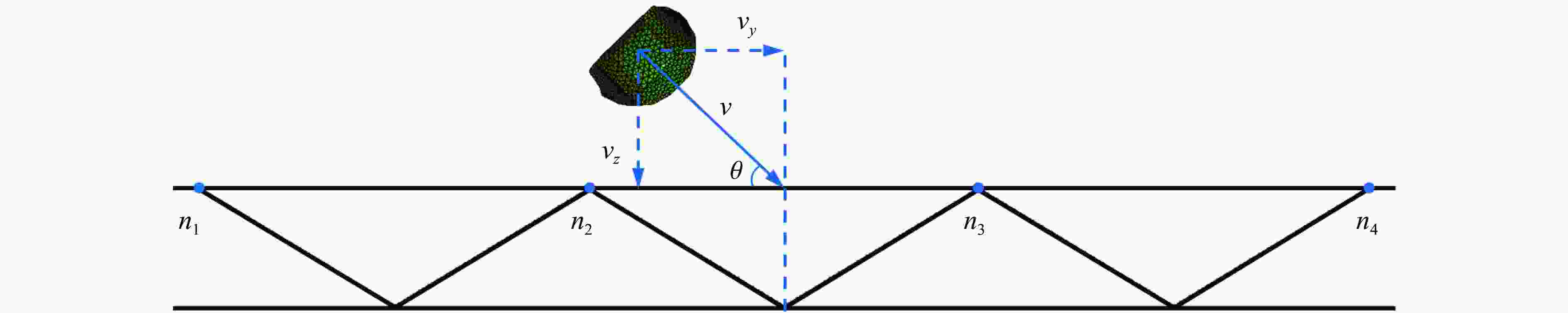
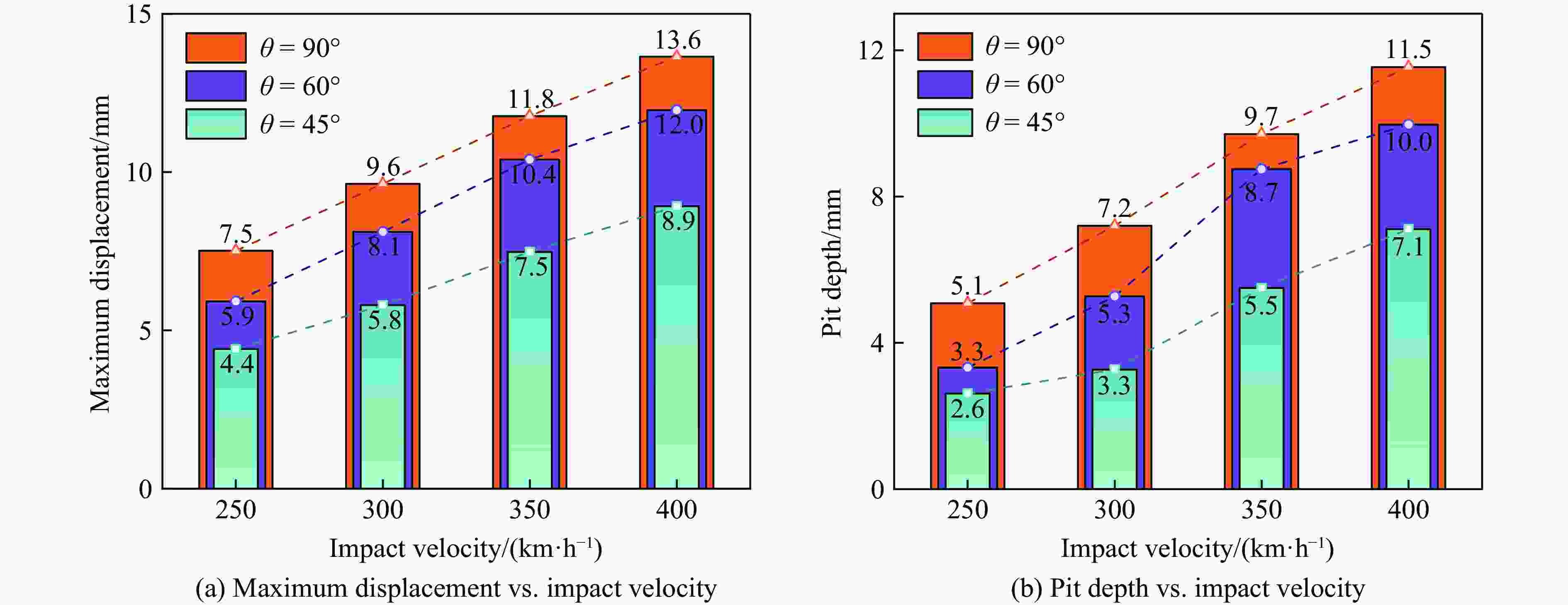
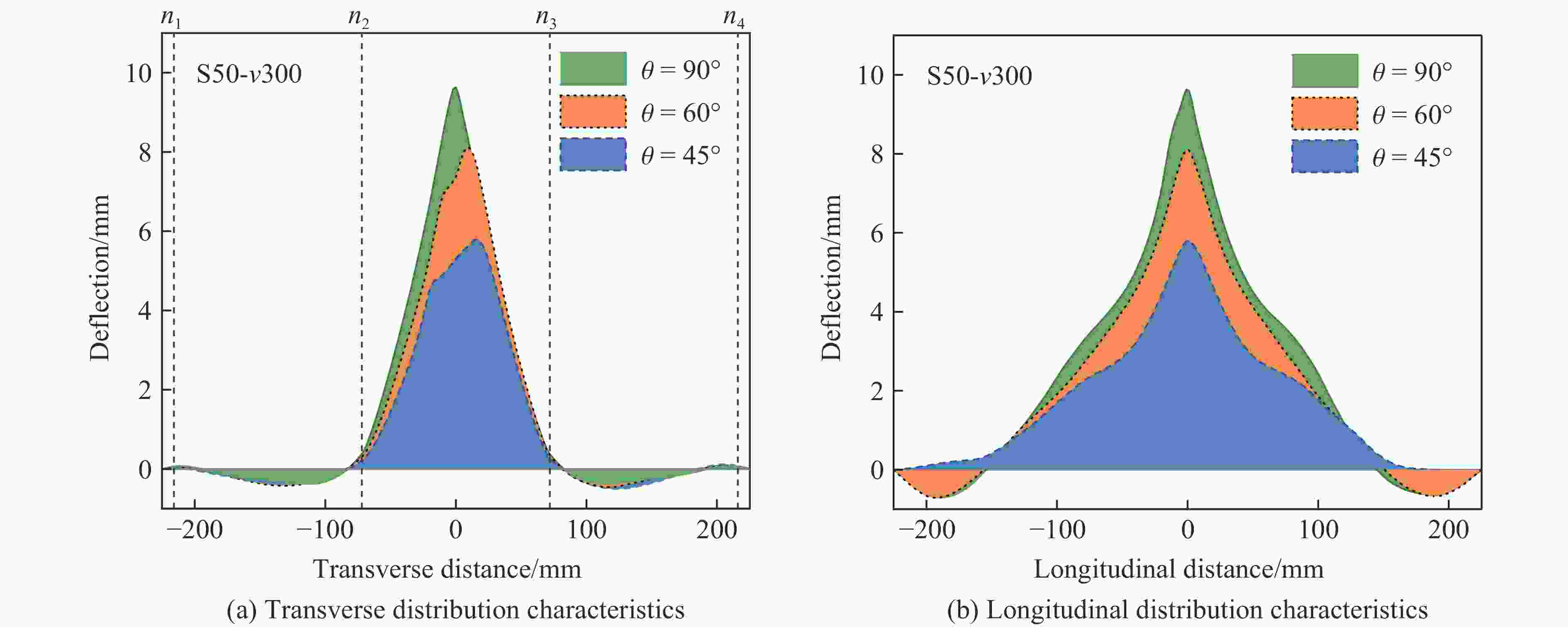
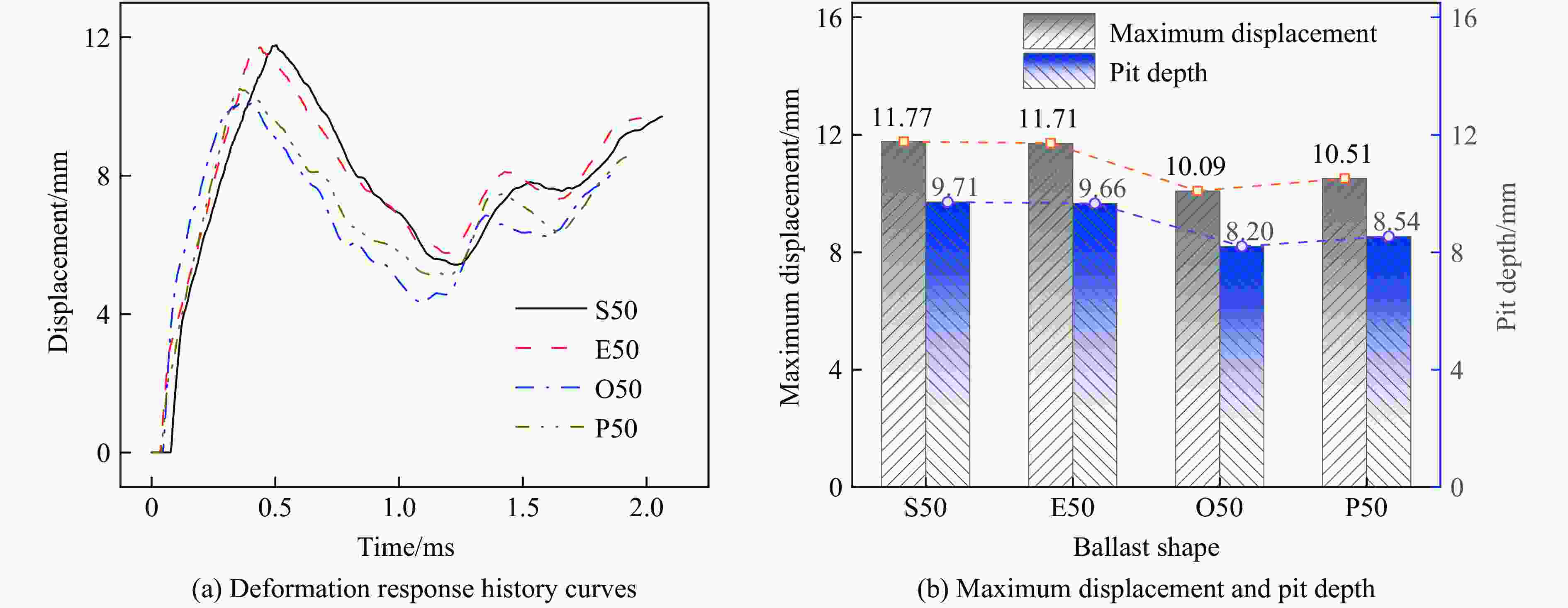
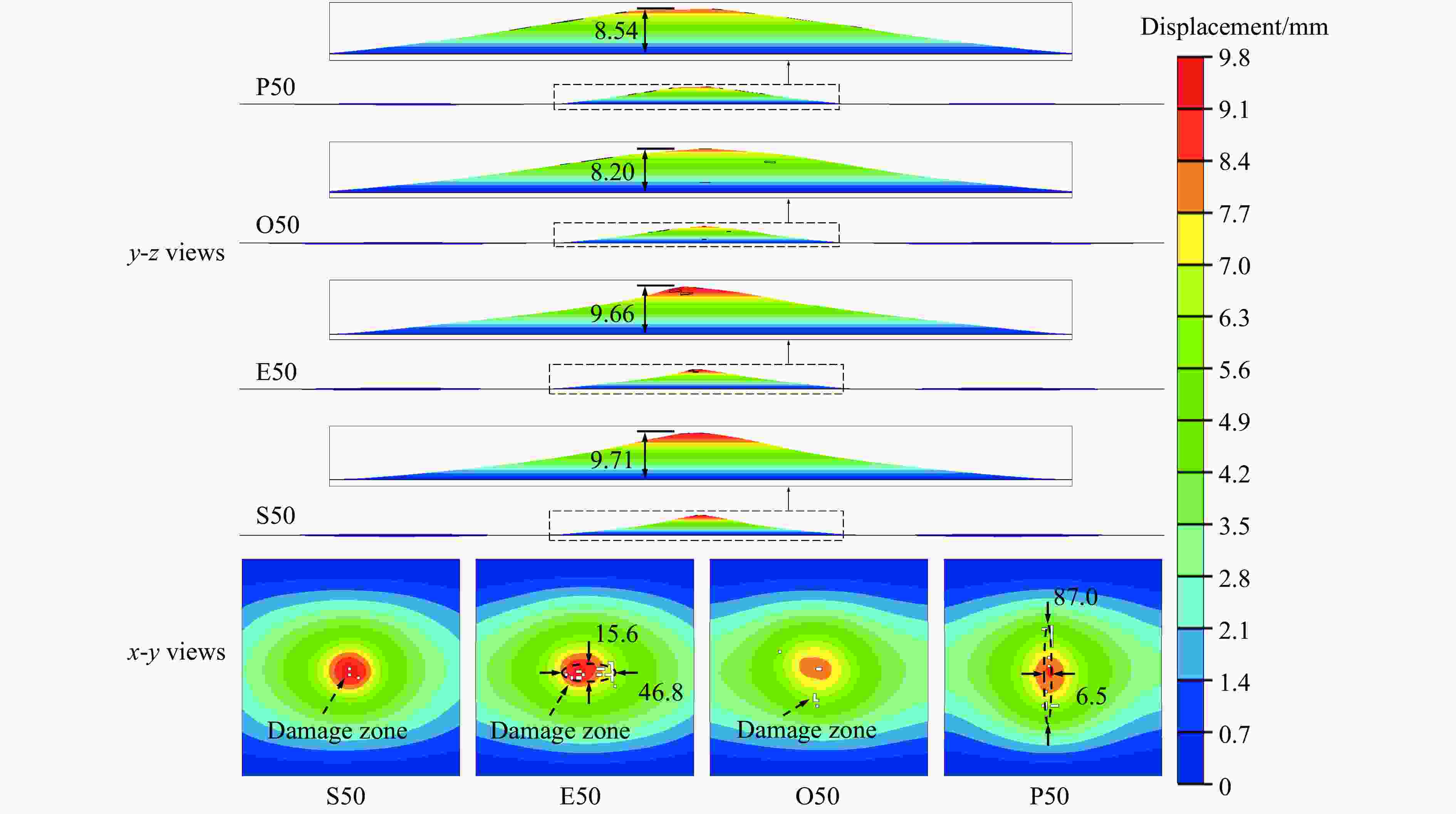
摘要: 考虑道砟真实的不规则几何形态特征与材料的应变率效应及失效行为,建立了道砟冲击高速列车设备舱底板的有限元模型,分析了设备舱前面板横向和纵向中心线节点的挠度时程响应,探究了设备舱底板与道砟间接触力的演化规律,讨论了冲击速度、冲击角度和道砟形状对设备舱底板冲击响应和破坏行为的影响,分析了不同工况下设备舱底板的失效模式和破坏形貌特征,量化了设备舱前面板的最大瞬态变形位移和凹坑深度与冲击速度的变化关系。结果表明,同一冲击工况下,设备舱底板最大瞬态变形位移和凹坑深度均分别随着冲击速度的提高和冲击角度的增大而增大;设备舱前面板最大变形区域的形状和范围大小以及前面板损伤失效区域的面积和分布特征与道砟几何形状密切相关,且椭球体道砟作用下列车设备舱底板的损伤失效最严重;不同冲击条件下设备舱前面板表现出不同程度的延性损伤,较大的道砟质量和冲击速度工况下还出现拉伸撕裂破坏甚至轻微冲塞现象。Abstract: Considering the real irregular geometrical characteristics of ballast and strain rate effect and failure behavior of material, finite element models of ballast impact on equipment cabin bottom plate of high-speed trains was established, and the deflection history response of transverse and longitudinal centerline nodes of equipment cabin front face sheet was analyzed. The history evolution regulation of contact force between equipment cabin bottom plate and ballast was investigated, and the effects of impact velocity, impact angle and ballast shape on impact response and damage behavior of equipment cabin bottom plate were also discussed, the failure mode and damage morphology characteristics of equipment cabin bottom plate under different conditions were analyzed, the relationship between the maximum transient deformation displacement as well as pit depth and impact velocity were quantified. The results show that, under the same impact condition, the maximum transient deformation displacement and pit depth of equipment cabin bottom plate increase with the increase of impact velocity and impact angle separately; the shape and size of maximum deformation zone of front face sheet of equipment cabin, and the area and distribution characteristics of front face sheet damage failure region are closely related to ballast shapes, the most severe damage failure occurs in ellipsoid ballast conditions; equipment cabin bottom plate under different impact conditions shows different degrees of ductile damage, and the larger ballast mass and impact velocity conditions also show tensile tear damage or even slight punching plug phenomenon.
-
Key words:
- high-speed train /
- ballast /
- equipment cabin /
- sandwich structure /
- deformation failure characteristics
-
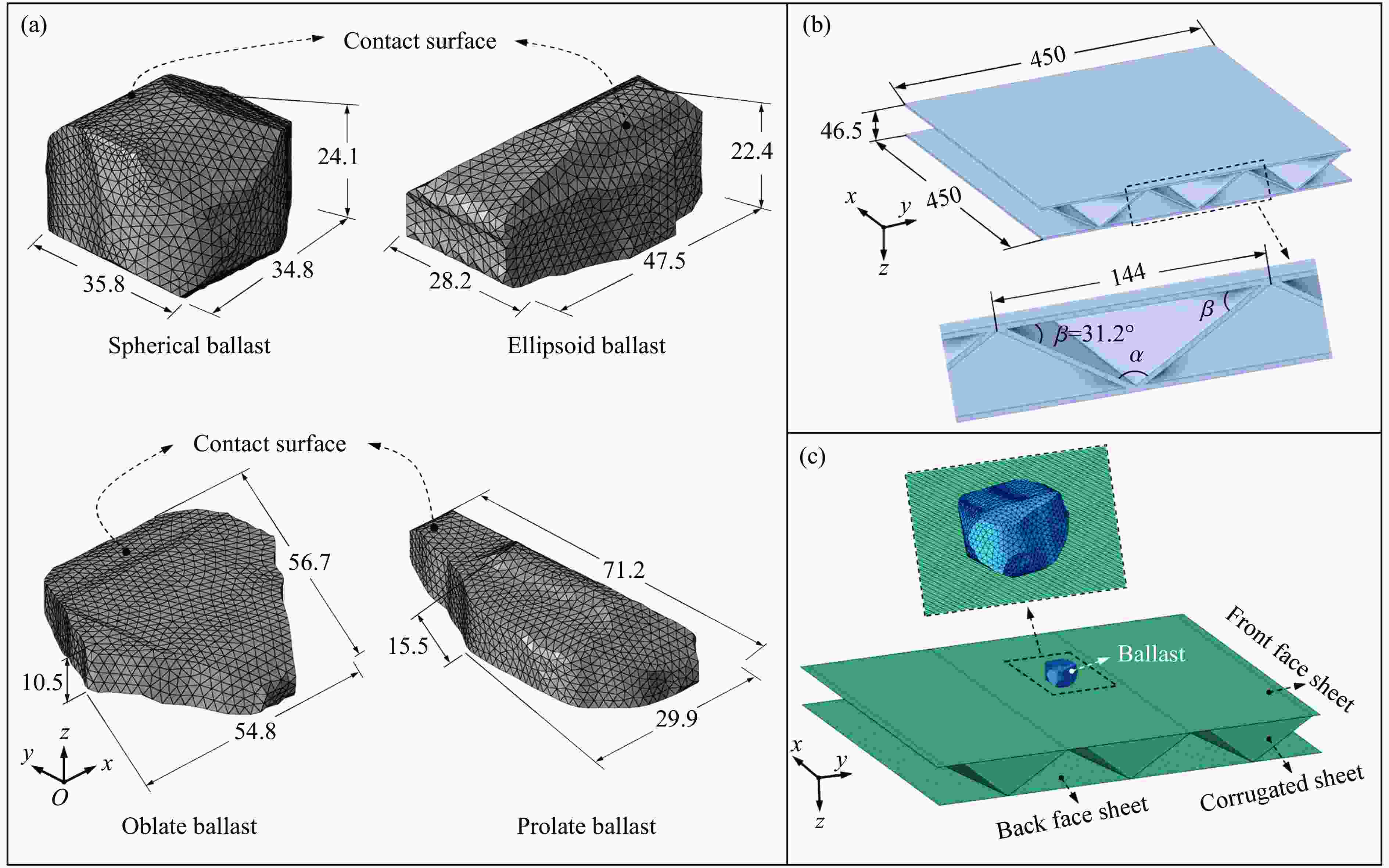
图 1 道砟冲击列车设备舱底板的有限元模型:(a) 道砟颗粒有限元模型;(b) 设备舱底板的几何模型;(c) 设备舱底板的有限元模型(单位:mm)
Figure 1. Finite element model of ballast impact at equipment cabin bottom plate: (a) finite element model of ballast particles; (b) geometric model of equipment cabin bottom plate; (c) finite element model of equipment cabin bottom plate (Unit: mm)
ρ/(kg·m−3) fc/MPa AH BH CH Smax G/GPa T/MPa DH1 DH2 2600 154 0.28 2.5 0.00186 5 28.7 12.2 0.04 1 pcrush/MPa μcrush plock/GPa μlock K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa εf,min N εf 51 0.00162 1.2 0.012 12 25 42 0.01 0.79 0.035 表 2 6061-T6铝合金的Johnson-Cook本构模型和失效模型参数[19]
Table 2. Johnson-Cook constitutive model parameters and failure model parameters of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy[19]
ρ/(kg·m−3) E/GPa μ ${\dot \varepsilon {_0}}$/s−1 AJ/MPa BJ/MPa 2700 70 0.33 0.001 275.96 288.39 CJ/MPa n D1 D2 D3 D4 0.0064 0.59 0.362 −4.57×10−6 17.434 0.0112 表 3 不同道砟质量下冲击点最大位移及凹坑深度与冲击速度间的拟合参数
Table 3. Fitted correlation parameters between maximum displacement at the impact point as well as pit depth and impact velocity for different ballast masses
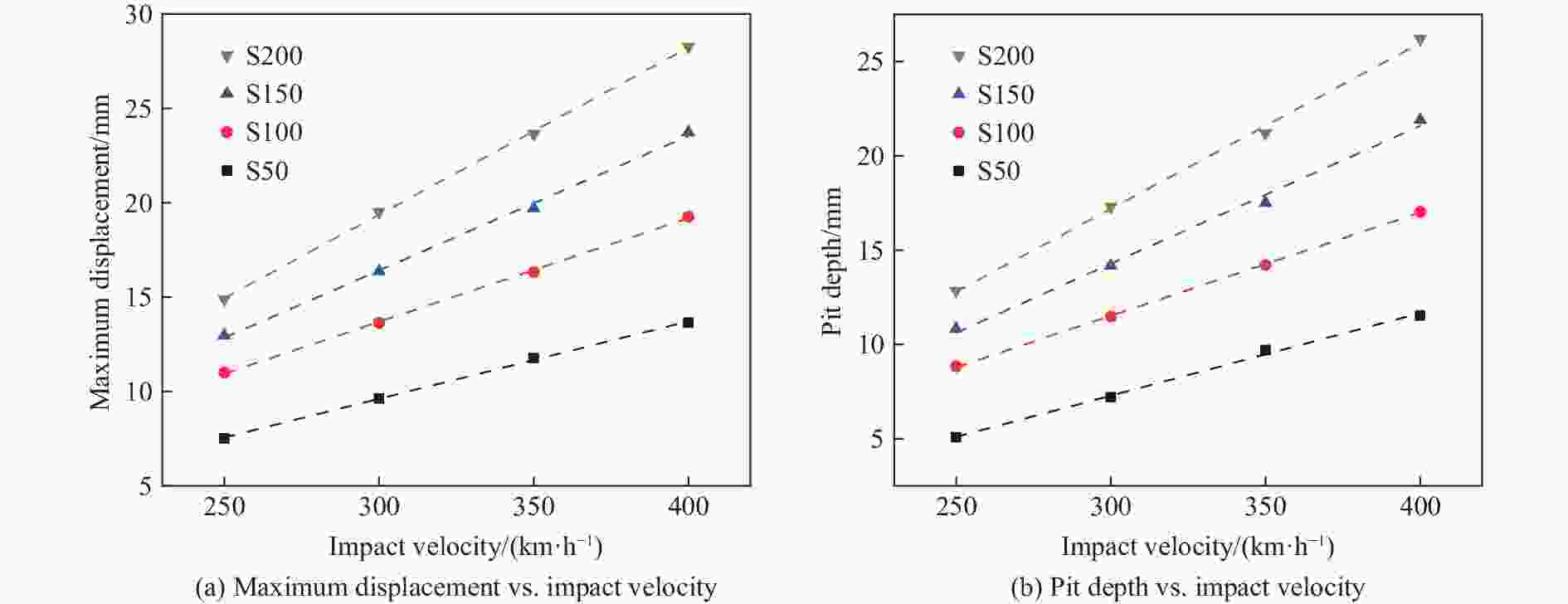
Ballast mass kv1/(m2·h–1) bv1/mm $ R_{v1}^2 $ kv2/(m2·h–1) bv2/mm $ R_{v2}^2 $ S50 0.04106 −2.70781 0.9991 0.04376 −5.84193 0.9968 S100 0.05496 −2.80024 0.9994 0.05472 −4.89442 0.9998 S150 0.07130 −4.97576 0.9980 0.07313 −7.66026 0.9950 S200 0.08851 −7.18340 0.9995 0.08794 −9.19038 0.9978 -
[1] FAROOQ M A, NIMBALKAR S, FATAHI B. Three-dimensional finite element analyses of tyre derived aggregates in ballasted and ballastless tracks [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 136: 104220. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104220 [2] QUINN A D, HAYWARD M, BAKER C J, et al. A full-scale experimental and modelling study of ballast flight under high-speed trains [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2010, 224(2): 61–74. doi: 10.1243/09544097JRRT294 [3] DING D, OUAHSINE A, XIAO W X, et al. Numerical study of ballast-flight caused by dropping snow/ice blocks in high-speed railways using discontinuous deformation analysis (DDA) [J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 22: 100314. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2019.100314 [4] YU Z H, LIU K, ZHOU X F, et al. Low-velocity impact response of aluminum alloy corrugated sandwich beams used for high-speed trains [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 183: 110375. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110375 [5] LAZARO B J, GONZALEZ E, RODRIGUEZ M, et al. Characterization and modeling of flying ballast phenomena in high-speed train lines [C]//9th World Congress Railway Research. Lille, France, 2011. [6] SAUSSINE G. Ballast flying and projection phenomena: issues and challenges [C]//WILLIAM W. Hay Railroad Engineering Seminar. Paris, France, 2013. [7] 姜成, 姚曙光, 曹武雄, 等. 砾石冲击下动车组裙板的变形影响因素分析 [J]. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(2): 23–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.02.004JIANG C, YAO S G, CAO W X, et al. Study of deformation factors for electric multiple unit skirt boards under impact of ballast [J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(2): 23–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.02.004 [8] SAKLY A, LAKSIMI A, KEBIR H, et al. Experimental and modelling study of low velocity impacts on composite sandwich structures for railway applications [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 68: 22–31. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.03.001 [9] 刘杰夫, 雷紫平, 朱玉雯, 等. 高速列车设备舱底板夹芯结构异物冲击压痕行为及抗性强化 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(5): 1976–1988.LIU J F, LEI Z P, ZHU Y W, et al. Impact indentation behavior and resistance enhancement of high-speed train equipment cabin bottom plate with honeycomb sandwich structure [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(5): 1976–1988. [10] 敬霖, 韩亮亮, 周彭滔. 基于SPH方法铁路车轴遭受道砟撞击的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(3): 603–615.JING L, HAN L L, ZHOU P T. A numerical simulation of railway axles subjected to ballast impact based on SPH method [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(3): 603–615. [11] JING G Q, DING D, LIU X. High-speed railway ballast flight mechanism analysis and risk management: a literature review [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 223: 629–642. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.194 [12] 中国铁道研究院. 铁路碎石道砟: TB/T 2140—2008 [S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2008. [13] YIN H, GAO L. Experimental and numerical investigation on ballast flight from perspective of individual particles [J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 10(1): 286. doi: 10.3390/app10010286 [14] KWON H B, PARK C S. An experimental study on the relationship between ballast-flying phenomenon and strong wind under high-speed train [C]//7th World Congress on Rail Research. Montreal, QC, Canada, 2006. [15] HUANG H, TUTUMLUER E. Image-aided element shape generation method in discrete-element modeling for railroad ballast [J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2014, 26(3): 527–535. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000839 [16] 丁东, 李杰, 王辰永, 等. 高速铁路飞砟问题影响因素与研究进展 [J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(11): 3117–3126. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.t20211476DING D, LI J, WANG C Y, et al. Influence factors and research progress of ballast flight in high-speed railways [J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(11): 3117–3126. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.t20211476 [17] 毕程程. 华山花岗岩HJC本构参数标定及爆破损伤数值模拟 [D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2018.BI C C. Calibration of HJC constitutive parameters of Huashan granite and its blasting damage numerical simulation [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018. [18] BAYKASOGLU C, SUNBULOGLU E, BOZDAG S E, et al. Crash and structural analyses of an aluminium railroad passenger car [J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2012, 17(5): 519–528. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2012.690591 [19] 周伦, 苏兴亚, 敬霖, 等. 6061-T6铝合金动态拉伸本构关系及失效行为 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(9): 091407.ZHOU L, SU X Y, JING L, et al. Dynamic tensile constitutive relationship and failure behavior of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(9): 091407. -






 下载:
下载: