Progress in Preparation of Transparent Ceramics under High Pressure
-
摘要: 透明陶瓷是一种具有广阔应用前景的新一代无机非金属材料。本文介绍一种非传统的透明陶瓷制备方法——超高压烧结。相对于传统的制备方法,超高压烧结具有烧结温度低、烧结时间短、致密度高、抑制晶粒长大等特点,对制备纳米结构透明陶瓷具有独特的优势。着重介绍了近年来超高压烧结透明陶瓷的研究成果和进展,包括钇铝石榴石(YAG)、镁铝尖晶石、氧化铝等常见透明陶瓷的超高压低温烧结,以及纳米聚晶金刚石(NPD)、B-C-N、Si3N4等超硬透明陶瓷的高温高压制备,并对透明陶瓷的高压烧结机理进行分析和总结。Abstract: Transparent ceramics is a novel kind of inorganic non-metallic materials with a prospect of broad applications.In the present paper we present a novel method-ultra-high pressure sintering-for fabricating transparent ceramics, characterized by its low sintering temperature, short sintering time, high density and inhibition of grain growth which, compared with the sintering methods traditionally adopted, offers unique advantages in the preparation of nano-structured transparent ceramics.We reviewed the latest progresses made in the ultra-high pressure sintering of transparent ceramics, including the ultra-high pressure sintering of YAG, spinel and alumina under low temperature, and the ultra-high pressure synthesis of nano polycrystalline diamond (NPD), B-C-N, Si3N4 under high temperature, and analyzed and summarized the high pressure sintering mechanism of transparent ceramics.
-
Key words:
- transparent ceramics /
- nanoceramic /
- ultra-high pressure /
- sintering
-
图 5 (a) 超高压处理后的样品照片(插图为素坯); (b)切薄、抛光后的样品在反射光下能看见蓝十字; (c)切薄、抛光后的样品在透射光下能看见蓝线[62]
Figure 5. (a) Image of high pressure compacted spinel after recovery from high pressure cell (The inset shows the green impact.); (b) image of blue cross-hair visible below thinned and polished spinel using reflected light; (c) image of blue line below thinned and polished spinel using transmitted light[62]
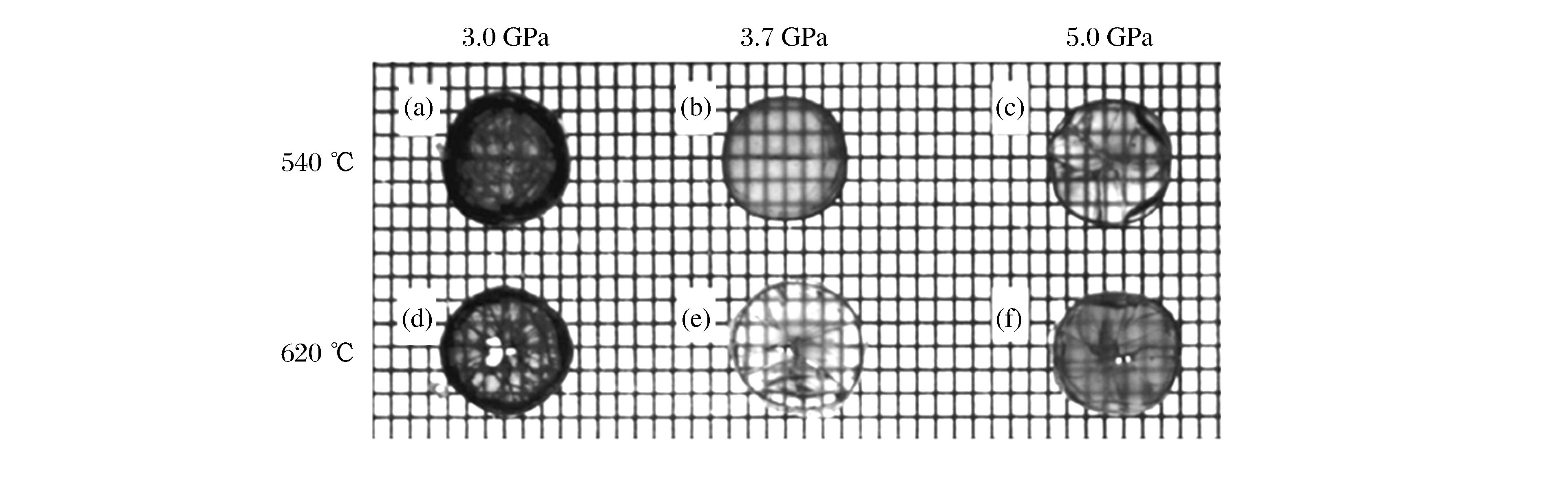
图 13 在5.0GPa、不同温度下烧结的氧化铝陶瓷样品金相显微图像及光学图像
(样品厚度为0.6mm; (a)、(b)、(c)为纯微米球形粉体烧结样品,(d)、(e)、(f)为混合粉体烧结样品; (a)和(d)的烧结条件为5.0GPa、700℃; (b)和(e)的烧结条件为5.0GPa、900℃; (c)和(f)的烧结条件为5.0GPa、1100℃)[89]
Figure 13. Metallographic and corresponding optical images of alumina ceramic sintered at 5.0GPa and various temperatures
(The sample thickness is 0.6mm; (a), (b) and (c) are samples sintered with pure spherical powder, and (d), (e) and (f) are samples sintered with mixed powder; (a) and (d) are samples sintered at 5.0GPa and 700℃, (b) and (e) are samples sintered at 5.0GPa and 900℃; (c) and (f) are samples sintered at 5.0GPa and 1100℃.)[89]
-
[1] 潘裕柏, 徐军, 吴玉松, 等.Nd:YAG透明陶瓷的制备与激光输出[J].无机材料学报, 2006, 21(5):1278-1280. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_gsyxb200909011.aspxPAN Y B, XU J, WU Y S, et al.Fabrication and laser output of Nd:YAG transparent ceramic[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(5):1278-1280. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_gsyxb200909011.aspx [2] 吴玉松, 潘裕柏, 李江, 等.Yb:YAG透明陶瓷的制备和激光输出[J].无机材料学报, 2007, 22(6):1086-1088. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_wjclxb200706013.aspxWU Y S, PAN Y B, LI J, et al.Fabrication and laser output of transparent Yb:YAG ceramic[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(6):1086-1088. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_wjclxb200706013.aspx [3] 雷牧云, 黄存新, 闻芳, 等.透明尖晶石陶瓷的研究进展[J].人工晶体学报, 2007, 36(2):319-322. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rgjtxb98200702018LEI M Y, HUANG C X, WEN F, et al.Development of transparent ceramic spinel[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2007, 36(2):319-322. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rgjtxb98200702018 [4] COBLE R L.Preparation of transparent ceramic Al2O3[J]. American Ceramic Society Bulletin, 1959, 38(10):507-510. [5] KRELL A, KLIMKE J, HUTZLER T.Advanced spinel and sub-μm Al2O3 for transparent armour applications[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(2):275-281. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.03.024 [6] DANG K Q, TAKEI S, KAWAHARA M, et al.Pulsed electric current sintering of transparent Cr-doped Al2O3[J]. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(3):957-963. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2010.11.009 [7] KIM B N, HIRAGA K, MORITA K, et al.Spark plasma sintering of transparent alumina[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(7):607-610. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.06.009 [8] LI W, ZHOU S, LIU N, et al.Effect of additives on optical characteristic of thulium doped yttria transparent ceramics[J]. Optical Materials, 2010, 32(9):971-974. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2010.01.037 [9] HE M S, LI J B, LIN H, et al.Fabrication of transparent polycrystalline yttria ceramics by combination of SPS and HIP[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2006, 24(1):222-224. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(07)60365-2 [10] ZHANG J, AN L, LIU M, et al.Sintering of Yb3+:Y2O3 transparent ceramics in hydrogen atmosphere[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(2):305-309. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.03.006 [11] JIN L, ZHOU G, SHIMAI S, et al.ZrO2-doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics via slip casting and vacuum sintering[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(10):2139-2143. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.04.004 [12] YAMASHITA I, TSUKUMA K.Light scattering by residual pores in transparent zirconia ceramics[J]. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2011, 119(1386):133-135. doi: 10.2109/jcersj2.119.133 [13] PEUCHERT U, OKANO Y, MENKE Y, et al.Transparent cubic-ZrO2 ceramics for application as optical lenses[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(2):283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.03.028 [14] ITATANI K, TSUJIMOTO T, KISHIMOTO A.Thermal and optical properties of transparent magnesium oxide ceramics fabricated by post hot-isostatic pressing[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(4):639-645. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0955221905005674 [15] ZOU Y T, HE D W, WEI X K, et al.Nanosintering mechanism of MgAl2O4 transparent ceramics under high pressure[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 123(2):529-533. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248263777_Nanosintering_Mechanism_of_MgAl2O4_Transparent_Ceramics_Under_High_Pressure [16] WANG C, ZHAO Z.Transparent MgAl2O4 ceramic produced by spark plasma sintering[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(2):193-196. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.03.039 [17] DERICIOGLU A F, KAGAWA Y.Effect of grain boundary microcracking on the light transmittance of sintered transparent MgAl2O4[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2003, 23(6):951-959. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00205-4 [18] MORITA K, KIM B N, HIRAGA K, et al.Fabrication of transparent MgAl2O4 spinel polycrystal by spark plasma sintering processing[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58(12):1114-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.02.008 [19] CHEN Q Y, MENG C M, LU T C, et al.Enhancement of sintering ability of magnesium aluminate spinel (MgAl2O4) ceramic nanopowders by shock compression[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 200(1):91-95. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229106430_Enhancement_of_Sintering_Ability_of_Magnesium_Aluminate_Spinel_MgAl2O4_Ceramic_Nanopowders_by_Shock_Compression [20] MORITA K, KIM B N, YOSHIDA H, et al.Densification behavior of a fine-grained MgAl2O4 spinel during spark plasma sintering (SPS)[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63(6):565-568. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.06.012 [21] MORITA K, KIM B N, YOSHIDA H, et al.Spark-plasma-sintering condition optimization for producing transparent MgAl2O4 spinel polycrystal[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(6):1208-1216. doi: 10.1111/jace.2009.92.issue-6 [22] MAZZONI A D, SAINZ M A, AGLIETTI E F, et al.Carbon coating and reaction on magnesia-alumina spinel[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2007, 101(1):211-216. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.04.060 [23] ZHANG H J, JIA X L, LIU Z J, et al.The low temperature preparation of nanocrystalline MgAl2O4 spinel by citrate sol-gel process[J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58(10):1625-1628. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2003.09.051 [24] LI J G, IKEGAMI T, LEE J H, et al.Synthesis of Mg-Al spinel powder via precipitation using ammonium bicarbonate as the precipitant[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21(2):139-148. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00188-6 [25] GRANON A, GOEURIOT P, THEVENOT F.Aluminum magnesium oxynitride:a new transparent spinel ceramic[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1995, 15(3):249-254. doi: 10.1016/0955-2219(95)93946-Z [26] AL-SHARAB J F, COSANDEY F, SINGHAL A, et al.TEM characterization of nanostructured MgAl2O4 synthesized by a direct conversion process from γ-Al2O3[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(7):2279-2285. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0079642514000796 [27] WANG Y, LU T, GONG L, et al.Light extinction by pores in AlON ceramics:the transmission properties[J]. Journal of Physics D, 2010, 43(27):275403. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/27/275403 [28] KURAMOTO N, TANIGUCHI H.Transparent AIN ceramics[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1984, 3(6):471-474. doi: 10.1007/BF00720974 [29] YEH T S, SACKS M D.Low-temperature sintering of aluminum oxide[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1988, 71(10):841-844. doi: 10.1111/jace.1988.71.issue-10 [30] BIRRINGER R, GLEITER H, KLEIN H P, et al.Nanocrystalline materials an approach to a novel solid structure with gas-like disorder?[J]. Physics Letters A, 1984, 102(8):365-369. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(84)90300-1 [31] ZHANG L D, MO C M, WANG T, et al.Structure and bond properties of compacted and heat-treated silicon nitride particles[J]. Physica Status Solidi, 1993, 136(2):291-300. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-396X [32] ZHOU J, ZHANG W, LI J, et al.Upconversion luminescence of high content Er-doped YAG transparent ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(1):193-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.07.018 [33] WU Y, LI J, QIU F, et al.Fabrication of transparent Yb, Cr:YAG ceramics by a solid-state reaction method[J]. Ceramics International, 2006, 32(7):785-788. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2005.06.002 [34] LUPEI V, LUPEI A, IKESUE A.Transparent polycrystalline ceramic laser materials[J]. Optical Materials, 2008, 30(11):1781-1786. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2008.03.003 [35] KANG Y C, ROH H S, PARK S B.Sodium carbonate flux effects on the luminescence characteristics of (Y0.5Gd0.5)2O3:Eu phosphor particles prepared by spray pyrolysis[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(2):447-449. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223631395_Effect_of_LiCl_on_the_Crystallization_Behavior_and_Luminescence_of_Y3Al5O12Tb [36] WANG G, LI X, GENG Y.Preparation of gadolinium gallium garnet polycrystalline powders for transparent ceramics[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 505(1):213-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.06.031 [37] GOROKHOVA E I, DEMIDENKO V A, ERON'KO S B, et al.Spectrokinetic characteristics of the emission of Gd2O2S-Tb (Ce) ceramics[J]. Journal of Optical Technology, 2005, 72(1):53-57. doi: 10.1364/JOT.72.000053 [38] GAZZA G E.Hot-pressing of LiAl5O8 [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1972, 55(3):172-173. doi: 10.1111/jace.1972.55.issue-3 [39] ROY D W, HASTERT J L, COUBROUGH L E, et al. Method for producing transparent polycrystalline body with high ultraviolet transmittance: US5244849[P]. 1993-09-14. [40] BARJ M, BOCQUET J F, CHHOR K, et al.Submicronic MgAl2O4 powder synthesis in supercritical ethanol[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1992, 27(8):2187-2192. doi: 10.1007/BF01117935 [41] 戴遐明.纳米陶瓷材料及其应用[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2005. [42] 曾令可, 李秀艳.纳米陶瓷技术[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社, 2006. [43] 史琳琳, 曾令可, 王慧, 等. 纳米陶瓷的性能及其应用[C]//中国纳微粉体制备与技术应用研讨会, 2003: 288. [44] 施锦行.纳米陶瓷的制备及其特性[J].中国陶瓷, 1997, 33(3):36-38.SHI J X.The production and characteristic of nanocrystalline ceramics[J]. China Ceramics, 1997, 33(3):36-38. [45] 王世敏, 许祖勋, 傅晶.纳米材料制备技术[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2002. [46] 高濂, 李蔚.纳米陶瓷[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2001. [47] YEH T S, SACKS M D.Low-temperature sintering of aluminum oxide[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1988, 71(10):841-844. doi: 10.1111/jace.1988.71.issue-10 [48] BIRRINGER R, GLEITER H, KLEIN H P, et al.Nanocrystalline materials an approach to a novel solid structure with gas-like disorder?[J]. Physics Letters A, 1984, 102(8):365-369. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(84)90300-1 [49] ZHANG L D, MO C M, WANG T, et al.Structure and bond properties of compacted and heat-treated silicon nitride particles[J]. Physica Status Solidi, 1993, 136(2):291-300. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-396X [50] 倪文.硅钙石型硅酸钙保温材料的特点与发展趋势[J].新材料产业, 2002(11):32-35. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/fbc77466960590c69fc376c3.html [51] IRIFUNE T, KURIO A, SAKAMOTO S, et al.Materials:ultrahard polycrystalline diamond from graphite[J]. Nature, 2003, 421(6923):599-600. [52] LU T C, CHANG X H, QI J Q, et al.Low-temperature high-pressure preparation of transparent nanocrystalline MgAl2O4 ceramics[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(21):213120. doi: 10.1063/1.2207571 [53] HRENIAK D, FEDYK R, BEDNARKIEWICZ A, et al.Luminescence properties of Nd:YAG nanoceramics prepared by low temperature high pressure sintering method[J]. Optical Materials, 2007, 29(10):1244-1251. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2006.05.014 [54] PAZIK R, GLUCHOWSKI P, HRENIAK D, et al.Fabrication and luminescence studies of Ce:Y3Al5O12 transparent nanoceramic[J]. Optical Materials, 2008, 30(5):714-718. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2007.02.017 [55] FEDYK R, HRENIAK D, LOJKOWSKI W, et al.Method of preparation and structural properties of transparent YAG nanoceramics[J]. Optical Materials, 2007, 29(10):1252-1257. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2006.05.016 [56] TAN N, KOU Z, DING Y, et al.Novel substantial reductions in sintering temperatures for preparation of transparent hydroxyapatite bioceramics under ultrahigh pressure[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(9):819-822. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.07.047 [57] LIU K, HE D, WANG H, et al.High-pressure sintering mechanism of yttrium aluminum garnet (Y3Al5O12) transparent nanoceramics[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 66(6):319-322. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.11.012 [58] NISHIYAMA N, TANIGUCHI T, OHFUJI H, et al.Transparent nanocrystalline bulk alumina obtained at 7.7GPa and 800℃[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 69(5):362-365. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.05.017 [59] IRIFUNE T, KAWAKAMI K, ARIMOTO T, et al.Pressure-induced nano-crystallization of silicate garnets from glass[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7:13753. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13753 [60] NISHIYAMA N, ISHIKAWA R, OHFUJI H, et al.Transparent polycrystalline cubic silicon nitride[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7:44755. doi: 10.1038/srep44755 [61] LIU F M, HE D W, LIU P P, et al.Plastic deformation and sintering of alumina under high pressure[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(23):233504. doi: 10.1063/1.4844495 [62] WOLLMERSHAUSER J A, FEIGELSON B N, QADRI S B, et al.Transparent nanocrystalline spinel by room temperature high-pressure compaction[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 69(4):334-337. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.05.014 [63] 施剑林, 冯涛.无机光学透明材料:透明陶瓷[M].上海:上海科学普及出版社, 2008. [64] ВЫДРИК Г А. 透明陶瓷[M]. 陈婉华, 译. 北京: 轻工业出版社, 1987. [65] PALOSZ B, STEL'MAKH S, GRZANKA E, et al.High pressure X-ray diffraction studies on nanocrystalline materials[J]. Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 2004, 16(5):S353. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/16/5/003 [66] PALOSZ B, STELMAKH S, GRZANKA E, et al.Origin of macrostrains and microstrains in diamond-SiC nanocomposites based on the core-shell model[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(7):074303. doi: 10.1063/1.2785025 [67] 李霞, 刘宏, 王继扬, 等.钇铝石榴石透明激光陶瓷的研究进展[J].硅酸盐学报, 2004, 32(4):485-489. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_cldb201421024LI X, LIU H, WANG J Y, et al.Progress in transparent polycrystalline aluminum-yttrium garnet laser ceramic[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(4):485-489. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_cldb201421024 [68] 李适民, 黄维玲.激光器件原理与设计[M].第2版.北京:国防工业出版社, 2005. [69] IKESUE A, KINOSHITA T, KAMATA K, et al.Fabrication and optical properties of high-performance polycrystalline Nd:YAG ceramics for solid-state lasers[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(4):1033-1040. doi: 10.1111/jace.1995.78.issue-4 [70] ALANIZ J E, PEREZ-GUTIERREZ F G, AGUILAR G, et al.Optical properties of transparent nanocrystalline yttria stabilized zirconia[J]. Optical Materials, 2009, 32(1):62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2009.06.004 [71] VOVK E A, DEINEKA T G, DOROSHENKO A G, et al.Production of the Y3Al5O12 transparent nanostructured ceramics[J]. Journal of Superhard Materials, 2009, 31(4):252-259. doi: 10.3103/S1063457609040066 [72] YAVETSKIY R P, VOVK E A, DOROSHENKO A G, et al.Y3Al5O12 translucent nanostructured ceramics-obtaining and optical properties[J]. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(7):2477-2484. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.03.041 [73] LU J, YAGI H, TAKAICHI K, et al.110W ceramic Nd3+:Y3Al5O12 laser[J]. Applied Physics B, 2004, 79(1):25-28. doi: 10.1007/s00340-004-1511-9 [74] 刘科. YAG纳米透明陶瓷的高压烧结机理及第一性原理物性研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2012: 36-37.LIU K. High-pressure sintering mechanism of Y3Al5O12 transparent nanoceramics and its properties from first-principles[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2012: 36-37. [75] 张小锋, 于国强, 姜林文.氧化铝陶瓷的应用[J].佛山陶瓷, 2010, 20(2):38-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fstc201002012 [76] 朱志斌, 郭志军, 刘英, 等.氧化铝陶瓷的发展与应用[J].陶瓷, 2003(1):5-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tc200301001 [77] COBLE R L. Transparent alumina and method of preparation: US3026210[P]. 1962-03-20. [78] ZHANG X, LIANG S, ZHANG P, et al.Fabrication of transparent alumina by rapid vacuum pressureless sintering technology[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(7):2116-2119. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05256.x [79] CHENG J, AGRAWAL D, ZHANG Y, et al.Microwave sintering of transparent alumina[J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 56(4):587-592. doi: 10.1016/S0167-577X(02)00557-8 [80] HAYASHI K, KOBAYASHI O, TOYODA S, et al.Transmission optical properties of polycrystalline alumina with submicron grains[J]. Materials Transactions JIM, 1991, 32(11):1024-1029. doi: 10.2320/matertrans1989.32.1024 [81] APETZ R, BRUGGEN M P B.Transparent alumina:a light-scattering Model[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2003, 86(3):480-486. doi: 10.1111/jace.2003.86.issue-3 [82] MAO X, WANG S, SHIMAI S, et al.Transparent polycrystalline alumina ceramics with orientated optical axes[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(10):3431-3433. doi: 10.1111/jace.2008.91.issue-10 [83] KIM B N, HIRAGA K, MORITA K, et al.Spark plasma sintering of transparent alumina[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(7):607-610. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.06.009 [84] GRASSO S, YOSHIDA H, PORWAL H, et al.Highly transparent α-alumina obtained by low cost high pressure SPS[J]. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(3):3243-3248. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.012 [85] WACHTMAN J B, MAXWELL I H.Plastic deformation of ceramic-oxide single crystals[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1954, 37(7):291-299. doi: 10.1111/jace.1954.37.issue-7 [86] KRONBERG M I.Dynamical flow properties of single crystals of sapphire, Ⅰ[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1962, 45(6):274-279. doi: 10.1111/jace.1962.45.issue-6 [87] YOSHIZAWA Y, SAKUMA T.Improvement of tensile ductility in high-purity alumina due to magnesia addition[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1992, 40(11):2943-2950. doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(92)90458-Q [88] WARSHAW S I, NORTON F H.Deformation behavior of polycrystalline aluminum oxide[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1962, 45(10):479-486. doi: 10.1111/jace.1962.45.issue-10 [89] LIU F M, HE D W, WANG Q, et al.Bimodal transparent alumina ceramics prepared with micro/nano-particles under high pressure[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2016, 122:54-58. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.05.017 [90] MCMILLAN P F.New materials from high-pressure experiments[J]. Nature Materials, 2002, 1(1):19-25. doi: 10.1038/nmat716 [91] MCMILLAN P F.Chemistry of materials under extreme high pressure-high-temperature conditions[J]. Chemical Communications, 2003(8):919-923. doi: 10.1039/b300963g [92] MCMILLAN P F.Chemistry at high pressure[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2006, 35(10):855-857. doi: 10.1039/b610410j [93] LIU A Y, COHEN M L.Prediction of new low compressibility solids[J]. Science, 1989, 245(4920):841-843. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4920.841 [94] VEPREK S.The search for novel, superhard materials[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 1999, 17(5):2401-2420. https://mediatum.ub.tum.de/doc/958917/958917.pdf [95] LIU A Y, WENTZCOVITCH R M.Stability of carbon nitride solids[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 50(14):10362. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.10362 [96] MA H A, JIA X P, CHEN L X, et al.High-pressure pyrolysis study of C3N6H6:a route to preparing bulk C3N4[J]. Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 2002, 14(44):11269. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/14/44/466 [97] FANG L, OHFUJI H, SHINMEI T, et al.Experimental study on the stability of graphitic C3N4 under high pressure and high temperature[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2011, 20(5):819-825. [98] HUBERT H, DEVOUARD B, GARVIE L A J, et al.Icosahedral packing of B12 icosahedra in boron suboxide (B6O)[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6665):376-378. doi: 10.1038/34885 [99] HE D W, ZHAO Y S, DAEMEN L, et al.Boron suboxide:as hard as cubic boron nitride[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81(4):643-645. doi: 10.1063/1.1494860 [100] CHEN C, HE D W, KOU Z L, et al.B6O-based composite to rival polycrystalline cubic boron nitride[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(23):4288-4291. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 [101] SOLOZHENKO V L, KURAKEVYCH O O, ANDRAULT D, et al.Ultimate metastable solubility of boron in diamond:synthesis of superhard diamondlike BC5[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(1):015506. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.015506 [102] ZININ P V, MING L C, KUDRYASHOV I, et al.Raman spectroscopy of the BC3 phase obtained under high pressure and high temperature[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2007, 38(10):1362-1367. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4555 [103] BADZIAN A R.Cubic boron nitride-diamond mixed crystals[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1981, 16(11):1385-1393. doi: 10.1016/0025-5408(81)90057-X [104] SASAKI T, AKAISHI M, YAMAOKA S, et al.Simultaneous crystallization of diamond and cubic boron nitride from the graphite relative boron carbide nitride (BC2N) under high pressure/high temperature conditions[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 1993, 5(5):695-699. doi: 10.1021/cm00029a020 [105] SOLOZHENKO V L, ANDRAULT D, FIQUET G, et al.Synthesis of superhard cubic BC2N[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78(10):1385-1387. doi: 10.1063/1.1337623 [106] ZHAO Y, HE D W, DAEMEN L L, et al.Superhard B-C-N materials synthesized in nanostructured bulks[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(12):3139-3145. doi: 10.1557/JMR.2002.0454 [107] SOLOZHENKO V L.High-pressure synthesis of novel superhard phases in the B-C-N system:recent achievements[J]. High Pressure Research, 2009, 29(4):612-617. doi: 10.1080/08957950903414987 [108] KNITTLE E, KANER R B, JEANLOZ R, et al.High-pressure synthesis, characterization, and equation of state of cubic c-BN solid solutions[J]. Physical Review B, 1995, 51(18):12149-12156. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.51.12149 [109] Diamond[EB/OL]. [2016-09-20]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diamond. [110] HARANO K, SATOH T, SUMIYA H.Cutting performance of nano-polycrystalline diamond[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2012, 24:78-82. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2011.11.005 [111] 许超. 纳米聚晶金刚石的高温高压合成与表征[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2014: 91-92.XU C. High pressure and high temperature synthesis and characterization of nano polycrystalline diamond[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2014: 91-92. [112] SUMIYA H, IRIFUNE T, KURIO A, et al.Microstructure features of polycrystalline diamond synthesized directly from graphite under static high pressure[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(2):445-450. doi: 10.1023/B:JMSC.0000011496.15996.44 [113] SUMIYA H, IRIFUNE T.Microstructure and mechanical properties of high-hardness nano-polycrystalline diamonds[J]. SEI Technical Review, 2008, 66:85-92. [114] WANG P, HE D W, WANG L P, et al.Diamond-cBN alloy:a universal cutting material[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 107(10):101901. doi: 10.1063/1.4929728 [115] RILEY F L.Silicon nitride and related materials[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(2):245-265. [116] TANAKA I, OBA F, SEKINE T, et al.Hardness of cubic silicon nitride[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(4):731-733. doi: 10.1557/JMR.2002.0105 [117] ZERR A, KEMPF M, SCHWARZ M, et al.Elastic moduli and hardness of cubic silicon nitride[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2002, 85(1):86-90. [118] WANG W D, HE D W, TANG M J, et al.Superhard composites of cubic silicon nitride and diamond[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2012, 27:49-53. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925963512001380 -







 下载:
下载: